River publishes multidisciplinary hydrological research on all applications of river systems and traditional water-related areas, including river science, technology, engineering, conservation, and governance and strategy. The scope includes geotechnical engineering and dam construction, estuarine and offshore engineering, water culture, policy, and security, and water resources including environment, ecology, disaster, hydraulics, and irrigation.
Journal Metrics
- 2.6CiteScore
- 76%Acceptance rate
- 59 days Submission to first decision
Why publish in River?
- Publish open access at no cost. Article processing charges are currently waived.
- Join a community of authors reaching global audiences from engineering, ecology and policy with their work.
- River is indexed by SCOPUS and the DOAJ, which maximizes the discoverability and status of your research.
- Benefit from the insight and support of a global editorial board with extensive research and practical experience.
- Published on behalf of the world leading China Institute of Water Resources and Hydropower Research.
Articles
Occurrence characteristics of microplastics in Dongting Lake, China
- 24 June 2025
Numerical model in water quality: The case study of Da Nang City in central Vietnam
- 149-161
- 23 June 2025
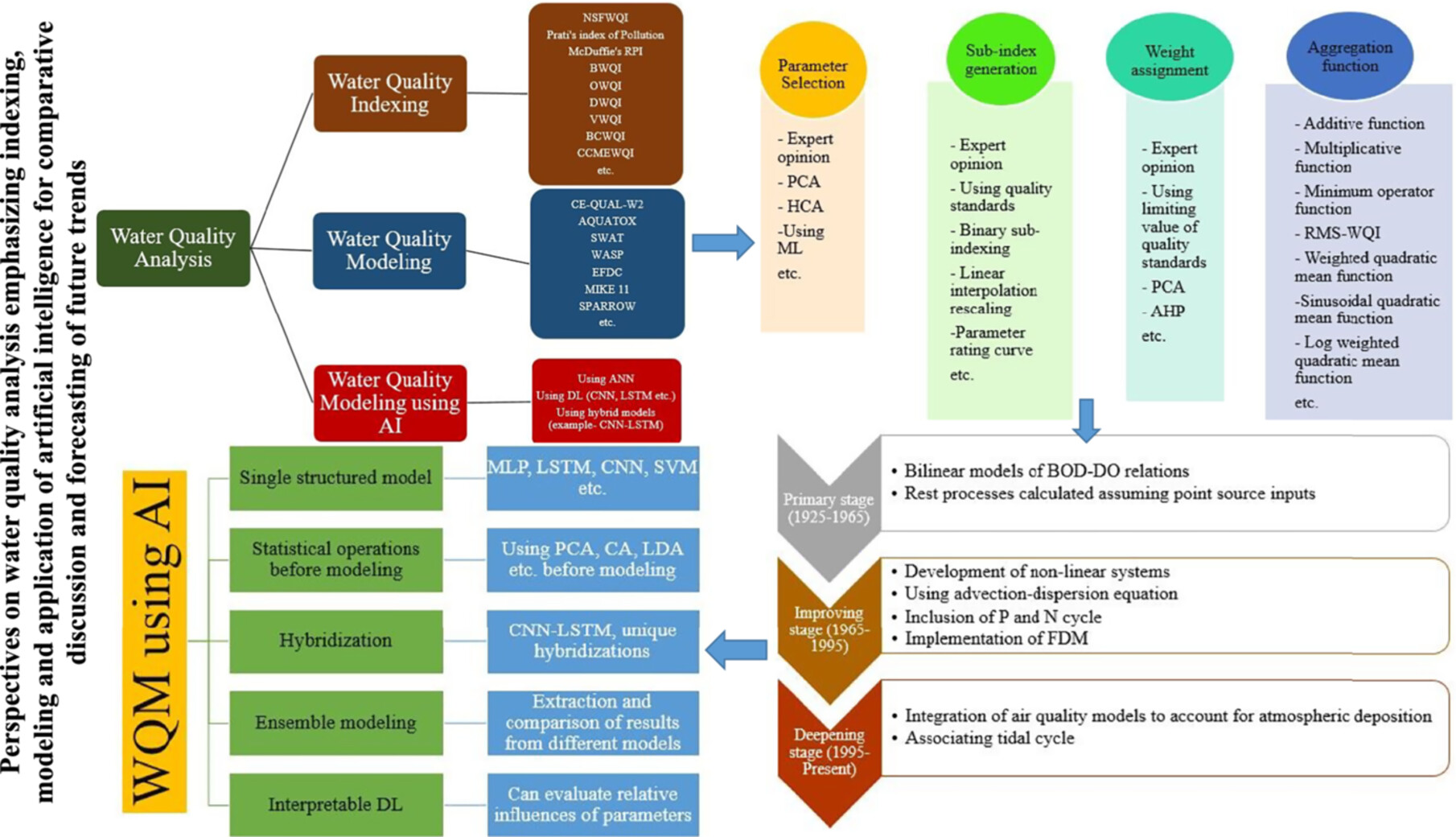
Perspectives on water quality analysis emphasizing indexing, modeling, and application of artificial intelligence for comparison and trend forecasting
- 265-286
- 3 June 2025
A review on effects of human activities on aquatic organisms in the Yangtze River Basin since the 1950s
- River
- 104-119
- 28 August 2022
The 2022 extreme drought in the Yangtze River Basin: Characteristics, causes and response strategies
- River
- 162-171
- 5 December 2022
Effect of water depth and waterway obstructions on the divergence and confluence areas of Dongting Lake and the Yangtze River after the operation of the Three Gorges Project
- River
- 88-108
- 3 January 2023
Assessment of meander‐bend migration of a major distributary of the Ganges River within Bangladesh
- River
- 240-255
- 15 November 2022
Graphical Abstract
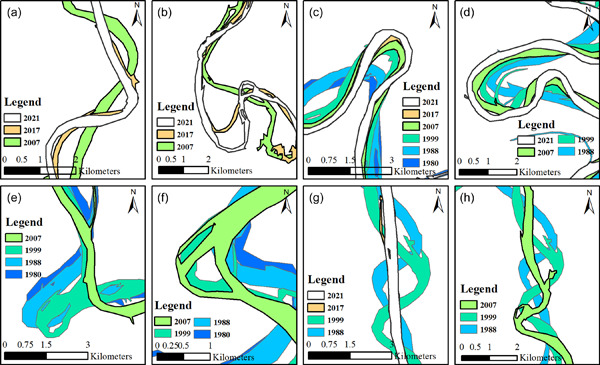
The offtake of the Arial Khan River, an important distributary of the Ganges River, shifts periodically. This shifting of the offtake exerts an important control on the morphology of the river itself. The upper reach of the river is found to be morphologically more unstable than the middle and lower reaches and the bend migration rate is also found to be higher in this reach. An envelope curve depicting the relation between the relative curvature of a bend and its migration is developed for the first time for any Bangladesh river.
Recent advances in the investigation of a slow‐moving landslide in the Three Gorges Reservoir area, China
- River
- 91-103
- 17 July 2022
Beyond natural flow: Human‐directed course change of the Kolong river in Nagaon, Assam, (India) and its socio‐ecological implications
- River
- 408-415
- 1 December 2024
Graphical Abstract
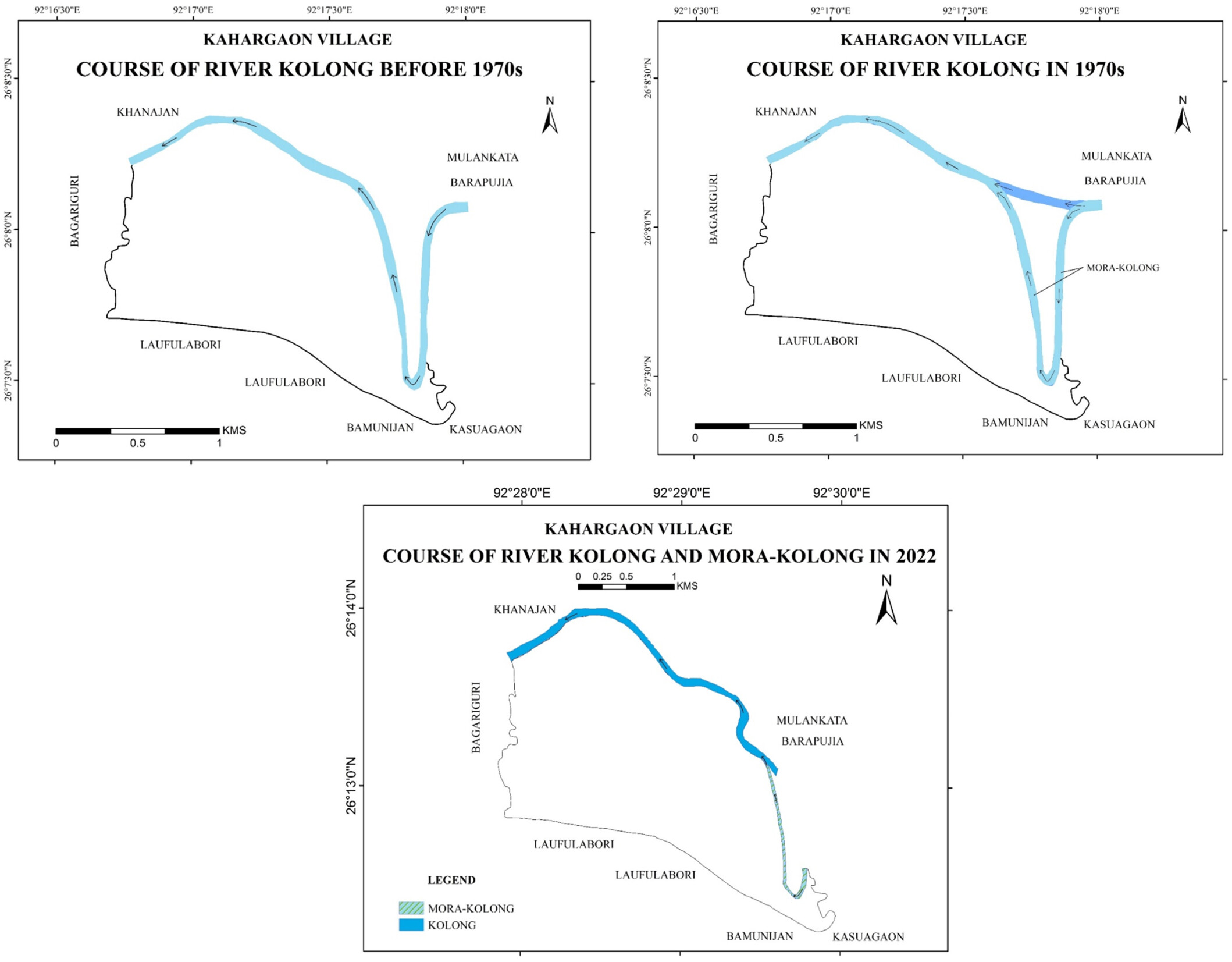
This study investigates the socio-ecological impacts of the artificial course change of the Kolong River in Kahargaon village, Nagaon district. Employing a mixed-methods approach, the research integrates field observations, stakeholder interviews, community forums, and secondary data analysis to assess the river's dynamics and its effects on local livelihoods and ecosystems. Findings reveal that while flood mitigation efforts have provided immediate relief, they have also led to ecological degradation and disrupted traditional livelihoods, particularly those dependent on the river's natural flow.
Sedimentation and regulation technologies in the Three Gorges Reservoir
- River
- 123-132
- 7 December 2022
Graphical Abstract

Sedimentation is one of the key technical problems present throughout feasibility demonstration, design, construction, and operation of the Three Gorges Project. Since the Three Gorges Reservoir began impoundment operation in 2003, important progress has been made in sedimentation and regulation technologies through systematic research and practices. This paper reveals the asynchronous propagation pattern of flood and sediment peak inflows, sediment movement in the backwater area during drawdown period, sediment flocculation, and sediment deposition that compromises the flood control reservoir storage, and puts forward new sediment regulation techniques, including sediment peak discharge regulation during flood season, siltation reduction in the backwater area during drawdown period, dynamic adjustment of the reservoir level during flood season, and joint sediment regulation in cascade reservoirs. A real-time monitoring, forecasting and dynamic regulation platform for water and sediment inflow in the Three Gorges Reservoir was developed; a new mode of dynamic sediment regulation called “regulating sediment for greater benefits” is proposed, which addresses the constraints of sedimentation on the optimal operation of Three Gorges Reservoir. By enabling more flexible operation, this mode improves the process and pattern of sedimentation, ensures the safety of reservoir operation, and significantly augments the comprehensive benefits of the Three Gorges Reservoir.
Projection of future dry‐wet evolution in Northwest China and its uncertainty attribution analysis
- River
- 65-78
- 9 March 2023
Graphical Abstract
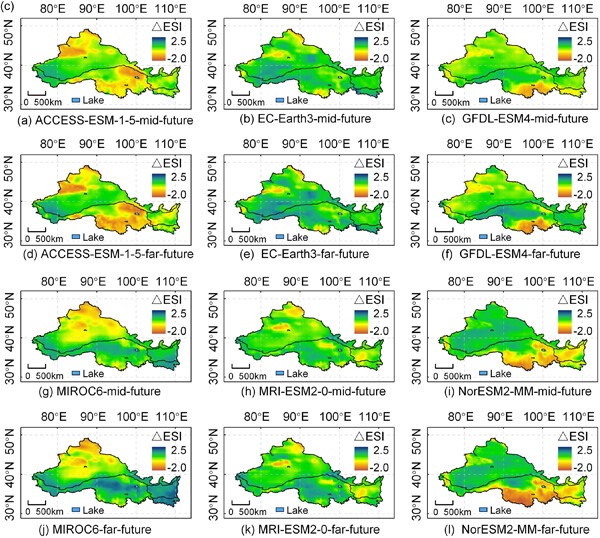
This paper established a framework for dry-wet projections that took into account uncertainties from Global Climate models, climate scenarios, and potential evapotranspiration models; and then obtained a objective and comprehensive ensemble consisting of 108 projection results. Finally, we quantified the contribution of each uncertainty source to the total uncertainty.
Strategies for a resilient, sustainable, and equitable Mississippi River basin
- River
- 336-349
- 20 September 2023
Resolving the Ganges pollution paradox: A policy‐centric systematic review
- River
- 126-141
- 28 February 2023
The 2022 extreme drought in the Yangtze River Basin: Characteristics, causes and response strategies
- River
- 162-171
- 5 December 2022
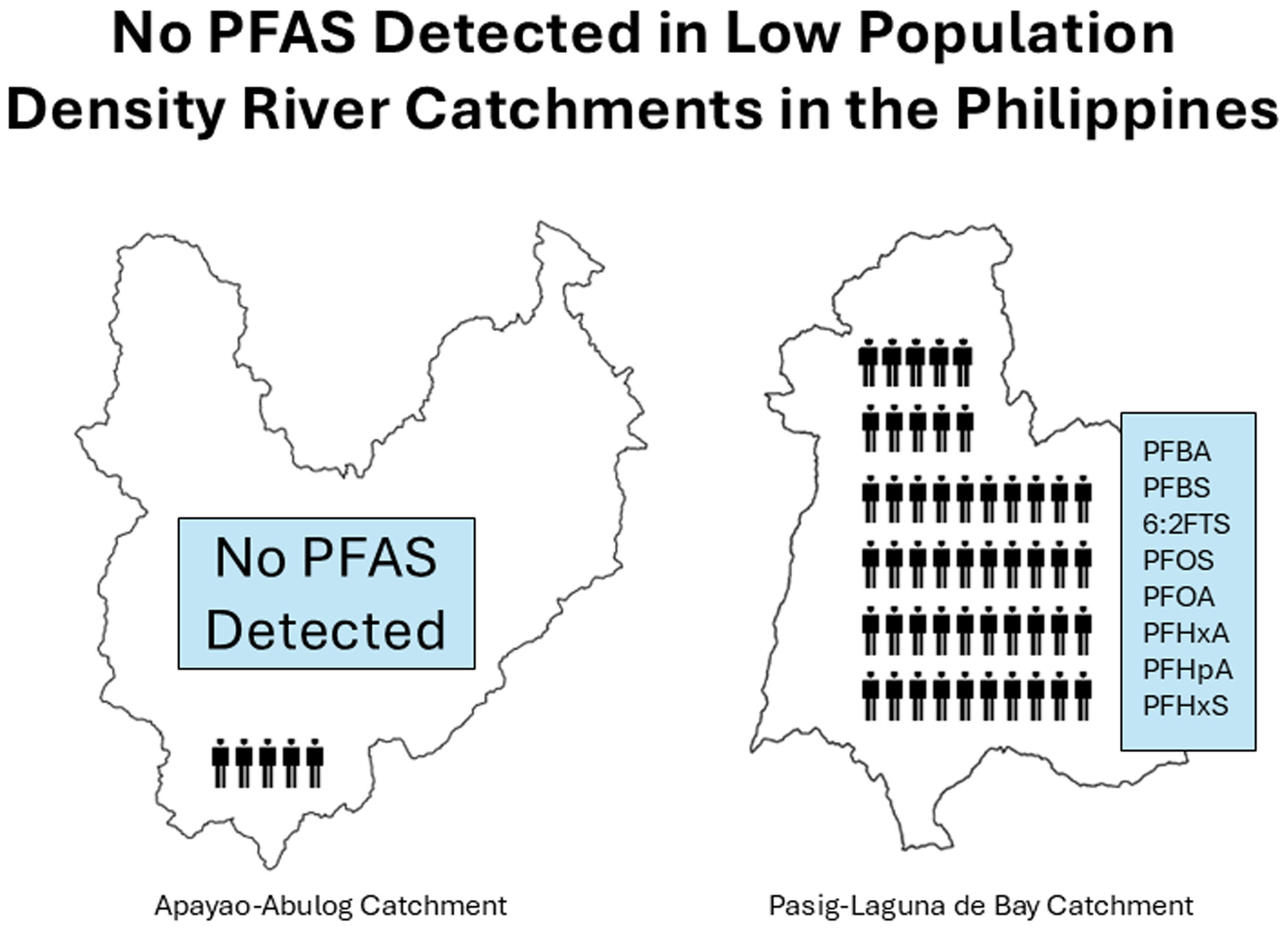
Forever but not everywhere? Unexpected non‐detection of per‐ and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in major Philippines rivers
- River
- 29-35
- 21 February 2025
A review on effects of human activities on aquatic organisms in the Yangtze River Basin since the 1950s
- River
- 104-119
- 28 August 2022
Assessing the impacts of urbanization and climate change on urban drainage system
- River
- 181-190
- 16 April 2024
Water level recognition based on deep learning and character interpolation strategy for stained water gauge
- River
- 506-517
- 11 December 2023