Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture: Chiral Centers in the Side Chains of α-Amino Acids Control the Helical Screw Sense of Peptides (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 40/2004)
- Page: 5275
- First Published: 05 October 2004
A tidal vortex (helix) is formed, both right- and left-handed, where a violent tidal current meets a peaceful sea (the picture from Naruto City Tourist Association shows an example at Naruto channel, Japan). In contrast, α-helices of proteins almost always show a right-handed helical screw sense because of the stereogenic α-carbon center of α-amino acids. M. Tanaka et al. now demonstrate on page 5360 ff. how the left-handedness of a α-helical peptide is controlled by the side-chain stereogenic centers.
Graphical Abstract: Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 40/2004
- Pages: 5278-5286
- First Published: 05 October 2004
Jacques van Boom (1937–2004): Biopolymers
- Pages: 5288-5289
- First Published: 05 October 2004
Handbook of Metalloproteins. Vol. 3. Edited by Albrecht Messerschmidt, Wolfram Bode and Mirek Cygler.
- Page: 5290
- First Published: 05 October 2004
NMR—From Spectra to Structures. An Experimental Approach. By Terence N. Mitchell and Burkhard Costisella.
- Pages: 5290-5291
- First Published: 05 October 2004
Color Chemistry. Synthesis, Properties and Applications of Organic Dyes and Pigments. 3rd revised edition. By Heinrich Zollinger.
- Pages: 5291-5292
- First Published: 05 October 2004
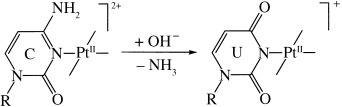
Recent Advances in Chiral Resolution through Membrane-Based Approaches
- Pages: 5293-5295
- First Published: 05 October 2004
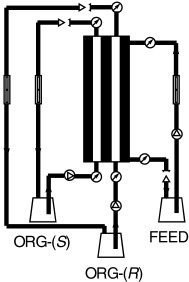
Hollow-fiber membrane contactors, which can be combined with enzymatic resolution, have already emerged as a potential technology for enantiomeric resolution under continuous operation (see scheme; ORG denotes the organic phase). Furthermore, recently reported optically active polyelectrolyte multilayer (PEMU) membranes appear extremely promising for future applications in preparative chiral separations.
On the Noninnocent Nature of 1,3-Dialkylimidazolium Ionic Liquids†
- Pages: 5296-5297
- First Published: 05 October 2004
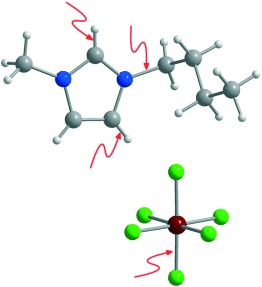
Presumed innocent, room-temperature ionic liquids are clean, often reusable, media for carrying out many synthetic, catalytic, separation, and analytical processes. However, they are not simply inert solvents, and a variety of decomposition pathways have been detected. In the structure of 1-n-butyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate shown, reactive bonds are marked with arrows (C grey, N blue, F green, P red).
Multimetallic Cooperative Activation of N2
- Pages: 5298-5308
- First Published: 05 October 2004
How important is the cooperative attack of two or more metal centers for dinitrogen activation? The most recent literature, which provides the focus for this Minireview, helps to improve our understanding of the factors that determine such important processes as dinitrogen fixation, cleavage, and elementary transformations.
Quantifying Intermolecular Interactions: Guidelines for the Molecular Recognition Toolbox
- Pages: 5310-5324
- First Published: 05 October 2004
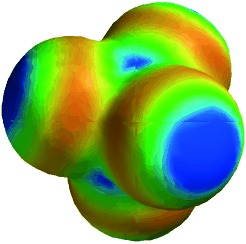
Noncovalent interactions are treated as a form of hydrogen bonding to produce a new universal scale that can be used to estimate the free energies of interaction between any pair of neutral functional groups in any solvent. The important parameters are provided by the molecular electrostatic potential surface (the example depicted is that for carbon tetrachloride).
Luminescent Probes of Crystal Growth: Surface Charge and Polar Axis Sense in Dye-Doped Potassium Hydrogen Phthalate†
- Pages: 5328-5331
- First Published: 05 October 2004

Stunning tricolored crystals with distinct regions of green, yellow, and orange luminescence (see picture) are deposited in solutions of potassium hydrogen phthalate that contain proflavin. The dye serves as a fluorescent probe of surface charge while identifying the polar crystallographic axis. Optical probes, common in biochemistry, can be used widely to study the specificity of noncovalent chemistry crystal growth from solution.
Arylamine-Substituted Hexa-peri-hexabenzocoronenes: Facile Synthesis and Their Potential Applications as “Coaxial” Hole-Transport Materials†
- Pages: 5331-5335
- First Published: 05 October 2004
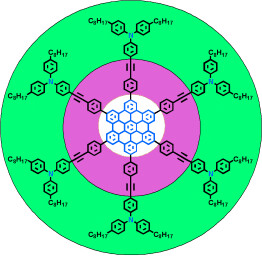
The hole story: using a new synthetic concept the title hexa-peri-hexabenzocoronenes (HBCs) were synthesized with high atom economy. The coaxial arrangement of the HBCs and arylamines allowed a “double-cable” hole transport (see picture), that is, transport through the central core (white) and the outer shell (green).
A DNA Nanomachine Based on a Duplex–Triplex Transition†
- Pages: 5335-5338
- First Published: 05 October 2004

Making DNA work: A DNA nanomachine with a mechanism based on a DNA duplex–triplex transition (see figure) was constructed. The key component is a DNA triplex that contains C+GC triplets and is only stable under acidic conditions. The DNA machine uses H+ and OH− ions as fuel and its only waste products are H2O and NaCl.
A Strategy for Functional Proteomic Analysis of Glycosidase Activity from Cell Lysates†
- Pages: 5338-5342
- First Published: 05 October 2004
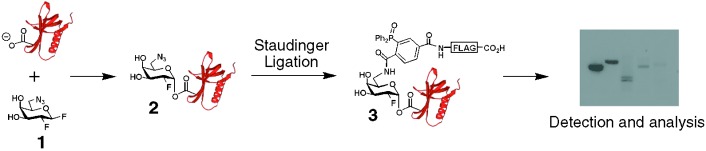
A multipurpose flag: The inactivator 1 covalently labels the catalytic nucleophiles of retaining β-glycosidases to form species 2. The small azide group allows labeling of enzymes with sterically congested active sites. Staudinger ligation of 2 with phosphine–FLAG yields adduct 3, which can be used to detect and profile retaining β-glycosidase activities in complex mixtures.
A β-Carboline-1-one Mimic of the Anticancer Amaryllidaceae Constituent Pancratistatin: Synthesis and Biological Evaluation†
- Pages: 5342-5346
- First Published: 05 October 2004
The Development of Descriptors for Solids: Teaching “Catalytic Intuition” to a Computer
- Pages: 5347-5349
- First Published: 05 October 2004
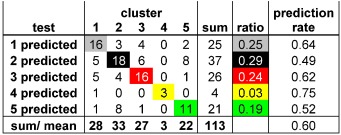
Virtual screening: Based on parameters which do not have to be measured, sets of attributes for solids are derived and used to predict whether a catalyst falls into one of five performance classes in propene oxidation, with a predictive power substantially exceeding the statistically expected values (see table (a confusion matrix): prediction rate indicates the correct assignment by the new method, ratio indicates the statistical expectation value).
Gold(I)-Catalyzed 5-endo-dig Carbocyclization of Acetylenic Dicarbonyl Compounds†
- Pages: 5350-5352
- First Published: 05 October 2004
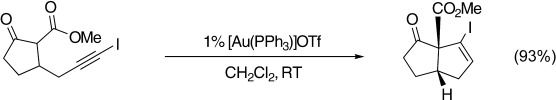
Cyclopentenoid structures including compounds containing vinyl iodide, 1,3-diene, and heterocyclic moieties are obtained through the gold(I)-catalyzed 5-endo-dig addition of β-dicarbonyl compounds to unactivated alkynes under neutral conditions and at room temperature (RT). Both monocyclic and bicyclic cyclopentenes can be formed in excellent yields and with good diastereoselectivity (see scheme).
The Strongest Isolable Acid†
- Pages: 5352-5355
- First Published: 05 October 2004
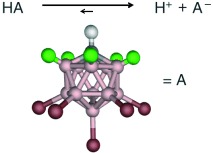
Measure for measure: Several measures indicate that carborane acids of the type H(CHB11R5X6) (see scheme, green R, red X, gray H, pink B) for R=H, Cl and X=Cl, Br, I are the strongest pure Brønsted acids. Based on NMR and IR spectroscopy, H(CHB11Cl11) can lay claim to be the strongest isolable acid presently known.
Imine-Stabilized Zinc Trimethylsilylchalcogenolates: Powerful Reagents for the Synthesis of II-II′-VI Nanocluster Materials†
- Pages: 5355-5357
- First Published: 05 October 2004
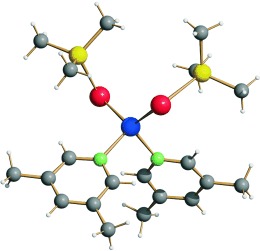
That zinc in feeling: The complexes [(3,5-Me2C5H3N)2Zn(ESiMe3)2] (E=Se, 1; E=Te, 2) are prepared and found to be good reagents for the generation of ternary MM′E materials. From 2 (see structure; Te red, Zn blue, Si yellow, N green), the ternary ZnCdTe nanocluster [Zn2.6Cd7.4Te4(TePh)12(PnPr3)4] (3) is prepared. The optical properties of 3 are shown to be modulated relative to those of related binary CdTe cluster molecules.
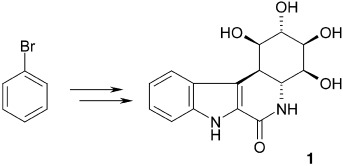
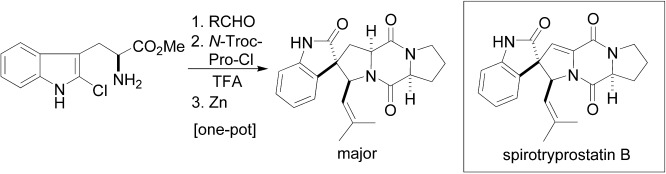
Preparation and Synthetic Applications of 2-Halotryptophan Methyl Esters: Synthesis of Spirotryprostatin B†
- Pages: 5357-5360
- First Published: 05 October 2004
Chiral Centers in the Side Chains of α-Amino Acids Control the Helical Screw Sense of Peptides†
- Pages: 5360-5363
- First Published: 05 October 2004
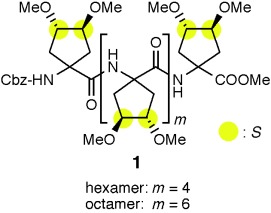
Chirality on the side suffices: The screw sense of 310- and α-helices formed by the oligopeptides 1, which have no α-carbon chiral centers, is controlled by the chiral centers in their side chains. These results imply that just the side chain chiral centers of isoleucine and threonine would affect the secondary structure of their oligopeptides.
Ionic Liquids as Moderators in Exothermic Polymerization Reactions†
- Pages: 5363-5366
- First Published: 05 October 2004
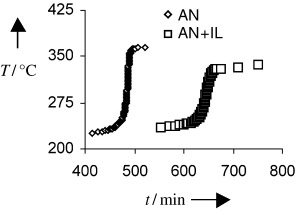
Highly exothermic polymerization reactions of monomers have been carried out in ionic liquids (ILs) by employing an accelerating-rate calorimeter (ARC) to assess the role of the IL. The results indicate that the IL acts as an ideal heat sink in controlling the potential for the reactions to reach thermal runaway as well as contributing to a significant pressure reduction (see the acrylonitrile (AN) example depicted).
Cross-Metathesis of Propane and Methane: A Catalytic Reaction of CC Bond Cleavage of a Higher Alkane by Methane†
- Pages: 5366-5369
- First Published: 05 October 2004
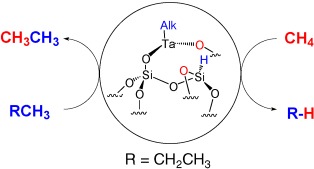
Methane, a building block for basic chemicals through its incorporation into alkanes: when a methane/propane mixture is passed over a tantalum hydride catalyst at 250 °C, propane is transformed into two ethane molecules through the incorporation of one methane unit. This reaction corresponds to a cross-metathesis of propane and methane (see scheme; Alk=alkyl).
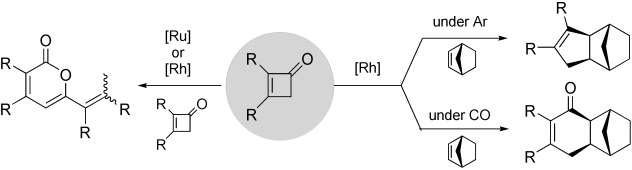
Ru- and Rh-Catalyzed CC Bond Cleavage of Cyclobutenones: Reconstructive and Selective Synthesis of 2-Pyranones, Cyclopentenes, and Cyclohexenones†
- Pages: 5369-5372
- First Published: 05 October 2004
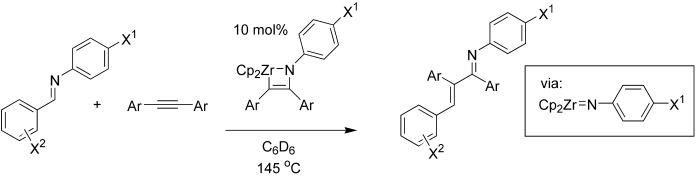
Carboamination: Additions of Imine CN Bonds Across Alkynes Catalyzed by Imidozirconium Complexes†
- Pages: 5372-5374
- First Published: 05 October 2004
Zirconium-Mediated Conversion of Amides to Nitriles: A Surprising Additive Effect†
- Pages: 5375-5377
- First Published: 05 October 2004
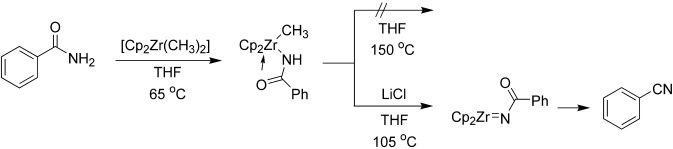
Chloride coordination is the key: Dimethylzirconocene reacts with amides to form methylzirconium amide complexes. On heating, in the presence of a chloride source, these compounds are converted into N-acylimidozirconocene complexes that react intramolecularly to form the corresponding nitrile compounds (see scheme; Cp=C5H5). Mechanistic studies reveal that chloride coordination to zirconium is required for this transformation to occur.
Radical-Mediated γ-Functionalizations of α,β-Unsaturated Carboxylic Amides†
- Pages: 5378-5380
- First Published: 05 October 2004
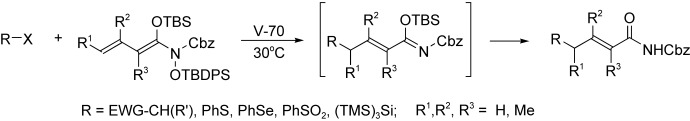
Highly successful tin-free, radical-mediated alkylations of α,β-unsaturated carboxylic amides have been carried out. Alkyl iodides and bromides bearing α-electron-withdrawing groups undergo selective γ-additions to diene O,N-acetals (see scheme). This approach to γ-functionalization was further extended to the use of hetero groups, such as phenylsulfanyl and phenylsulfonyl species.
CuCl Nanoplatelets from an Ionic Liquid-Crystal Precursor†
- Pages: 5380-5382
- First Published: 05 October 2004

Green approach to inorganic nanostructures: CuCl nanoplatelets (see picture) were synthesized from mixtures of a Cu-containing ionic liquid crystal and 6-O-palmitoyl ascorbic acid. The particle size, thickness, and connectivity can be adjusted through varying the reaction temperature. The copper-containing precursor acts as both the template and the copper source. The ligand is not consumed in the precipitation and can be reused.
Reversible Addition Fragmentation Chain Transfer (RAFT) Polymerization from Unprotected Cadmium Selenide Nanoparticles†
- Pages: 5383-5386
- First Published: 05 October 2004
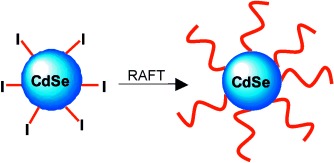
Nanoparticles functionalized with a trithiocarbonate ligand allow RAFT polymerization to be performed from their surface. Homopolymers, random copolymers, and block copolymers can be grown radially from trithiocarbonate-covered CdSe nanoparticles (see scheme). This technique gives excellent nanoparticle dispersion in a wide range of polymers, while maintaining the unique photophysical properties of the nanoparticles.
Mechanism of 4,6-O-Benzylidene-Directed β-Mannosylation as Determined by α-Deuterium Kinetic Isotope Effects†
- Pages: 5386-5389
- First Published: 05 October 2004
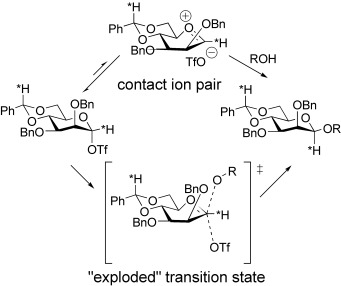
Considerable oxacarbenium ion character may be in the transition state of a highly β-selective mannosylation reaction that proceeds via an α-mannosyl triflate. An α-deuterium kinetic isotope effect of 1.2 was measured at −78 °C (≡1.1 at 25 °C). This information may be interpreted in terms of a stereoselective trapping of a transient contact ion pair or, alternatively, as representative of an “exploded” transition state (see scheme).
A Highly Efficient Synthesis of the Erythrina and B-Homoerythrina Skeleton by an AlMe3-Mediated Domino Reaction†
- Pages: 5391-5393
- First Published: 05 October 2004
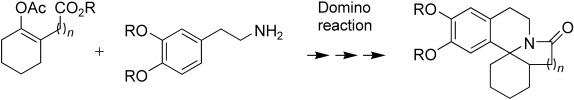
Domino effect: The skeleton of erythrina and B-homoerythrina alkaloids can be constructed in an efficient manner from readily available substrates (see Scheme) by a three-step domino reaction. These natural products constitute an interesting class of compounds because of their extensive biological activity.
Single Quantum Dots in Spherical Silica Particles†
- Pages: 5393-5396
- First Published: 05 October 2004
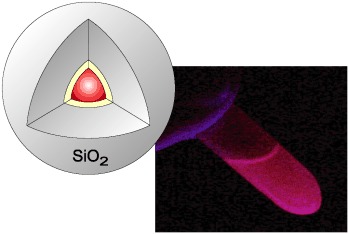
Bright particles: The optical properties of luminescent nanocrystals (quantum dots, QDs) can be exploited only if they are have an appropriate surface derivatization. A straightforward method is presented to encapsulate single QDs with a homogeneous silica shell, while retaining their high luminescence (see picture).
Metal-Mediated Deamination of Cytosine: Experiment and DFT Calculations†
- Pages: 5396-5399
- First Published: 05 October 2004
Chameleon Labels for Staining and Quantifying Proteins
- Pages: 5400-5402
- First Published: 05 October 2004
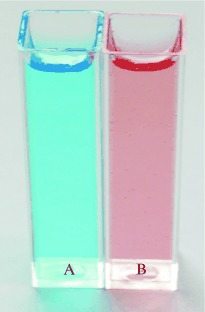
Glowing marks: A new class of protein stains, the pyrylium dyes, undergo a strong color change (typically from blue to red, see picture) on covalently binding to proteins. While the free stains are almost nonfluorescent, the protein-conjugated forms are highly fluorescent. The dyes do not alter the charge of a protein, and thus do not change its electrophoretic properties. The stains also can be used in quantitative protein assays.
Electrophilic Alkylations in Neutral Aqueous or Alcoholic Solutions†
- Pages: 5402-5405
- First Published: 05 October 2004
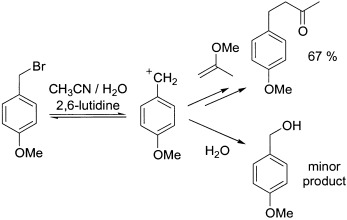
Acid-free Friedel–Crafts chemistry: A paradox? Nucleophilicity scales, based on reactions with benzhydrylium ions, show that many π systems are more nucleophilic than aqueous or alcoholic solutions that are generally employed as solvents for SN1 reactions. Solvolytically generated carbocations can, therefore, be trapped by donor-substituted arenes and alkenes to form products of Friedel–Crafts-type reactions in neutral aqueous solutions (see scheme).
Novel Polysilanols by Selective Functionalizations of Oligosilanes
- Pages: 5406-5408
- First Published: 05 October 2004
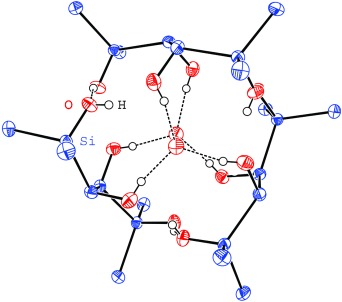
As part of a succinct synthesis, a new functionalization method leads to hitherto unknown polysilanols with an oligosilane backbone, a class of compounds with remarkable electronic properties. The trifluoroacetolysis of phenyl-substituted hydroxyoligosilanes yield trifluoroacetoxyoligosilanes almost quantitatively, and these can be converted into tri- and tetrasilanol, such as that shown, simply by hydrolysis.