Can Aggressive Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma Variants With Oncocytıc Morphology (Tall Cell and Hobnail Variants) be Detected Cytologically? Is the Differentiation as Straightforward as Reported?
Funding: The authors received no specific funding for this work.
ABSTRACT
Objective
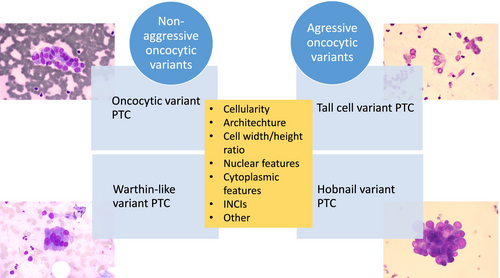
Identifying aggressive variants of throid papillary carcinoma correctly is paramount, as their diagnosis requires more extensive surgical interventions. Numerous cytologic scoring systems have been proposed to distinguish non-aggressive from aggressive variants. Oncocytic morphology is characterised by cells with abundant granular cytoplasm resulting from mitochondrial accumulation. This feature is particularly prominent in specific PTC variants. Tall cell and hobnail variants are aggressive variants with oncocytic morphology. The present study aims to evaluate the cytomorphological features of 51 histologically confirmed papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC) cases with oncocytic morphology and to identify cytological features that could facilitate the distinction between aggressive (tall cell and hobnail) and non-aggressive (oncocytic and Warthin-like) variants during the FNA stage, thereby enabling early detection of aggressive variants.
Methods
We retrospectively examined the cytological features of cases diagnosed with histologically confirmed aggressive variants with poor prognosis (tall cell and hobnail) and non-aggressive variants with good prognosis (oncocytic and Warthin-like), obtained from the pathology department of our hospital between 2014 and 2020.
Results
39 cases (76.5%) classified into the good prognosis group, which included oncocytic variant (O-PTC) (33 cases) and Warthin-like variant (WL-PTC) (6 cases). The poor prognosis group included 12 cases (23.5%), comprising hobnail variant (HN-PTC) (2 cases) and tall cell variant (TC-PTC) (10 cases). The swirl pattern was significantly more frequent in the poor prognosis group (83.3% vs. 43.6%, p = 0.022), with a sensitivity of 83.3% and specificity of 56.4%. The presence of nuclear grooves was observed in all cases of the poor prognosis group (100%) while in 61.5% of the good prognosis group (p = 0.011). This feature exhibited 100% sensitivity and 38.4% specificity. Concerning cytoplasmic volume, scant-medium amount cytoplasmic volume was significantly more common in the poor prognosis group (66.7% vs. 20.5%, p = 0.005), showing 66.7% sensitivity and 79.4% specificity, and yielding the highest accuracy rate (76.4%) among all characteristics.
Conclusions
Oncocytic morphology-based approaches may help identify poor prognosis variants and guide clinical decisions. In our study, cellular swirls, grooves and scant-medium cytoplasmic volume were the most significant cytological indicators for identifying poor prognosis variants. Despite previous emphasis on cell width/height ratio and foamy INCIs for TC-PTC diagnosis, no significant differences were found between the two groups in our study.
Graphical Abstract
The cytological diagnosis of aggressive variants of papillary thyroid carcinoma is quite challenging; however, it has become essential in contemporary practice as it impacts treatment approaches. The oncocytic morphology-based approach can be beneficial in the cytological diagnosis of the most commonly encountered aggressive variants, such as the tall cell and the hobnail variant. This study investigated cytomorphological features that could serve as potential clues in distinguishing aggressive variants in oncocytic morphology-based PTC variants.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Open Research
Data Availability Statement
We do not have any shareable or accessible data.