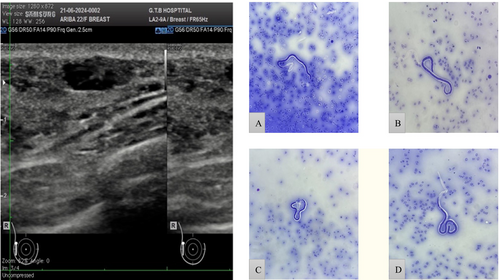
Breast Filariasis—Diagnosed by Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology: A Rare Case Report
ABSTRACT
Filariasis and its consequences are a major health problem in tropical countries, including the Indian subcontinent. Lymphatic filariasis affects 90 million people worldwide. Despite the huge number of people affected all around the world, it is quite infrequent to find microfilaria in routine cytological smears and body fluids. The breast is an uncommon site for the occurrence of a filarial nodule, and only a few cases have been documented. We report a case of a young female who presented with a painful right breast lump. Clinically suspected of neoplasm, and ultrasound was suspicious for filariasis. FNAC (fine needle aspiration cytology) was used to make the final diagnosis of filariasis.
Graphical Abstract
This case report highlights a rare presentation of breast filariasis in a young female, diagnosed through fine needle aspiration cytology. Despite the high prevalence of lymphatic filariasis in endemic regions, extranodal involvement of the breast is uncommon and can mimic neoplastic lesions. The report emphasises the importance of FNAC in the rapid and accurate diagnosis of such cases, aiding in timely management.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Open Research
Data Availability Statement
The data supporting the findings of this study are available upon request from the corresponding author. Due to the nature of the data, some restrictions may apply to protect sensitive or proprietary information. The images used in this study have been included in the manuscript as Supporting Information.