Palladium-Catalyzed Skeletal Reorganization of Cyclobutanones Invoving Successive C—C Bond/C—H Bond Cleavage
Ruirui Li
State Key Laboratory and Institute of Elemento-Organic Chemistry, College of Chemistry, Nankai University, Tianjin, 300071 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorXiaonan Shi
State Key Laboratory and Institute of Elemento-Organic Chemistry, College of Chemistry, Nankai University, Tianjin, 300071 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Dongbing Zhao
State Key Laboratory and Institute of Elemento-Organic Chemistry, College of Chemistry, Nankai University, Tianjin, 300071 China
E-mail: [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorRuirui Li
State Key Laboratory and Institute of Elemento-Organic Chemistry, College of Chemistry, Nankai University, Tianjin, 300071 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorXiaonan Shi
State Key Laboratory and Institute of Elemento-Organic Chemistry, College of Chemistry, Nankai University, Tianjin, 300071 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Dongbing Zhao
State Key Laboratory and Institute of Elemento-Organic Chemistry, College of Chemistry, Nankai University, Tianjin, 300071 China
E-mail: [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorComprehensive Summary
The utilization of cyclobutanones as the synthon in transition metal catalysis has been made great success. Because C(carbonyl)−C bond of cyclobutanones can be cleaved through strain release. Despite those advancements, the main catalysts in literature are Rh catalysts or Ni catalysts and the reaction with C—H bond is still underdeveloped. Herein, we realized the first palladium-catalyzed skeletal reorganization of cyclobutanones involving successive cleavage of C(carbonyl)−C bonds and C—H bond cleavage, which constitutes an rapid access to diverse indanones. In contrast to the previous Rh-catalytic system, the Pd-catalytic system herein involves different mechanism and features several advantages: 1) no need of directing group to facilitate the C(carbonyl)−C bond cleavage; 2) much milder reaction condition and 3) simplified work-up.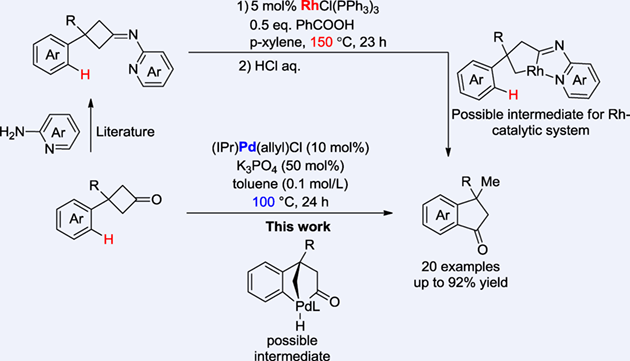
Supporting Information
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| cjoc202300044-sup-0001-supinfo.pdfPDF document, 3 MB |
Appendix S1: Suppporting Information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1For selected reviews, see: (a) Seiser, T.; Saget, T.; Tran, D. N.; Cramer, N. Cyclobutanes in Catalysis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 7740–7752; (b) Fumagalli, G.; Stanton, S.; Bower, J. F. Recent Methodologies That Exploit C–C Single-Bond Cleavage of Strained Ring Systems by Transition Metal Complexes. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 9404–9432; (c) Souillart, L.; Cramer, N. Catalytic C–C Bond Activations via Oxidative Addition to Transition Metals. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 9410–9464; (d) Chen, J.; Zhou, Q.; Fang, H.; Lu, P. Dancing on Ropes−Enantioselective Functionalization of Preformed Four-Membered Carbocycles. Chin. J. Chem. 2022, 40, 1346–1358.
- 2For selected reviews, see: (a) Murakami, M.; Makino, M.; Ashida, S.; Matsuda, T. Construction of Carbon Frameworks through β-Carbon Elimination Mediated by Transition Metals. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2006, 79, 1315–1321; (b) Sietmann, J.; Wiest, J. M. Enantioselective Desymmetrization of Cyclobutanones: A Speedway to Molecular Complexity. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 6964–6974; (c) Deng, L.; Dong, G. Carbon–Carbon Bond Activation of Ketones. Trends Chem. 2020, 2, 183–198; (d) Xue, Y.; Dong, G. Deconstructive Synthesis of Bridged and Fused Rings via Transition-Metal-Catalyzed “Cut-and- Sew” Reactions of Benzocyclobutenones and Cyclobutanones. Acc. Chem. Res. 2022, 55, 2341–2354.
- 3(a) Murakami, M.; Itahashi, T.; Ito, Y. Catalyzed Intramolecular Olefin Insertion into a Carbon−Carbon Single Bond. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 13976–13977; (b) Souillart, L.; Cramer, N. Highly Enantioselective Rhodium(I)-Catalyzed Carbonyl Carboacylations Initiated by C–C Bond Activation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 9640–9644; (c) Souillart, L.; Parker, E.; Cramer, N. Highly enantioselective rhodium(I)-catalyzed activation of enantiotopic cyclobutanone C–C bonds. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 3001–3005; (d) Parker, E.; Cramer, N. Asymmetric Rhodium(I)-Catalyzed C−C Activations with Zwitterionic Bis-phospholane Ligands. Organometallics 2014, 33, 780–787; (e) Deng, L.; Fu, Y.; Lee, S. Y.; Wang, C.; Liu, P.; Dong, G. Kinetic Resolution via Rh-Catalyzed C-C Activation of Cyclobutanones at Room Temperature. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 16260–16265; (f) Hou, S.-H.; Yu, X.; Zhang, R.; Deng, L.; Zhang, M.; Prichina, A. Y.; Dong, G. Enantioselective Type II Cycloaddition of Alkynes via C–C Activation of Cyclobutanones: Rapid and Asymmetric Construction of [3.3.1] Bridged Bicycles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 13180–13189; (g) Yu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Dong, G. Catalytic Enantioselective Synthesis of γ-Lactams with β-Quaternary Centers via Merging of C–C Activation and Sulfonyl Radical Migration. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 9222–9228.
- 4(a) Murakami, M.; Ashida, S.; Matsuda, T. Nickel-Catalyzed Intermolecular Alkyne Insertion into Cyclobutanones. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 6932–6933; (b) Murakami, M.; Ashida, S.; Matsuda, T. Eight-membered ring construction by [4+2+2] annulation involving beta-carbon elimination. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 2166–2167; (c) Liu, L.; Ishida, N.; Murakami, M. Atom- and Step-Economical Pathway to Chiral Benzobicyclo[2.2.2]octenones through Carbon–Carbon Bond Cleavage. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 2485–2488; (d) Zhou, X.; Dong, G. Nickel-Catalyzed Chemo- and Enantioselective Coupling between Cyclobutanones and Allenes: Rapid Synthesis of [3.2.2] Bicycles. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 15091–15095.
- 5 Matsuda, T.; Yuihara, I. A rhodium(i)-catalysed formal intramolecular C–C/C–H bond metathesis. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 7393–7396.
- 6(a) Li, R.; Li, B.; Zhang, H.; Ju, C.-W.; Qin, Y.; Xue, X.-S.; Zhao, D. A ring expansion strategy towards diverse azaheterocycles. Nat. Chem. 2021, 13, 1006–1016; (b) Okumura, S.; Sun, F.; Ishida, N.; Murakami, M. Palladium-Catalyzed Intermolecular Exchange between C−C and C−Si σ-Bonds. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 12414–12417.
- 7For selected reviews see: (a) He, J.; Wasa, M.; Chan, K. S. L.; Shao, Q.; Yu, J.-Q. Palladium-Catalyzed Transformations of Alkyl C–H Bonds. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 8754–8786; (b) He, C.; Whitehurst, W. G.; Gaunt, M. J. Palladium-Catalyzed C(sp3)–H Bond Functionalization of Aliphatic Amines. Chem 2019, 5, 1031–1058; (c) Shao, Q.; Wu, K.; Zhuang, Z.; Qian, S.; Yu, J.-Q. From Pd(OAc)2 to Chiral Catalysts: The Discovery and Development of Bifunctional Mono-N-Protected Amino Acid Ligands for Diverse C–H Functionalization Reactions. Acc. Chem. Res. 2020, 53, 833–851; (d) Lucas, E. L.; Lam, N. Y. S.; Zhuang, Z.; Chan, H. S. S.; Strassfeld, D. A.; Yu, J.-Q. Palladium-Catalyzed Enantioselective β-C(sp3)–H Activation Reactions of Aliphatic Acids: A Retrosynthetic Surrogate for Enolate Alkylation and Conjugate Addition. Acc. Chem. Res. 2022, 55, 537–550.
- 8(a) Matsuda, T.; Shigeno, M.; Makino, M.; Murakami, M. Enantioselective C−C Bond Cleavage Creating Chiral Quaternary Carbon Centers. Org. Lett. 2006, 8, 3379–3381; (b) Chen, P.-H.; Sieber, J.; Senanayake, C. H.; Dong, G. Rh-catalyzed reagent-free ring expansion of cyclobutenones and benzocyclobutenones. Chem. Sci. 2015, 6, 5440–5445; (c) Xia, Y.; Wang, J.; Dong, G. Distal-Bond-Selective C−C Activation of Ring-Fused Cyclopentanones: An Efficient Access to Spiroindanones. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 2376–2380; (d) Sun, F.-N.; Yang, W.-C.; Chen, X.-B.; Sun, Y-L.; Cao, J.; Xua, Z.; Xu, L.-W. Enantioselective palladium/copper-catalyzed C-C σ-bond activation synergized with Sonogashira-type C(sp3)-C(sp) cross-coupling alkynylation. Chem. Sci. 2019, 10, 7579–7583; (e) Sun, Y.-L.; Wang, X.-B.; Sun, F.-N.; Chen, Q.-Q.; Cao, J.; Xu, Z.; Xu, L.-W. Enantioselective Cross-Exchange between C−I and C−C σ Bonds. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 6747–6751; (f) Cao, J.; Chen, L.; Sun, F.-N.; Sun, Y.-L.; Jiang, K.-Z.; Yang, K.-F.; Xu, Z.; Xu, L.-W. Pd-Catalyzed Enantioselective Ring Opening/Cross-Coupling and Cyclopropanation of Cyclobutanones. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 897–901; (g) Ding, D.; Dong, H.; Wang, C. Nickel-Catalyzed Asymmetric Domino Ring Opening/Cross-Coupling Reaction of Cyclobutanones via a Reductive Strategy. iScience 2020, 23, 101017.
- 9When we are submitting this manuscript, a similar study has been reported, see: Ano, Y.; Takahashi, D.; Yamada, Y.; Chatani, N. Palladium-Catalyzed Skeletal Rearrangement of Cyclobutanones via C−H and C−C Bond Cleavage. ACS Catal. 2023, 13, 2234–2239.




