Application of Nanopore Single Molecule Detection Technology in Analysis of Xylan Dissolved in Ionic Liquid†
Wanyi Xie
Chongqing Key Laboratory of Multi-scale Manufacturing Technology, Chongqing Institute of Green and Intelligent Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chongqing, 400714 China
Chongqing School, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chongqing, 400714 China
Search for more papers by this authorShaoxi Fang
Chongqing Key Laboratory of Multi-scale Manufacturing Technology, Chongqing Institute of Green and Intelligent Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chongqing, 400714 China
Search for more papers by this authorBohua Yin
Chongqing Key Laboratory of Multi-scale Manufacturing Technology, Chongqing Institute of Green and Intelligent Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chongqing, 400714 China
Changchun University of Science and Technology, Changchun, Jilin, 130022 China
Search for more papers by this authorRong Tian
Chongqing Key Laboratory of Multi-scale Manufacturing Technology, Chongqing Institute of Green and Intelligent Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chongqing, 400714 China
Chongqing School, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chongqing, 400714 China
Search for more papers by this authorLiyuan Liang
Chongqing Key Laboratory of Multi-scale Manufacturing Technology, Chongqing Institute of Green and Intelligent Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chongqing, 400714 China
Chongqing School, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chongqing, 400714 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Shixuan He
Chongqing Key Laboratory of Multi-scale Manufacturing Technology, Chongqing Institute of Green and Intelligent Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chongqing, 400714 China
Chongqing School, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chongqing, 400714 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Deqiang Wang
Chongqing Key Laboratory of Multi-scale Manufacturing Technology, Chongqing Institute of Green and Intelligent Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chongqing, 400714 China
Chongqing School, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chongqing, 400714 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorWanyi Xie
Chongqing Key Laboratory of Multi-scale Manufacturing Technology, Chongqing Institute of Green and Intelligent Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chongqing, 400714 China
Chongqing School, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chongqing, 400714 China
Search for more papers by this authorShaoxi Fang
Chongqing Key Laboratory of Multi-scale Manufacturing Technology, Chongqing Institute of Green and Intelligent Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chongqing, 400714 China
Search for more papers by this authorBohua Yin
Chongqing Key Laboratory of Multi-scale Manufacturing Technology, Chongqing Institute of Green and Intelligent Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chongqing, 400714 China
Changchun University of Science and Technology, Changchun, Jilin, 130022 China
Search for more papers by this authorRong Tian
Chongqing Key Laboratory of Multi-scale Manufacturing Technology, Chongqing Institute of Green and Intelligent Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chongqing, 400714 China
Chongqing School, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chongqing, 400714 China
Search for more papers by this authorLiyuan Liang
Chongqing Key Laboratory of Multi-scale Manufacturing Technology, Chongqing Institute of Green and Intelligent Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chongqing, 400714 China
Chongqing School, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chongqing, 400714 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Shixuan He
Chongqing Key Laboratory of Multi-scale Manufacturing Technology, Chongqing Institute of Green and Intelligent Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chongqing, 400714 China
Chongqing School, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chongqing, 400714 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Deqiang Wang
Chongqing Key Laboratory of Multi-scale Manufacturing Technology, Chongqing Institute of Green and Intelligent Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chongqing, 400714 China
Chongqing School, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chongqing, 400714 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorDedicated to the Special Issue of Single-Molecule Measurement and Imaging.
Comprehensive Summary
Xylan is the most abundant hemicellulose in nature. As a new type of green organic solvent, ionic liquid shows good preservation ability for the functional groups of hemicellulose. In this paper, a single molecule detection technology based on glass nanopore was established to analyze xylan dissolved in ionic liquid. Arabino-xylan (AX) and beech xylan (BX) are respectively taken as the representatives of heterogeneous xylan and homogeneous xylan. Firstly, unmodified glass nanopore was used to detect the dissolved xylan in ionic liquid, and then poly(ethylene imine) (PEI) was used to modify the nanopore to change the surface charge in the nanopore and further enhance the interaction between the nanopore and the xylan molecule. It was found that before and after nanopore modification, at negative voltage and low positive voltage, AX didn't generate current blocking signal. On the contrary, BX didn't generate current blocking signal at positive voltage. This phenomenon may be due to the current disturbance driven by electrophoresis and electroosmosis of xylan molecules with weak negative charge. After statistics analysis, the current blocking signal of AX showed that the modified nanopore showed multiple peaks. It indicates that heterogeneous xylan and PEI modified nanopore had stronger interaction. The results show that the nanopore detection technology can show the structural difference of heterogenous branched chain and homogeneous straight chain based on the single characteristic current blocking signal and statistical information, providing a research basis for the structural analysis of water insoluble polysaccharides.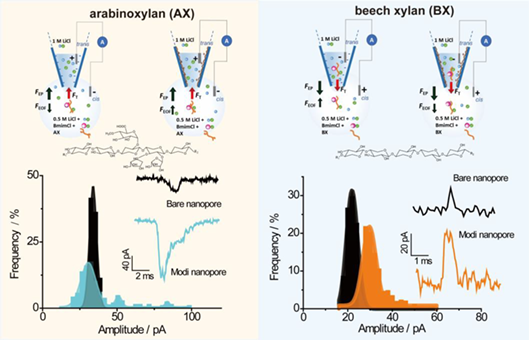
Supporting Information
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| cjoc202300031-sup-0001-supinfo.pdfPDF document, 794.1 KB |
Appendix S1: Supporting Information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1 Hu, L.; Peng, H.; Zhang, Y.; Xia, Q.; He, H.; Ruan, R.; Liu, Y.; Liu, A. Insight into the Interaction between Arabinoxylan and Imidazolium Acetate-Based Ionic Liquids. Carbohyd. Polym. 2020, 231, 115699.
- 2 Kulkarni, N.; Shendye, A.; Rao, M. Molecular and Biotechnological Aspects of Xylanases. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 1999, 23, 411–456.
- 3 Cao, L.; Zhang, R.; Zhou, J.; Huang, Z. Biotechnological Aspects of Salt-Tolerant Xylanases: A Review. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 8610–8624.
- 4 Savitha Prashanth, M. R.; Shruthi, R. R.; Muralikrishna, G. Immunomodulatory Activity of Purified Arabinoxylans from Finger Millet (Eleusine coracana, v. Indaf 15) bran. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 52, 6049–6054.
- 5 Bijalwan, V.; Ali, U.; Kesarwani, A. K.; Yadav, K.; Mazumder, K. Hydroxycinnamic Acid Bound Arabinoxylans from Millet Brans-Structural Features and Antioxidant Activity. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 88, 296–305.
- 6 Liu, X.; Lin, Q.; Yan, Y.; Peng, F.; Sun, R.; Ren, J. Hemicellulose from Plant Biomass in Medical and Pharmaceutical Application: A Critical Review. Curr. Med. Chem. 2019, 26, 2430–2455.
- 7 Urtiga, S.; Marcelino, H. R.; Egito, E.; Oliveira, E. E. Xylan in Drug Delivery: A Review of Its Engineered Structures and Biomedical Applications. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2020, 151, 199–208.
- 8 Cai, Y.; Zhang, B.; Liang, L.; Wang, S.; Zhang, L.; Wang, L.; Cui, H.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, D. A Solid-State Nanopore-Based Single-Molecule Approach for Label-Free Characterization of Plant Polysaccharides. Plant Commun. 2021, 2, 100106.
- 9 Zhang, S.; Cao, Z.; Fan, P.; Wang, Y., Jia, W.; Wang, L.; Wang, K.; Liu, Y.; Du, X.; Hu, C.; Zhang, P.; Chem, H.-Y.; Huang, S. A Nanopore-Based Saccharide Sensor. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202203769
- 10 Feng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ying, C.; Wang. D.; Du, C. Nanopore-Based Fourth-Generation DNA Sequencing Technology. Genom. Proteom. Bioinf. 2015, 13, 4–16.
- 11 Ying, Y.-L.; Hu, Z.-L.; Zhang, S.; Qing Y., Fragasso, A.; Maglia, G.; Meller, A.; Bayley, H.; Dekker, C.; Long, Y.-T. Nanopore-Based Technologies Beyond DNA Sequencing. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2022, 17, 1136–1146.
- 12 Lu, G.; Lin, N.; Chen, Z.; Jiang, W.; Hu, J.-J.; Xia, F.; Lou X. Nanopores/Nanochannels Based on Electrical and Optical Dual Signal Response for Application in Biological Detection. Chin. J. Chem. 2023, 41, https://doi.org/10.1002/cjoc.202200718.
- 13 Cui, M.; Ge, Y.; Zhuge, X.; Zhou, X.; Xi, D.; Zhang, S. Recent Advances in Nanopore Sensing. Chin. J. Chem. 2021, 39, 2035–2043.
- 14 Ding, X; Wu, Z.-Q.; Li, Z.-Q.; Xia, X.-H. Electric Field Driven Surface Ion Transport in Hydrophobic Nanopores. Chin. J. Chem. 2021, 39, 1511–1516.
- 15 Hagan, J. T.; Sheetz, B. S.; Bandara, Y. M. N. D. Y.; Karawdeniya, B. I.; Morris, M. A.; Chevalier, R. B.; Dwyer, J. R. Chemically Tailoring Nanopores for Single-Molecule Sensing and Glycomics. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2020, 412, 6639–6654.
- 16 Karawdeniya, B. I.; Bandara, Y. M. N. D. Y.; Nichols, J. W.; Chevalier, R. B.; Dwyer, J. R. Surveying Silicon Nitride Nanopores for Glycomics and Heparin Quality Assurance. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3278.
- 17 Rivas, F.; DeAngelis, P. L.; Rahbar, E.; Hall, A. R. Optimizing the Sensitivity and Resolution of Hyaluronan Analysis with Solid-State Nanopores. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 4469.
- 18 Rivas, F.; Zahid, O. K.; Reesink, H. L.; Peal, B.; Nixon, A. J.; DeAngelis, P. L.; Skardal, A.; Rahbar E.; Hall, A. R. Label-Free Analysis of Physiological Hyaluronan Size Distribution with a Solid-State Nanopore Sensor. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1037.
- 19 Ma, T.; Balanzat, E.; Janot, J.-M.; Balme, S. Single Conical Track- Etched Nanopore for A Free-Label Detection of OSCS Contaminants in Heparin. Biosens. Bioelectronics. 2019, 137, 207–212.
- 20 Im, J.; Lindsay, S.; Wang, X.; Zhang, P. Single Molecule Identification and Quantification of Glycosaminoglycans Using Solid-State Nanopores. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 6308–6318.
- 21 Ma, T.; Janot, J.-M.; Balme, S. Dynamics of Long Hyaluronic Acid Chains Through Conical Nanochannels for Characterizing Enzyme Reactions in Confined Spaces. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 7231.
- 22 Xia, K.; Hangan, J. T.; Fu, L.; Sheetz, B. S.; Bhattacharya, S.; Zhang, F.; Dwyer, J. R.; Linhardt, R. J. Synthetic Heparan Sulfate Standards and Machine Learning Facilitate the Development of Solid-State Nanopore Analysis. PNAS 2021, 118, e2022806118.
- 23 lv, B. The Studies on the Solubility and Dissolution Mechanism of Cellulose and Xylan in Ionic Liquids. Ph.D. Dissertation, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou, 2016 (in Chinese).
- 24 Banerjee, P.N.; Pranovich, A.; Dax, D.; Willför, S. Non-Cellulosic Heteropolysaccharides from Sugarcane Bagasse-Sequential Extraction with Pressurized Hot Water and Alkaline Peroxide at Different Temperatures. Bioresource Technol. 2014, 155, 446–450.
- 25 Jaafar, Z.; Mazeau, K.; Boissière, A.; Gall, S. L.; Villares, A.; Vigouroux, J.; Beury, N.; Moreau, C.; Lahaye, M.; Cathala, B. Meaning of Xylan Acetylation on Xylan-Cellulose Interactions: A Quartz Crystal Microbalance with Dissipation (QCM-D) and Molecular Dynamic Study. Carbohyd. Polym. 2019, 226, 115315.
- 26 Swatloski, R. P.; Spear, S. K.; Holbrey, J. D.; Rogers, R. D. Dissolution of Cellose with Ionic Liquids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 4974–4975.
- 27 Fukaya, Y.; Sugimoto, A.; Ohno, H. Superior Solubility of Polysaccharides in Low Viscosity, Polar, and Halogen-Free 1,3-Dialkylimidazolium Formats. Biomacromolecules 2006, 7, 3295–3297.
- 28 Kilpeläinen, I.; Xie, H.; King, A.; Granstrom, M.; Heikkinen, S.; Dimitris S. Argyropoulos, Dissolution of Wood in Ionic Liquids. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 9142–9148.
- 29 Zhu, S.; Wu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yu, Z.; Wang, C.; Jin, S.; Ding, Y.; Wu, G. Dissolution of Cellulose with Ionic Liquids and Its Application: A Mini-Review. Green Chem. 2006, 8, 325–327.
- 30 Sha, J.; Si, W.; Xu, W.; Zou, Y.; Chen, Y. Glass Capillary Nanopore for Single Molecule Detection. Sci. China Tech. Sci. 2015, 58, 803–812.
- 31 Yu, R.-J.; Ying, Y.-L.; Gao, R.; Long, Y.-T. Confined Nanopipette Sensing: From Single Molecules, Single Nanoparticles, to Single Cells. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 2–11.
- 32 Gao, R.; Lin, Y.; Ying, Y.-L.; Hu, Y.-X.; Xu, S.-W.; Ruan, L.-Q.; Yu, R.-J.; Li, Y.-J.; Li, H.-W.; Cui, L.-F.; Long, Y.-T. Wireless Nanopore Electrodes for Analysis of Single Entities. Nat. Protoc. 2019, 14, 2015–2035
- 33 Yan, H.; Zhou, D.; Shi, B.; Zhang, Z.; Tian, H.; Yu, L.; Wang, Y.; Guan, X.; Wang, Z.; Wang, D. Slowing Down DNA Translocation Velocity Using a LiCl Salt Gradient and Nanofiber Mesh. Eur. Biophys. J. 2019, 48, 261–266.
- 34 Wanunu, M.; Morrison, W.; Rabin, Y.; Groberg, A. Y.; Meller, A. Electrostatic Focusing of Unlabelled DNA into Nanoscale Pores Using a Salt Gradient. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2010, 5, 160–165.
- 35 Laohakunakorn, N.; Thacker, V. V.; Muthukumar, M.; Keyser, U. F. Electroosmotic Flow Reversal Outside Glass Nanopores. Nano Lett. 2015, 15, 695–702.
- 36 Bell, N. A. W.; Muthukumar, M.; Keyser, U. F. Translocation frequency of double-stranded DNA through a solid-state nanopore. Phys. Rev. E 2016, 93, 022401.
- 37 Chen, K.; Juhasz, M.; Gularek, F.; Weinhold, E.; Tian, Y.; Keyser, U. F.; Bell, N. A. W. Ionic Current-Based Mapping of Short Sequence Motifs in Single DNA Molecules Using Solid-State Nanopores. Nano. Lett. 2017, 17, 5199–5205.
- 38 Amara, M.; Kerdjoudj, H. Modification of the Cation Exchange Resin Properties by Impregnation in Polyethyleneimine Solutions Application to the Separation of Metallic Ions. Talanta 2003, 60, 991–1001.
- 39 Liu, S.; Dong, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Xie, X.; Ji, T.; Yin, X.; Yin, X.; Liu, Y.; Liang, Z.; Momotenko, D.; Liang, D.; Girault, H. H.; Shao, Y. Studies of Ionic Current Rectification Using Polyethyleneimines Coated Glass Nanopipettes. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 556–55573.
- 40 Shi, W.; Sa, N.; Thakar, R.; Baker, L. A. Nanopipette delivery: influence of surface charge. Analyst 2015, 140, 4835–4842.
- 41 Qiu, Y.; Vlassiouk, I.; Chen, Y.; Siwy, Z. S. Direction Dependence of Resistive-Pulse Amplitude in Conically Shaped Mesopores. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 4917–4925.




