Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Cover Picture
- Page: 449
- First Published: 01 February 2024

Nonfused-ring electron acceptors (NFREAs) can be considered as one of the most promising candidates for low-cost active-layer materials. Through the incorporation of asymmetric end-group engineering, the resulting asymmetric acceptor demonstrates improved optophysical properties and packing behavior, such as a more coplanar π-conjugated backbone, a broader light absorption range, and appropriate crystallinity. More details are discussed in the article by Liu et al. on page 485—490.
Inside Cover Picture
Inside Cover Picture
- Page: 450
- First Published: 01 February 2024

Functionalization of unactivated sp3 C—H bonds of cyclic and linear alkanes to high-value-added chemicals is one of the most important classes of chemical transformations and has high synthetic potential in synthetic chemistry. A metal-free, green, and sustainable functionalization of unactivated alkyl sp3 C—H bonds is reported using iodine(III) as a feasible dehydrogenation agent under visible light or KBr, and alkyl chlorides, bromides, alcohols, and ketones could be constructed by addition of different coupling reagents. More details are discussed in the article by Zhai et al. on page 505—510.
Contents
Breaking Report
Modular Synthesis of Multi-substituted Cyclobutanones Enabled by Oxyallyl Cations
- Pages: 459-463
- First Published: 12 October 2023
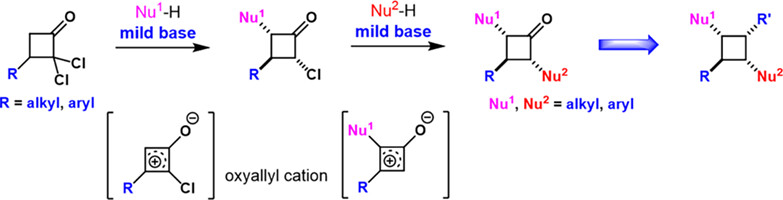
We report here a practical and robust approach for the synthesis of 2,3,4-trisubstituted cyclobutanones from readily available dichlorocyclobutanones via oxyallyl cations. Both aryl and alkyl substituents could be introduced efficiently. Further synthetic utility leads to the preparation of 1,2,3,4-tetrasubstituted cyclobutane.
Concise Reports
Palladium-Catalyzed anti-Markovnikov Halosulfonamidation of Unactivated Alkene
- Pages: 464-470
- First Published: 14 October 2023
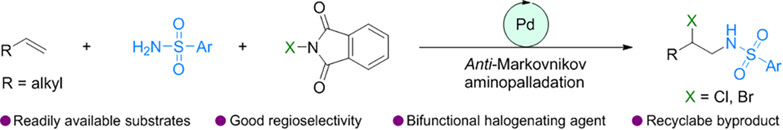
A novel strategy for palladium-catalyzed regioselective aminohalogenation between unactivated olefin, sulfonamide, and N-halo compounds with anti-Markovnikov regioselectivity has been established to build architecturally versatile and functionally diverse vicinal haloamine in a single step. This protocol broadens the breadth of the direct anti-Markovnikov chemistry of simple olefin feedstock. The N-halo compound is hypothesized to serve a dual role: as a halide regulator to facilitate anti-Markovnikov amination of the olefin substrate and as an oxidant to enable C-X bond formation.
Unusual Single Electron Transfer Reactions between Alkenes and Iodine Electrophiles
- Pages: 471-477
- First Published: 01 November 2023
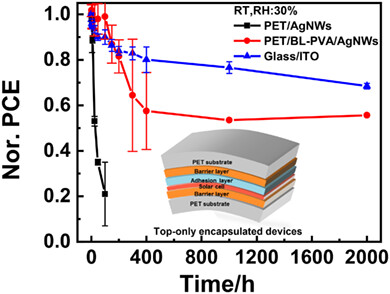
Large-Area Gravure-Printed AgNWs Electrode on Water/Oxygen Barrier Substrate for Long-Term Stable Large-Area Flexible Organic Solar Cells
- Pages: 478-484
- First Published: 20 November 2023
Enhancing Photovoltaic Performance of Nonfused-Ring Electron Acceptors via Asymmetric End-Group Engineering and Noncovalently Conformational Locks
- Pages: 485-490
- First Published: 14 October 2023
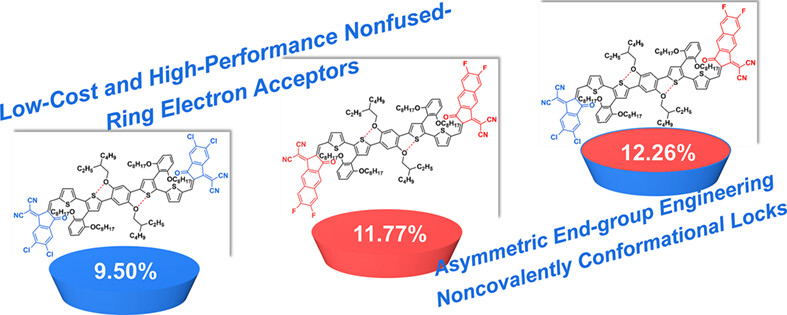
The asymmetric end-group engineering was employed to construct a new nonfused-ring electron acceptor (NFREA), namely NoCA-19 containing two distinct end-groups. Compared with symmetric acceptors, asymmetric acceptor NoCA-19 possesses broad light absorption range, more coplanar π-conjugated backbone, and appropriate crystallinity. Thus, NoCA-19-based organic solar cell shows a considerable power conversion efficiency of 12.26%, demonstrating the potential of asymmetric end-group engineering in achieving low-cost and high-performance NFREAs.
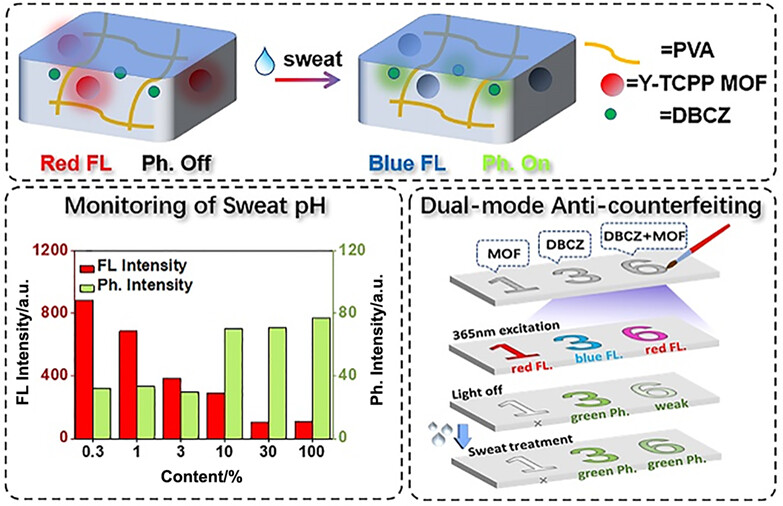
Monitoring of Sweat pH and Dual-Mode Anti-Counterfeiting from Metal-Organic Framework-Based Multifunctional Gel
- Pages: 491-498
- First Published: 24 October 2023
Copper-Free Click Chemistry-Mediated Assembly of Single Quantum Dot Nanosensor for Accurately Monitoring Locus-Specific m6A in Cancer Cells
- Pages: 499-504
- First Published: 26 October 2023
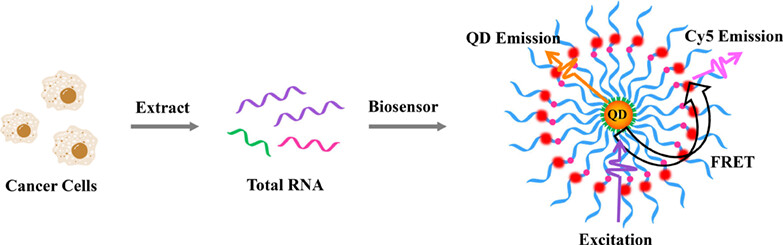
A copper-free click chemistry-mediated assembly of single quantum dot (QD) nanosensor was constructed for accurately monitoring locus-specific m6A in cancer cells. This assay can be homogenously performed without the involvement of copper catalyst, m6A-specific antibody, radioactive labeling, ligase enzyme, enzymatic reverse transcription, and next-generation sequencing. Moreover, it can discriminate even 0.01% m6A level in complex samples and accurately measure cellular m6A-RNA expression, providing a promising avenue for clinical diagnostics and biomedical research.
Efficient Photolytic Halogenation and Oxidation of Unactivated Alkyl sp3 C—H Bonds with Iodine(III)
- Pages: 505-510
- First Published: 20 November 2023
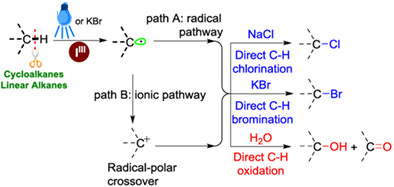
A metal-free, green, and sustainable functionalization of unactivated alkyl sp3 C—H bonds is reported using iodine(III) as a feasible dehydrogenation agent under visible light or KBr to activate the alkyl sp3 C—H bond in a highly efficient manner, which can construct different alkylation products by adding corresponding coupling reagents.
Cooperative NHC/Photoredox Catalysis: Three-Component Reaction of Aroyl Fluorides, Styrenes and Oxalates
- Pages: 511-515
- First Published: 01 November 2023
Comprehensive Reports
Water-Driven Malleable, Weldable and Eco-Friendly Recyclable Carbon Fiber Reinforced Dynamic Composites
- Pages: 516-522
- First Published: 13 November 2023
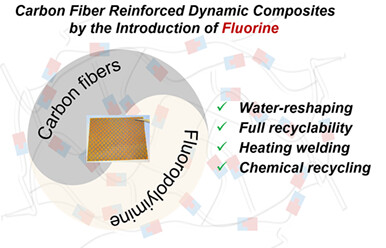
It is still important and promising for the development of dynamic polymer materials containing trifluoromethyl as well as their application in advanced resin matrix composites. We demonstrated that the reversibility of imine bond formation and temperature-dependent rate of the imine exchange enabled heat or water-driven malleability of such crosslinked polyimines derived from trifluoromethyl diphenoxybenzene backbones.
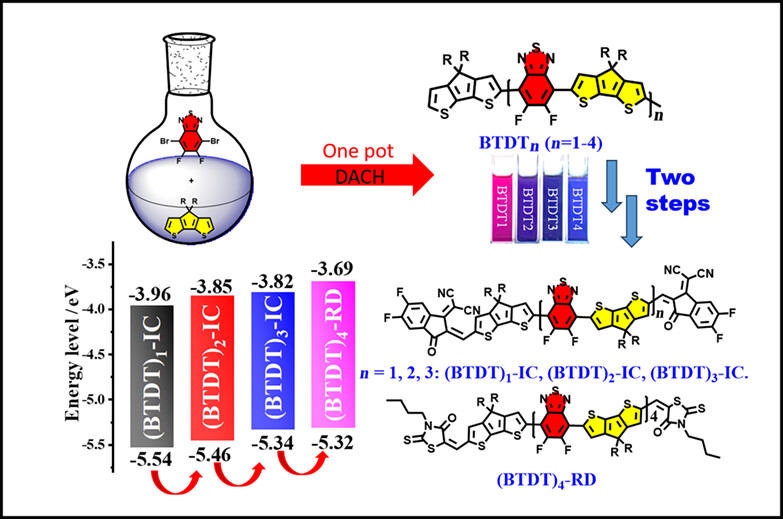
Synthesis of Long-Chain Oligomeric Donor and Acceptors via Direct Arylation for Organic Solar Cells
- Pages: 523-532
- First Published: 26 October 2023
Recent Advances
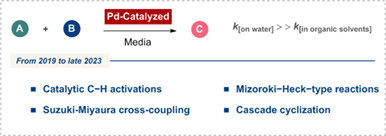
Recent Advances in Pd-Catalyzed Reactions Involving the “On-Water” Mechanism†
- Pages: 533-542
- First Published: 07 December 2023
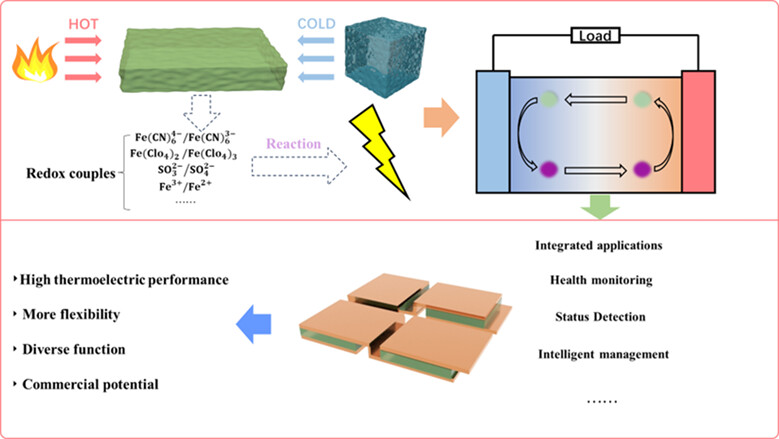
Exploring the Mechanism, Advancements, and Application of Thermogalvanic Effect in Hydrogels
- Pages: 543-556
- First Published: 09 November 2023
Inside Back Cover
Back Cover
Back Cover
- Page: 560
- First Published: 01 February 2024

Oxyallyl cations, as powerful electrophilic intermediates, have shown versatile utilities in organic synthesis. Modular synthesis of multi-substituted cyclobutanones enabled by oxyallyl cations provides facile access to multi-substituted cyclobutanones via direct nucleophilic substitution of (di)chlorocyclobutanones under mild basic conditions. Both aryl or alkyl substituents could be efficiently introduced on the four-membered ring skeleton. Further transformation leads to tetrasubstituted cyclobutane derivatives in a stereoselective manner, demonstrating potential synthetic utility. More details are discussed in the article by Lu et al. on page 459—463.