Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Cover Picture
- Page: 1657
- First Published: 15 June 2023

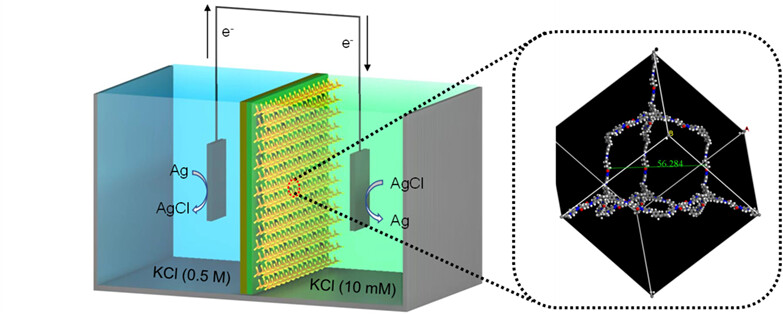
Herein, a single molecule detection technology based on glass nanopore is established to analyze xylan dissolved in ionic liquid. The nanopore detection technology shows the structural difference of heterogenous branched chain and homogeneous straight chain based on the single characteristic current blocking signal and statistical information, providing a research basis for the structural analysis of water insoluble polysaccharides. More details are discussed in the article by He et al. on page 1720—1726.
Inside Cover Picture
Inside Cover Picture
- Page: 1658
- First Published: 15 June 2023

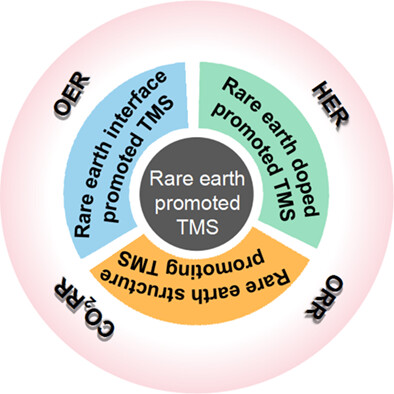
According to the existing forms of rare earth elements, we classify rare earth promoted transition metal sulfides into rare earth doped transition metal sulfides, rare earth interface promoted transition metal sulfides, and rare earth structure promoted transition metal sulfides. We also prospect their applications in OER, HER, ORR, and CO2RR, as well as in other electrocatalytic fields. In today's increasingly serious energy problem, it is of great significance to rationally utilize rare earths to promote the regulation of transition metals, enabling them to achieve more efficient and stable energy storage and conversion. More details are given in the article by Xi et al. on page 1740—1752.
Contents
Breaking Report
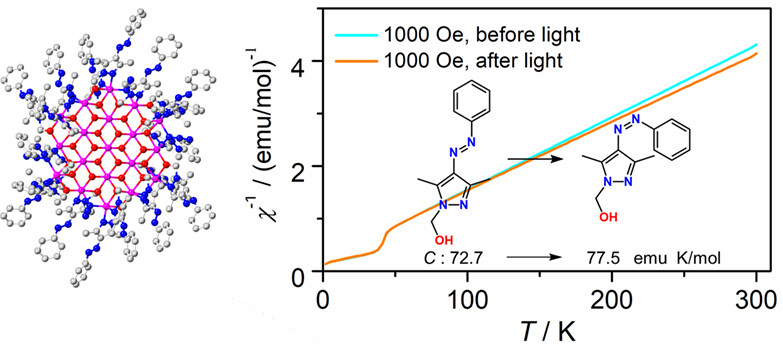
Synthesis, Structure, and Optical-response Magnetic Property of a Heteroarene-azo Functionalized Mn19 Cluster
- Pages: 1667-1672
- First Published: 27 March 2023
Concise Reports
Nickel/Quinim Enabled Asymmetric Carbamoyl-Acylation of Unactivated Alkenes
- Pages: 1673-1678
- First Published: 14 February 2023
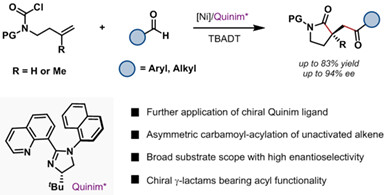
A nickel/photo-cocatalyzed and chiral Quinim ligand promoted asymmetric carbamoyl-acylation of unactivated alkenes tethered to carbamoyl chloride with various aldehydes is reported here. The reaction is featured by broad substrate scope with high enantioselectivity, providing diverse valuable γ-lactam products carrying an acyl transformable functionality. The success application of Quinim ligand in this reaction demonstrates more applicable possibilities in other catalytic asymmetric transformations.
Palladium-Catalyzed Skeletal Reorganization of Cyclobutanones Invoving Successive C—C Bond/C—H Bond Cleavage
- Pages: 1679-1683
- First Published: 22 February 2023
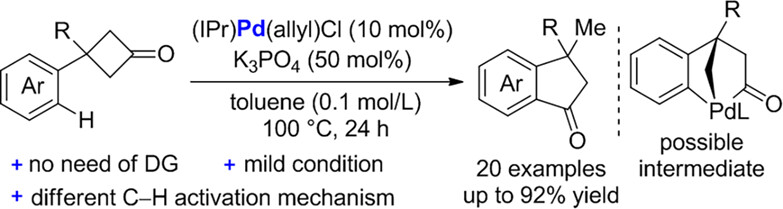
Skeletal Reorganisation of Cyclobutanones: We for the first time demonstrates that Pd-catalyst is also capable of cleaving C(carbonyl)−C bonds of cyclobutanones via oxidative addition. According to Pd-catalyzed condition, the skeletal reorganization of cyclobutanones involving successive cleavage of C(carbonyl)−C bonds and C—H bond cleavage proceeds smoothly to deliver diverse indanones.
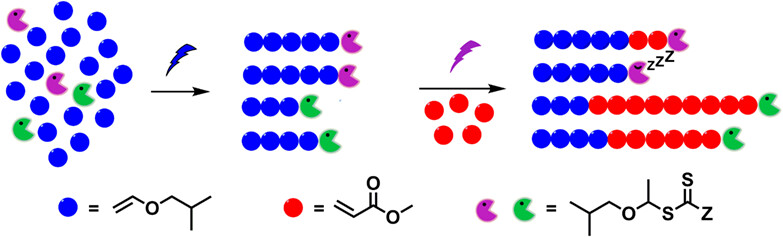
Tuning Polymer Molecular Weight Distribution in Cationic RAFT Polymerization by Mixing Chain Transfer Agents
- Pages: 1684-1690
- First Published: 16 February 2023
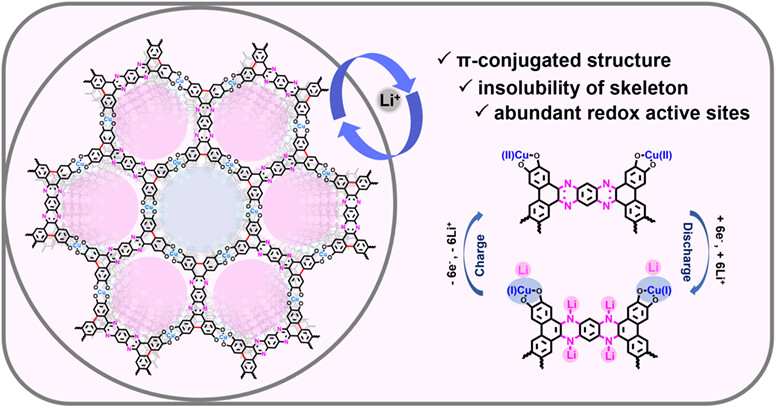
A Pyrazine-Based 2D Conductive Metal-Organic Framework for Efficient Lithium Storage
- Pages: 1691-1696
- First Published: 27 February 2023
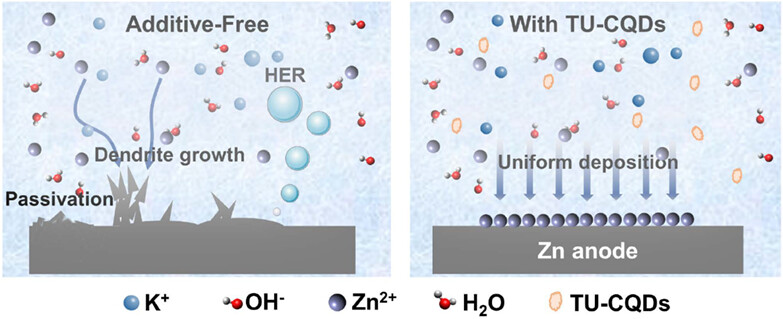
N, S-Doped Carbon Dots as Additive for Suppression of Zinc Dendrites in Alkaline Electrolyte
- Pages: 1697-1704
- First Published: 15 February 2023
Nucleophilic Substitution Polymerization-Induced Emission of 1,3-Dicarbonyl Compounds as a Versatile Approach for Aggregation-Induced Emission Type Non-Traditional Intrinsic Luminescence
- Pages: 1705-1712
- First Published: 16 February 2023
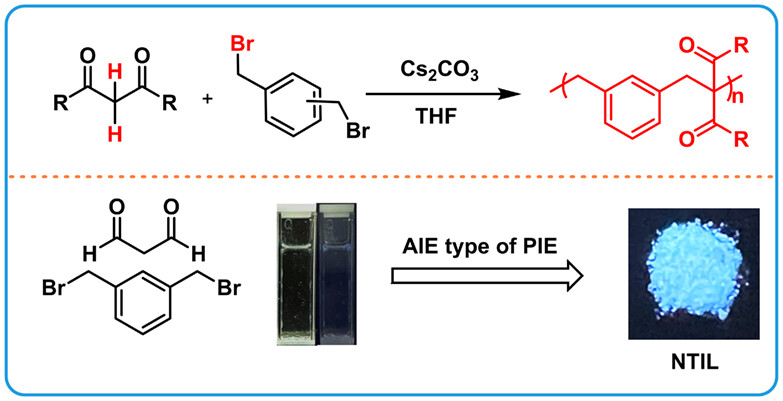
Nucleophilic substitution reaction and 1,3-dicarbonyl compounds have become an emerging research area in organic chemistry. Here, we demonstrate the successful nucleophilic substitution polymerization of 1,3-dicarbonyl compounds, where non-traditional intrinsic luminescent poly(1,3-dicarbonyl)s have been successfully prepared with high yield (up to >99%) under mild conditions.
Flexible Organic Framework-Modified Membranes for Osmotic Energy Harvesting
- Pages: 1713-1719
- First Published: 23 February 2023
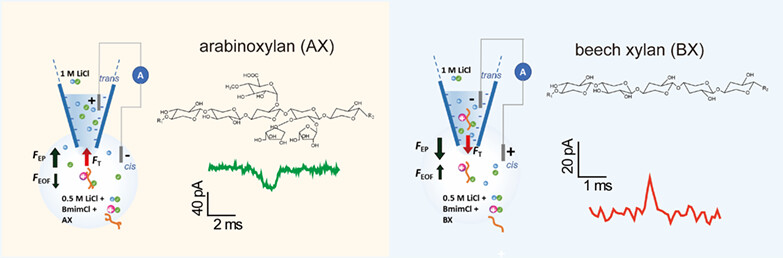
Application of Nanopore Single Molecule Detection Technology in Analysis of Xylan Dissolved in Ionic Liquid
- Pages: 1720-1726
- First Published: 15 March 2023
Hierarchical Self-assembly of G-Quadruplexes Based Hydrogel Consisting of Guanine and Peptide Epitope
- Pages: 1727-1732
- First Published: 17 March 2023
Synthesis of [60]Fullerene-Fused Allylbenzofurans via Palladium-Catalyzed Migration Reaction
- Pages: 1733-1739
- First Published: 19 March 2023
![Synthesis of [60]Fullerene-Fused Allylbenzofurans via Palladium-Catalyzed Migration Reaction†](/cms/asset/ad4260dd-2359-4968-8ab6-0354101d0446/cjoc202300046-toc-0001-m.jpg)
An unprecedented Pd-catalyzed migration reaction of [60]fullerene with allyloxy-tethered aryl iodides is presented for the preparation of rare [60]fullerene-fused allylbenzofurans. The reaction features high chemo- and regio-selectivity. This transformation proceeds via a sequential C—O bond cleavage/allyl-migration/intermolecular cycloaddition cascade process.
Recent Advances
Applications of Rare Earth Promoted Transition Metal Sulfides in Electrocatalysis
- Pages: 1740-1752
- First Published: 03 March 2023
Strategies toward Highly Efficient Monolithic Perovskite/Organic Tandem Solar Cells
- Pages: 1753-1768
- First Published: 15 February 2023
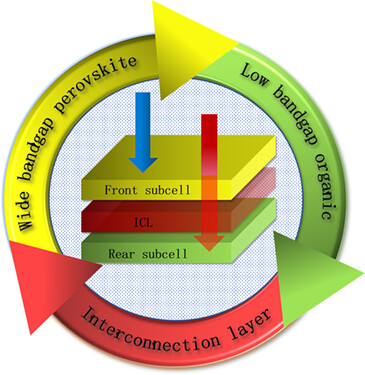
Constructing monolithic tandem solar cells (TSCs) is an effective method to break the Shockley–Queisser (S–Q) radiative efficiency limit for single-junction solar cells. Here, we summarize the current progresses in monolithic perovskite/organic TSCs. The front subcell based on wide bandgap mixed halide perovskites, rear subcell based on low bandgap organic molecules and the interconnection layer (ICL) are discussed, respectively, which aims to open a pathway to realize highly efficient monolithic perovskite/organic tandem device.
Inside Back Cover
Inside Back Cover
- Page: 1771
- First Published: 15 June 2023

This cover picture shows a ligand-controlled, palladium-catalyzed migration reaction of [60]fullerene with allyloxy-tethered aryl iodides. Using 1,2-bis(diphenylphosphino)benzene (DPPBz) as a ligand, the chemoselectivity is switched to synthesize [60]fullerene-fused allylbenzofurans instead of previous spirocyclic derivatives through a sequential C—O bond cleavage/allyl-migration/intermolecular cycloaddition cascade process. Such transformation provides a unique and efficient route to rare [60]fullerene-fused benzofurans. More details are discussed in the article by Liu et al. on page 1733—1739.
Back Cover
Back Cover
- Page: 1772
- First Published: 15 June 2023

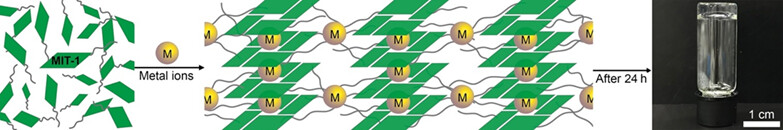
This work developed a G-quadruplexes-based hydrogel consisting of guanine and peptide epitope to form a supramolecular hydrogel in the presence of metal cations. Using the metal ion-responsive peptide epitope from the ion channel to replace sugar motif at N9 position of guanosine results in a novel nucleopeptide. The results show that the gelation time, the diameter of nanofibers, the anisotropic property, and the mechanical property of the nucleopeptide hydrogel can be simply controlled using metal cations. This work may provide a strategy for gluing pre-existing fibers to form a hydrogel with tailored structures. More details are discussed in the article by Wang et al. on page 1727—1732.