Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Lung Cancer
Gene amplification-driven RNA methyltransferase KIAA1429 promotes tumorigenesis by regulating BTG2 via m6A-YTHDF2-dependent in lung adenocarcinoma
- First Published: 21 June 2022
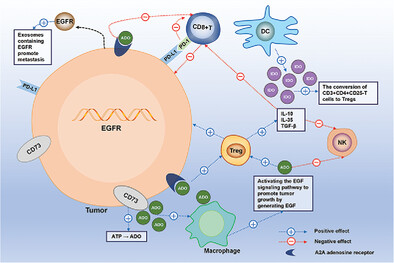
Essential roles of exosome and circRNA_101093 on ferroptosis desensitization in lung adenocarcinoma
- First Published: 20 February 2022
Anti-PD-L1/TGF-βR fusion protein (SHR-1701) overcomes disrupted lymphocyte recovery-induced resistance to PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors in lung cancer
- First Published: 03 January 2022
Association between antipsychotic agents and risk of lung cancer: a nested case-control study
- First Published: 04 January 2022
Genomic Evolution of Lung Cancer Metastasis: Current Status and Perspectives
- First Published: 29 November 2021
The efficacy and possible mechanisms of immune checkpoint inhibitors in treating non-small cell lung cancer patients with epidermal growth factor receptor mutation
- First Published: 26 October 2021
Clinical characteristics and outcomes of Chinese patients with KRAS-mutant non-small cell lung cancer after chemotherapy
- First Published: 17 October 2021
Combined treatment of non-small cell lung cancer using radiotherapy and immunotherapy: challenges and updates
- First Published: 17 October 2021
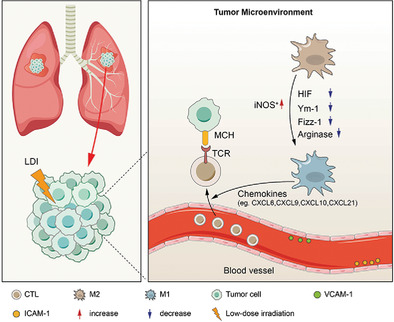
In recent years, immunotherapy has been considered the most promising method to overcome cancer and extend survival. It has been widely reported in preclinical and clinical studies that radiotherapy induces immunomodulatory effects by releasing TAAs and activating immunoregulation-related signaling pathways, initiating tumor-specific cytotoxic T cells, and promoting T cells to enter into tumor tissues. In this manuscript, we summarize the current status of immunotherapy and iRT and the development and additional combination strategies to enhance the efficacy of iRT.
Paclitaxel liposome for injection (Lipusu) plus cisplatin versus gemcitabine plus cisplatin in the first-line treatment of locally advanced or metastatic lung squamous cell carcinoma: A multicenter, randomized, open-label, parallel controlled clinical study
- First Published: 26 October 2021
Cisplatin plus Lipusu (LP) regimen has comparable efficacy and more favorable toxicity profiles compared with cisplatin plus gemcitabine (GP) regimen for patients with advanced LSCC. The study also demonstrated that LP had a significant impact on the levels of plasma cytokines and a spectrum of cytokines were associated with clinical benefit in patients who received LP. Thus, our results provided a new option for patients with advanced LSCC.
Genetic alternations and immune characteristics in patients with small cell lung cancer
- First Published: 24 August 2021
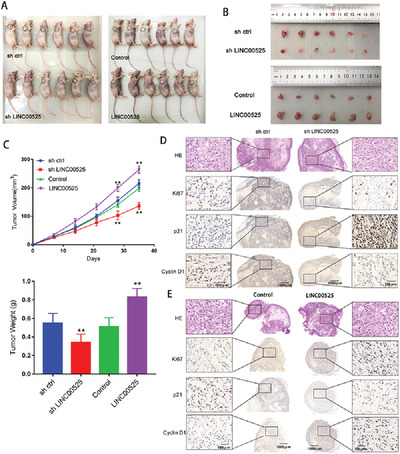
LncRNA LINC00525 suppresses p21 expression via mRNA decay and triplex-mediated changes in chromatin structure in lung adenocarcinoma
- First Published: 09 June 2021
Bevacizumab biosimilar LY01008 compared with bevacizumab (Avastin) as first-line treatment for Chinese patients with unresectable, metastatic, or recurrent non-squamous non–small-cell lung cancer: A multicenter, randomized, double-blinded, phase III trial
- First Published: 29 June 2021
Meiotic nuclear divisions 1 (MND1) fuels cell cycle progression by activating a KLF6/E2F1 positive feedback loop in lung adenocarcinoma
- First Published: 18 March 2021
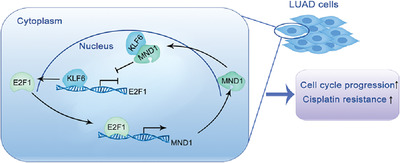
In this study, a novel cell cycle regulator named meiotic nuclear divisions 1 (MND1) was firstly screened out as a potential oncogene in LUAD using different bioinformatic and statistical analyses. In mechanism, MND1 could directly bind to tumor suppressor kruppel-like factor 6 (KLF6) to protect E2F1 from the transcriptional repression of KLF6. Interestingly, in return, E2F1 could activate MND1 transcription by binding to a specific site in the promoter region of MND1.
Neoadjuvant immunotherapy for non–small cell lung cancer: State of the art
- First Published: 10 March 2021
High-throughput sequencing detection and ensartinib treatment of lung cancer harboring NTRK1 fusion
- First Published: 16 January 2021
Lung adenocarcinoma patients with novel ALK fusion variants and their clinical responses to ALK inhibitors
- First Published: 12 January 2021
Activity and bioavailability of tepotinib for leptomeningeal metastasis of NSCLC with MET exon 14 skipping mutation
- First Published: 02 January 2021
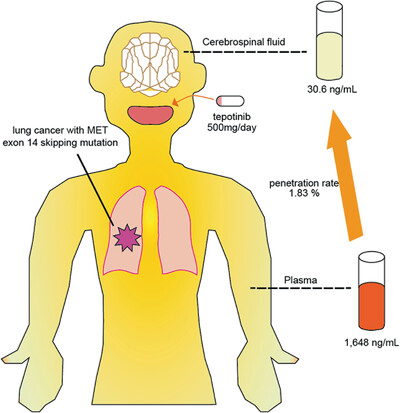
Tepotinib have high retention in the tumor and sustained inhibition of MET and its downstream pathways. Tepotinib is a key drug for cancer patients with MET exon 14 skipping mutation. However, its bioavailability in the CSF in humans has not been elucidated. The blood brain barrier protects the CNS from toxicity, but also prevents therapeutic drugs from accessing the brain. We report a case of leptomeningeal metastasis successfully treated with tepotinib in a patient with poor PS and on the bioavailability of tepotinib in the CSF in humans.
The mortality of lung cancer attributable to smoking among adults in China and the United States during 1990–2017
- First Published: 08 October 2020
miR-495 and miR-5688 are down-regulated in non-small cell lung cancer under hypoxia to maintain interleukin-11 expression
- First Published: 28 July 2020