Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Cover Picture
- Page: 1669
- First Published: 01 July 2024

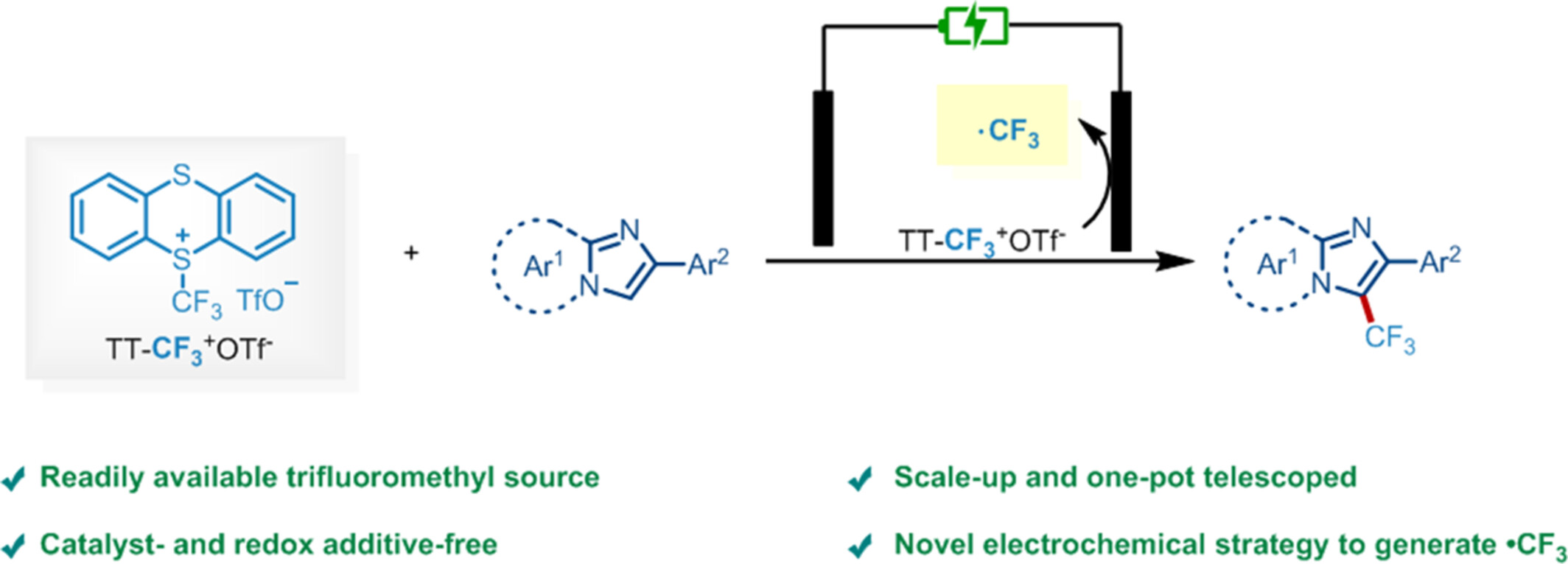
The cover image describes a novel and eco-friendly electrochemical strategy for the electrochemical activation of trifluoromethyl thianthrenium triflate (TT–CF3+OTf−). The technique demonstrates successful trifluoromethylation of a diverse range of imidazole-fused heteroaromatic compounds without the requirement of external oxidants or catalysts, aligning with the principles of green chemistry. More details are discussed in the article by Yu et al. on page 1679—1685.
Inside Cover Picture
Inside Cover Picture
- Page: 1670
- First Published: 01 July 2024
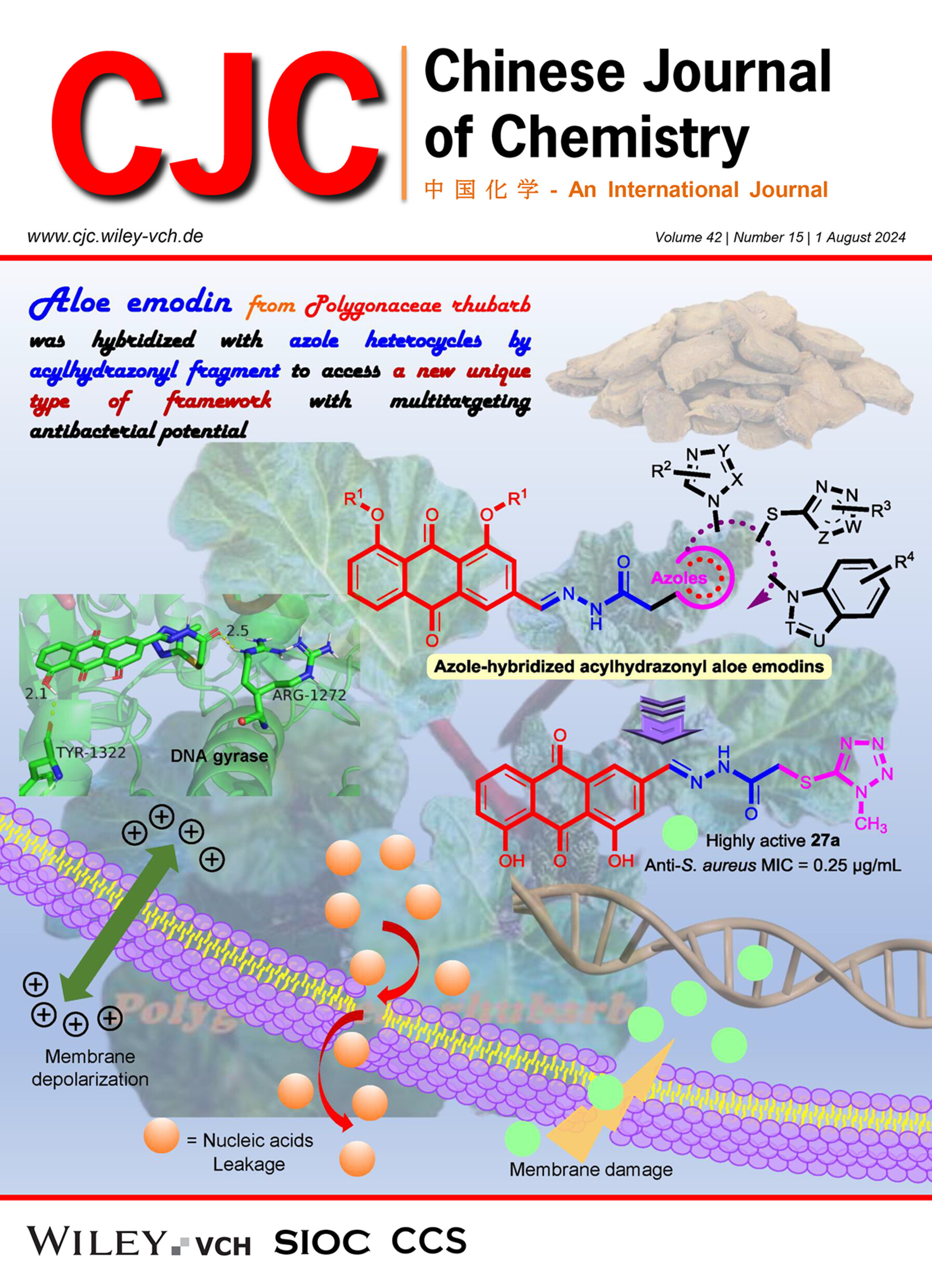
The acylhydrazonyl hybridization of aloe emodin and azole heterocycles afforded a new unique type of framework with multitargeting antibacterial potential. The highly active compound demonstrated strong antibacterial efficacy with broad antibacterial spectrum, low hemolysis and cytotoxicity, and favorable bioavailability. The active molecule could not only cause bacterial membrane depolarization and damage the cell membrane, resulting in nucleic acid leakage, but also intercalate into DNA to impede its replication and form DNA gyrase complex to disturb the function of DNA gyrase. More details are discussed in the article by Zhou et al. on page 1741—1758.
Contents
Concise Reports
Metal-Free Electrochemical Trifluoromethylation of Imidazole-Fused Heterocycles with Trifluoromethyl Thianthrenium Triflate
- Pages: 1679-1685
- First Published: 15 March 2024
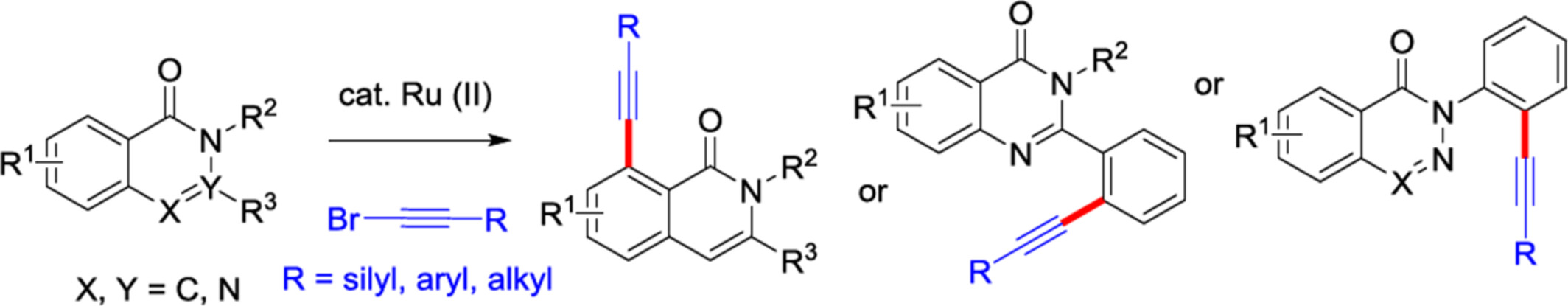
Ru(II)-Catalyzed Selective C—H Alkynylation of Isoquinolones, Quinazolones and Phthalazinones with Bromoalkynes
- Pages: 1686-1690
- First Published: 15 March 2024
Electrochemical Multicomponent Cascade Radical Process Enabling Synthesis of Iodomethyl Spiropyrrolidinyl-Oxindoles
- Pages: 1691-1698
- First Published: 19 March 2024
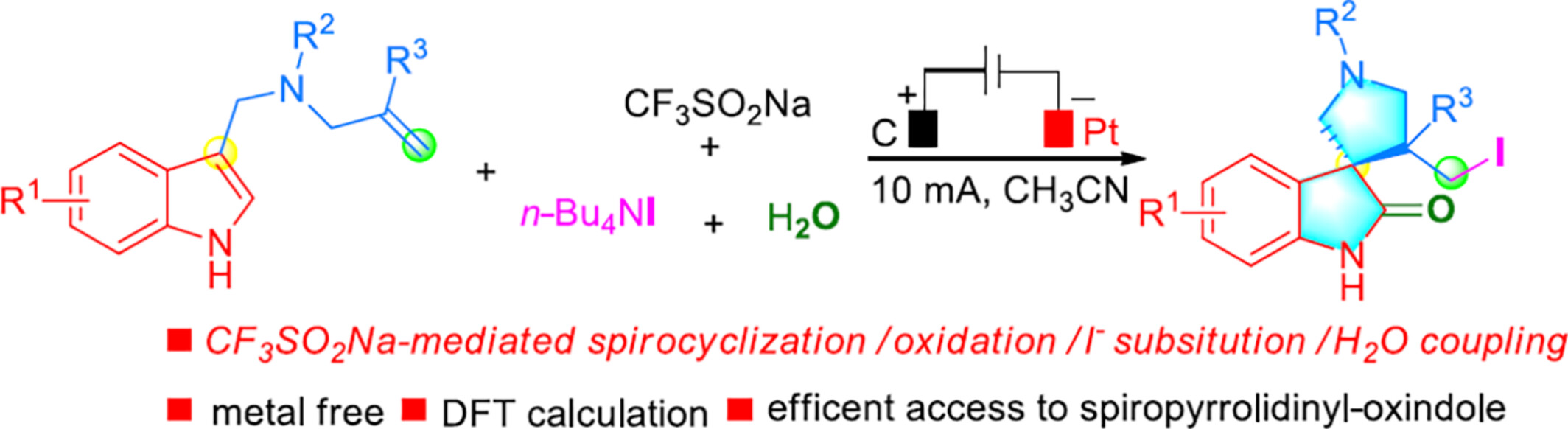
A novel electrochemical multicomponent cascade reaction of indole-tethered alkenes with CF3SO2Na, n-Bu4NI, and H2O has been developed, which proceeds via oxidation of CF3SO2Na, coupling with alkene, spirocyclization, oxidation of sulfinate, iodide substitution, and water coupling enabling the rapid assembly of iodomethyl spiropyrrolidinyl-oxindoles in good yields.
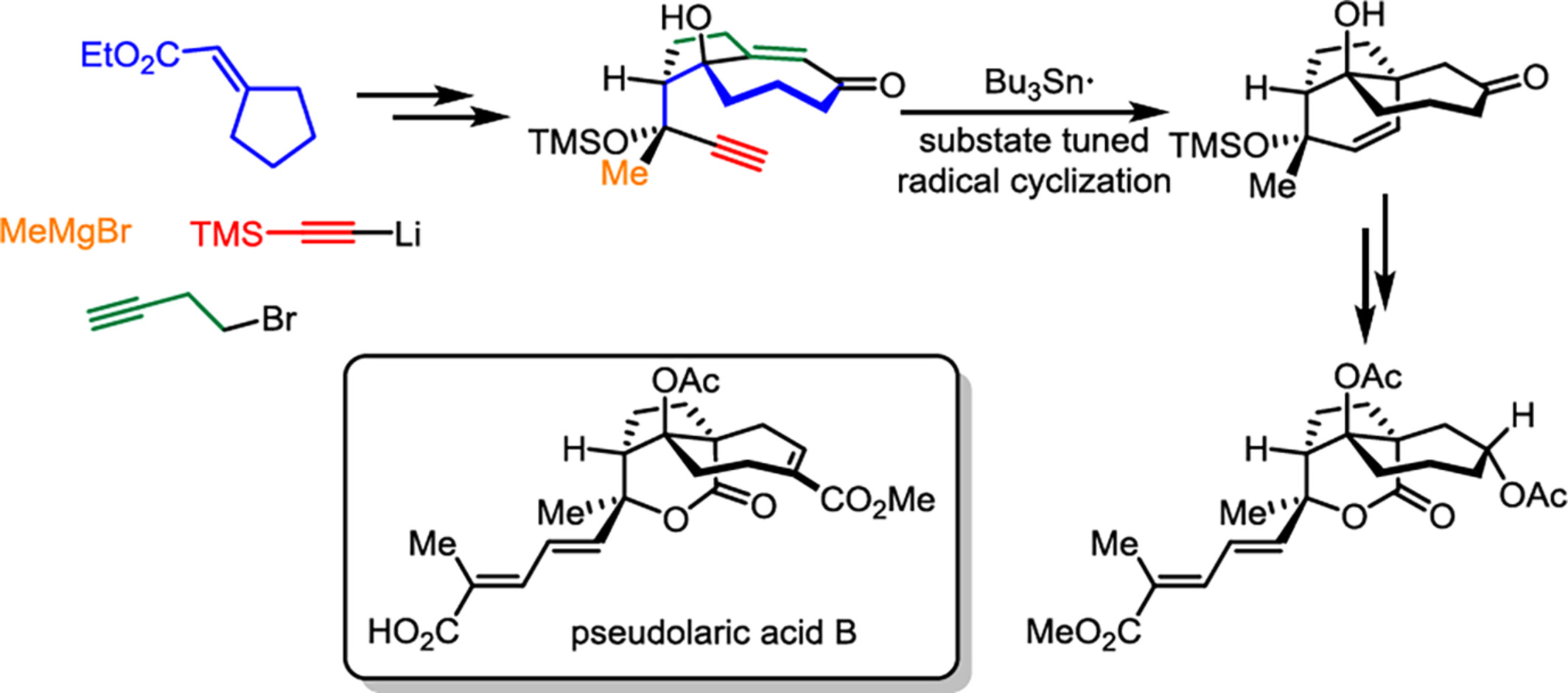
Synthetic Studies toward Pseudolaric Acids: Radical Cyclization to Form Bridged Scaffold
- Pages: 1699-1705
- First Published: 19 March 2024
Molecular Ferroelastic Induced by Mono-/Double-Protonation Strategy
- Pages: 1706-1712
- First Published: 25 March 2024
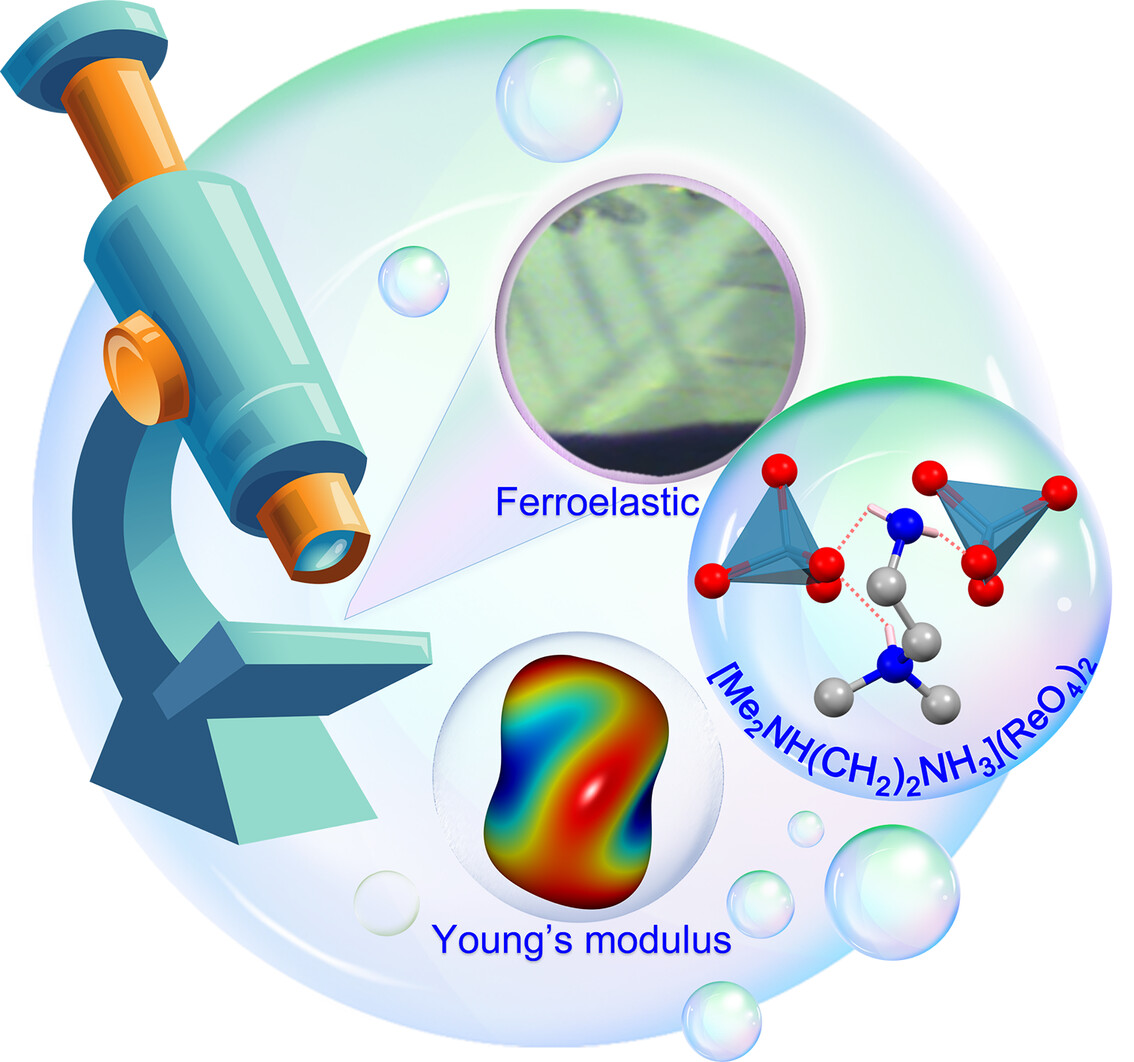
By the effective chemical strategy of mono-/double-protonating organic cations, a novel molecular ferroelastic [Me2NH(CH2)2NH3](ReO4)2 was successfully prepared. Notably, it exhibits excellent mechanical flexibility and demonstrates the bright prospects in wearable and human-compatible electromechanical applications.
Yeast-Controlled Double-Shelled CaCO3/CaF2 Hollow Nanospheres with Hierarchically Porous for Sustained pH-Sensitive Drug Release
- Pages: 1713-1720
- First Published: 30 March 2024
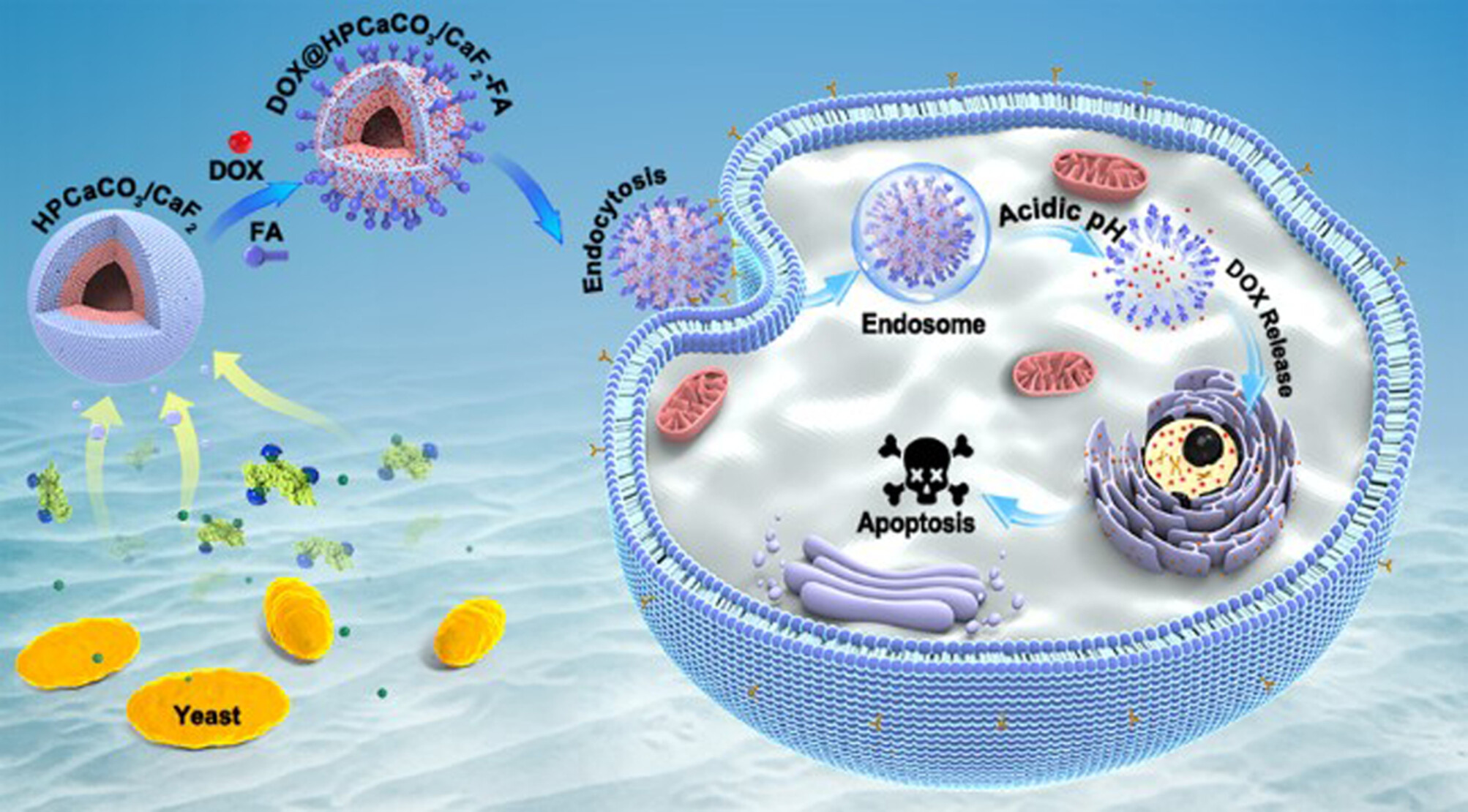
A novel biomimetic strategy is proposed to prepare the cell-tailored double-shelled CaCO3/CaF2 hollow nanospheres with hierarchically porous structure. The nanospheres exhibit excellent water dispersibility and favorable biocompatibility. Moreover, the nanospheres with special structure have a high drug loading capacity and a controlled drug release property, so it can be exploited as a sustained pH-sensitive drug delivery system.
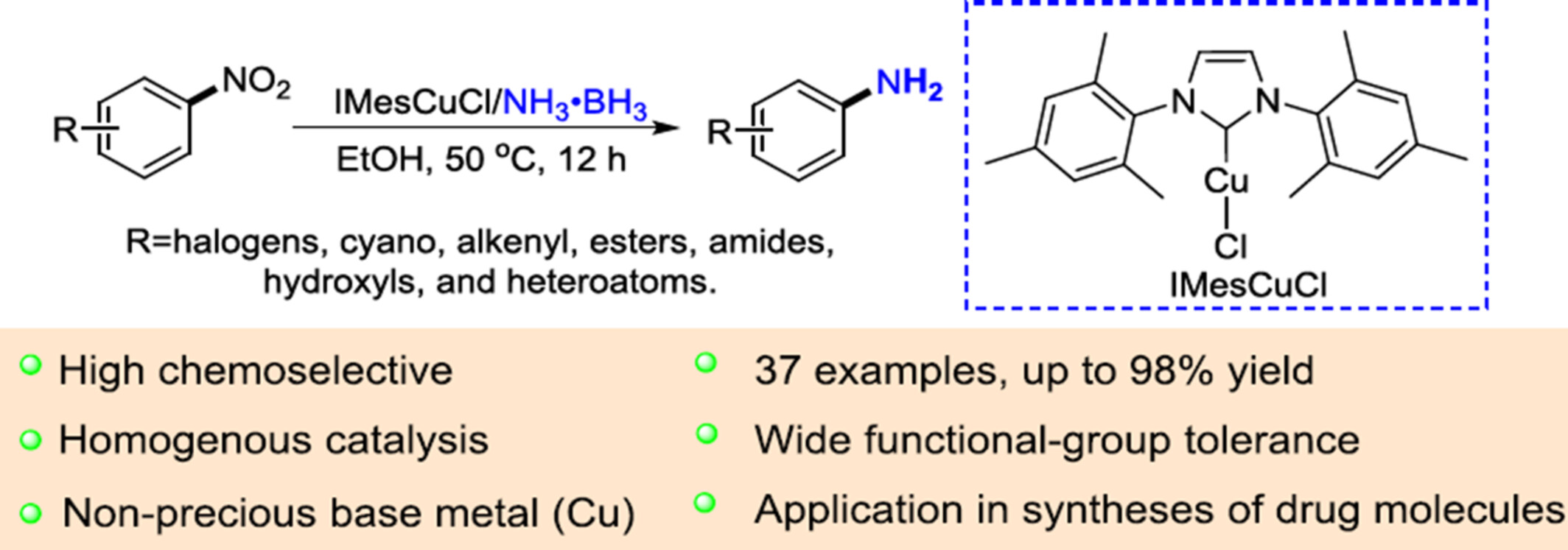
Chemoselective Transfer Hydrogenation of Nitroarenes with Ammonia Borane Catalyzed by Copper N-heterocyclic Carbene Complexes
- Pages: 1721-1726
- First Published: 26 March 2024
Chemodivergent Synthesis of Benzofurans and 2,3-Dihydrobenzofurans via Tandem Oxidative Annulation of Enaminones and Salicylaldehydes
- Pages: 1727-1733
- First Published: 26 March 2024
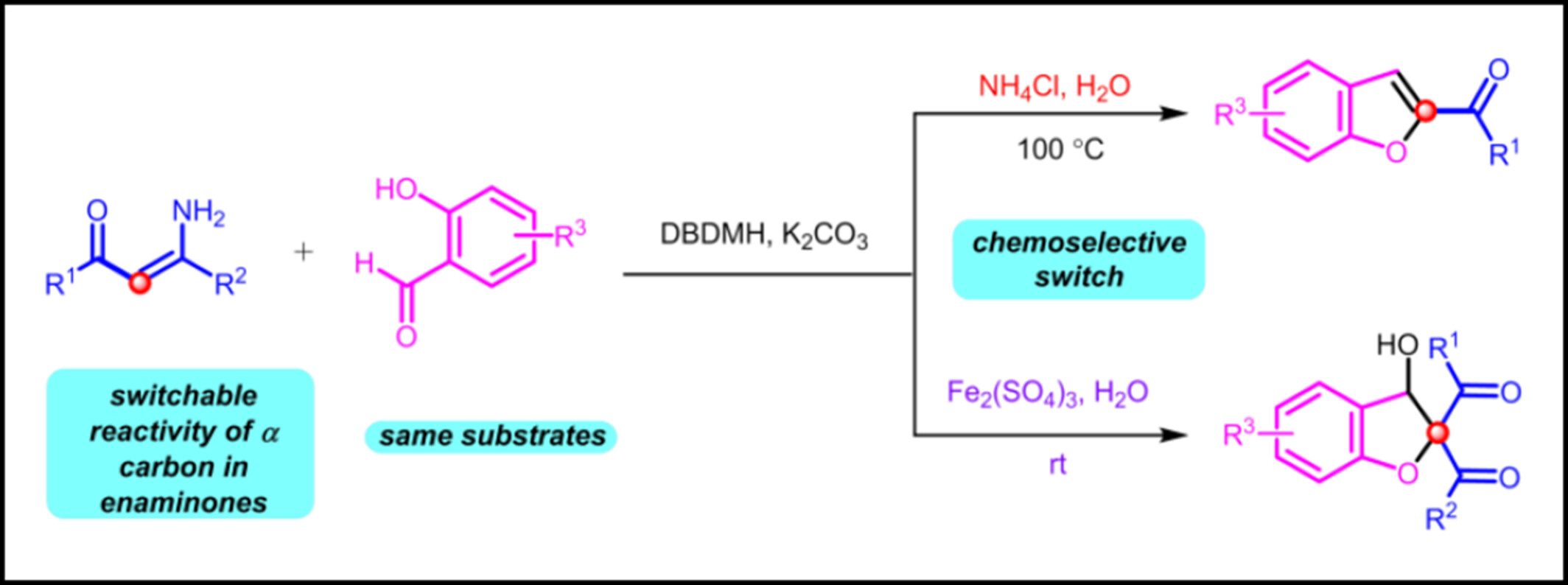
Under controlled conditions, a chemodivergent synthesis of benzofurans and 2,3-dihydrobenzofurans was achieved through the tandem reaction of enaminones and salicylaldehydes, employing a reaction system with DBDMH and K2CO3 promotors. The key to success was identifying the reaction parameters, wherein the imine intermediate formed through transient halogenation coupling and substitution processes underwent either aldol condensation/annulation or imine hydrolysis/aldol condensation.
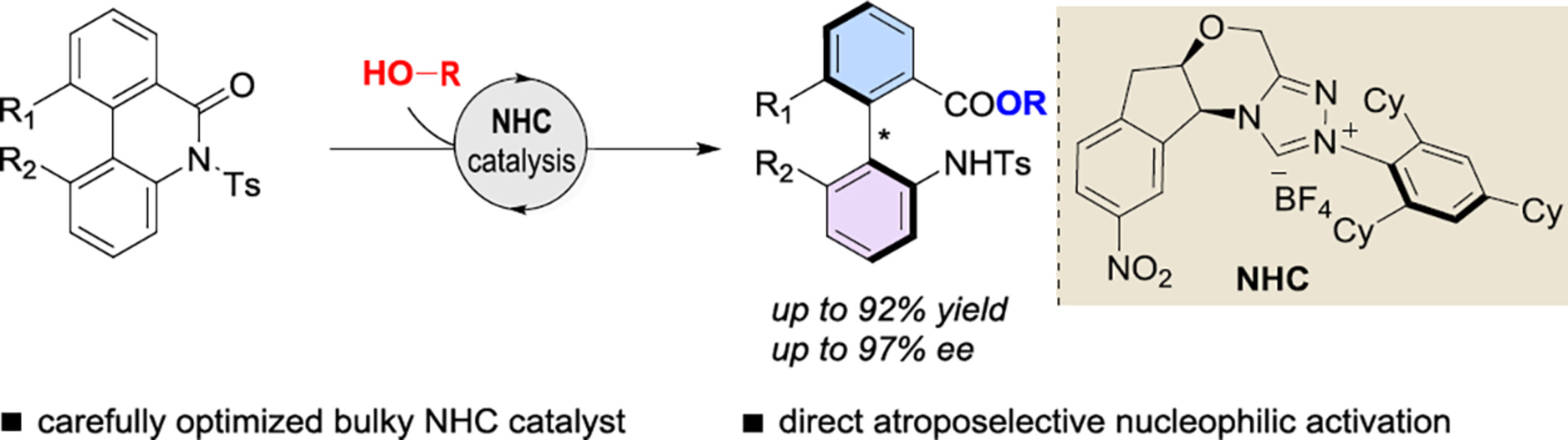
Carbene-Catalyzed Asymmetric Ring-Opening Reaction of Biaryl Lactams to Access Axially Chiral Biaryls
- Pages: 1734-1740
- First Published: 30 March 2024
Comprehensive Report
Unique Azolyl Acylhydrazonyl Hybridization of Aloe Emodins to Access Potential Antibacterial Agents
- Pages: 1741-1758
- First Published: 26 March 2024
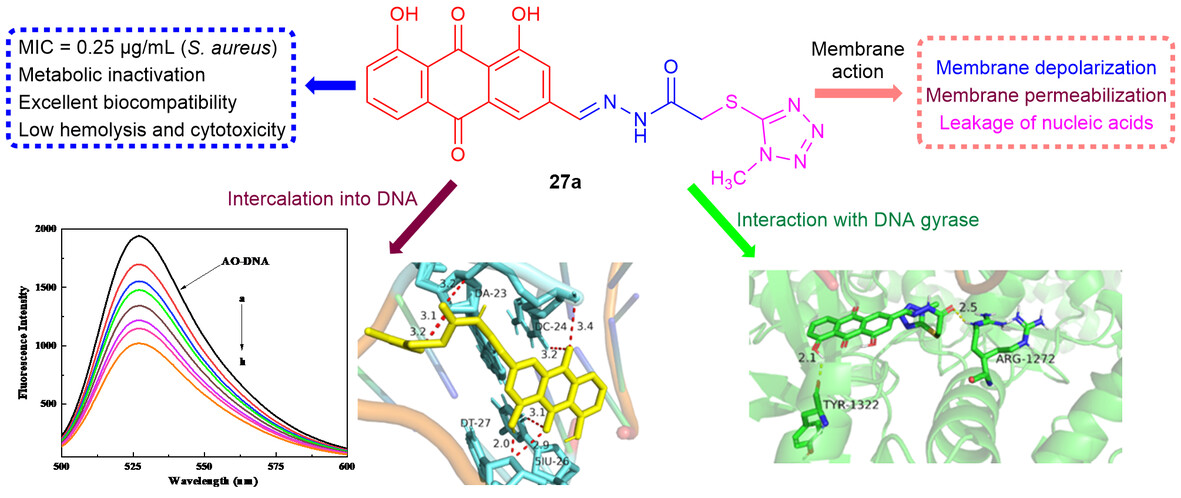
The three-component hybridization of aloe emodin and azole heterocycles with acylhydrazonyl group as linker afforded a new unique type of framework azolyl acylhydrazonyl aloe emodins. Their medicinal identification revealed that azole-hybridized acylhydrazonyl aloe emodins could act as the promising lead antibacterial agents.
Recent Advances
Recent Advances of Imide-Functionalized Polymer Donors for Non-fullerene Solar Cells†
- Pages: 1759-1780
- First Published: 12 April 2024
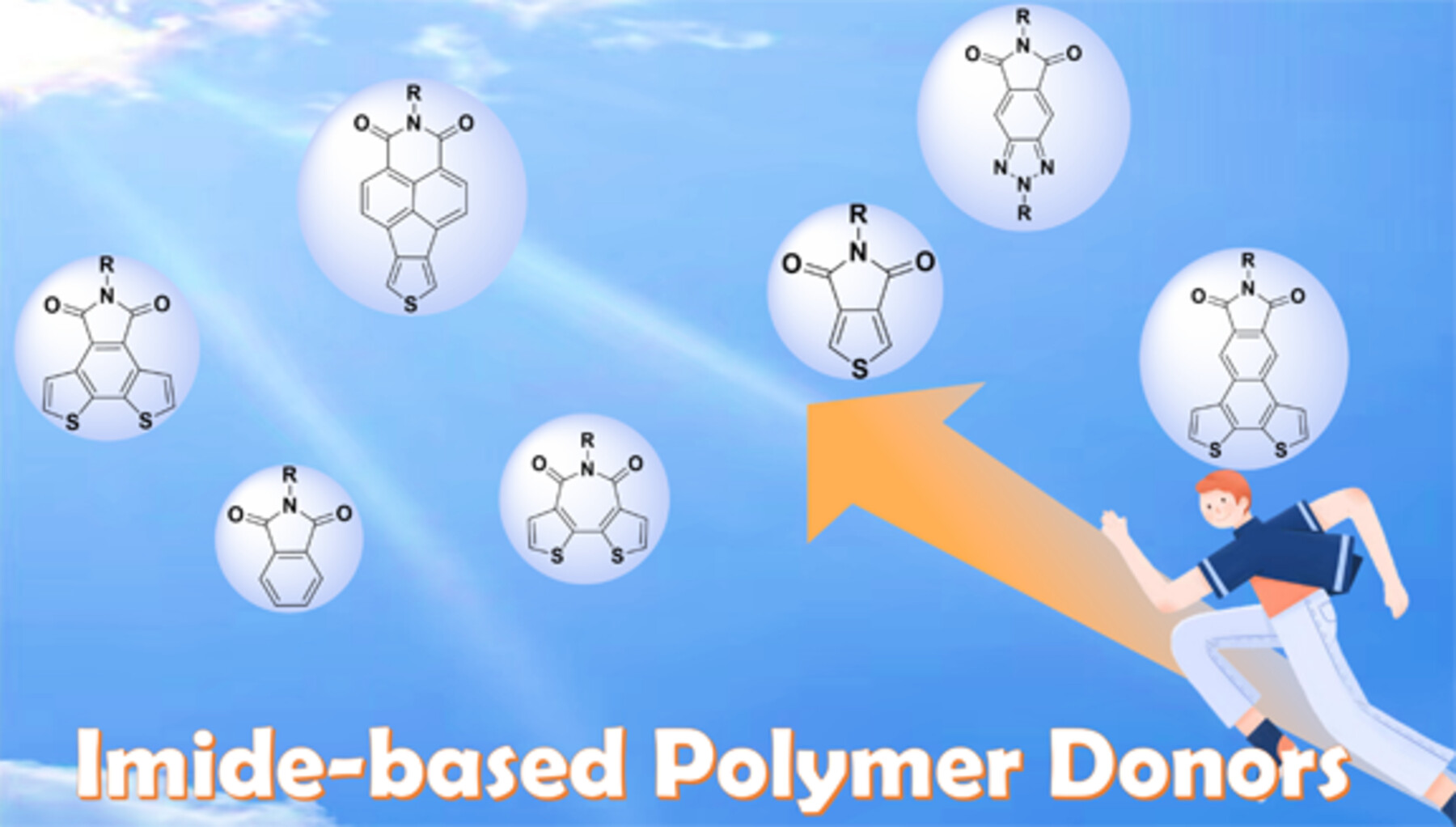
The imide-functionalized polymers are very promising donor materials for non-fullerene OSCs. Aiming to promote future innovation in imide-functionalized polymers, this review summarized the synthetic routes of imide building units, and the structural evolution of imide-functionalized polymer donors by focusing on the effects of polymer structure on their physical, optoelectronic, and photovoltaic properties
Critical Review
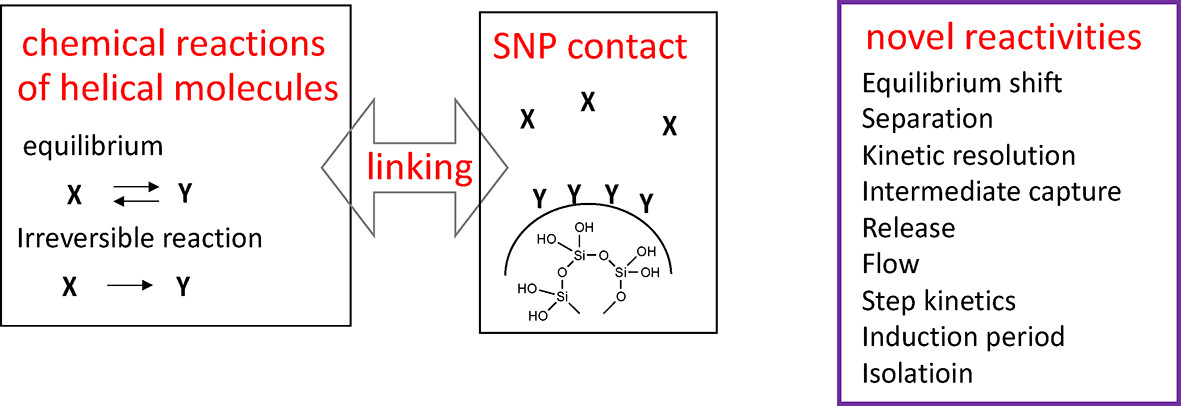
Linking of Chemical Reactions and Silica Nanoparticle Contact Using Synthetic Helical Molecules
- Pages: 1781-1796
- First Published: 22 April 2024
Meet Our New Editorial Board Members of Rising Stars
Meet Our New Editorial Board Members of Rising Stars
- Pages: 1797-1805
- First Published: 01 July 2024
Inside Back Cover
Inside Back Cover
- Page: 1807
- First Published: 01 July 2024

The method for the homogeneous hydrogenation of nitroarenes to produce aromatic amines using low catalyst loading (1 mo%) of air-stable copper N-heterocyclic carbene complexes as the catalyst and ammonia borane as the source of hydrogen is reported. More details are discussed in the article by Han et al. on page 1721—1726.
Back Cover
Back Cover
- Page: 1808
- First Published: 01 July 2024

Molecular ferroelastic materials have the natural properties of spontaneous strain switching and potential applications in intelligent actuator. Under the guidance of the single/double protonation strategy, we successfully obtained the molecular ferroelasticity [Me2NH(CH2)2NH3](ReO4)2 (Me2NH(CH2)2NH3 = N,N-dimethylethylenediamine). This work further enriches the family of ferroelastic molecules and demonstrates that single/double protonation is one of the effective molecular modification strategies for designing ferroelasticity. More details are discussed in the article by Fu et al. on page 1706—1712.