Journal list menu
 Issue
IssueEarly View
Online Version of Record before inclusion in an issue
Export Citations
Download PDFs
CASE REPORT
Large Cell Neuroendocrine Carcinoma of the Uterine Cervix With a Biphasic Synaptophysin Staining Pattern and Followed Vaginal Intraepithelial Recurrence: A Case Report
- Version of Record online: 25 July 2025
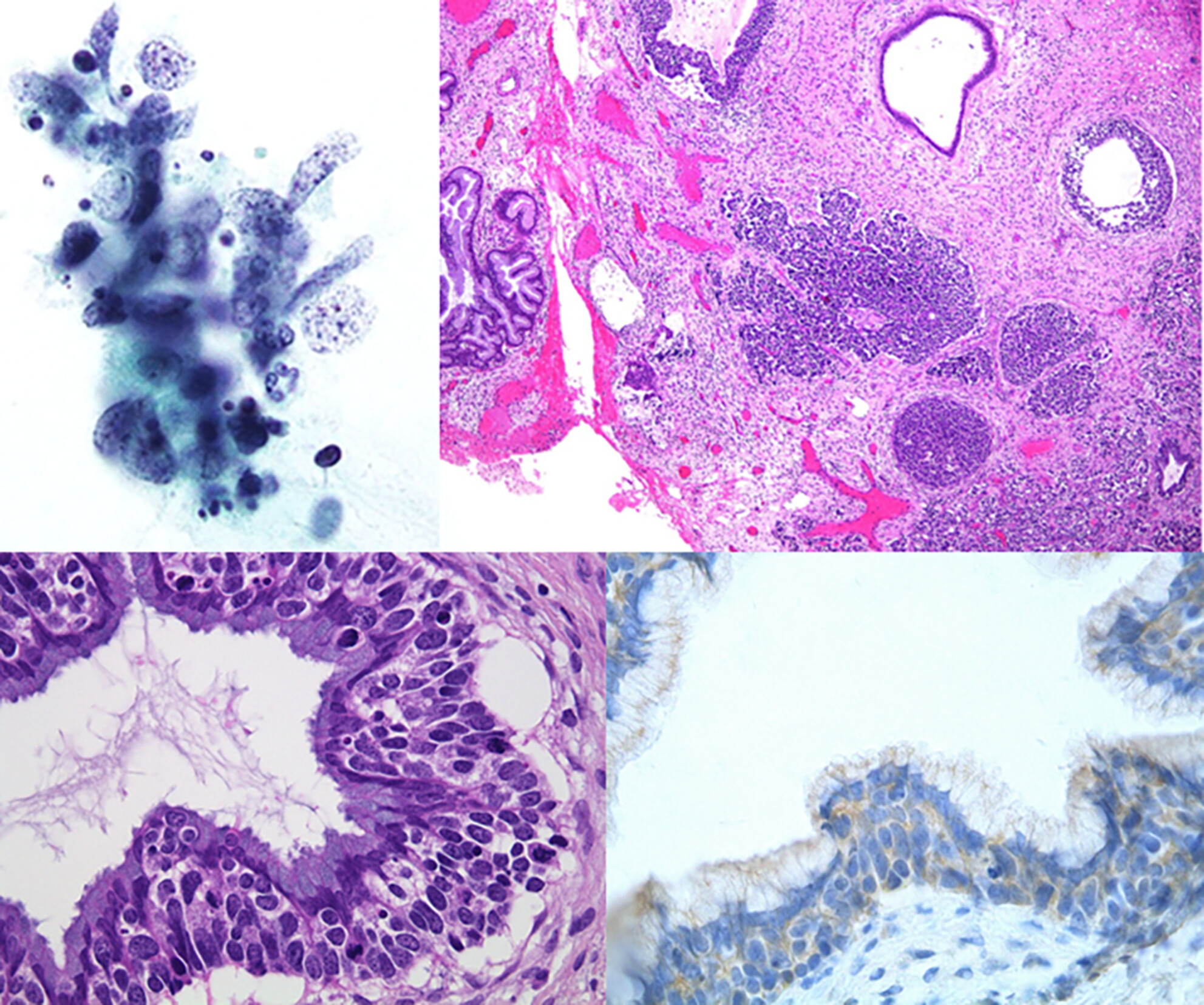
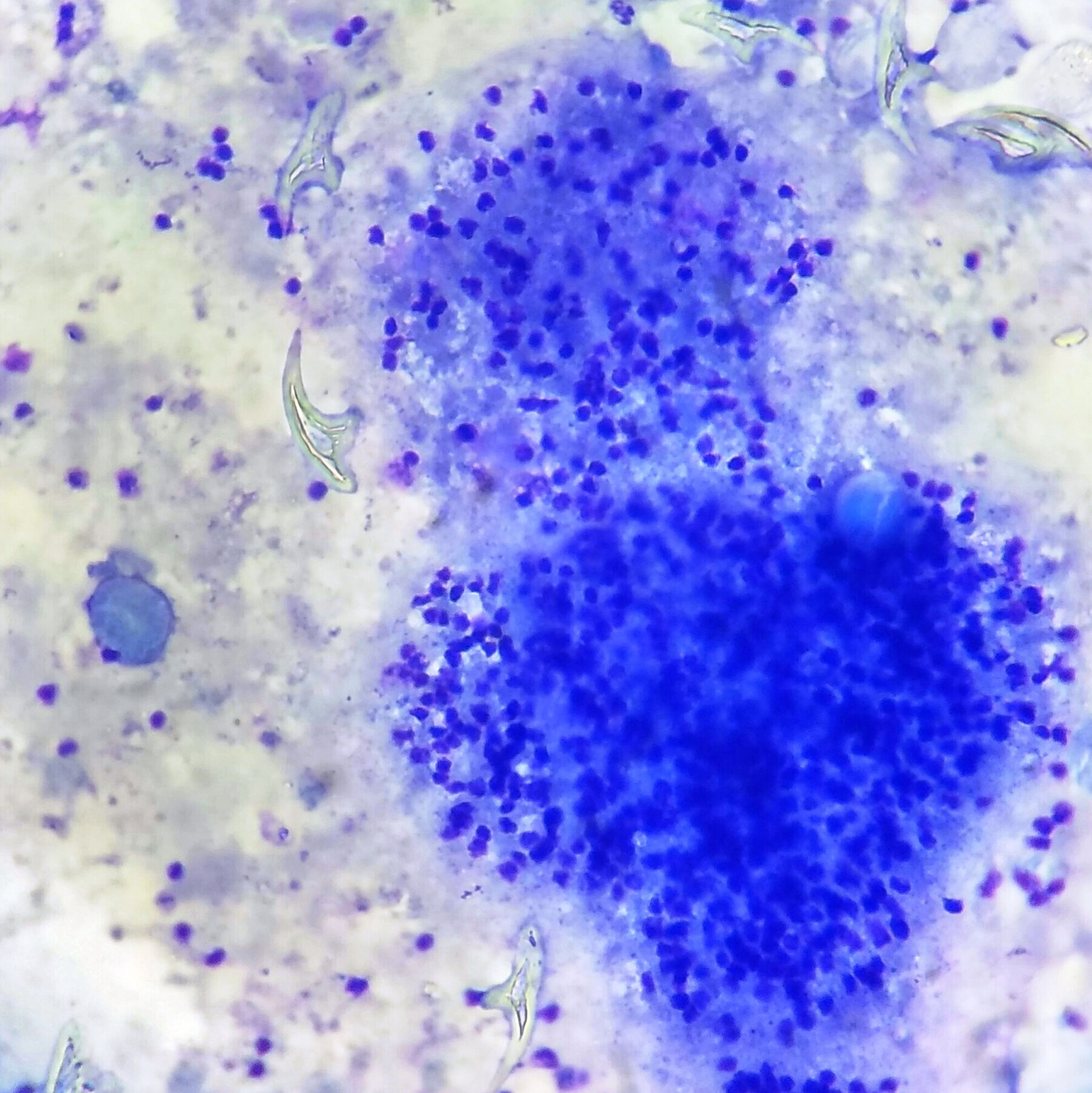
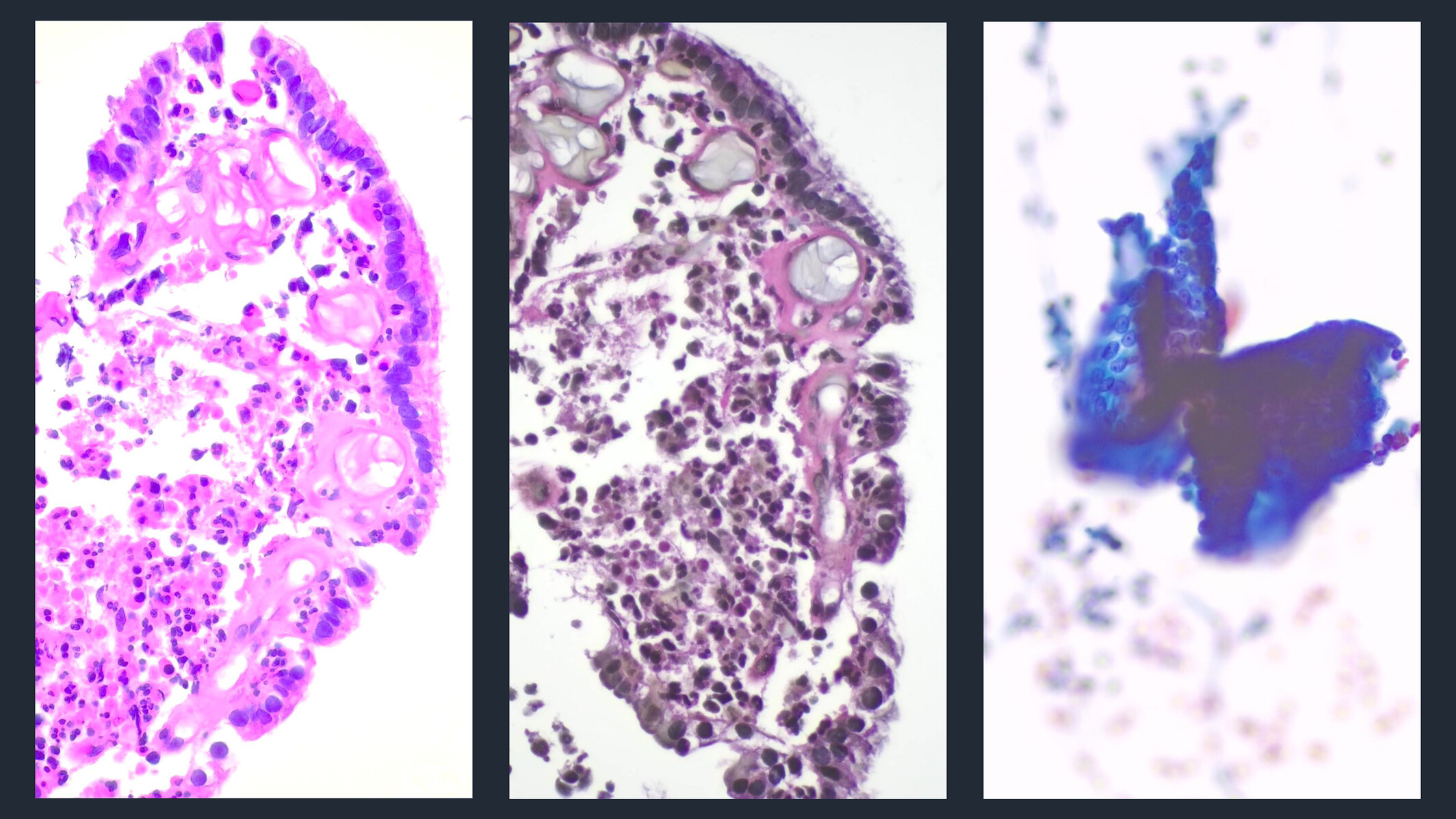
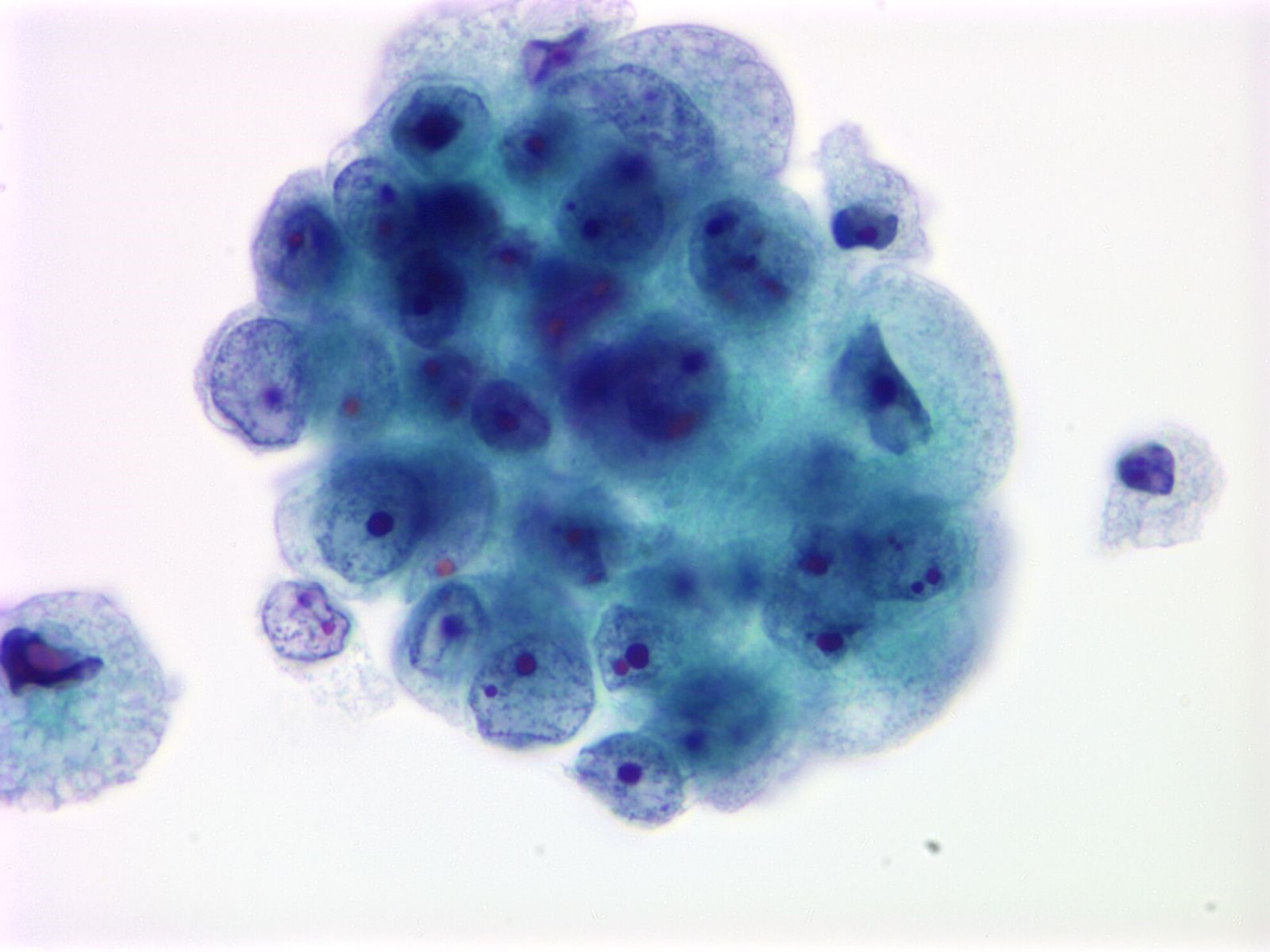
This case highlights the importance of early, aggressive surgery for large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma and continuous cytological monitoring in detecting recurrence at the early intraepithelial stage. The pagetoid spread pattern with a biphasic synaptophysin staining differentiated LCNEC from CIN3 and AIS.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Increased Diagnoses of Follicular Neoplasms Among Thyroid Nodules Submitted to Fine-Needle Aspiration With Ultrasound-Classification Indication and Adoption of the 3rd Edition of the Bethesda System
- Version of Record online: 21 July 2025
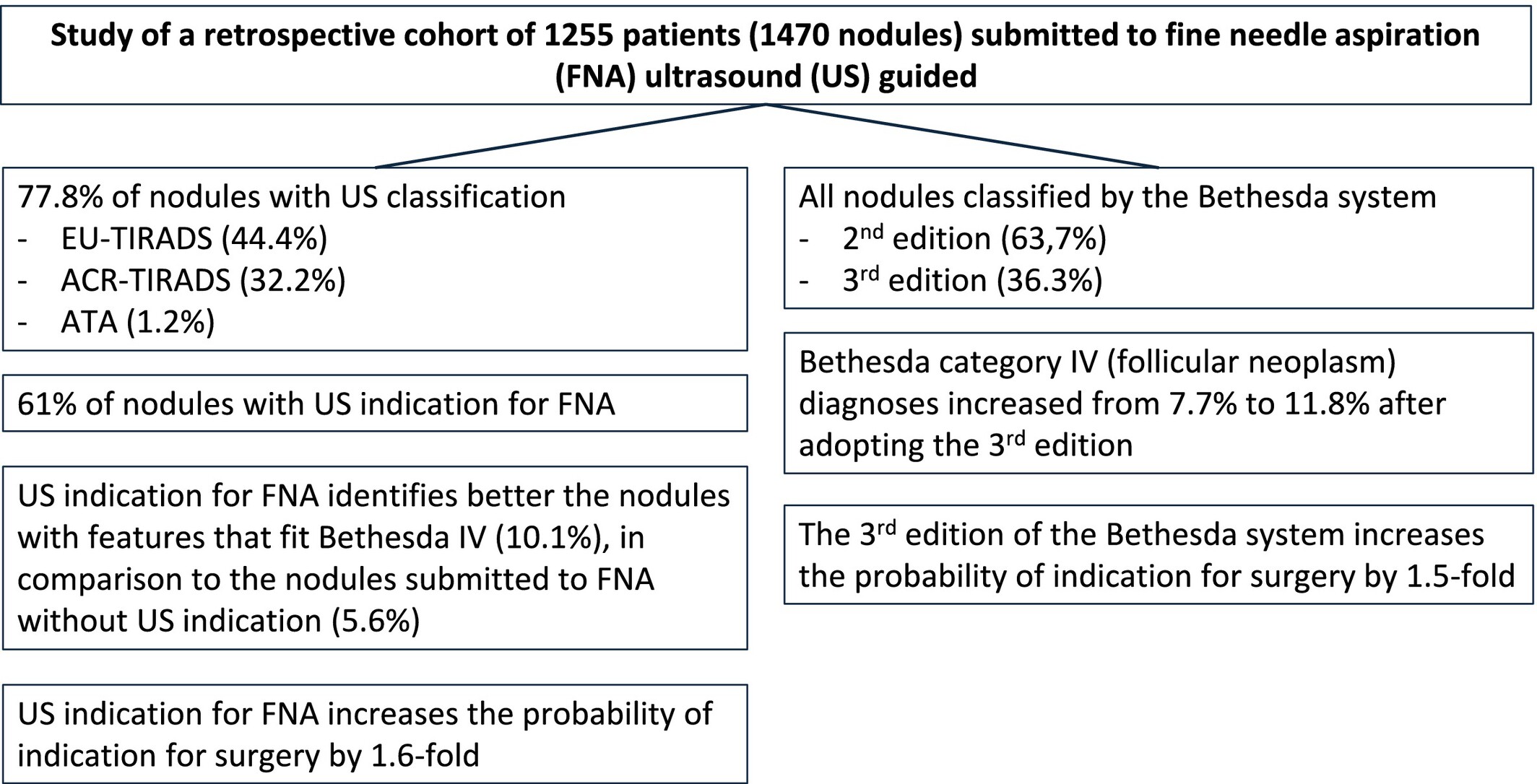
The study highlights the increase in follicular neoplasms among nodules with ultrasound (US) indication for fine needle aspiration due to the adoption of the 3rd edition of the Bethesda system (increases indication for surgery by 1.5-fold) and US classifications (increasing the indication for surgery by 1.6-fold).
CASE REPORT
Primary Cutaneous Rosai-Dorfman Disease: A Cyto-Histo Correlate
- Version of Record online: 21 July 2025
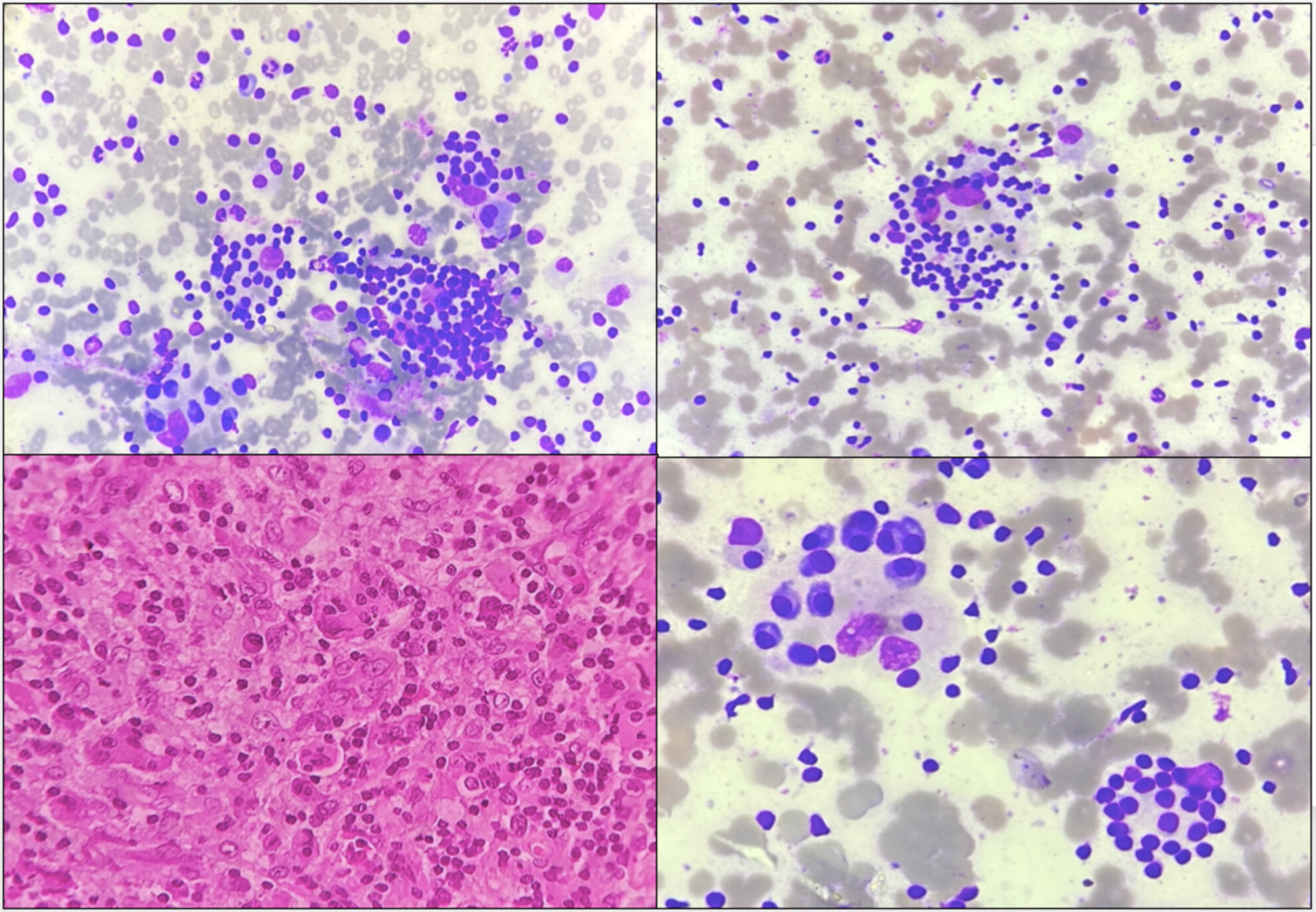
Primary cutaneous Rosai Dorfman disease (RDD) is a rare proliferative disorder of histiocytes involving skin exclusively. Cytomorphological features of two such cases affecting a 20-year-old male (multicentric) and an 8-year-old male are presented here. The diagnosis is challenging and a high index of suspicion and systemic correlation are necessary for early diagnosis and treatment.
ENIGMA PORTAL
Cytomorphology of Renal Hydatid Cyst Mimicking as Simple Renal Cyst
- Version of Record online: 10 July 2025
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
From the Daily Peer Review of Abnormal Pap Test Slides to the Monitoring of Individual and Laboratory Performances: 5 Years of Data Collection and New Potential (Key) Performance Indicators
- Version of Record online: 05 July 2025
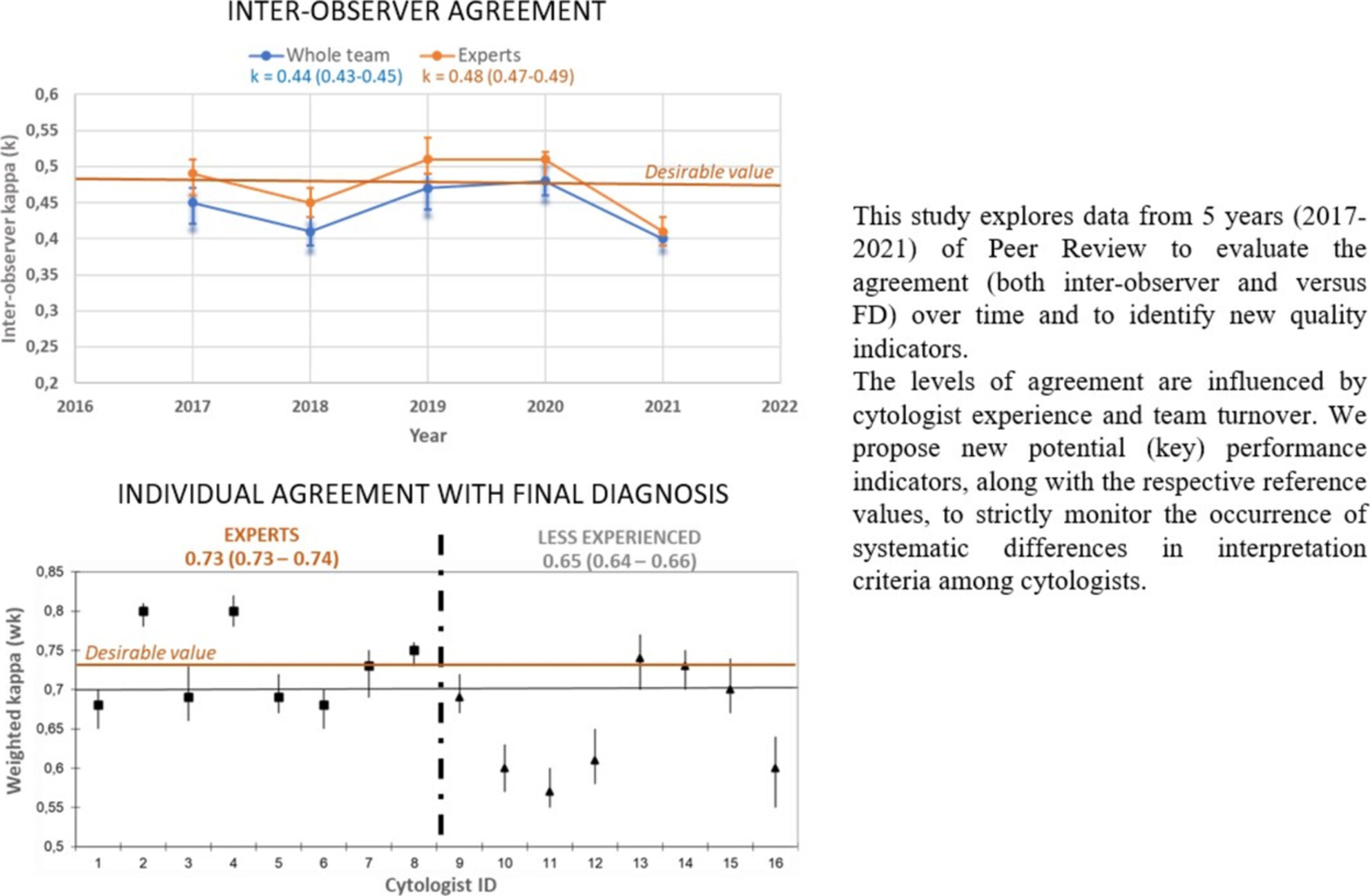
The study explores data from 5 years of Peer Review to evaluate the trend of agreement level (inter-observer and versus final diagnosis) over time and proposes new potential key performance indicators (KPIs), along with the relative reference values. These KPIs should be used to strictly monitor the occurrence of systematic differences in interpretation criteria among cytologists and to implement prompt corrective actions in case of significant deviations in diagnostic accuracy.
CASE REPORT
Cytological Diagnosis of Amyloidosis From Orbital Papules
- Version of Record online: 01 July 2025

We report a case of systemic amyloidosis with eyelid papules, diagnosed on FNAC. A 43-year-old male presented with periocular papules for 2 months. FNAC revealed acellular glassy pale eosinophilic material with apple green birefringence on Congo Red stain under polarised light. Periorbital papules are an uncommon presentation of amyloidosis. Any periorbital infiltrative dermatosis should raise suspicion of local or systemic amyloidosis.
IMAGES IN CYTOLOGY
Metastatic Malignant Phaeochromocytoma in Ascitic Fluid: Cytological Diagnosis of a Rare Entity
- Version of Record online: 30 June 2025
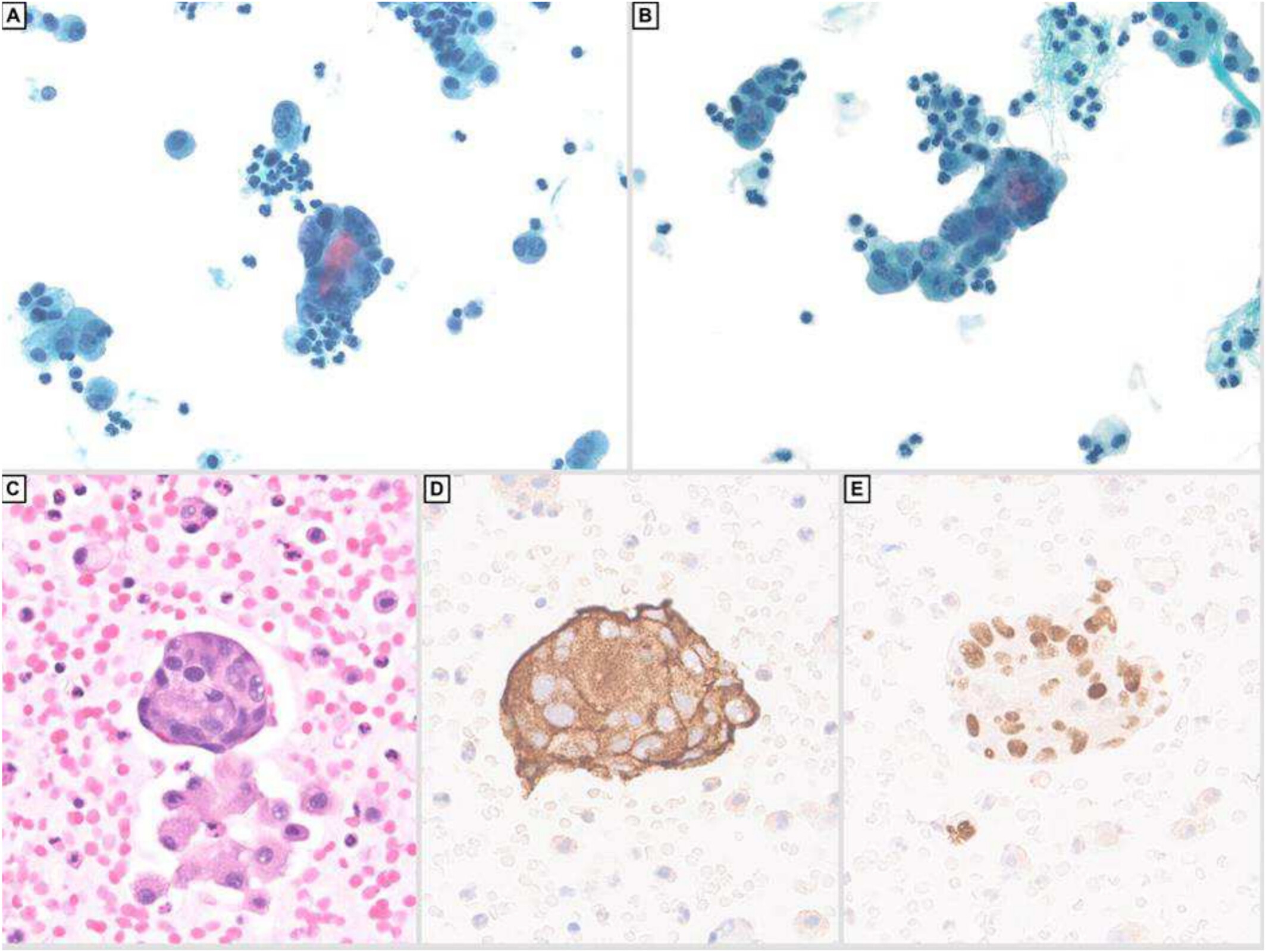
In summary, a review of the literature showed that there are only isolated case reports of ruptured pheochromocytoma and to the best of our knowledge this report is the first to document metastatic phaeochromocytoma in peritoneal fluid within the cytopathology literature. Our case report emphasises the importance of clinical history in the context of the cytopathologic evaluation, and good cell block preparation, which allows the use of IHCs in challenging cases as it may lead to the discovery of unusual metastatic sources.
Detection of Toxoplasma Gondii Tachyzoites in Cerebrospinal Fluid: Once in a Blue Moon Finding
- Version of Record online: 23 June 2025
Tachyzoites of Toxoplasma gondii were detected in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), confirming the diagnosis of central nervous system (CNS) toxoplasmosis in a 20-year-old male. CSF was collected via lumbar puncture, and cytology smears were prepared using cytocentrifugation. One smear was stained with May-Grünwald Giemsa (MGG), and the other with Papanicolaou stain. Light microscopy revealed pleocytosis with numerous intracellular and extracellular tachyzoites, characteristic of Toxoplasma gondii. Diagnosis was further confirmed by elevated anti-Toxoplasma IgM levels in serum.
CORRESPONDENCE
Implementation of a Multi-Gene Molecular Panel at Fine Needle Aspiration Biopsy (FNAB) Thyroid Samples: A Compelling Diagnostic and Prognostic Model
- Version of Record online: 18 June 2025
Application of a multi-gene panel in FNAB thyroid samples provides a patient-directed diagnostic and prognostic model. Several genetic mutations and molecular markers are correlated with histological subtypes of thyroid cancer, revealing the potential role of molecular techniques in targeted therapy. The combination of FNAB and multi-gene tests introduces clinicians to the benefits of precision oncology.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
The Methylation Test Is Highly Sensitive for HPV-Associated Endocervical Adenocarcinoma and Could Be Helpful as a Cytological Ancillary Test in Women With a PAP-Smear Diagnosis of Severe Glandular Lesion (AGC–NEO+)
- Version of Record online: 13 June 2025
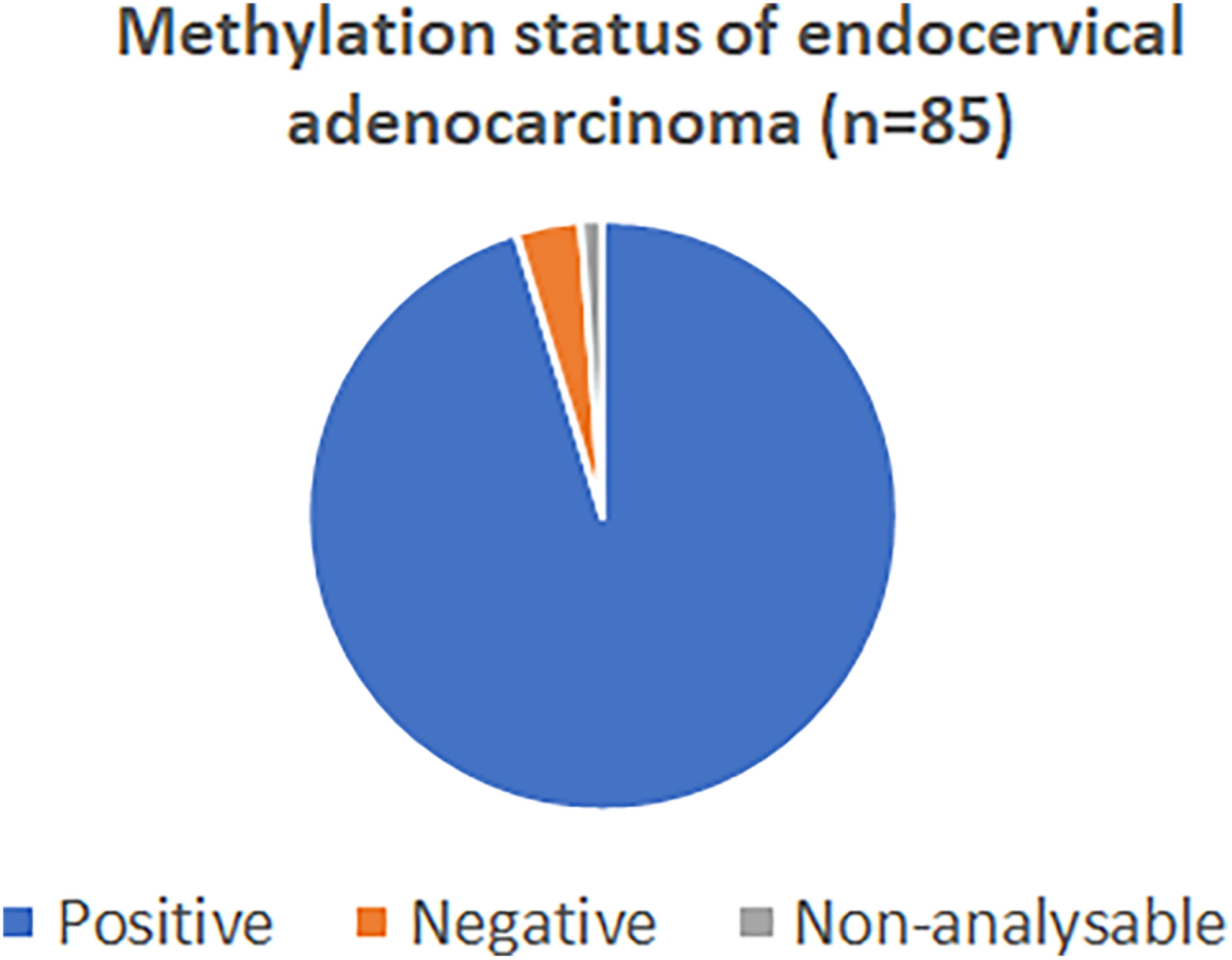
Based on an analysis of 85 endocervical adenocarcinoma (EA) cases with cytology–histology correlation, the authors document a methylation test sensitivity of 95.3% for diagnosing EA. If used as an ancillary test, the methylation test may improve the PAP test's reliability. The authors argue that this may be of special importance to young women.
CASE REPORT
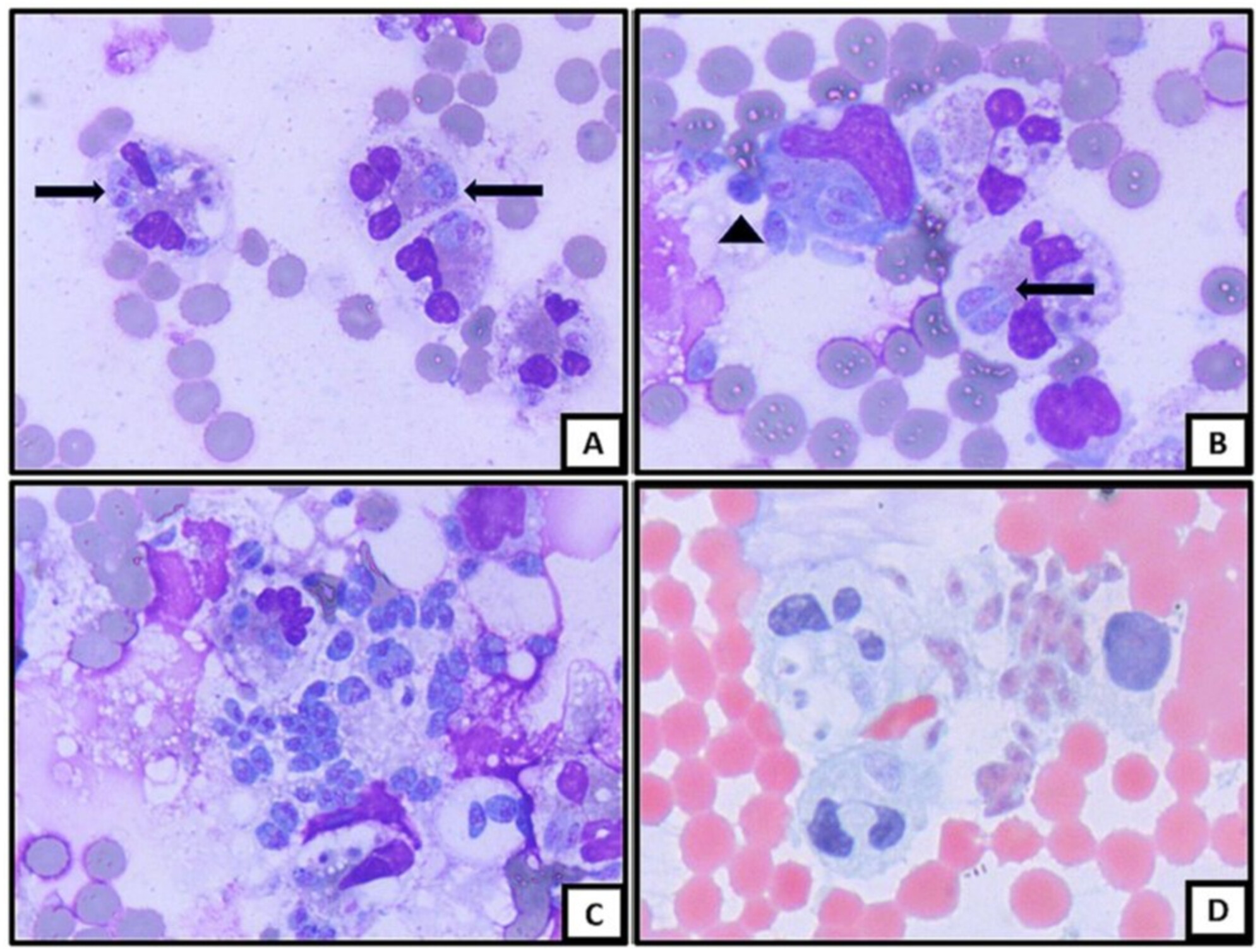
Unveiling Diagnostic Clues of BCOR-CCNB3 Sarcoma in Fine-Needle Aspiration Specimens
- Version of Record online: 11 June 2025
BCOR-CCNB3 sarcoma is an undifferentiated small round cell sarcoma characterised by distinct molecular genetic alterations. The diagnostic clues include tumour cells with oval to short spindle-shaped morphology, finely dispersed chromatin, inconspicuous nucleoli, and an arrangement around blood vessels that forms pseudopapillary structures.
Breast Filariasis—Diagnosed by Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology: A Rare Case Report
- Version of Record online: 27 May 2025
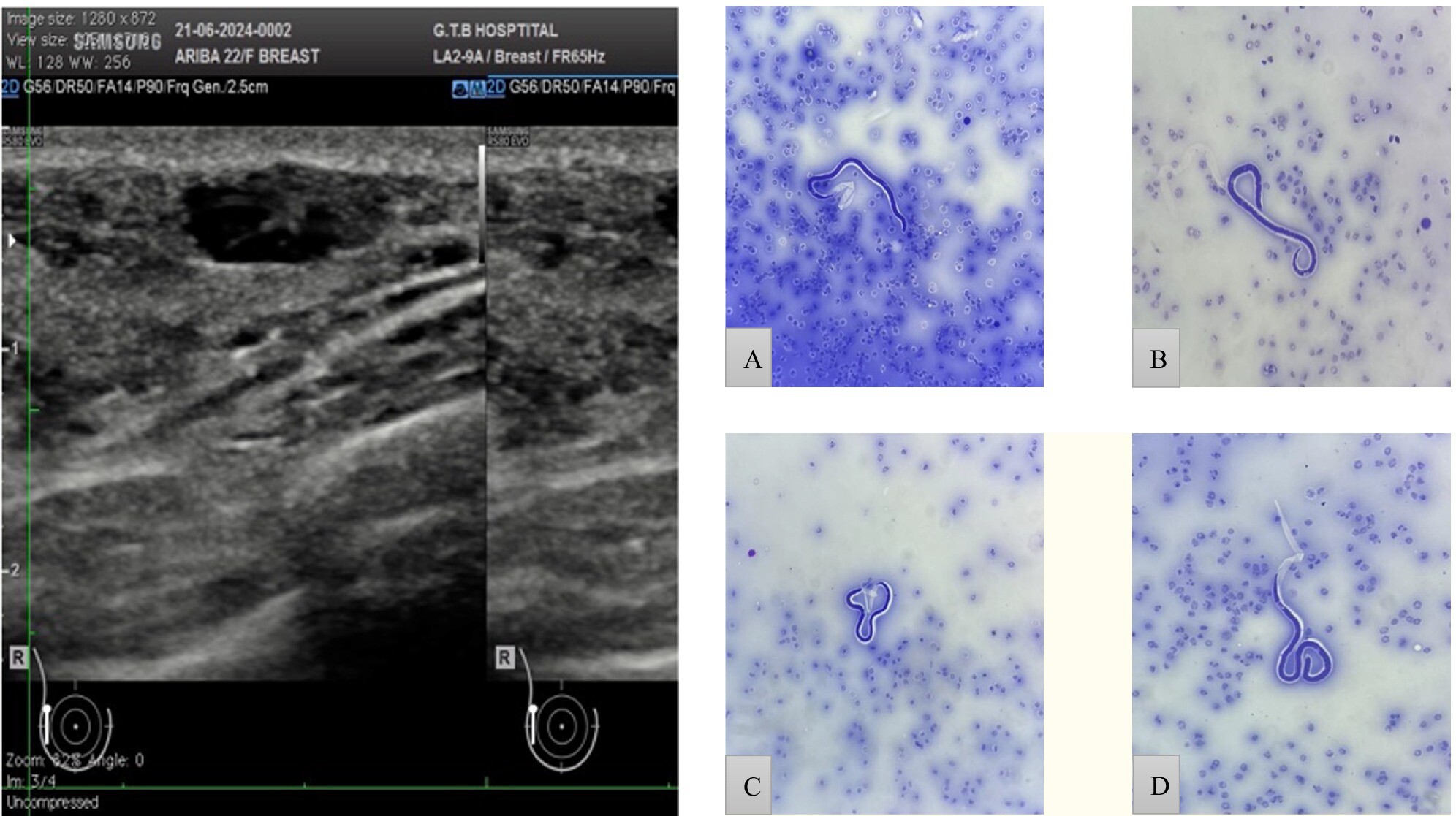
This case report highlights a rare presentation of breast filariasis in a young female, diagnosed through fine needle aspiration cytology. Despite the high prevalence of lymphatic filariasis in endemic regions, extranodal involvement of the breast is uncommon and can mimic neoplastic lesions. The report emphasises the importance of FNAC in the rapid and accurate diagnosis of such cases, aiding in timely management.
Unusual Pancreatic Metastasis of Solid Subtype Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma: Reappraisal of MYB and CD117 Immunostaining Utility in Liquid-Based Cytology
- Version of Record online: 21 May 2025
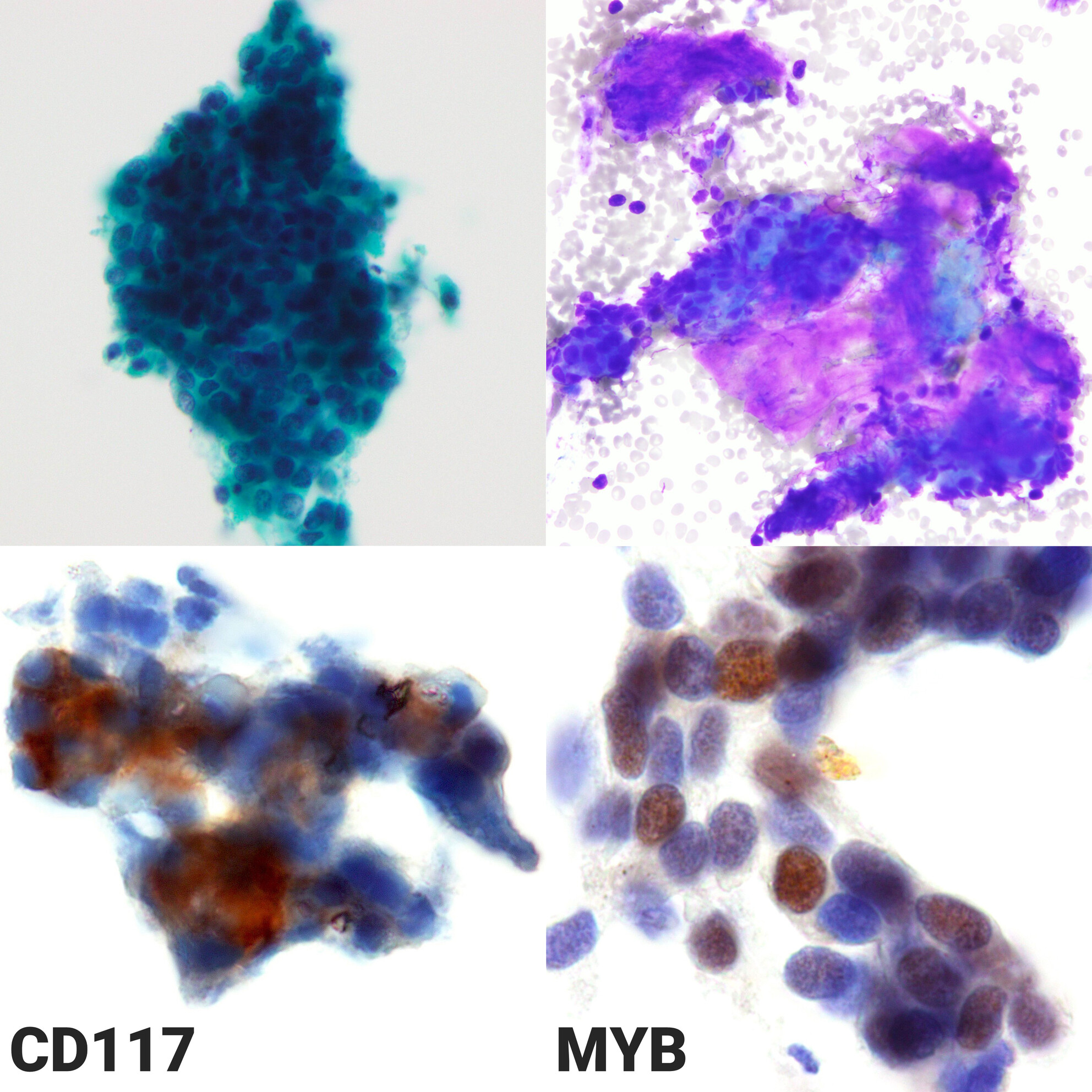
Fine-needle aspiration cytology of a pancreatic tumour revealed basaloid cells with immunocytochemical features of metastatic adenoid cystic carcinoma.
This article describes a rare case of pancreatic metastasis of adenoid cystic carcinoma diagnosed by fine-needle aspiration cytology. Immunocytochemical staining for MYB and CD117 provided critical diagnostic support, highlighting the utility of liquid-based cytology in rare metastatic tumours.
REVIEW
Diagnosing Malignant Epithelial Neoplasms of the Lung in Cytological Specimens: Cytomorphology, Ancillary Studies and Management
- Version of Record online: 21 May 2025
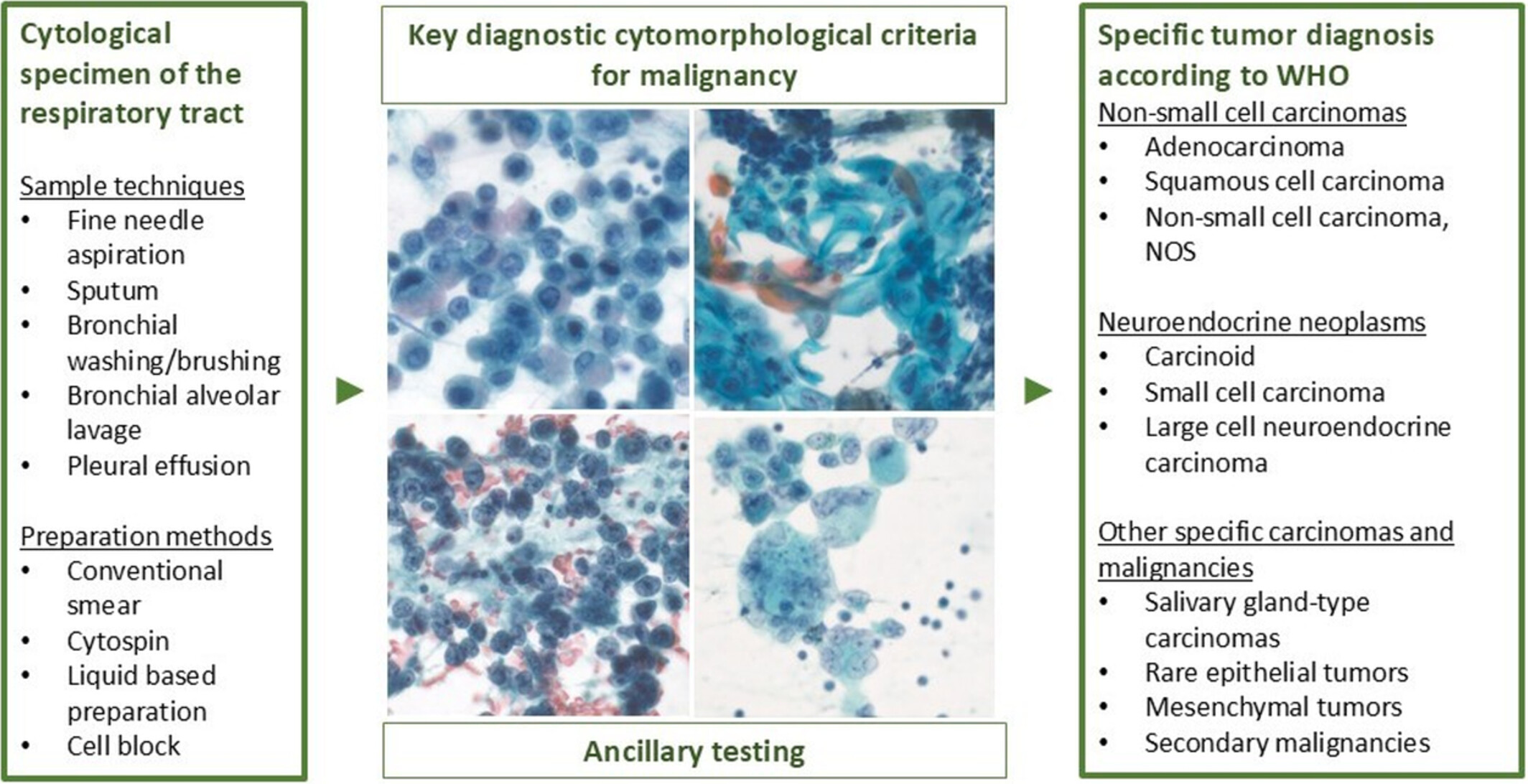
This review provides an overview of the key cytopathological features defining the ‘Malignant’ category of the World Health Organization's Reporting System for Lung Cytopathology and discusses the application of ancillary techniques in cytological specimens from the lung, including immunocytochemistry and molecular testing.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
An Institutional Experience in Lung Endobronchial Ultrasound-Guided Fine Needle Aspiration: Comparing Risk of Malignancy With WHO Reporting System for Lung Cytopathology
- Version of Record online: 14 May 2025
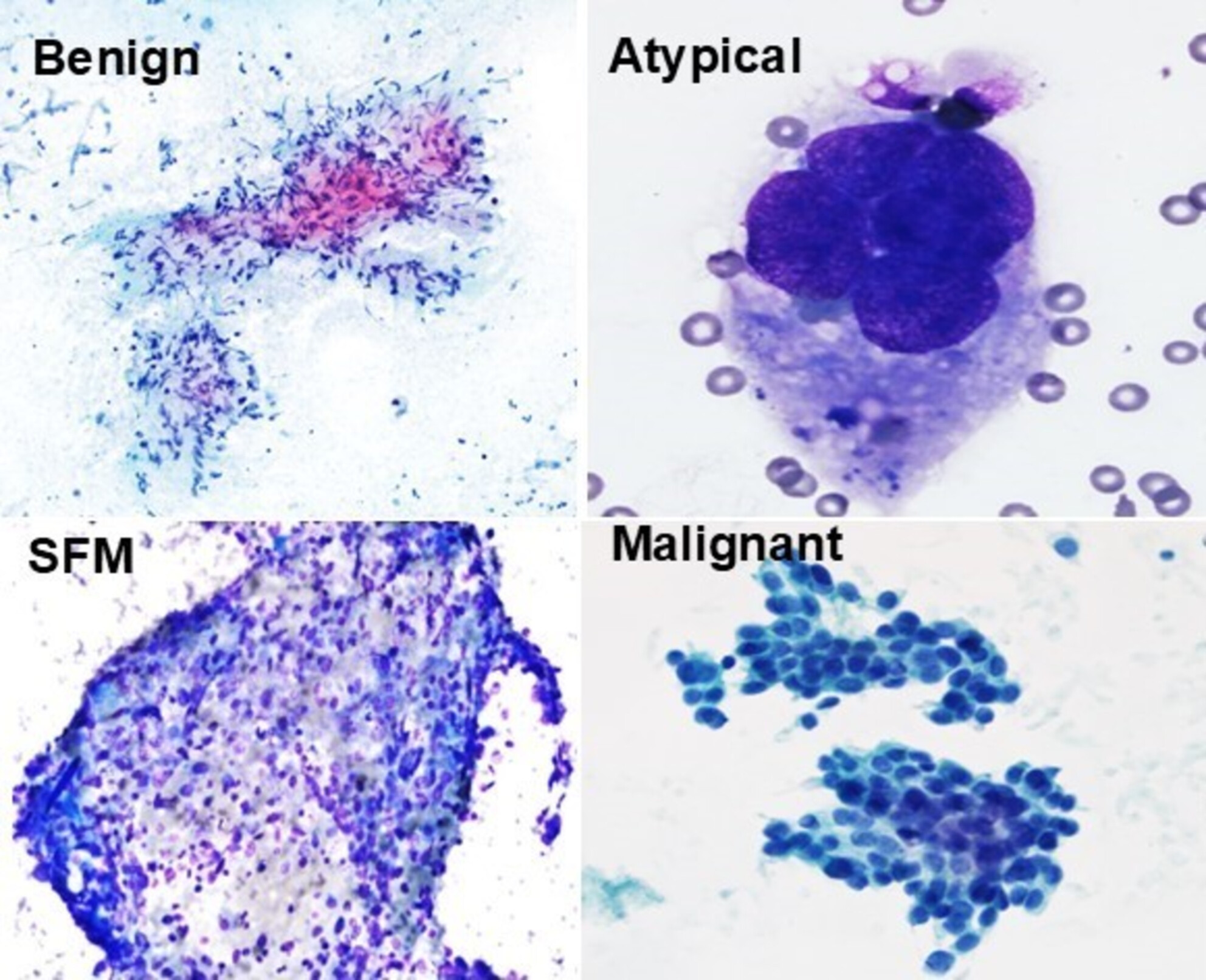
This study evaluates the risk of malignancy (ROM) in EBUS-guided lung FNA specimens using diagnostic categories aligned with the WHO Reporting System for Lung Cytopathology (WHORSLC). The findings demonstrate a higher ROM and cyto-histologic concordance in malignant and suspicious for malignancy (SFM) categories compared to WHORSLC data. The ROM was lower for the non-diagnostic category. These results contribute valuable insights to the limited literature and may help refine ROM estimates within the WHORSLC framework.
This study examines the risk of malignancy (ROM) in EBUS-guided lung FNA specimens using diagnostic categories aligned with the WHO Reporting System for Lung Cytopathology. The authors report a higher ROM and cytohistologic concordance in malignant and suspicious for malignancy categories, contributing important data to refine existing ROM estimates.
CASE REPORT
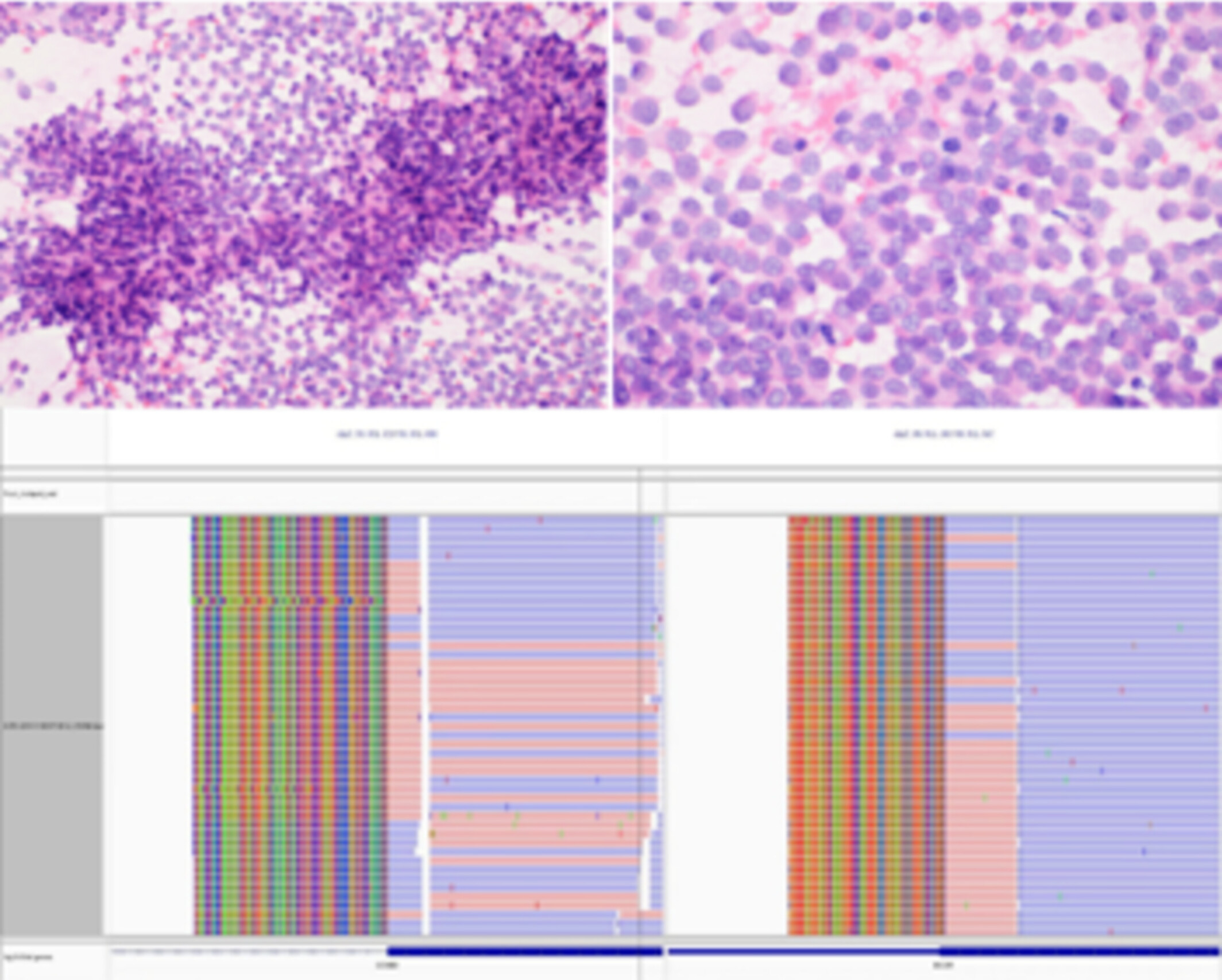
Well-Differentiated Adenocarcinoma With Papillary Architecture, Focal Residual Cilia, Apical Snouts, and CHEK2 and p53 Mutations
- Version of Record online: 14 May 2025
REVIEW
Fine-Needle Aspiration Cytology Diagnosis of Pleomorphic Adenoma With Spontaneous Infarction in the Salivary Gland: A Multicenter Retrospective Study
- Version of Record online: 27 April 2025
Fine-needle aspiration cytology (FNAC) plays a critical role in diagnosing salivary gland lesions. This study summarises and describes the cytopathological features of pleomorphic adenoma with infarction, aiming to differentiate it from malignant tumours by highlighting both similarities and differences. Furthermore, the importance of FNAC in preoperative clinical diagnosis is emphasised.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Evaluating the Diagnostic Impact of the IAC Yokohama System for Breast Fine Needle Aspiration Biopsy Cytopathology: A Prospective Institutional Study
- Version of Record online: 26 April 2025
REVIEW
Diagnostic Category: Suspicious for Malignancy
- Version of Record online: 26 April 2025
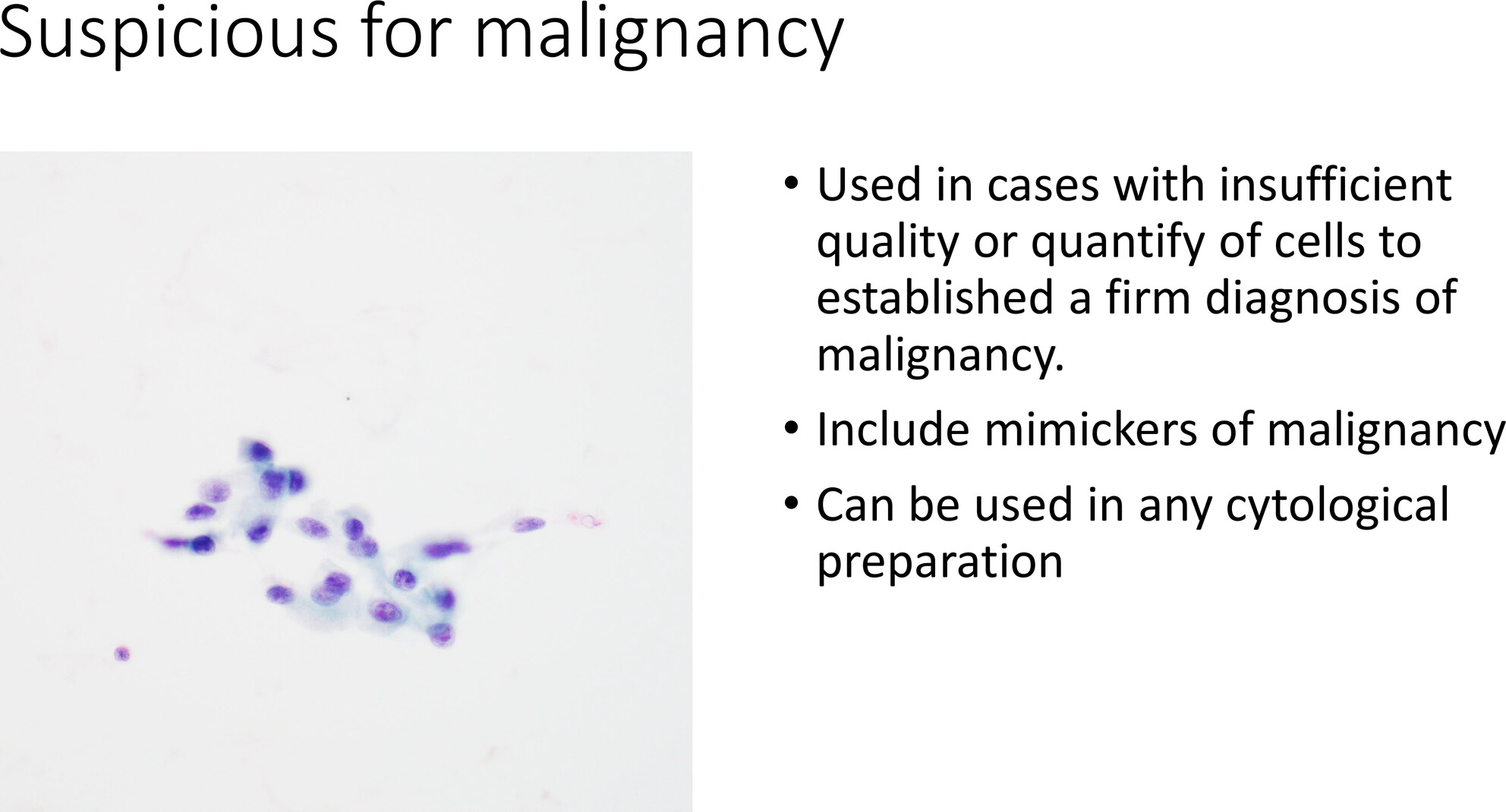
Used in cases with insufficient quality or quantity of cells to establish a firm diagnosis of malignancy. Include mimickers of malignancy. Can be used in any cytological preparation.
The suspicious for malignancy includes samples with insufficient quantify or quality for a definitive diagnosis and includes mimickers of malignancy. This article provides many illustration on possible scenarios in thoracic cytology where the category is used and provide insight of when the category can be upgrade to positive for malignacy.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Micronucleus and Nuclear Budding Help to Identify Malignancy in Thyroid Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology
- Version of Record online: 25 April 2025
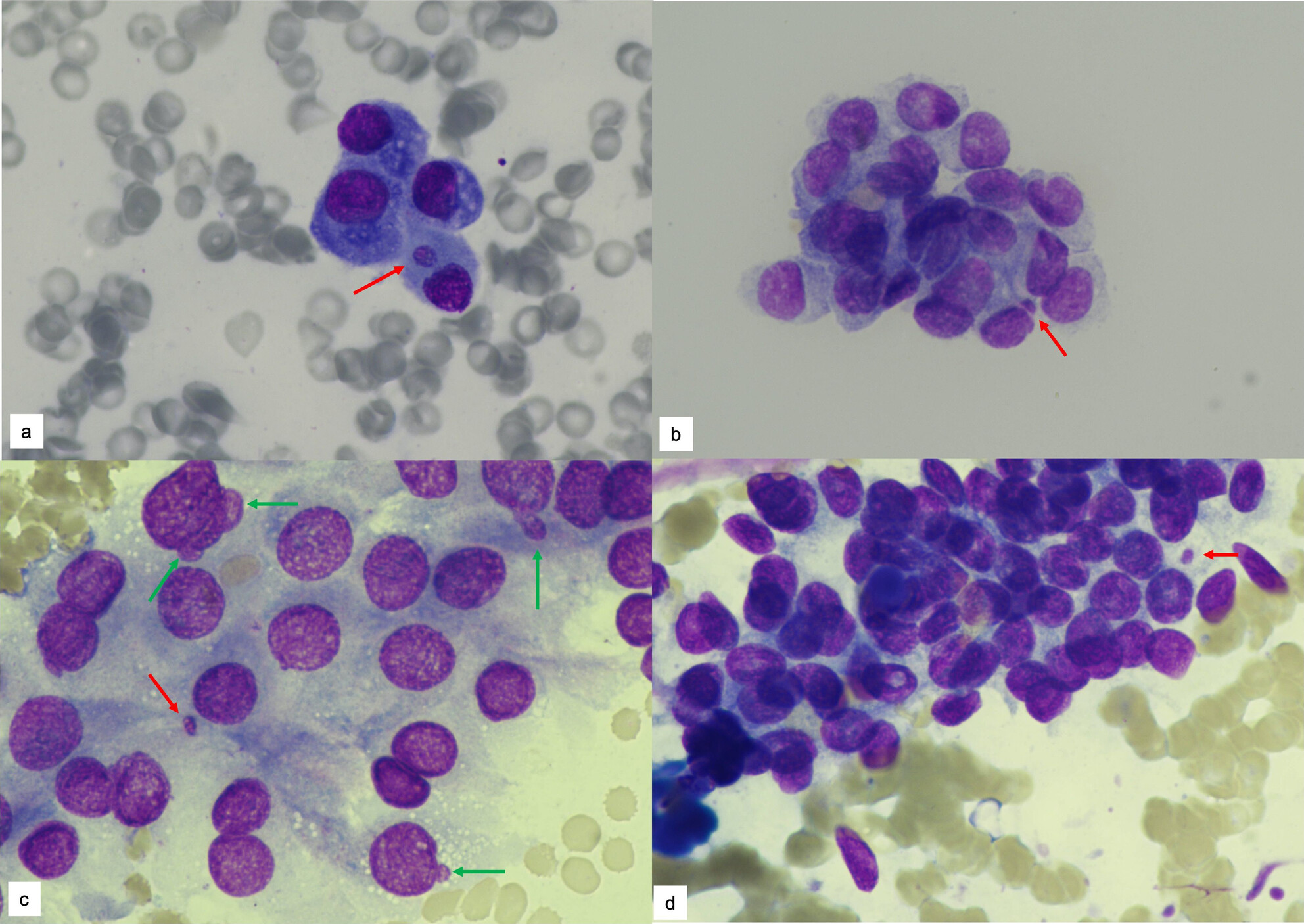
Increased frequency of micronucleus (MN) (red arrows) and nuclear budding (NB) (green arrows) closely associated with an increased risk of malignancy in thyroid FNA. The benign group have lower levels of MN and NB than other cytologic categories. MN and NB counts are greater in the AUS group for cases with a malignant histopathologic diagnosis than for those with a benign histopathologic diagnosis.
ENIGMA PORTAL
Primary Cutaneous Rosai–Dorfman Disease in a Treated Case of Breast Carcinoma—Cytological Diagnostic Enigma
- Version of Record online: 24 April 2025
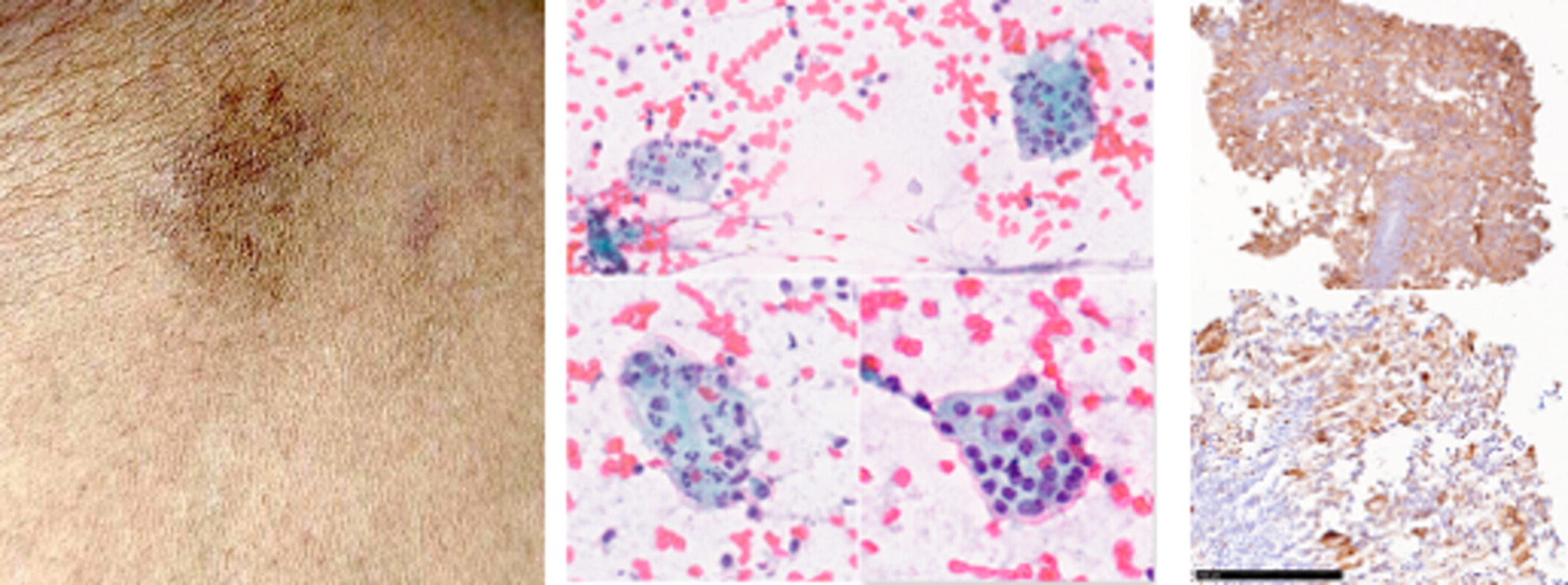
This enigma portal case highlights the cytological features of Primary cutaneous Rosai–Dorfman Disease, which is a breast cancer survivor. The classic morphological features, key diagnostic points and differentials are discussed.
In this report, the classical cytological features of primary cutaneous Rosai–Dorfman disease isare highlighted.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Can Aggressive Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma Variants With Oncocytıc Morphology (Tall Cell and Hobnail Variants) be Detected Cytologically? Is the Differentiation as Straightforward as Reported?
- Version of Record online: 24 April 2025
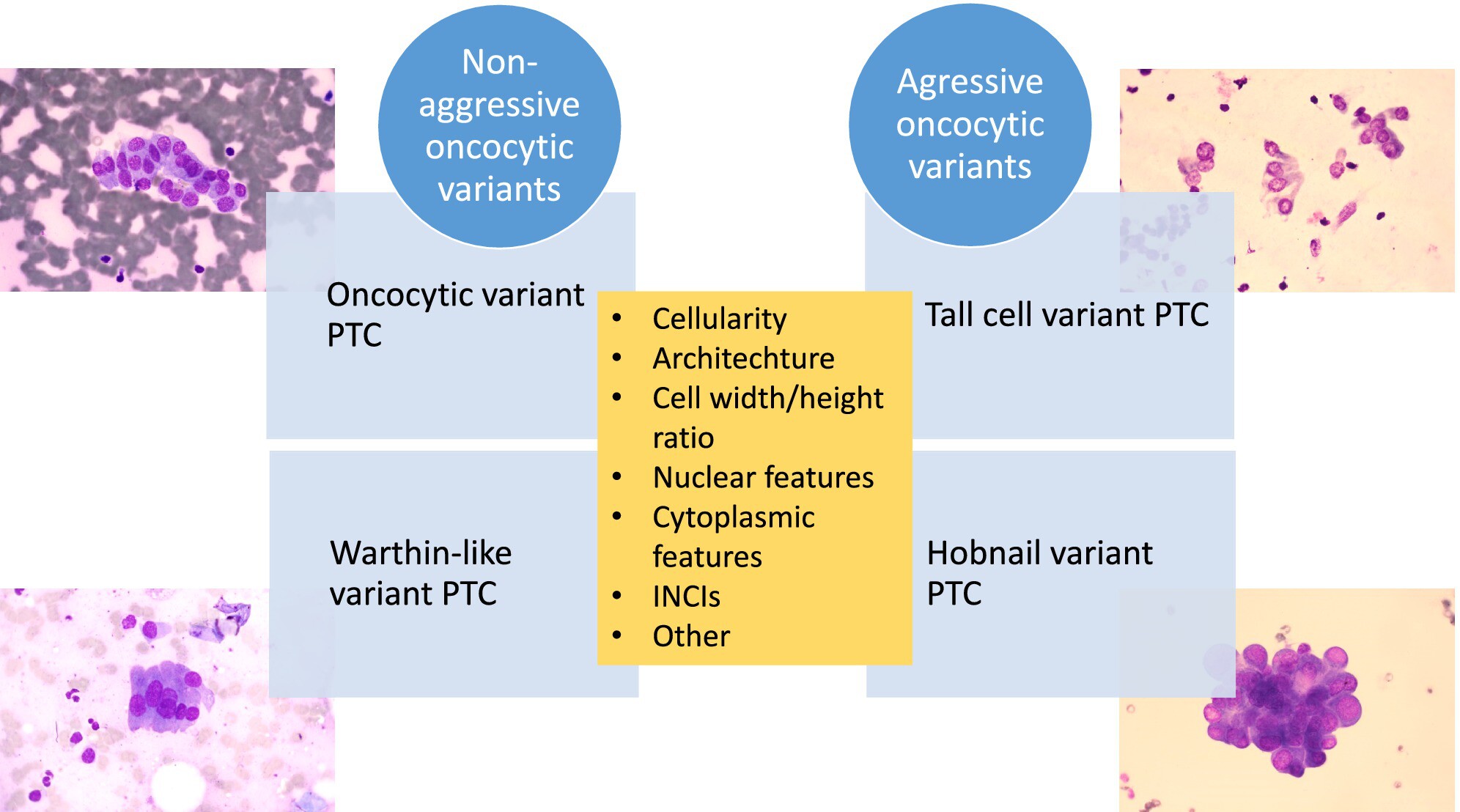
The cytological diagnosis of aggressive variants of papillary thyroid carcinoma is quite challenging; however, it has become essential in contemporary practice as it impacts treatment approaches. The oncocytic morphology-based approach can be beneficial in the cytological diagnosis of the most commonly encountered aggressive variants, such as the tall cell and the hobnail variant. This study investigated cytomorphological features that could serve as potential clues in distinguishing aggressive variants in oncocytic morphology-based PTC variants.
Malignancy Risk, Molecular Mutations, and Surgical Outcomes of Thyroid Nodules Classified as Atypia of Undetermined Significance in the Bethesda System: A Comprehensive Analysis
- Version of Record online: 24 April 2025
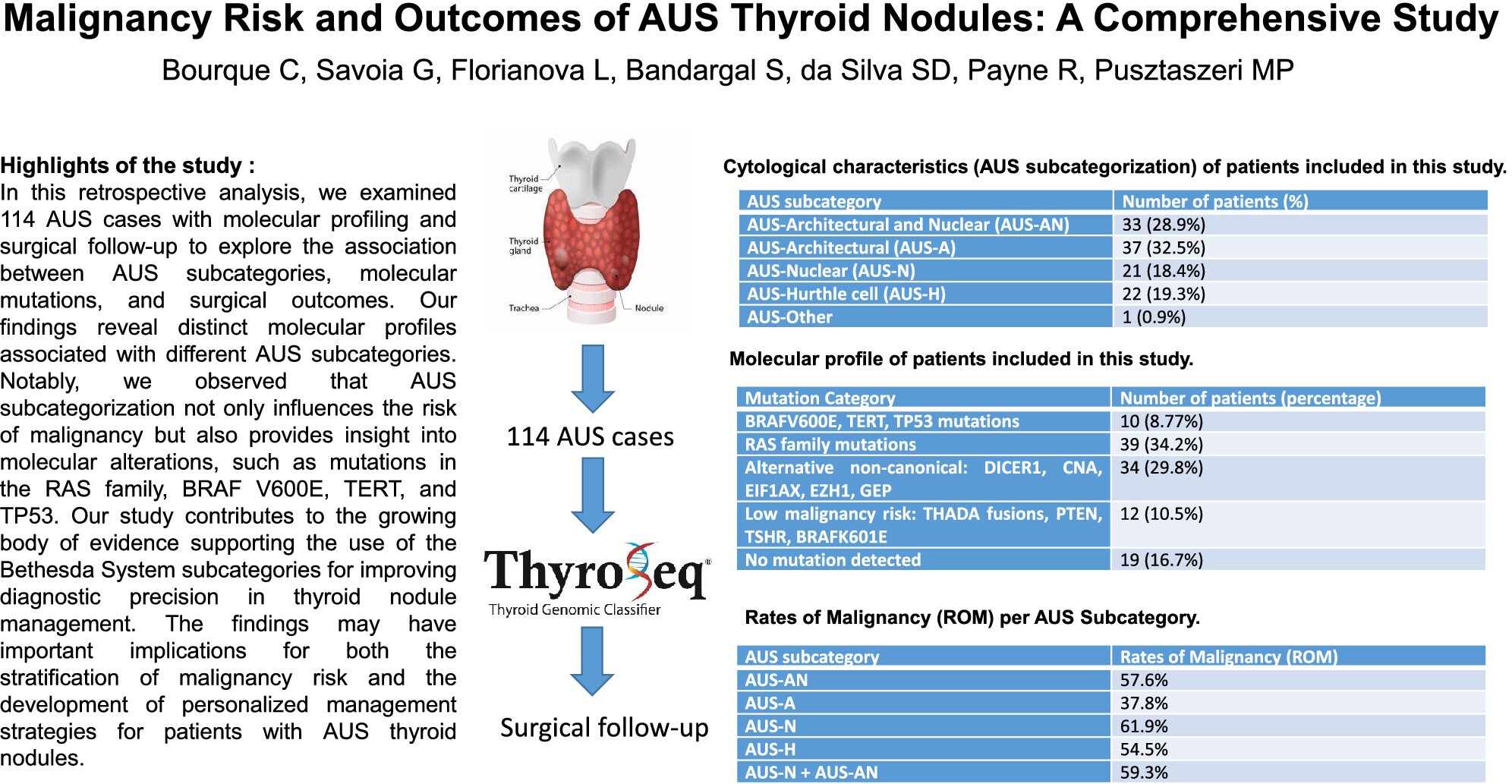
This study investigates the correlation between AUS subcategories, molecular mutations, and surgical outcomes in thyroid nodules classified as atypia of undetermined significance (AUS) under the Bethesda System for Reporting Thyroid Cytopathology. The findings reveal that AUS subcategories exhibit distinct molecular profiles and varying surgical outcomes, with RAS family mutations being the most common alteration. The results support the utility of AUS subclassification in improving risk stratification and guiding clinical management, though further validation through larger prospective studies is recommended.
REVIEW
Benign Category in the WHO Reporting System for Lung Cytopathology: Diagnostic Difficulties and Differential Diagnosis
- Version of Record online: 24 April 2025
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Clinical Performance of a Liquid Preservation Medium for Cervicovaginal Samples in DNA-HPV Testing and Liquid-Based Cytology for Cervical Cancer Screening
- Version of Record online: 23 April 2025
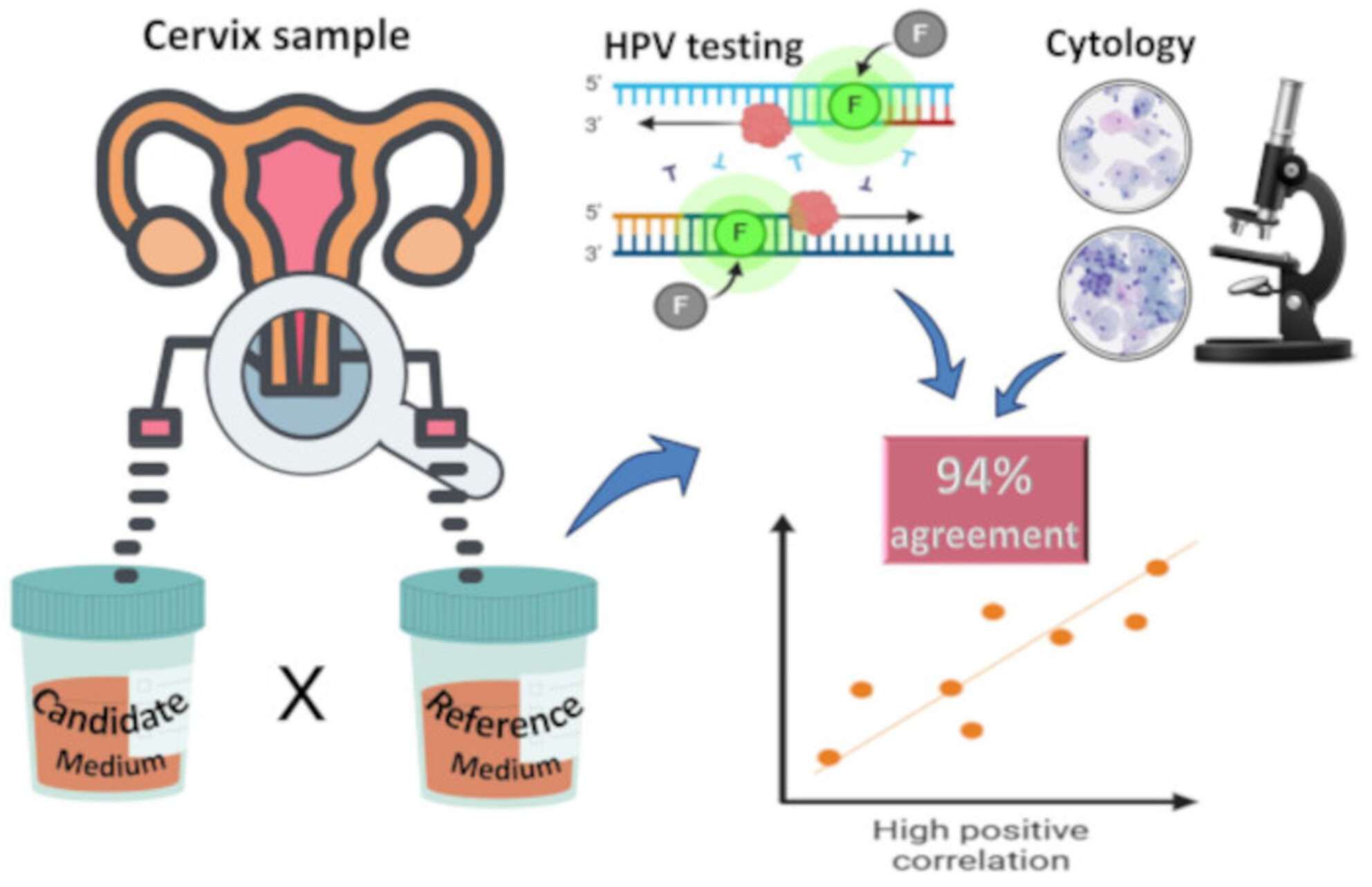
The study evaluated the performance of a new liquid preservation medium for cervical samples in DNA-HPV testing and liquid-based cytology. The candidate medium demonstrated a 94.5% agreement rate in HPV testing, 92.9% sensitivity for detecting CIN2+ and good performance in liquid-based cytology. The findings support its potential as a viable alternative for cervical cancer screening.
CASE REPORT
Cytomorphological and Immunohistochemical Features of Metastatic Malignant Phyllodes Tumour in Pleural Fluid: A Case Report With Literature Review
- Version of Record online: 21 April 2025
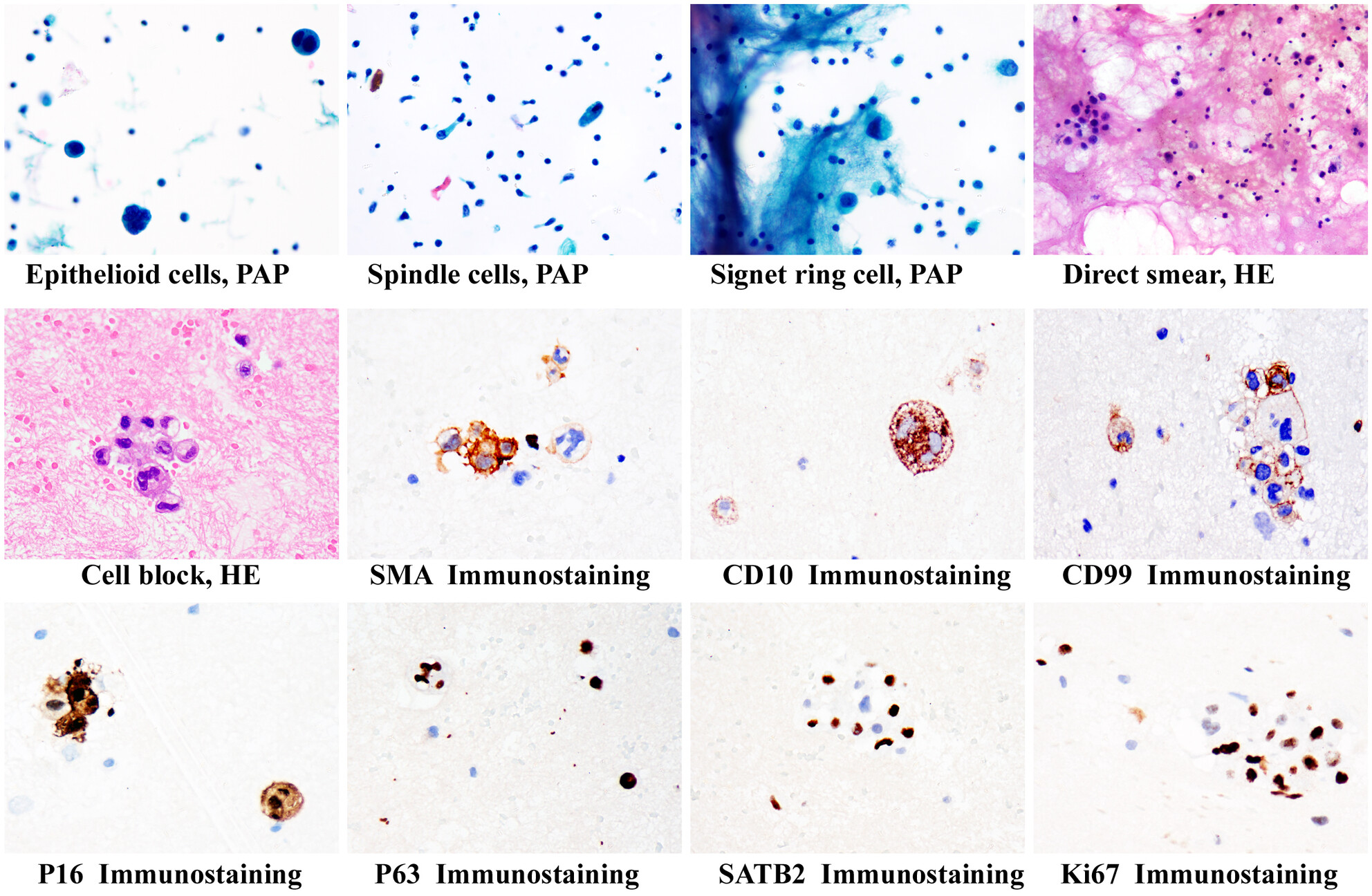
The cytomorphology of malignant phyllodes tumour (MPT) in effusion specimens is rarely described. In this paper, the detailed cytopathological and immunohistochemical characteristics of metastatic MPT have been described in pleural effusion. Patients' medical history and the judicious utilisation of ancillary studies including cellblock and immunocytochemistry contribute to ensure precise cytological diagnoses.
The cytomorphology of malignant phyllodes tumour (MPT) in effusion specimens can be diagnostically challenging. The author presents detailed cytopathological and immunohistochemical characteristics of a case of metastatic MPT in pleural effusion.
Villoglandular Carcinoma of the Uterine Cervix: Clinic-Cytopathological-Histological Features of a Rare Case With Brief Review of the Literature
- Version of Record online: 21 April 2025
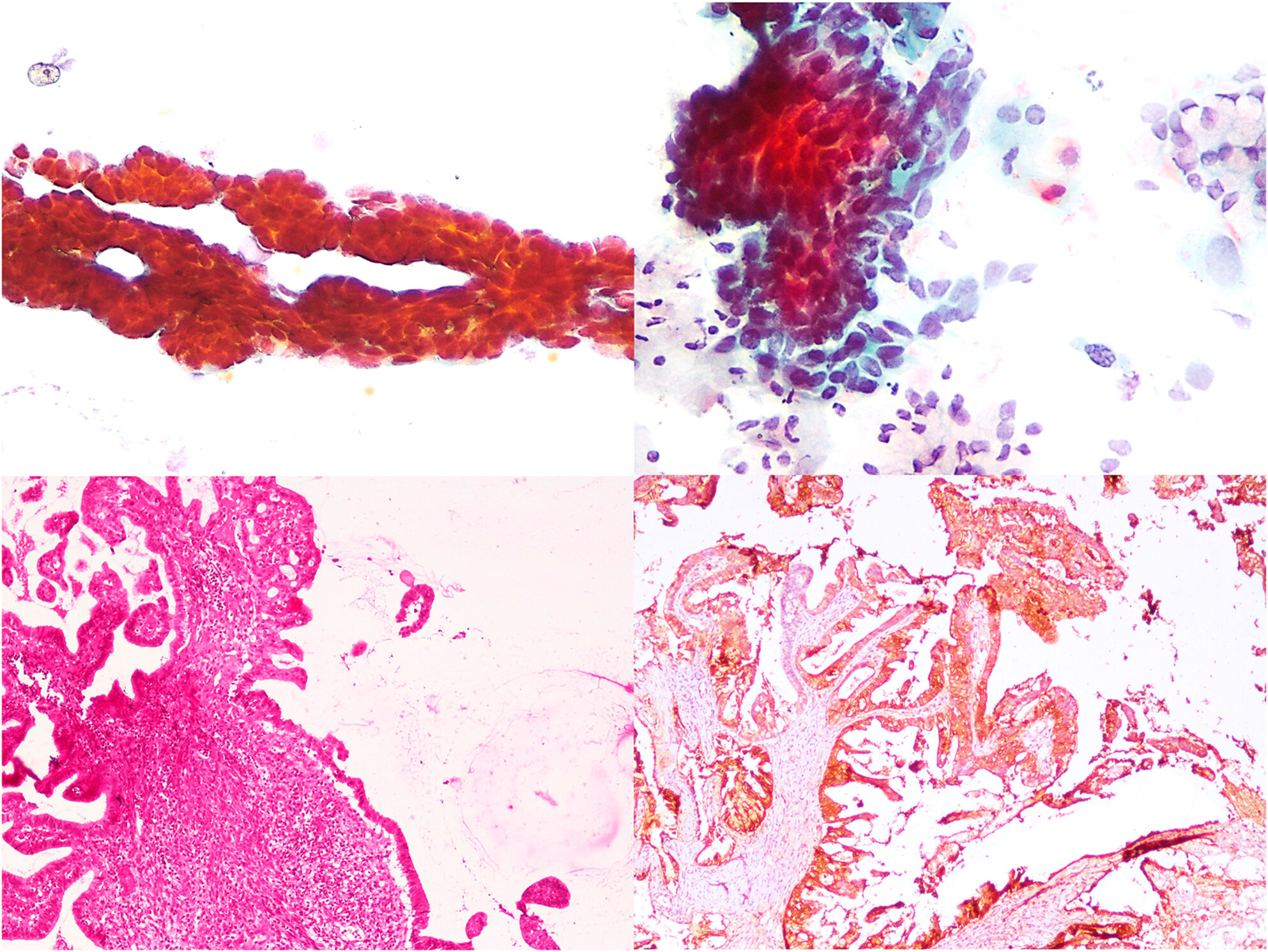
Villoglandular carcinoma of the cervix is a rare subtype of cervical adenocarcinoma that can be recognised on cytology by three-dimensional papillary fragments and relatively bland nuclear features. Knowledge of this entity is imperative for an accurate pre-operative diagnosis and appropriate management.
Primary Hepatoid Adenocarcinoma of the Lung: Clues for Cytological Diagnosis
- Version of Record online: 14 April 2025
Hepatoid carcinoma is an aggressive and infrequent type of tumour. Lung is a very infrequent location of this tumour. Hepatoid carcinoma can be suspected from cytological features. Immunocytochemistry can confirm suspicion in cytological samples.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Investigating Career Advancement in Academic Cytopathology Workforce: A Gender and Regional Comparison
- Version of Record online: 10 April 2025
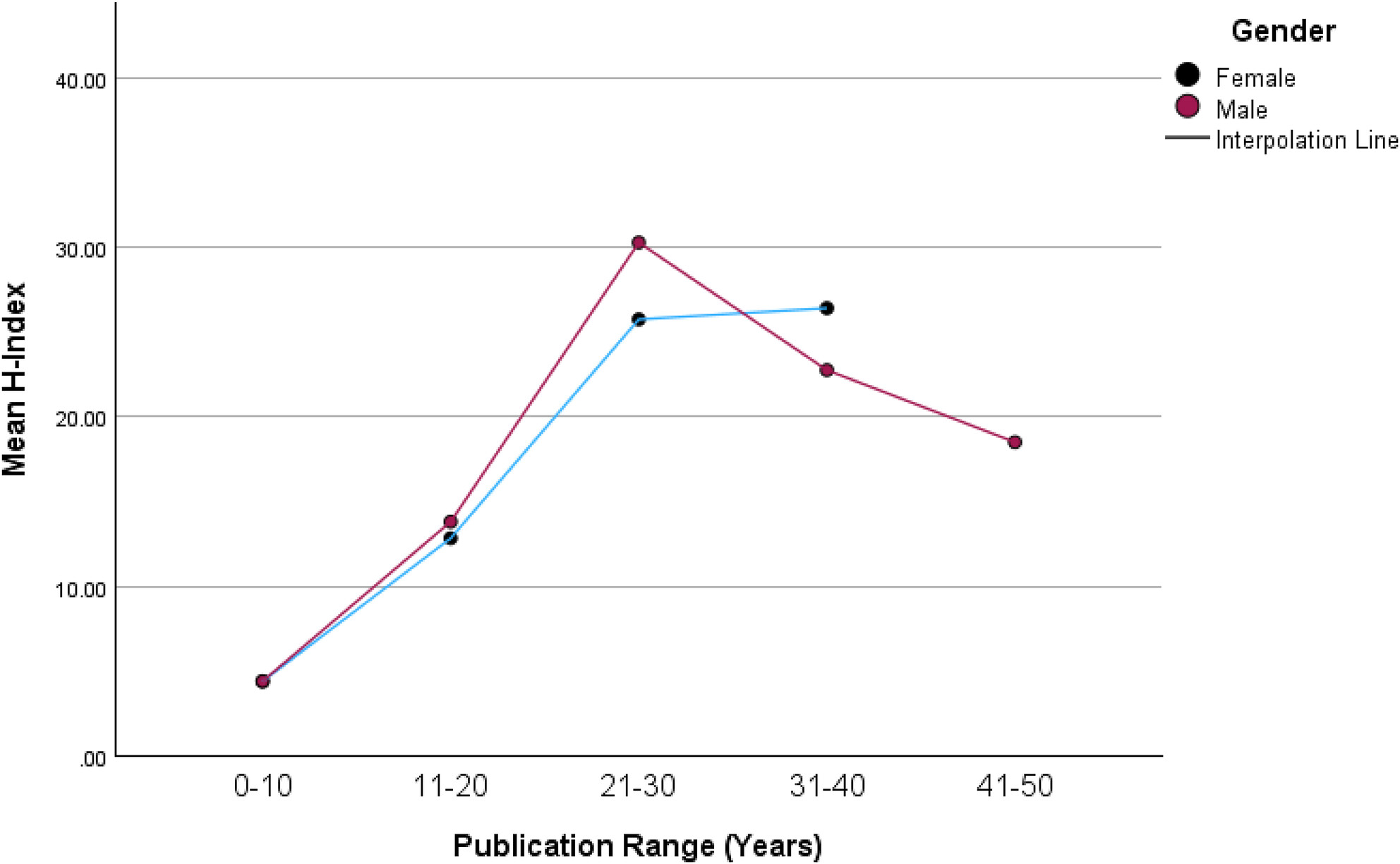
While initial research productivity was similar between genders, male cytopathologists showed a slightly faster rate of increase in the second to third decades, followed by a tapering off or decline. Female faculty exhibited a shorter maximum duration of research activity compared to males.
This bibliometric study examined factors in academic cytopathology faculty promotion, revealing a higher proportion of women in lower ranks despite gender not being a significant predictor of promotion. Promotion to full professor was influenced by regional location, publication experience and productivity. The findings suggest that targeted support for mid-career female cytopathologists, focusing on research resources and work–life balance, could further address the observed differences in gender distribution at the highest academic level.
Evaluation of Diagnostic Accuracy of Directly Sampled Endometrial Cytology Using ThinPrep for Endometrial Malignancies: Comparison With Existing Endometrial Liquid-Based Cytology
- Version of Record online: 07 April 2025
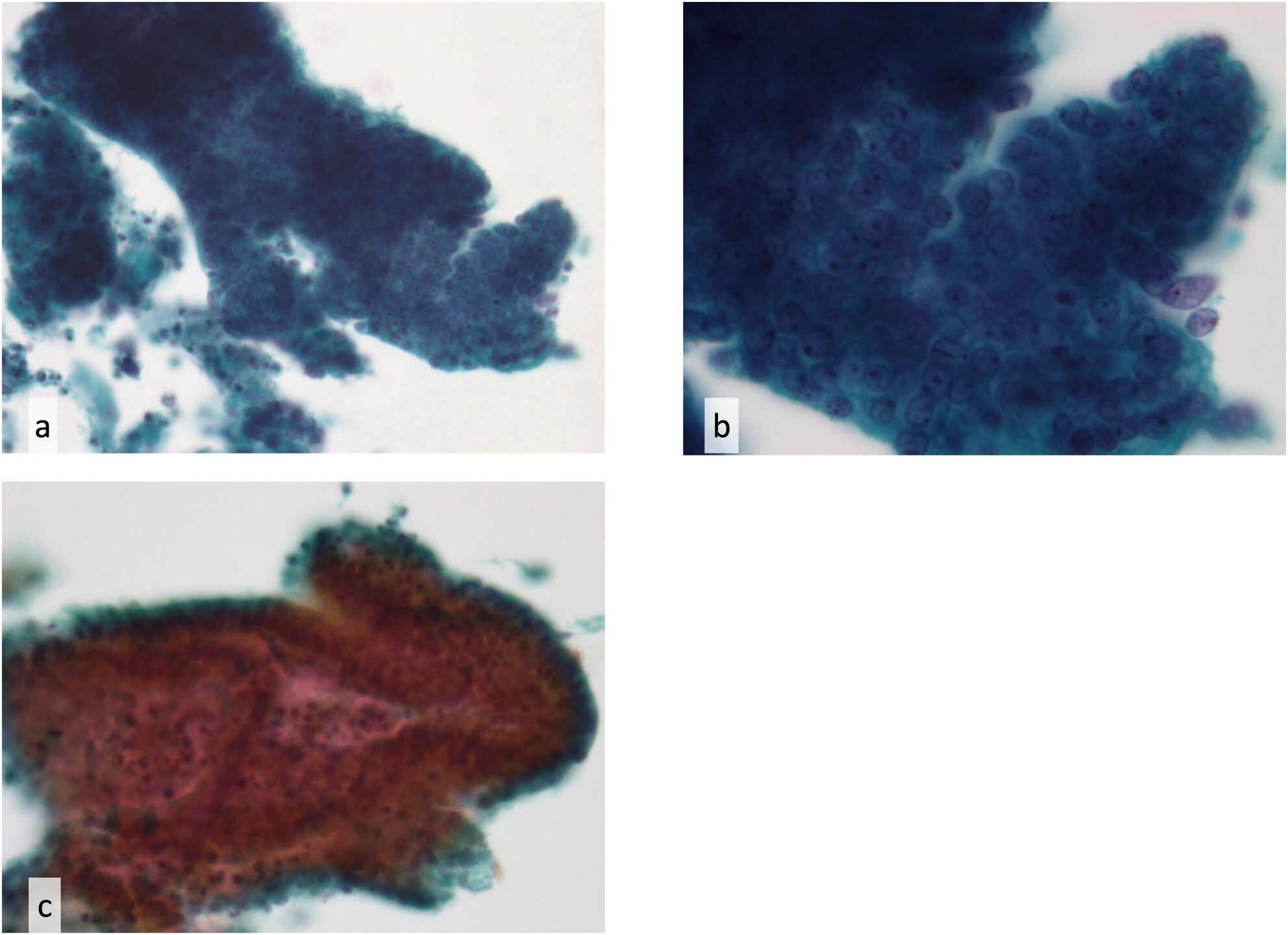
This study evaluated the diagnostic accuracy of directly sampled endometrial cytology using ThinPrep with a novel preparation method for detecting endometrial malignancies. The method yielded high-quality cytology samples, and examiners with minimal experience demonstrated high diagnostic accuracy using the Yokohama System, supporting its global clinical adoption.
CASE REPORT
FNA Diagnosis of Adult Rhabdomyoma of the Tongue and Floor of the Mouth
- Version of Record online: 28 March 2025
Awareness of rhabdomyoma and its distinct morphological features enables pathologists to differentiate it from other entities with abundant granular eosinophilic cytoplasm, ensuring accurate diagnosis and preventing unnecessary biopsies or radical surgical interventions.
Rhabdomyoma is a slow-growing mass occurring in the head and neck region. A definite diagnosis can be made in FNA cytology with the awareness of the classical morphological features (tumor cells in cohesive clusters, abundant granular eosinophilic cytoplasm without atypia and mitosis), obviating the need for a biopsy or frozen section. Immunocytochemistry can be performed on the smears, and immunohistochemistry on the cell blocks if available. Preoperative diagnosis is necessary to avoid aggressive or unnecessary radical surgery.
REVIEW
WHO Reporting System for Lung Cytopathology: Insights Into the Insufficient/Inadequate/Non-Diagnostic, Atypical and Suspicious for Malignancy Categories and How to Use Them
- Version of Record online: 26 March 2025
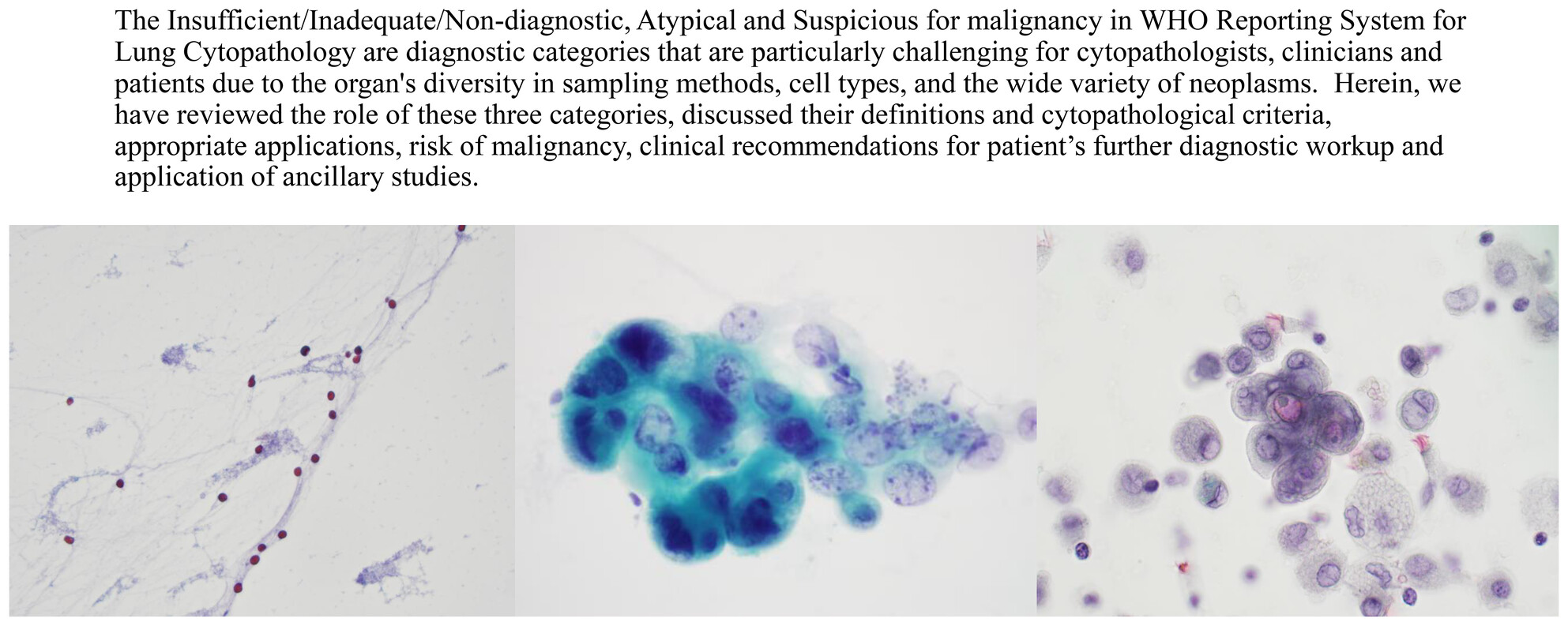
The WHO System is an international effort to standardise category definitions, establish the key diagnostic cytopathological features of entities of the lung, propose the best use of ancillary tests in lung specimens, encourage the use of standardised pathology reports containing essential components in an integrated report and propose estimates of the risk stratification for each diagnostic category based on the current literature, and recommend further diagnostic management. The ultimate aim was to improve patient care globally regardless of the available local medical resources by creating a common language between cytopathologists and clinicians, but the Inadequate/Insufficient/Non-diagnostic, Atypical and Suspicious for malignancy categories can often lead to miscommunication or frustration. There has to be clear discussion between pathologist and clinician because these categories frequently require additional cytopathological evaluation, CNB, appropriate ancillary tests and discussion in tumour boards whenever available to establish a specific diagnosis.
Insufficient, Atypical and Suspicious for malignancy categories in the WHO system for lung cytology are challenging. The clinician's expertise in obtaining specimens, the cytopathologist's diagnostic skill, the lesion's size, site and characteristics, ROSE access, specimen triaging and preparation techniques, ancillary tests and CNB are contributing factors.