Stacked-Cup Carbon Nanotubes for Photoelectrochemical Solar Cells†
We would like to thank GSI Creos Corporation, Japan for providing the sample of stacked-cup carbon nanotubes, and Tim Hall for his assistance in SEM characterization. This work was partially supported by Grant-in-Aid (No. 16205020) and by the COE program of Osaka University (Integrated Ecochemistry) from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology, Japan. T.H. acknowledges the support of Research Fellowships from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) for Young Scientists. P.V.K. acknowledges support from the Office of Basic Energy Science of the U.S. Department of the Energy. This is contribution No. NDRL 4623 from the Notre Dame Radiation Laboratory and from Osaka University.
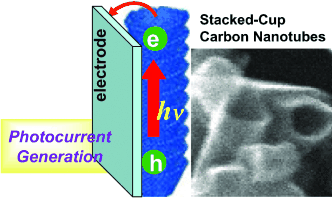
Graphical Abstract
Seeing the light: Stacked-cup carbon nanotubes (SCCNTs) have been electrophoretically deposited on conducting glass electrodes from a suspension in THF by using a dc field (see picture). These SCCNT films undergo charge separation and deliver photocurrent on irradiation with visible light. The photon conversion efficiency of 17 % observed with the SCCNT system is two orders of magnitude greater than those obtained with carbon nanotubes.