Anisotropic Plasmon Resonance Enables Spatially Controlled Photothermal and Photochemical Effects in Hot Carrier-Driven Catalysis
Jiaqi Wang
Institute of Functional Nano & Soft Materials (FUNSOM), Soochow University, Suzhou, Jiangsu, 215123 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorZhijie Zhu
Institute of Functional Nano & Soft Materials (FUNSOM), Soochow University, Suzhou, Jiangsu, 215123 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorKai Feng
Institute of Functional Nano & Soft Materials (FUNSOM), Soochow University, Suzhou, Jiangsu, 215123 China
Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Advanced Negative Carbon Technologies, Soochow University, Suzhou, Jiangsu, 215123 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorShuang Liu
Institute of Functional Nano & Soft Materials (FUNSOM), Soochow University, Suzhou, Jiangsu, 215123 China
Search for more papers by this authorYuxuan Zhou
Institute of Functional Nano & Soft Materials (FUNSOM), Soochow University, Suzhou, Jiangsu, 215123 China
Search for more papers by this authorIfra Urooj
Department of Chemistry, School of Natural Sciences, National University of Sciences and Technology, Islamabad, 44000 Pakistan
Search for more papers by this authorJiari He
Institute of Functional Nano & Soft Materials (FUNSOM), Soochow University, Suzhou, Jiangsu, 215123 China
Search for more papers by this authorZhiyi Wu
Institute of Functional Nano & Soft Materials (FUNSOM), Soochow University, Suzhou, Jiangsu, 215123 China
Search for more papers by this authorJiahui Shen
Institute of Functional Nano & Soft Materials (FUNSOM), Soochow University, Suzhou, Jiangsu, 215123 China
Search for more papers by this authorXu Hu
Institute of Functional Nano & Soft Materials (FUNSOM), Soochow University, Suzhou, Jiangsu, 215123 China
Search for more papers by this authorZhijie Chen
Institute of Functional Nano & Soft Materials (FUNSOM), Soochow University, Suzhou, Jiangsu, 215123 China
Search for more papers by this authorXudong Dong
Institute of Functional Nano & Soft Materials (FUNSOM), Soochow University, Suzhou, Jiangsu, 215123 China
Search for more papers by this authorManzar Sohail
Department of Chemistry, School of Natural Sciences, National University of Sciences and Technology, Islamabad, 44000 Pakistan
Search for more papers by this authorYanyun Ma
Institute of Functional Nano & Soft Materials (FUNSOM), Soochow University, Suzhou, Jiangsu, 215123 China
Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Advanced Negative Carbon Technologies, Soochow University, Suzhou, Jiangsu, 215123 China
Search for more papers by this authorJinxing Chen
Institute of Functional Nano & Soft Materials (FUNSOM), Soochow University, Suzhou, Jiangsu, 215123 China
Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Advanced Negative Carbon Technologies, Soochow University, Suzhou, Jiangsu, 215123 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Chaoran Li
Institute of Functional Nano & Soft Materials (FUNSOM), Soochow University, Suzhou, Jiangsu, 215123 China
Jiangsu Key Laboratory for Carbon-Based Functional Materials & Devices, Soochow University, Suzhou, Jiangsu, 215123 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Xingda An
Institute of Functional Nano & Soft Materials (FUNSOM), Soochow University, Suzhou, Jiangsu, 215123 China
Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Advanced Negative Carbon Technologies, Soochow University, Suzhou, Jiangsu, 215123 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Le He
Institute of Functional Nano & Soft Materials (FUNSOM), Soochow University, Suzhou, Jiangsu, 215123 China
Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Advanced Negative Carbon Technologies, Soochow University, Suzhou, Jiangsu, 215123 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorJiaqi Wang
Institute of Functional Nano & Soft Materials (FUNSOM), Soochow University, Suzhou, Jiangsu, 215123 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorZhijie Zhu
Institute of Functional Nano & Soft Materials (FUNSOM), Soochow University, Suzhou, Jiangsu, 215123 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorKai Feng
Institute of Functional Nano & Soft Materials (FUNSOM), Soochow University, Suzhou, Jiangsu, 215123 China
Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Advanced Negative Carbon Technologies, Soochow University, Suzhou, Jiangsu, 215123 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorShuang Liu
Institute of Functional Nano & Soft Materials (FUNSOM), Soochow University, Suzhou, Jiangsu, 215123 China
Search for more papers by this authorYuxuan Zhou
Institute of Functional Nano & Soft Materials (FUNSOM), Soochow University, Suzhou, Jiangsu, 215123 China
Search for more papers by this authorIfra Urooj
Department of Chemistry, School of Natural Sciences, National University of Sciences and Technology, Islamabad, 44000 Pakistan
Search for more papers by this authorJiari He
Institute of Functional Nano & Soft Materials (FUNSOM), Soochow University, Suzhou, Jiangsu, 215123 China
Search for more papers by this authorZhiyi Wu
Institute of Functional Nano & Soft Materials (FUNSOM), Soochow University, Suzhou, Jiangsu, 215123 China
Search for more papers by this authorJiahui Shen
Institute of Functional Nano & Soft Materials (FUNSOM), Soochow University, Suzhou, Jiangsu, 215123 China
Search for more papers by this authorXu Hu
Institute of Functional Nano & Soft Materials (FUNSOM), Soochow University, Suzhou, Jiangsu, 215123 China
Search for more papers by this authorZhijie Chen
Institute of Functional Nano & Soft Materials (FUNSOM), Soochow University, Suzhou, Jiangsu, 215123 China
Search for more papers by this authorXudong Dong
Institute of Functional Nano & Soft Materials (FUNSOM), Soochow University, Suzhou, Jiangsu, 215123 China
Search for more papers by this authorManzar Sohail
Department of Chemistry, School of Natural Sciences, National University of Sciences and Technology, Islamabad, 44000 Pakistan
Search for more papers by this authorYanyun Ma
Institute of Functional Nano & Soft Materials (FUNSOM), Soochow University, Suzhou, Jiangsu, 215123 China
Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Advanced Negative Carbon Technologies, Soochow University, Suzhou, Jiangsu, 215123 China
Search for more papers by this authorJinxing Chen
Institute of Functional Nano & Soft Materials (FUNSOM), Soochow University, Suzhou, Jiangsu, 215123 China
Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Advanced Negative Carbon Technologies, Soochow University, Suzhou, Jiangsu, 215123 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Chaoran Li
Institute of Functional Nano & Soft Materials (FUNSOM), Soochow University, Suzhou, Jiangsu, 215123 China
Jiangsu Key Laboratory for Carbon-Based Functional Materials & Devices, Soochow University, Suzhou, Jiangsu, 215123 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Xingda An
Institute of Functional Nano & Soft Materials (FUNSOM), Soochow University, Suzhou, Jiangsu, 215123 China
Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Advanced Negative Carbon Technologies, Soochow University, Suzhou, Jiangsu, 215123 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Le He
Institute of Functional Nano & Soft Materials (FUNSOM), Soochow University, Suzhou, Jiangsu, 215123 China
Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Advanced Negative Carbon Technologies, Soochow University, Suzhou, Jiangsu, 215123 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorComprehensive Summary
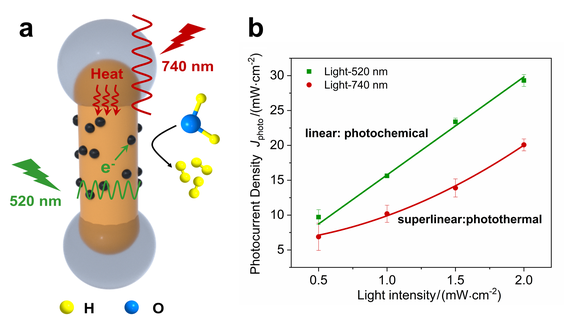
Localized surface plasmon resonance has been demonstrated to provide effective photophysical enhancement mechanisms in plasmonic photocatalysis. However, it remains highly challenging for distinct mechanisms to function in synergy for a collective gain in catalysis due to the lack of spatiotemporal control of their effect. Herein, the anisotropic plasmon resonance nature of Au nanorods was exploited to achieve distinct functionality towards synergistic photocatalysis. Photothermal and photochemical effects were enabled by the longitudinal and transverse plasmon resonance modes, respectively, and were enhanced by partial coating of silica nanoshells and epitaxial growth of a reactor component. Resonant excitation leads to a synergistic gain in photothermal-mediated hot carrier-driven hydrogen evolution catalysis. Our approach provides important design principles for plasmonic photocatalysts in achieving spatiotemporal modulation of distinct photophysical enhancement mechanisms. It also effectively broadens the sunlight response range and increases the efficacy of distinct plasmonic enhancement pathways towards solar energy harvesting and conversion.
Supporting Information
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| cjoc202400177_sup_0001_supinfo.pdfPDF document, 4.5 MB |
Appendix S1: Supporting Information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1 Aslam, U.; Rao, V. G.; Chavez, S. Catalytic conversion of solar to chemical energy on plasmonic metal nanostructures. Nat. Catal. 2018, 1, 656–665.
- 2 Zhang, J.; Mück-Lichtenfeld, C.; Studer, A. Photocatalytic phosphine- mediated water activation for radical hydrogenation. Nature 2023, 619, 506–513.
- 3 Naldoni, A. Catalysis in the hot spots. Nat. Catal. 2023, 6, 1109–1110.
- 4 Zhou, P.; Navid, I. A.; Ma, Y. Solar-to-hydrogen efficiency of more than 9% in photocatalytic water splitting. Nature 2023, 613, 66–70.
- 5 Gao, C.; Wang, J.; Xu, H. Coordination chemistry in the design of heterogeneous photocatalysts. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 2799–2823.
- 6 Ahn, W.; Ratchford, D. C.; Pehrsson, P. E. Surface plasmon polariton- induced hot carrier generation for photocatalysis. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 3010–3022.
- 7 Wu, Z.; Shen, J.; Li, C. Niche Applications of MXene Materials in Photothermal Catalysis. Chemistry 2023, 5, 492–510.
- 8 Zhu, Z.; Tang, R.; Li, C. Promises of Plasmonic Antenna-Reactor Systems in Gas-Phase CO2 Photocatalysis. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, 2302568.
- 9 Kale, M. J.; Avanesian, T.; Christopher, P. Direct Photocatalysis by Plasmonic Nanostructures. ACS Catal. 2013, 4, 116–128.
- 10 Li, S.; Miao, P.; Zhang, Y. Recent Advances in Plasmonic Nanostructures for Enhanced Photocatalysis and Electrocatalysis. Adv. Mater. 2020, 33, 2000086.
- 11 Li, J.; Cushing, S. K.; Meng, F. Plasmon-induced resonance energy transfer for solar energy conversion. Nat. Photonics 2015, 9, 601–607.
- 12 Cushing, S. K.; Li, J.; Meng, F. Photocatalytic Activity Enhanced by Plasmonic Resonant Energy Transfer from Metal to Semiconductor. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 15033–15041.
- 13 An, X.; Stelter, D.; Keyes, T. Plasmonic Photocatalysis of Urea Oxidation and Visible-Light Fuel Cells. Chem 2019, 5, 2228–2242.
- 14 Zhang, Y.; He, S.; Guo, W. Surface-Plasmon-Driven Hot Electron Photochemistry. Chem. Rev. 2017, 118, 2927–2954.
- 15 Linic, S.; Chavez, S.; Elias, R. Flow and extraction of energy and charge carriers in hybrid plasmonic nanostructures. Nat. Mater. 2021, 20, 916–924.
- 16 Tagliabue, G.; Jermyn, A. S.; Sundararaman, R. Quantifying the role of surface plasmon excitation and hot carrier transport in plasmonic devices. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3394.
- 17 Zhang, C.; Zhao, H.; Zhou, L. Al–Pd Nanodisk Heterodimers as Antenna–Reactor Photocatalysts. Nano Lett. 2016, 16, 6677–6682.
- 18 Verma, R.; Belgamwar, R.; Chatterjee, P. Nickel-Laden Dendritic Plasmonic Colloidosomes of Black Gold: Forced Plasmon Mediated Photocatalytic CO2 Hydrogenation. ACS Nano 2023, 17, 4526–4538.
- 19
Zhan, C.; Moskovits, M.; Tian, Z.-Q. Recent Progress and Prospects in Plasmon-Mediated Chemical Reaction. Matter 2020, 3, 42–56.
10.1016/j.matt.2020.03.019 Google Scholar
- 20 Cai, M.; Wu, Z.; Li, Z. Greenhouse-inspired supra-photothermal CO2 catalysis. Nat. Energy 2021, 6, 807–814.
- 21 Zhao, J.; Guo, X.; Shi, R. NiFe Nanoalloys Derived from Layered Double Hydroxides for Photothermal Synergistic Reforming of CH4 with CO2. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2204056.
- 22 Zhao, J.; Shi, R.; Waterhouse, G. I. N. Selective photothermal CO2 reduction to CO, CH4, alkanes, alkenes over bimetallic alloy catalysts derived from layered double hydroxide nanosheets. Nano Energy 2022, 102, 107650.
- 23 Li, Z.; Shi, R.; Zhao, J. Ni-based catalysts derived from layered-double- hydroxide nanosheets for efficient photothermal CO2 reduction under flow-type system. Nano Res. 2021, 14, 4828–4832.
- 24 Linic, S.; Christopher, P.; Ingram, D. B. Plasmonic-metal nanostructures for efficient conversion of solar to chemical energy. Nat. Mater. 2011, 10, 911–921.
- 25 Zhou, L.; Martirez, J. M. P.; Finzel, J. Light-driven methane dry reforming with single atomic site antenna-reactor plasmonic photocatalysts. Nat. Energy 2020, 5, 61–70.
- 26 Yuan, Y.; Zhou, L.; Robatjazi, H. Earth-abundant photocatalyst for H2 generation from NH3 with light-emitting diode illumination. Science 2022, 378, 889–893.
- 27 Swearer, D. F.; Zhao, H.; Zhou, L. Heterometallic antenna−reactor complexes for photocatalysis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2016, 113, 8916–8920.
- 28 Robatjazi, H.; Schirato, A.; Alabastri, A. Reply to: Distinguishing thermal from non-thermal contributions to plasmonic hydrodefluorination. Nat. Catal. 2022, 5, 247–250.
- 29 An, X.; Kays, J. C.; Lightcap, I. V. Wavelength-Dependent Bifunctional Plasmonic Photocatalysis in Au/Chalcopyrite Hybrid Nanostructures. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 6813–6824.
- 30 Ren, F.; Li, H.; Wang, Y. Enhanced photocatalytic oxidation of propylene over V-doped TiO2 photocatalyst: Reaction mechanism between V5+ and single-electron-trapped oxygen vacancy. Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 2015, 176–177, 160–172.
- 31 Sheng, H.; Wang, J.; Huang, J. Strong synergy between gold nanoparticles and cobalt porphyrin induces highly efficient photocatalytic hydrogen evolution. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 1528.
- 32 Du, S.; Bian, X.; Zhao, Y. Progress and Prospect of Photothermal Catalysis. Chem. Res. Chin. Univ. 2022, 38, 723–734.
- 33Wang, Z.-j.; Song, H.; Pang, H. Photo-assisted methanol synthesis via CO2 reduction under ambient pressure over plasmonic Cu/ZnO catalysts. Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 2019, 250, 1016.
- 34 Zhou, L.; Swearer, D. F.; Zhang, C. Quantifying hot carrier and thermal contributions in plasmonic photocatalysis. Science 2018, 362, 69–72.
- 35 Dubi, Y.; Un, I. W.; Baraban, J. H. Distinguishing thermal from non-thermal contributions to plasmonic hydrodefluorination. Nat. Catal. 2022, 5, 244–246.
- 36 Bagnall, A. J.; Ganguli, S.; Sekretareva, A. Hot or Not? Reassessing Mechanisms of Photocurrent Generation in Plasmon-Enhanced Electrocatalysis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024, 63, e202314352.
- 37 Chen, T.; Tong, F.; Enderlein, J. Plasmon-Driven Modulation of Reaction Pathways of Individual Pt-Modified Au Nanorods. Nano Lett. 2020, 20, 3326–3330.
- 38 Tong, F.; Liang, X.; Liu, M. Plasmon-Enhanced Water Activation for Hydrogen Evolution from Ammonia-Borane Studied at a Single- Particle Level. ACS Catal. 2022, 12, 3558–3565.
- 39 You, H.; Li, S.; Fan, Y. Accelerated pyro-catalytic hydrogen production enabled by plasmonic local heating of Au on pyroelectric BaTiO3 nanoparticles. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 6144.
- 40 Cai, M.; Li, C.; An, X. Supra-Photothermal CO2 Methanation over Greenhouse-Like Plasmonic Superstructures of Ultrasmall Cobalt Nanoparticles. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, 2308859.
- 41 Jia, Y.; Huang, T.-H.; Lin, S. Stable Pd–Cu Hydride Catalyst for Efficient Hydrogen Evolution. Nano Lett. 2022, 22, 1391–1397.
- 42 Ye, X.; Zheng, C.; Chen, J. Using Binary Surfactant Mixtures to Simultaneously Improve the Dimensional Tunability and Monodispersity in the Seeded Growth of Gold Nanorods. Nano Lett. 2013, 13, 765–771.
- 43 González-Rubio, G.; Mosquera, J.; Kumar, V. Micelle-directed chiral seeded growth on anisotropic gold nanocrystals. Science 2020, 368, 1472–1477.
- 44 Pedrazo-Tardajos, A.; Arslan Irmak, E.; Kumar, V. Thermal Activation of Gold Atom Diffusion in Au@Pt Nanorods. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 9608–9619.
- 45 Zheng, J.; Cheng, X.; Zhang, H. Gold Nanorods: The Most Versatile Plasmonic Nanoparticles. Chem. Rev. 2021, 121, 13342–13453.
- 46 Jia, H.; Li, F.; Chow, T. H. Construction of Spatially Separated Gold Nanocrystal/Cuprous Oxide Architecture for Plasmon-Driven CO2 Reduction. Nano Lett. 2022, 22, 7268–7274.
- 47
Wang, F.; Cheng, S.; Bao, Z. Anisotropic Overgrowth of Metal Heterostructures Induced by a Site-Selective Silica Coating. Angew. Chem. 2013, 125, 10534–10538.
10.1002/ange.201304364 Google Scholar
- 48 Rowe, L. R.; Chapman, B. S.; Tracy, J. B. Understanding and Controlling the Morphology of Silica Shells on Gold Nanorods. Chem. Mater. 2018, 30, 6249–6258.
- 49 Wu, B.; Liu, D.; Mubeen, S. Anisotropic Growth of TiO2 onto Gold Nanorods for Plasmon-Enhanced Hydrogen Production from Water Reduction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 1114–1117.
- 50 Tong, F.; Liang, X.; Ma, F. Plasmon-Mediated Nitrobenzene Hydrogenation with Formate as the Hydrogen Donor Studied at a Single- Particle Level. ACS Catal. 2021, 11, 3801–3809.
- 51 Baksi, A.; Bag, S.; Kruk, R. Structural insights into metal-metalloid glasses from mass spectrometry. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 17467.
- 52 Li, C.; Xu, Y.; Li, X. Unexpected Dual Action of Cetyltrimethylammonium Bromide (CTAB) in the Self-Assembly of Colloidal Nanoparticles at Liquid-Liquid Interfaces. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 7, 2000391.
- 53 Acharya, A.; Dubbu, S.; Kumar, S. Atomically Conformal Metal Laminations on Plasmonic Nanocrystals for Efficient Catalysis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 10582–10589.
- 54 Forcherio, G. T.; Ostovar, B.; Boltersdorf, J. Single-Particle Insights into Plasmonic Hot Carrier Separation Augmenting Photoelectrochemical Ethanol Oxidation with Photocatalytically Synthesized Pd–Au Bimetallic Nanorods. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 12377–12389.
- 55 Li, J.; Sheng, B.; Chen, Y. Nickel–Iron Bimetal as a Cost-Effective Cocatalyst for Light-Driven Hydrogen Release from Methanol and Water. ACS Catal. 2023, 13, 10153–10160.
- 56 Sivula, K. Mott–Schottky Analysis of Photoelectrodes: Sanity Checks Are Needed. ACS Energy Lett. 2021, 6, 2549–2551.
- 57
Zhao, Y.; Shi, R.; Bian, X. Ammonia Detection Methods in Photocatalytic and Electrocatalytic Experiments: How to Improve the Reliability of NH3 Production Rates? Adv. Sci. 2019, 6, 1802109.
10.1002/advs.201802109 Google Scholar
- 58 Hu, C.; Chen, X.; Low, J. Near-infrared-featured broadband CO2 reduction with water to hydrocarbons by surface plasmon. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 221.
- 59 Shao, T.; Wang, X.; Dong, H. A Stacked Plasmonic Metamaterial with Strong Localized Electric Field Enables Highly Efficient Broadband Light-Driven CO2 Hydrogenation. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2202367.
- 60 Ahn, W.; Boriskina, S. V.; Hong, Y. Electromagnetic Field Enhancement and Spectrum Shaping through Plasmonically Integrated Optical Vortices. Nano Lett. 2011, 12, 219–227.
- 61 An, X.; Majumder, A.; McNeely, J. Interfacial hydration determines orientational and functional dimorphism of sterol-derived Raman tags in lipid-coated nanoparticles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2021, 118, e2105913118.
- 62 Deng, J.; Ren, P.; Deng, D. Highly active and durable non-precious- metal catalysts encapsulated in carbon nanotubes for hydrogen evolution reaction. Energy Environ. Sci. 2014, 7, 1919–1923.
- 63 Kim, C.; Moon, I.; Lee, D. Fermi Level Pinning at Electrical Metal Contacts of Monolayer Molybdenum Dichalcogenides. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 1588–1596.
- 64 Hu, Y.; Zhan, F.; Wang, Q. Tracking Mechanistic Pathway of Photocatalytic CO2 Reaction at Ni Sites Using Operando, Time-Resolved Spectroscopy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 5618–5626.
- 65 Zhu, Z.; Feng, K.; Li, C. Stabilization of Exposed Metal Nanocrystals in High-Temperature Heterogeneous Catalysis. Adv. Mater. 2021, 34, 2108727.




