Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Cover Picture
- Page: 1809
- First Published: 15 July 2024

4-(2-Hydroxyethyl)piperazin-1-ium iodide (PZOI) is a functional ammonium salt that can simultaneously reduce shallow/deep-level defect densities by passivation effect and form 2D component, respectively. These advances reduce the energy loss of single-junction devices and significantly enhance the efficiency and stability of perovskite/organic tandems. More details are discussed in the article by Li et al. on page 1819—1827.
Inside Cover Picture
Inside Cover Picture
- Page: 1810
- First Published: 15 July 2024

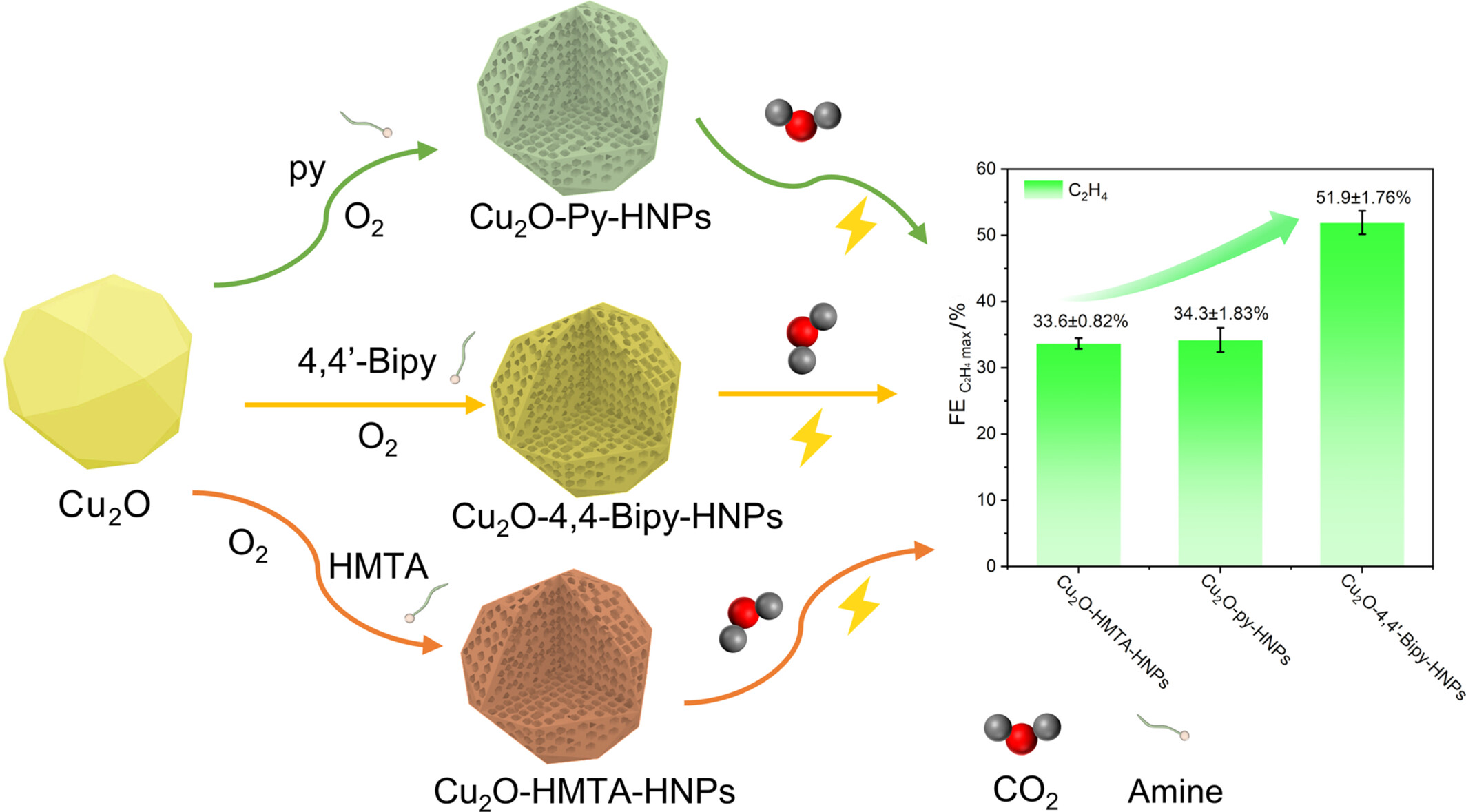
Copper-based catalysts are frequently employed for carbon dioxide reduction reactions (CO2RR), yet the regulation of pore structure and surface state of electrocatalysts remains a prominent challenge in previous research endeavors. In this study, we introduce a novel technique to produce mesoporous Cu2O nanocrystals, with finely tuned pore size and surface amine functionality leveraging the incorporation of various amine compounds during the oxidative process of copper nanocrystals. The synergistic effect of pore structure confinement and surface amine functionalization culminates in an impressive Faradaic efficiency (FE) of 51.9% for the selective production of C2H4. More details are discussed in the article by Huang et al. on page 1846—1852.
Contents
Concise Report
Piperazine-Assisted Construction of 2D/3D Wide-Bandgap Perovskite for Realizing High-Efficiency Perovskite/Organic Tandem Solar Cells
- Pages: 1819-1827
- First Published: 30 March 2024
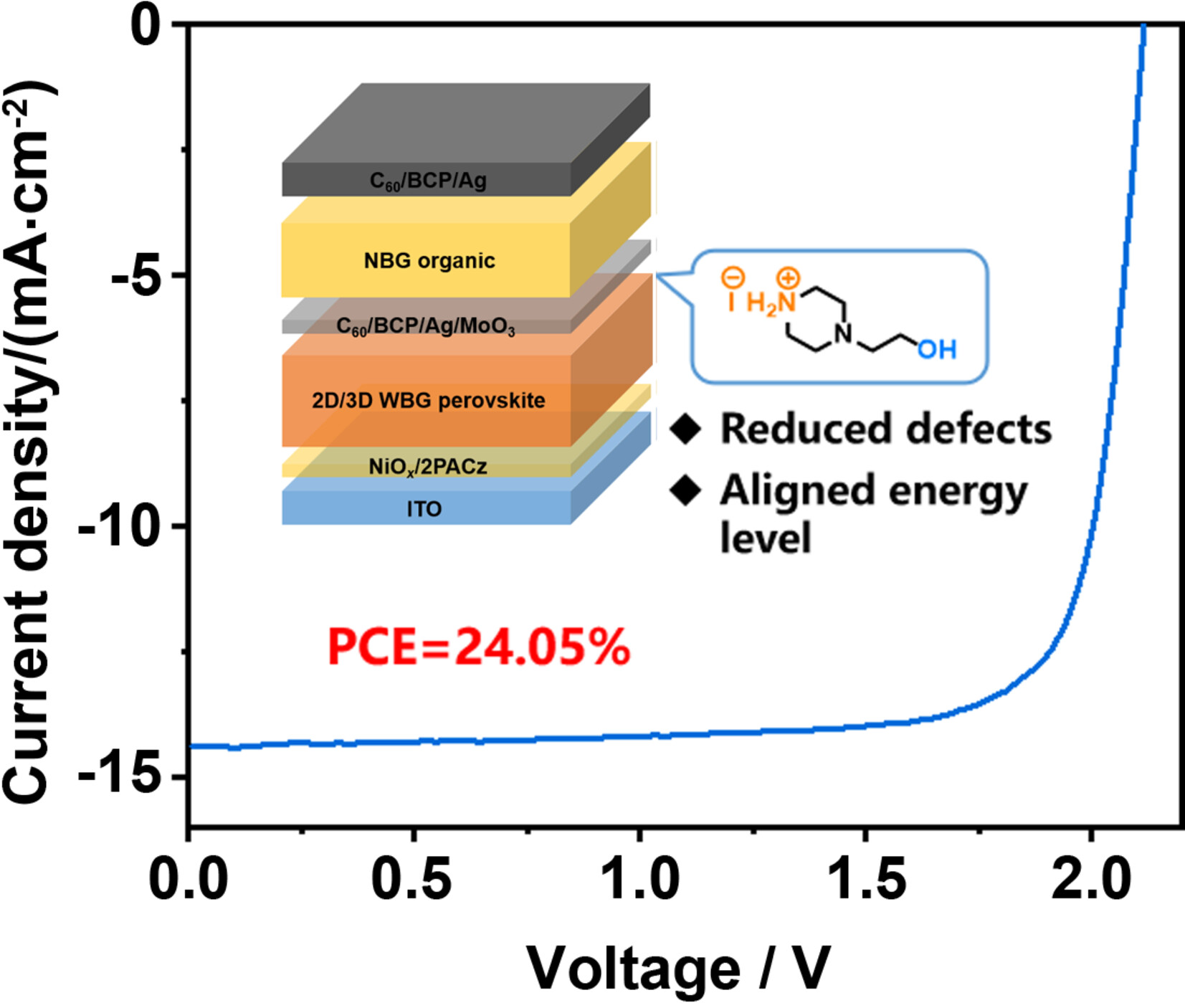
PZOI, consisting of a piperazine iodide and terminated hydroxyl, was used to post-treat the defect-rich wide-bandgap (WBG) perovskite film surface. This treatment can effectively reduce the shallow and deep-level defect densities by forming Pb—O coordination and 2D perovskite, respectively. These advances reduce the energy loss of WBG perovskite film surface by 40 meV, and significantly promote the power conversion efficiency of perovskite/organic TSCs to 24.05%.
Ruthenium-Catalysed Asymmetric Intramolecular Isomerization/Esterification Reaction: Direct Synthesis of Chiral Dihydrocoumarins
- Pages: 1828-1832
- First Published: 31 March 2024
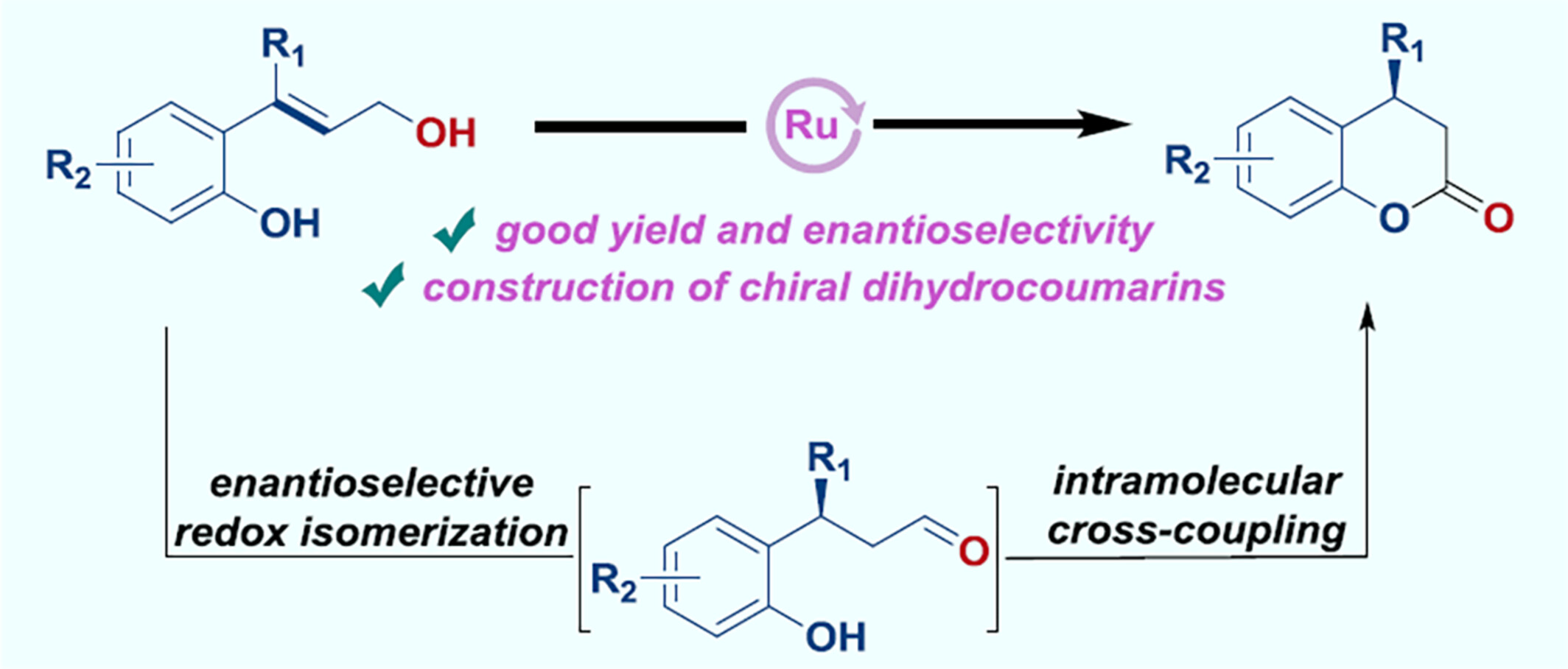
Herein, an asymmetric isomerization/intramolecular coupling reaction of allylic alcohols to synthesize chiral dihydrocoumarins was successfully accomplished through ruthenium catalysis. This method demonstrates a wide substrate applicability, excellent tolerance for various functional groups, and good enantioselectivities (up to 90% ee). It provides a convenient pathway to produce a diverse range of structurally distinct chiral dihydrocoumarins in good efficiency.
Electrochemical Cascade Annulation for the Synthesis of 3-Sulfanylquinoline Derivatives Under Mild Conditions
- Pages: 1833-1838
- First Published: 17 April 2024
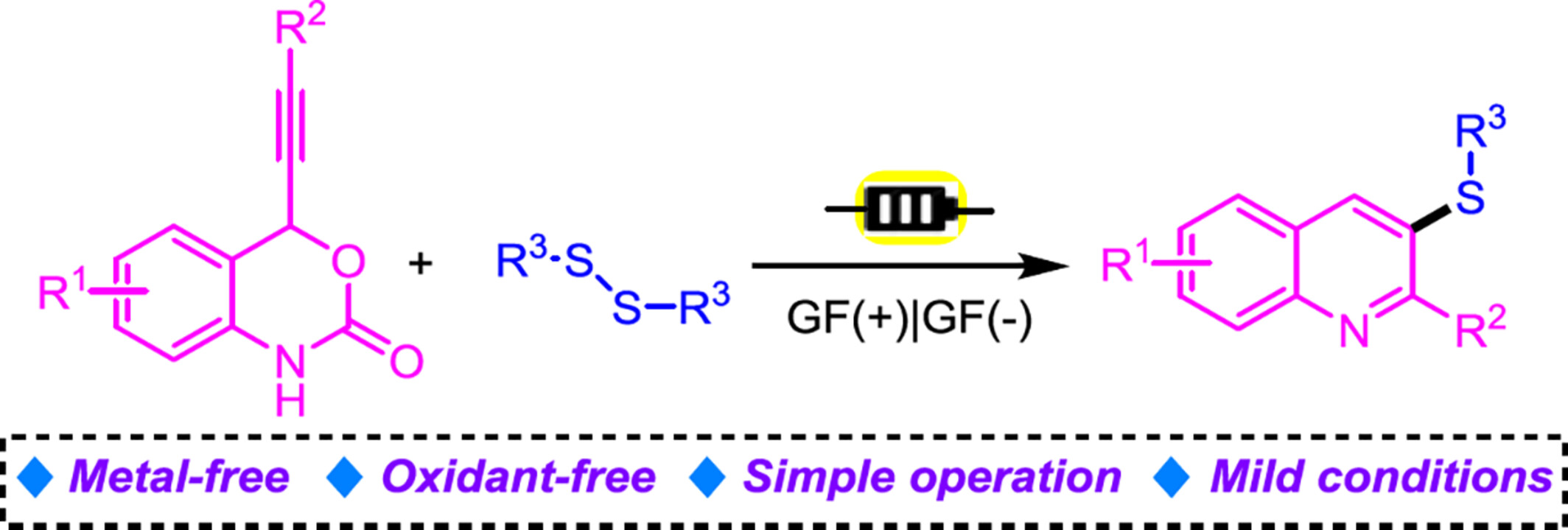
An efficient electrochemical approach has been developed for the construction of 3-sulfanylquinoline derivatives by treating phenylethynylbenzoxazinanones with disulfides in an undivided cell. The protocol provides a convenient route to functionalizing quinolines with good functional group tolerance. Moreover, and it does not require any metal catalysts or additives, furnishing a series of biological quinolines in moderate to good yields.
Controlling the Reactivity of IBA-N3 by Switching Halogen Salts: Providing a Universal Strategy for Haloazidation of Alkenes
- Pages: 1839-1845
- First Published: 14 April 2024
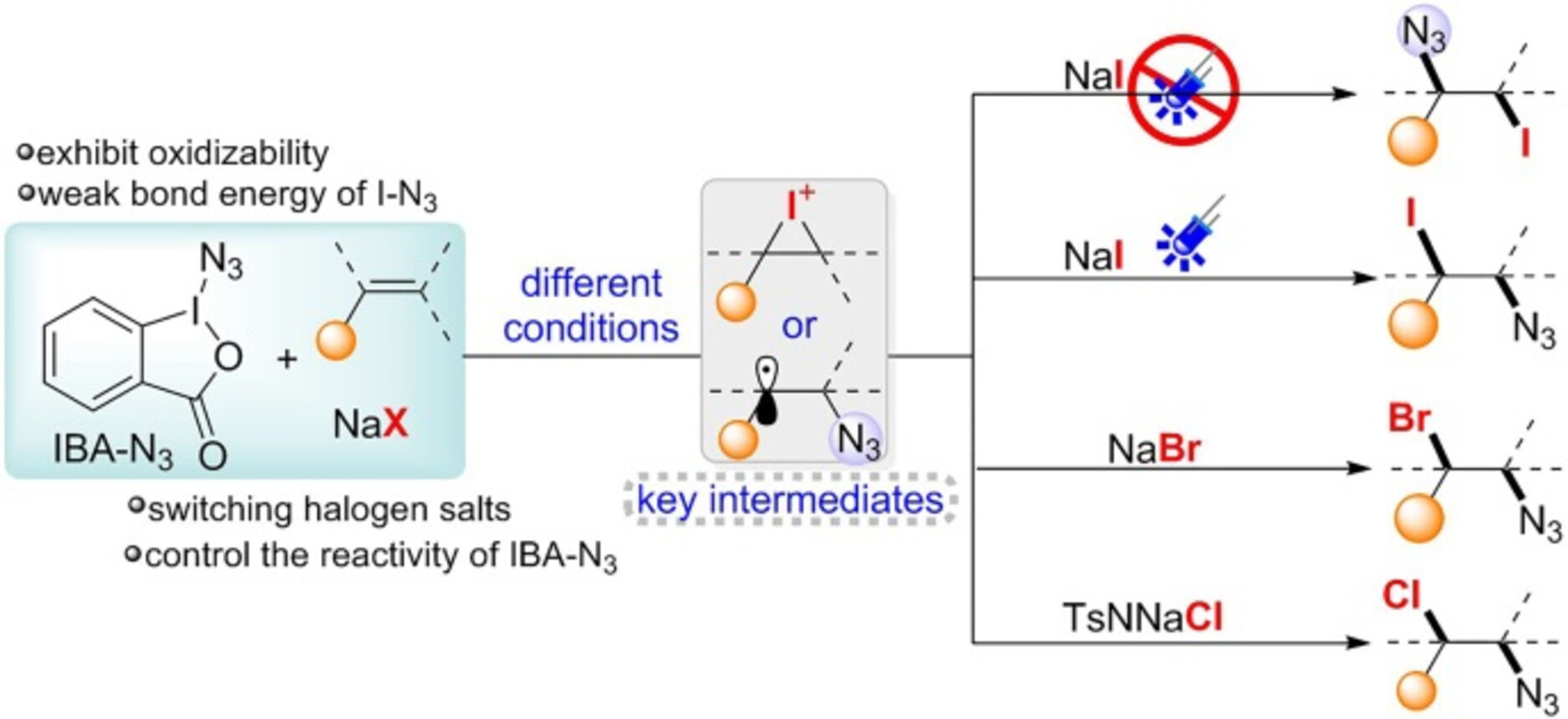
Herein, we developed a universal strategy for haloazidation of alkenes through controlling the reactivity of IBA-N3 by switching halogen salts, allowing for the synthesis of a diversity of halogen azide products. Mechanistic studies have shown that by tuning the reactivity of IBA-N3 via switching halogen salts, different intermediates can be controllably produced to achieve regioselectivity and chemoselectivity in the haloazidation of alkenes.
Preferential Formation of Ethylene via Electrocatalytic CO2 Reduction on Mesoporous Cu2O Nanoparticles: Synergistic Effects of Pore Structure Confinement and Surface Amine
- Pages: 1846-1852
- First Published: 17 April 2024
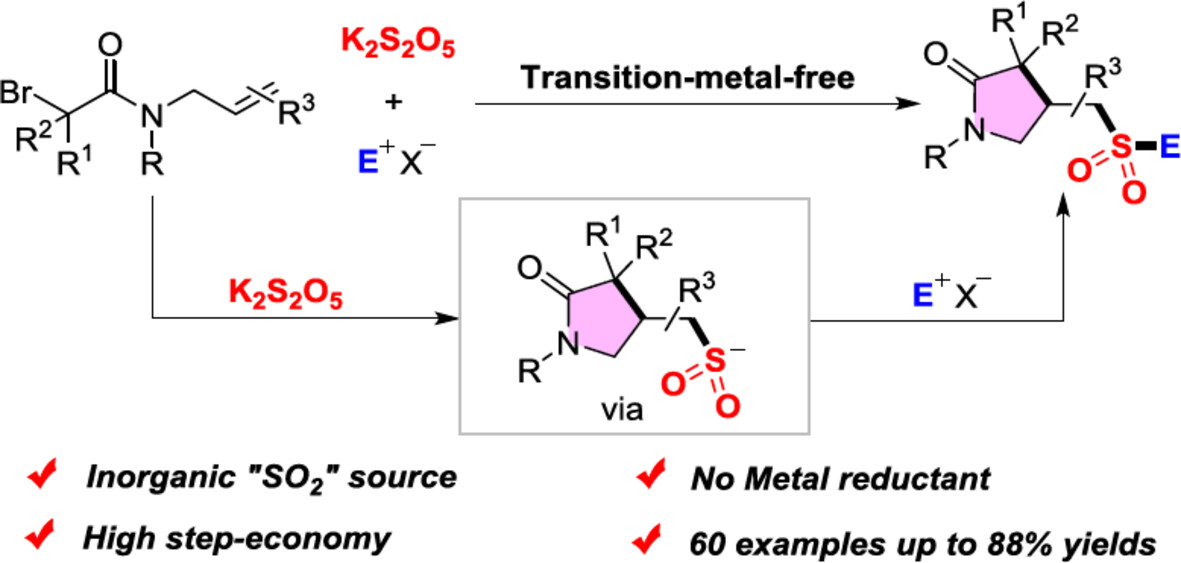
Alkyl Radical Initiated Cyclization/Cascade for Synthesizing Lactam-Substituted Alkyl Sulfones
- Pages: 1853-1859
- First Published: 17 April 2024
Co/Fe Dual Catalysis for Sequential Hydrosilylation–Isomerization: Access to Trisubstituted (E)-Alkenyl Silanes from Terminal Alkynes
- Pages: 1860-1866
- First Published: 18 April 2024
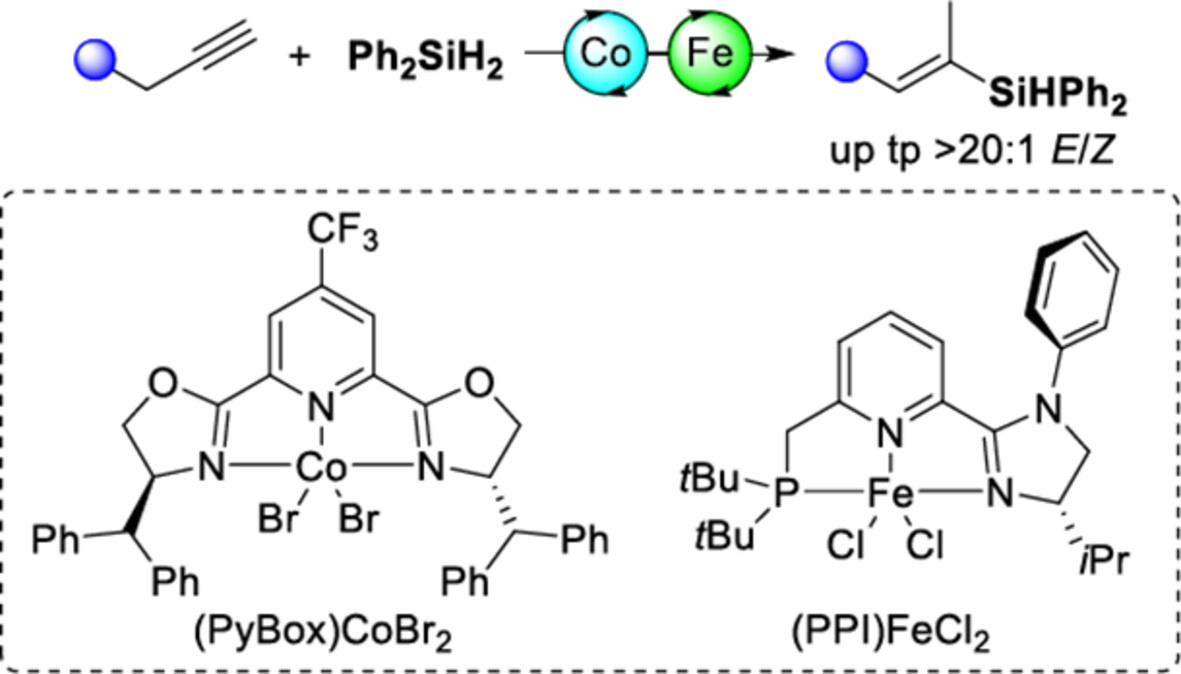
A relay bicatalysis system involving (PyBox)Co catalyzed Markovnikov hydrosilylation of terminal alkynes and subsequent alkene isomerization enabled by (PPI)Fe was developed. This Co/Fe dual catalysis offers an atom-economical and efficient approach to trisubstituted (E)-alkenyl silanes from widely accessible terminal alkynes with high regio- and stereoselectivities under mild conditions.
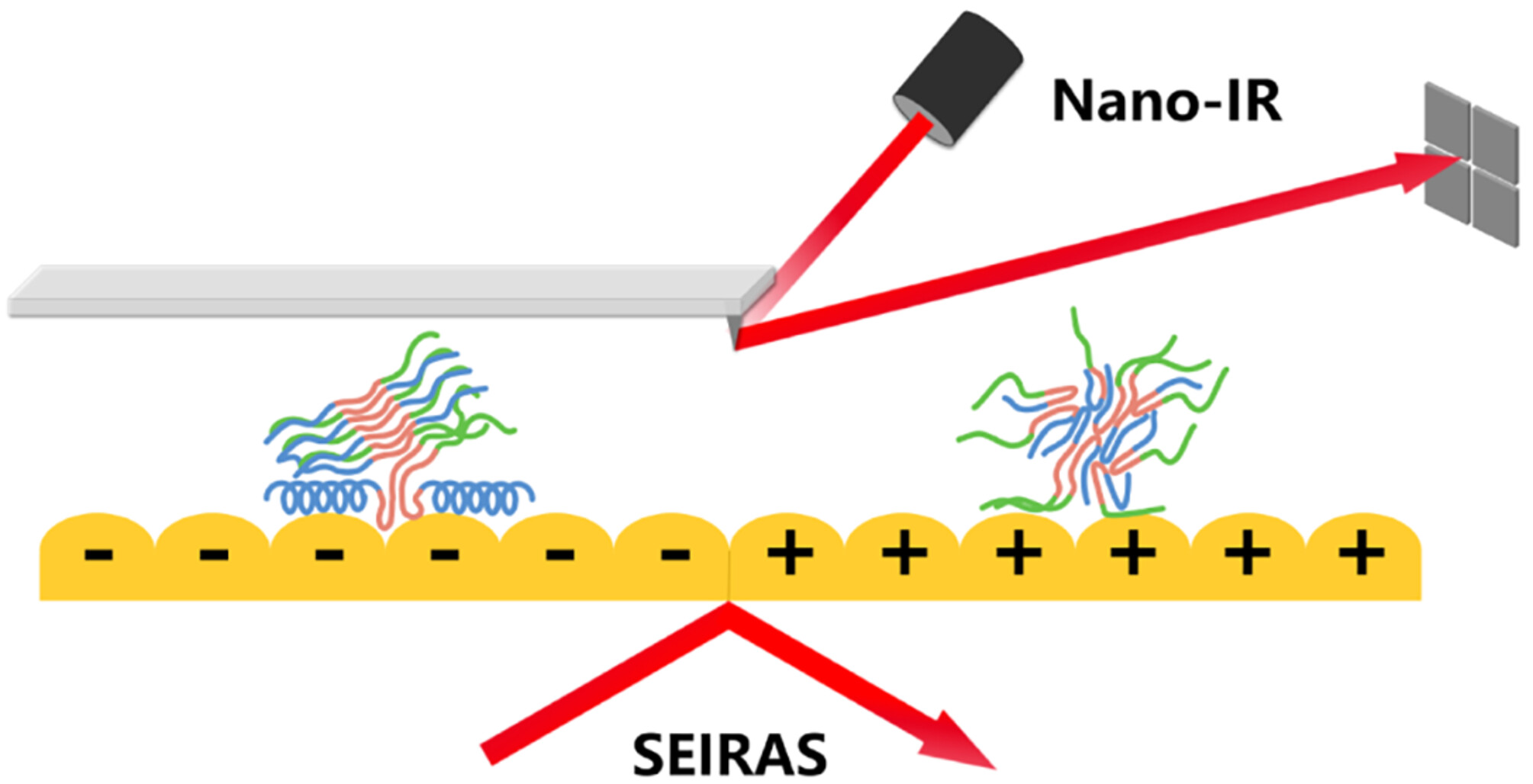
Revealing the Regulation Effect of Surface Charge at Aromatic Interface to Dynamic Conformational Changes of α-Synuclein at Early Aggregation Stage
- Pages: 1867-1876
- First Published: 24 April 2024
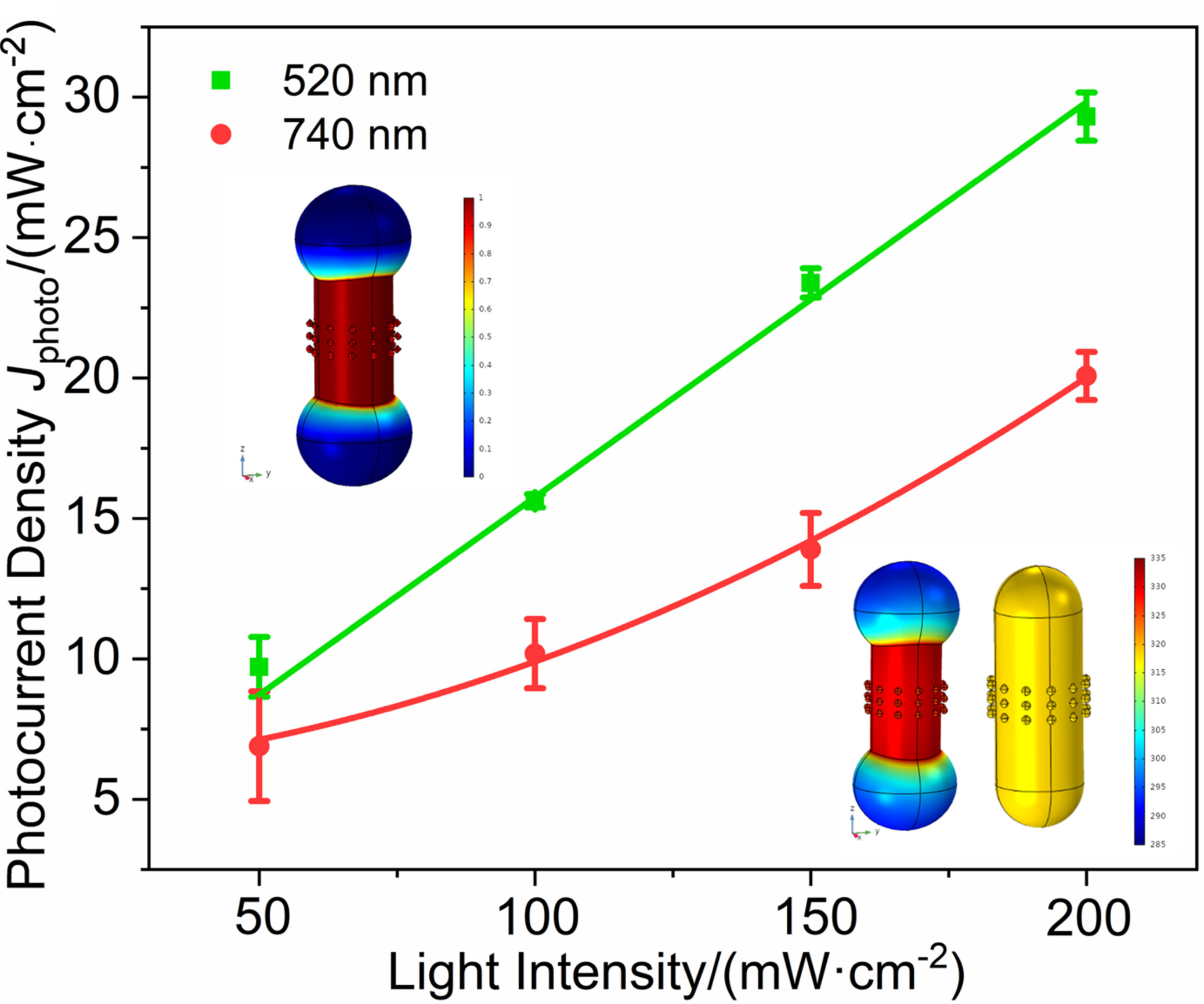
Anisotropic Plasmon Resonance Enables Spatially Controlled Photothermal and Photochemical Effects in Hot Carrier-Driven Catalysis
- Pages: 1877-1885
- First Published: 25 April 2024
Multistimuli-Responsive Luminescent Porous Organic Polymers with Chiroptical Properties and Acid-Induced Degradation
- Pages: 1886-1894
- First Published: 24 April 2024
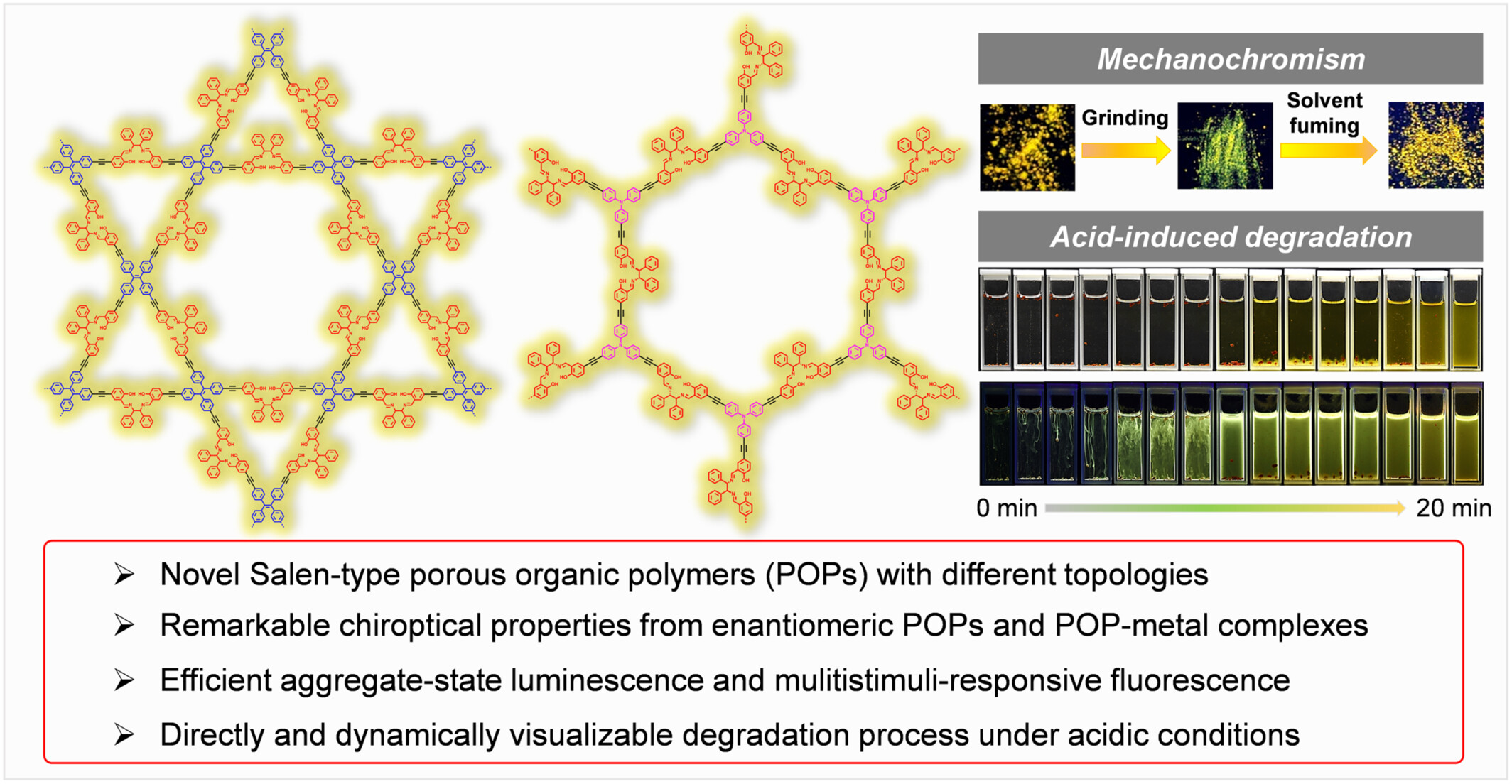
A series of novel Salen-type luminescent porous organic polymers (POPs) with different topologies were designed and facilely synthesized by the catalyst-free and one-pot polycondensation reactions between polyfunctional aggregation-induced emission luminogen-containing salicylaldehyde derivatives and chiral diamines. With the Salen units in polymer backbones as tetradentate ligands, a series of POP-metal complexes were further prepared. The obtained POPs possess remarkable chiroptical properties, multistimuli-responsive fluorescence and acid-induced degradation capabilities, and the degradation process can be directly visualized and dynamically monitored via fluorescence variation.
Breaking Report
Redox-Active Dihydrophenazine-Based Macrocycle: Synthesis, Conformation-Adaptive Behavior and Host-Guest Complexation with Tetracyanoquinodimethane
- Pages: 1895-1900
- First Published: 17 April 2024
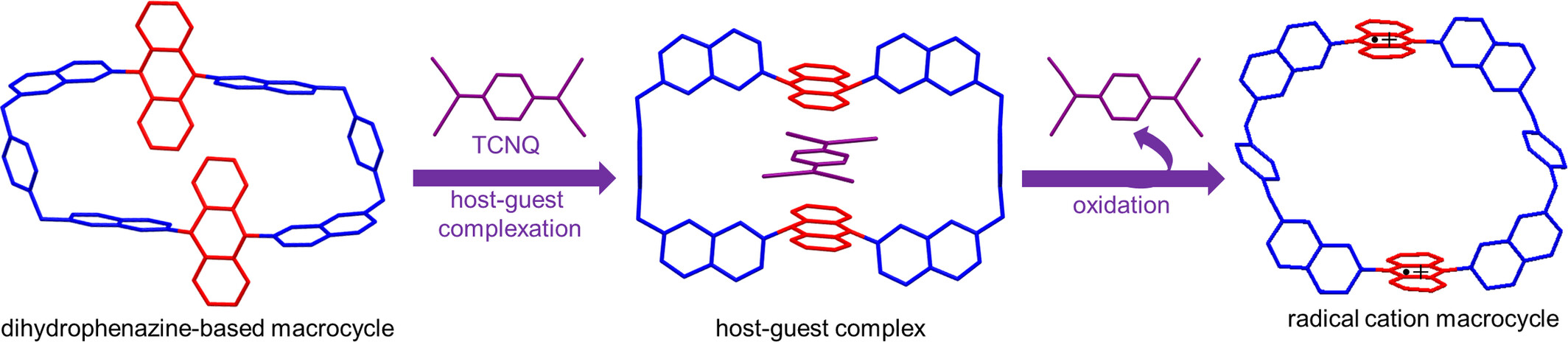
A novel macrocycle based on conformation-adaptive and electron-rich dihydrophenazine was designed and synthesized, and its host-guest properties and radical cation species were investigated. The resultant macrocycle could bind electron-deficient guest TCNQ to form a host-guest complex, and the oxidation of the macrocycle generated a stable diradical cation and induced the release of the guest molecule.
Comprehensive Report
Three Types of Isocoumarins with Unusual Carbon Skeletons from Artemisia dubia var. subdigitata and Their Antihepatoma Activity
- Pages: 1901-1912
- First Published: 17 April 2024
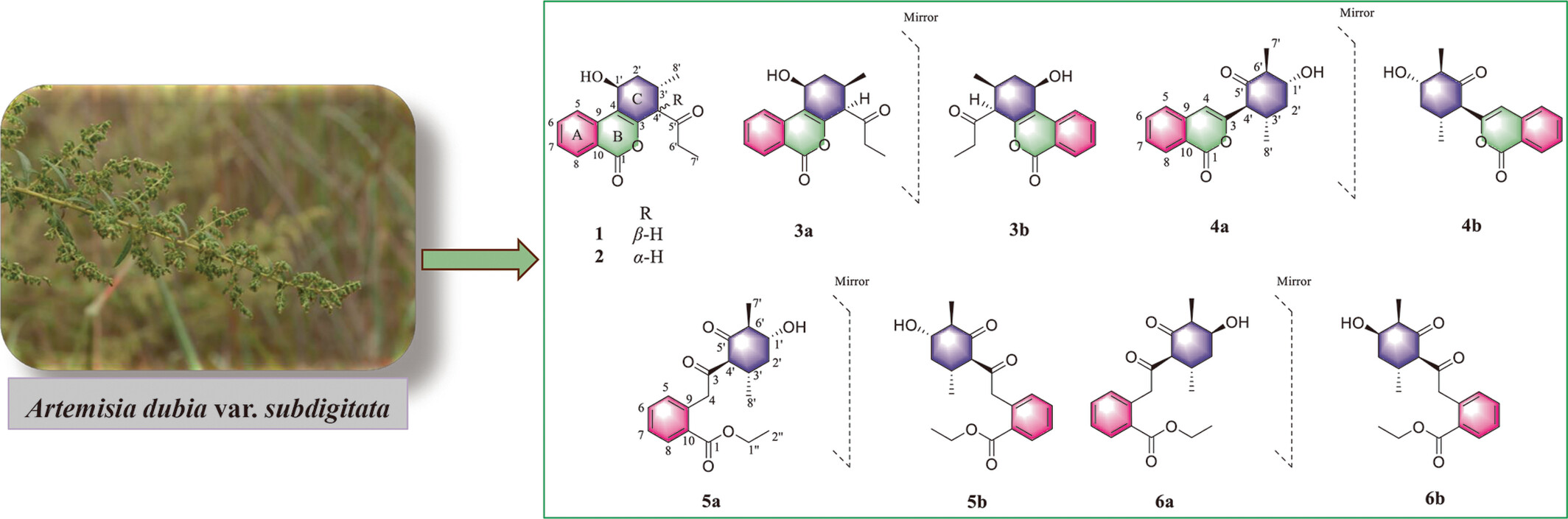
Artemdubones A—F (1—6) were isolated from Artemisia dubia var. subdigitata. Compounds 1, 2 and 3a/3b possessed a unique 6/6/6-tricyclic system comprising an unusual 1-(2-methylcyclohexyl) propan-1-one moiety fused with isocoumarin core skeleton. Compounds 4a/4b were characterized as an unexpected 2,5-dimethylcyclohexan-1-one scaffold, and compounds 5a/5b and 6a/6b were rare 1,2-seco-isocoumarin
Recent Advances
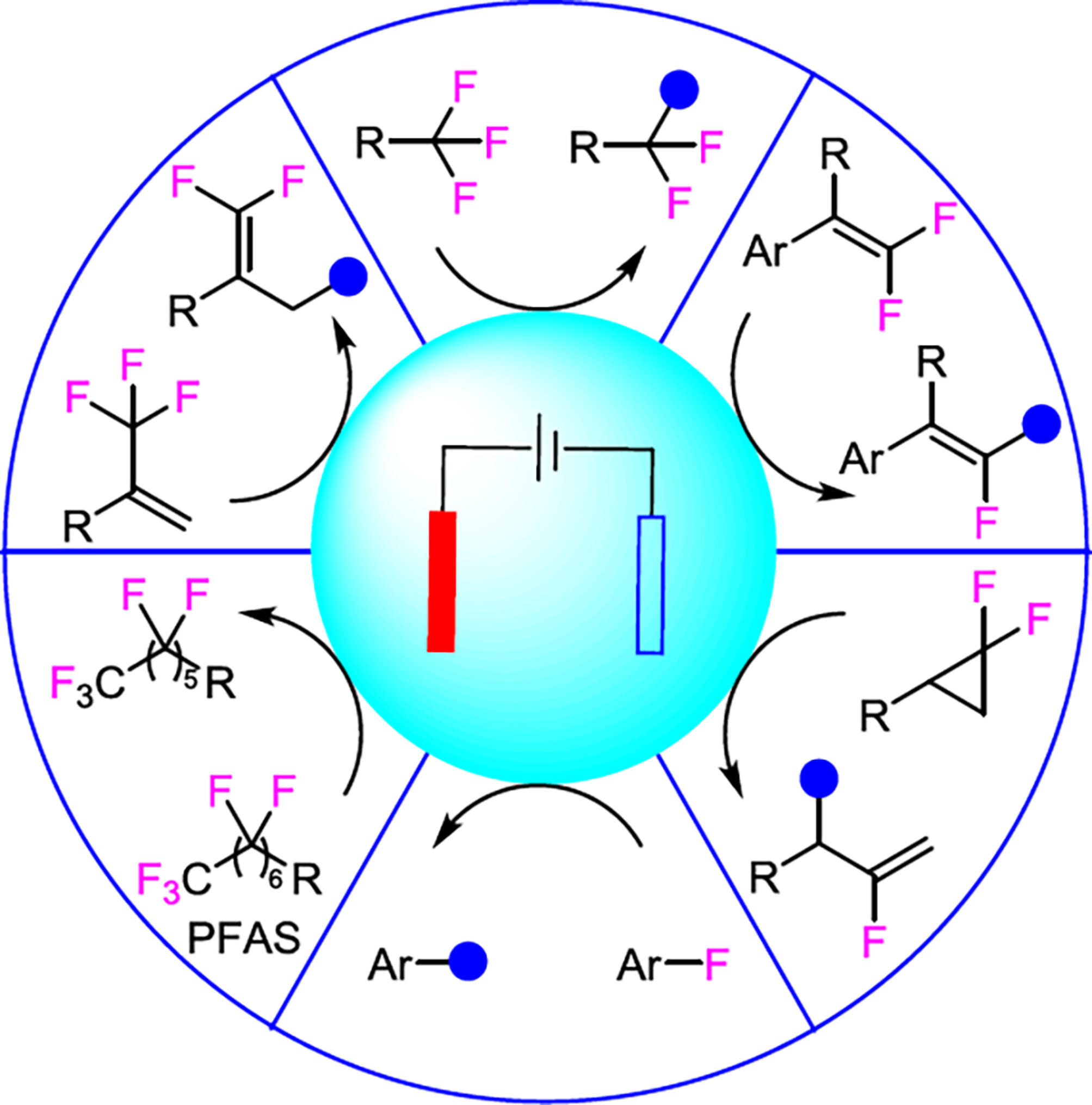
Recent Advances in the Electrochemical Defluorinative Transformations of C—F Bonds
- Pages: 1913-1928
- First Published: 24 April 2024
Meet Our New Editorial Board Members of Rising Stars
Meet Our New Editorial Board Members of Rising Stars
- Pages: 1929-1931
- First Published: 15 July 2024
Meet Our New Editorial Board Members of Spotlights
Meet Our New Editorial Board Members of Spotlights
- Pages: 1932-1936
- First Published: 15 July 2024
Inside Back Cover
Inside Back Cover
- Page: 1939
- First Published: 15 July 2024

Anisotropic localized surface plasmon resonance in gold nanorods achieves spatiotemporal control over the photochemical and photothermal functional modules towards wavelength-dependent, site-selective plasmonic photocatalytic hydrogen production through water splitting. More details are discussed in the article by He et al. on page 1877—1885.
Back Cover
Back Cover
- Page: 1940
- First Published: 15 July 2024

This paper presents a novel macrocycle based on conformation-adaptive and electron-rich dihydrophenazine. The macrocycle exhibits host-guest interaction with tetracyanoquinodimethane (TCNQ) driving by charge transfer interaction between them. The host-guest complex forms stable radical cation species upon oxidation, resulting in the release of TCNQ from the macrocyclic cavity, thereby successfully achieving the reversible binding of guest molecules. More details are discussed in the article by Yang et al. on page 1895—1900.