Preferential Formation of Ethylene via Electrocatalytic CO2 Reduction on Mesoporous Cu2O Nanoparticles: Synergistic Effects of Pore Structure Confinement and Surface Amine
Haifeng Zhang
School of Chemistry, Chemical Engineering and Materials, Jining University, Qufu, Shandong, 273155 China
These authors contribute equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorDun Li
College of Materials Science and Engineering, Hunan University, Changsha, Hunan, 410082 China
These authors contribute equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorZhifang Chen
School of Chemistry, Chemical Engineering and Materials, Jining University, Qufu, Shandong, 273155 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Yingying Wang
Health Management Department, Shandong Vocational College of Light Industry, Zibo, Shandong, 255300 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorHaoyu Sun
School of Chemistry, Chemical Engineering and Materials, Jining University, Qufu, Shandong, 273155 China
Search for more papers by this authorFeng Liu
International Research Center for Renewable Energy, National Key Laboratory of Multiphase Flow in Power Engineering, Xi'an Jiaotong University, Xi'an, Shaanxi, 710049 China
Search for more papers by this authorMaochang Liu
International Research Center for Renewable Energy, National Key Laboratory of Multiphase Flow in Power Engineering, Xi'an Jiaotong University, Xi'an, Shaanxi, 710049 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Yiqun Zheng
School of Chemistry, Chemical Engineering and Materials, Jining University, Qufu, Shandong, 273155 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Hongwen Huang
College of Materials Science and Engineering, Hunan University, Changsha, Hunan, 410082 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorHaifeng Zhang
School of Chemistry, Chemical Engineering and Materials, Jining University, Qufu, Shandong, 273155 China
These authors contribute equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorDun Li
College of Materials Science and Engineering, Hunan University, Changsha, Hunan, 410082 China
These authors contribute equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorZhifang Chen
School of Chemistry, Chemical Engineering and Materials, Jining University, Qufu, Shandong, 273155 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Yingying Wang
Health Management Department, Shandong Vocational College of Light Industry, Zibo, Shandong, 255300 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorHaoyu Sun
School of Chemistry, Chemical Engineering and Materials, Jining University, Qufu, Shandong, 273155 China
Search for more papers by this authorFeng Liu
International Research Center for Renewable Energy, National Key Laboratory of Multiphase Flow in Power Engineering, Xi'an Jiaotong University, Xi'an, Shaanxi, 710049 China
Search for more papers by this authorMaochang Liu
International Research Center for Renewable Energy, National Key Laboratory of Multiphase Flow in Power Engineering, Xi'an Jiaotong University, Xi'an, Shaanxi, 710049 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Yiqun Zheng
School of Chemistry, Chemical Engineering and Materials, Jining University, Qufu, Shandong, 273155 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Hongwen Huang
College of Materials Science and Engineering, Hunan University, Changsha, Hunan, 410082 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorComprehensive Summary
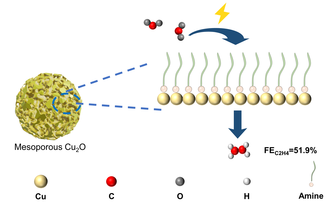
We present a facile synthetic strategy to create mesoporous Cu2O nanocrystals with tunable pore structures and surface functional groups of amine derivatives for efficient and preferable electrochemical conversion of CO2 into ethylene. The structural characteristics of these Cu2O nanocrystals can be manipulated using a set of amine derivatives, such as pyridine, 4,4'-bipyridine, and hexamethylenetetramine, during the oxidative etching process of Cu nanocrystals by bubbling gaseous oxygen in N,N-dimethylformamide solution. These amine derivatives not only serve as surface functional groups but also significantly affect the resulting pore structures. The synergistic effect of pore structure confinement and surface amine functionalization leads to the superb Faradaic efficiency (FE) of 51.9% for C2H4, respectively, together with the C2H4 partial current density of –209.4 mA·cm−2 at –0.8 V vs. reversible hydrogen electrode (RHE). The relatively high selectivity towards C2H4 was investigated using DFT simulations, where 4,4'-bipyridine functionalized Cu2O seemed to favor the C2H4 formation with the low free energy of the intermediates. This study provides a feasible strategy to manipulate the pore structure and surface functionalization of mesoporous Cu2O nanocrystals by regulating the oxidative etching process, which sheds light on the rational preparation of high-performance CO2RR electrocatalysts.
Supporting Information
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| cjoc202400046-sup-0001-supinfo.pdfPDF document, 1.2 MB |
Appendix S1: Supporting Information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1 Tan, X. Y.; Yu, C.; Ren, Y. W.; Cui, S.; Li, W. B.; Qiu, J. S. Recent advances in innovative strategies for the CO2 electroreduction reaction. Energy Environ. Sci. 2021, 14, 765–780.
- 2 Jin, S.; Hao, Z. M.; Zhang, K.; Yan, Z. H.; Chen, J. Advances and Challenges for the Electrochemical Reduction of CO2 to CO: From Fundamentals to Industrialization. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 20627–20648.
- 3 Liu, J. Y.; Li, P. S.; Bi, J. H.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, Q. G.; Sun, X. F.; Zhang, J. L.; Liu, Z. M.; Han, B. X. Sm and S Co-doping to Construct Homo-hetero Cu Catalysts for Synergistic Enhancing CO2 Electroreduction. Chin. J. Chem. 2023, 41, 1443–1449.
- 4 Wei, Z. M.; Liu, Y. H.; Ding, J.; He, Q. Y.; Zhang, Q.; Zhai, Y. M. Promoting Electrocatalytic CO2 Reduction to CO via Sulfur-Doped Co-N-C Single-Atom Catalyst. Chin. J. Chem. 2023, 41, 3553–3559.
- 5 Zheng, Y. Q.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, Y. L.; Huang, H. W. Metal-based Heterogeneous Electrocatalysts for Electrochemical Reduction of Carbon Dioxide to Methane: Progress and Challenges. ChemNanoMat 2021, 7, 502–514.
- 6 Birdja, Y. Y.; Pérez, G, E.; Figueiredo, M. C.; Göttle, A. J.; Calle–Vallejo, F.; Koper, M. T. M. Advances and challenges in understanding the electrocatalytic conversion of carbon dioxide to fuels. Nat. Energy 2019, 4, 732–745.
- 7 Yoon Suk Lee, L.; Wong, K. Y. Electrocatalytic Reduction of Carbon Dioxide. Chem 2017, 3, 717–718.
- 8 Liu, W.; Zhai, P. B.; Li, A. W.; Wei, B.; Si, K. P.; Wei, Y.; Wang, X. G.; Zhu, G. D.; Chen, Q.; Gu, X. K., et al. Electrochemical CO2 reduction to ethylene by ultrathin CuO nanoplate arrays. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1877.
- 9 Song, Z.; Wang, X.; Ren, Z.; Fu, H. Relationships between structural design and synthesis engineering of Cu-based catalysts for CO2 to C2 electroreduction. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 479, 147606.
- 10 Zhao, Z. X.; Wang, H. T.; Yu, Q.; Roy, S.; Yu, X. H. Photo/electrocatalytic approaches to CO2 conversion on Cu2O-based catalysts. Appl. Catal. 2023, 667, 119445.
- 11 Kim, J. Y. T.; Sellers, C.; Hao, S.; Senftle, T. P.; Wang, H. Different distributions of multi-carbon products in CO2 and CO electroreduction under practical reaction conditions. Nat. Catal. 2023, 6, 1115–1124.
- 12 Liu, Y. H.; Hou, Z. H.; Jiang, H. J. Local concentration effect on nano-electrocatalytic CO2 reduction. Carbon Capture Sci. Technol. 2022, 3, 100047.
- 13 Liu, G. M.; Zhan, J. Y.; Zhang, Z. S.; Zhang, L. H.; Yu, F. S. Front Cover: Recent Advances of the Confinement Effects Boosting Electrochemical CO2 Reduction. Chem. Asian J. 2023, 18, e202201250.
- 14 Li, J. X.; Fan, L.; Hua, Q.; Geng, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, X.; Ma, L.; Wang, C.; Zhu, W.; Feng, X., et al. Ordered macroporous carbonous skeletons implanted with dual-phase Co/CoFe nanoparticles for boosting electrocatalytic performance. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 470, 144399.
- 15 Du, D.; Geng, Q.; Ma, L.; Ren, S.; Li, J. X.; Dong, W.; Hua, Q.; Fan, L.; Shao, R.; Wang, X., et al. Mesoporous PdBi nanocages for enhanced electrocatalytic performances by all direction accessibility and steric site activation. Chem. Sci. 2022, 13, 3819–3825.
- 16 Li, C.; Jiang, B.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Hossain, M. S. A.; Kim, J. H.; Takei, T.; Henzie, J.; Dag, Ö.; Bando, Y., et al. First Synthesis of Continuous Mesoporous Copper Films with Uniformly Sized Pores by Electrochemical Soft Templating. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 12746–12750.
- 17 Lu, Q.; Rosen, J.; Zhou, Y.; Hutchings, G. S.; Kimmel, Y. C.; Chen, J. G. G.; Jiao, F. A selective and efficient electrocatalyst for carbon dioxide reduction. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3242.
- 18 Kim, C.; Cho, K. M.; Park, K.; Kim, J. Y.; Yun, G. T.; Toma, F. M.; Gereige, I.; Jung, H. T. Cu/CuO Interconnected Porous Aerogel Catalyst for Highly Productive Electrosynthesis of Ethanol from CO2. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2102142.
- 19 Dutta, A.; Rahaman, M.; Luedi, N. C.; Broekmann, P. Morphology Matters: Tuning the Product Distribution of CO2 Electroreduction on Oxide–Derived Cu Foam Catalysts. ACS Catal. 2016, 6, 3804–3814.
- 20 Yang, K. D.; Ko, W. R.; Lee, J. H.; Kim, S. J.; Lee, H.; Lee, M. H.; Nam, K. T. Morphology-Directed Selective Production of Ethylene or Ethane from CO on a Cu Mesopore Electrode. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 796–800.
- 21 Fan, L.; Geng, Q.; Ma, L.; Wang, C.; Li, J. X.; Zhu, W.; Shao, R.; Li, W.; Feng, X.; Yamauchi, Y., et al. Evoking C2+ production from electrochemical CO2 reduction by the steric confinement effect of ordered porous Cu2O. Chem. Sci. 2023, 14, 13851–13859.
- 22 Ma, L.; Geng, Q.; Fan, L.; Li, J. X.; Du, D.; Bai, J.; Li, C. Enhanced electroreduction of CO2 to C2+ fuels by the synergetic effect of polyaniline/CuO nanosheets hybrids. Nano Res. 2023, 16, 9065–9072.
- 23 Yan, C. L.; Yuan, H. M.; Wang, X. Y.; Hao, R.; Liu, G. Y.; Luo, W.; Wang, Z. Q.; Liu, K.; Wang, Z. Y.; Lan, Y. C., et al. Sn-doping stabilizes residual oxygen species to promote intermediate desorption for enhanced CO2 to CO conversion. Sci. China Mater. 2023, 66, 3547–3554.
- 24 Shi, R.; Guo, J. H.; Zhang, X. R.; Waterhouse, G. I. N.; Han, Z. J.; Zhao, Y. X.; Shang, L.; Zhou, C.; Jiang, L.; Zhang, T. R. Efficient wettability-controlled electroreduction of CO2 to CO at Au/C interfaces. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3028.
- 25 Hou, L.; Han, J. Y.; Wang, C.; Zhang, Y. W.; Wang, Y. B.; Bai, Z. M.; Gu, Y. S.; Gao, Y.; Yan, X. Q. Ag nanoparticle embedded Cu nanoporous hybrid arrays for the selective electrocatalytic reduction of CO2 towards ethylene. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2020, 7, 2097–2106.
- 26 Lee, S.; Park, G.; Lee, J. Importance of Ag–Cu Biphasic Boundaries for Selective Electrochemical Reduction of CO2 to Ethanol. ACS Catal. 2017, 7, 8594–8604.
- 27 Zheng, Y. Q.; Zhang, J. W.; Ma, Z. S.; Zhang, G. G.; Zhang, H. F.; Fu, X. W.; Ma, Y. Y.; Liu, F.; Liu, M. C.; Huang, H. W. Seeded Growth of Gold–Copper Janus Nanostructures as a Tandem Catalyst for Efficient Electroreduction of CO2 to C2+ Products. Small 2022, 18, 2201695.
- 28 Li, C. C.; Guo, Z. Y.; Liu, Z. L.; Zhang, T. T.; Shi, H. J.; Cui, J. L.; Zhu, M. H.; Zhang, L.; Li, H.; Li, H. H., et al. Boosting Electrochemical CO2 Reduction via Surface Hydroxylation over Cu-Based Electrocatalysts. ACS Catal. 2023, 13, 16114–16125.
- 29 Woldu, A. R.; Huang, Z. L.; Zhao, P. X.; Hu, L. S.; Astruc, D. Electrochemical CO2 reduction (CO2RR) to multi-carbon products over copper–based catalysts. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2022, 454, 214340.
- 30 Petrovic, B.; Gorbounov, M.; Soltani, S. M. Influence of surface modification on selective CO2 adsorption: A technical review on mechanisms and methods. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2021, 312, 110751.
- 31 Li, F. W.; Thevenon, A.; Rosas-Hernández, A.; Wang, Z. Y.; Li, Y. L.; Gabardo, C. M.; Ozden, A.; Dinh, C. T.; Li, J.; Wang, Y. H., et al. Molecular tuning of CO2 to ethylene conversion. Nature 2019, 577, 509–513.
- 32 Yao, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, D.; Chi, X.; Wang, X.; Zhao, R.; Zhang, H.; Sun, Y., et al. Restraining lattice oxygen of Cu2O by enhanced Cu–O hybridization for selective and stable production of ethylene with CO2 electroreduction. J. Mater. Chem. A 2022, 10, 20914–20923.
- 33 Holder, C. F.; Schaak, R. E. Tutorial on Powder X-ray Diffraction for Characterizing Nanoscale Materials. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 7359–7365.
- 34 Xiang, D.; Li, K. Z.; Miao, K. H.; Long, R.; Xiong, Y. J.; Kang, X. W. Amine-Functionalized Copper Catalysts: Hydrogen Bonding Mediated Electrochemical CO2 Reduction to C2 Products and Superior Rechargeable Zn-CO2 Battery Performance. Acta Phys.-Chim. Sin. 2024, 40, 2308027.




