Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Bone Tumor Suppression in Rabbits by Hyperthermia below the Clinical Safety Limit Using Aligned Magnetic Bone Cement (Small 3/2022)
- First Published: 20 January 2022

Bone Tumor Suppression
Magnetic bone cement incorporating magnetically soft zinc ferrite nanoparticles and aligned in a direct current magnetic field realized exceptionally high heating power in live animals under clinically safe field parameters for hyperthermia. Suppression of osteosarcoma in rabbits by hyperthermia substantially enhances survival rate. More details can be found in article number 2104626 by Shuli He, Qinggang Ge, Yang Lv, Hao Zeng, and co-workers.
Inside Front Cover
Intaglio Contact Printing of Versatile Carbon Nanotube Composites and Its Applications for Miniaturizing High-Performance Devices (Small 3/2022)
- First Published: 20 January 2022

Device Miniaturization
Intaglio contact printing enables the realization of highly precise carbon nanotube (CNT) network patterns exhibiting multi-functionalities without restrictions on the substrate. In article number 2106174, Soonmin Seo, Yoon-Kyu Song, Ju-Hyung Kim, and co-workers present this method for the fabrication and miniaturization of high-performance devices, including flexible fringe-effect capacitive sensors.
Back Cover
3D Carbiyne Nanospheres Boosting Excellent Lithium and Sodium Storage Performance (Small 3/2022)
- First Published: 20 January 2022

3D Carbon Electrodes
Three-dimensional spirobifluorene-based carbiyne nanospheres (SBFCY-NSs) are prepared by Jinchong Xiao, Jianjiang He, Changshui Huang, and co-workers in article number 2106328. The rationally designed chemical structure contributes to the formation of an ion diffusion pathway protected by a robust solid electrolyte interface film in a lithium ion battery.
Masthead
Reviews
Progress in Solid Polymer Electrolytes for Lithium-Ion Batteries and Beyond
- First Published: 28 September 2021
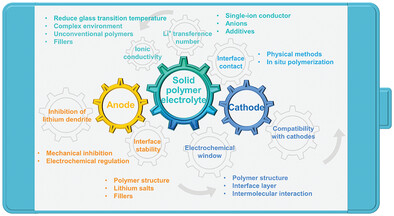
The underlying mechanisms to improve the poor ionic conductivity, low Li+ transference number, poor electrode/electrolyte interface contact, narrow electrochemical oxidation window, and poor long-term stability of the Li metal for solid-state polymer electrolytes (SPEs) are discussed systematically, and strategies for SPEs in safe, high-performance lithium-ion batteries are proposed.
Luminescent Covalent Organic Frameworks for Biosensing and Bioimaging Applications
- First Published: 03 October 2021
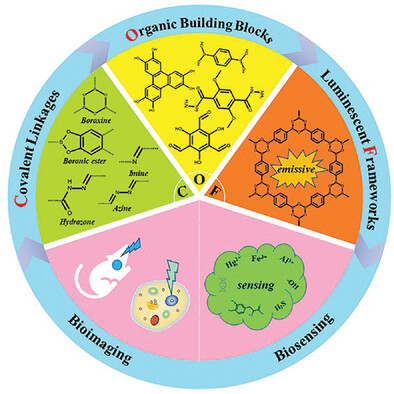
The synthetic chemistry of luminescent covalent organic frameworks (LCOFs) highlights chemical linkages for concreting the monomers, affecting emission and being responsive sites. Their structure manipulations are conducive to brightening LCOFs. The responsive and bright LCOFs can be utilized in biosensing and bioimaging, respectively. Opportunities and challenges of the development of LCOFs come together from chemistry, physics to the applications.
Core-Shell Structured Micro-Nanomotors: Construction, Shell Functionalization, Applications, and Perspectives
- First Published: 05 October 2021
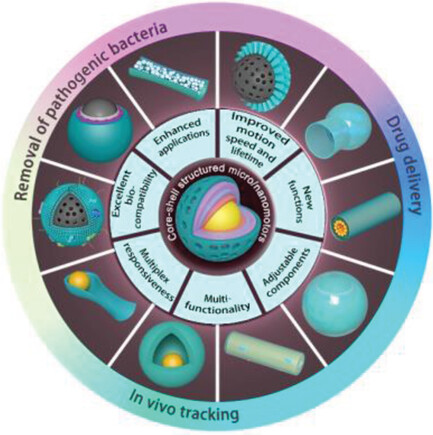
Core-shell structured micro-nanomotor (MNM) systems have attracted significant attention in various important fields, especially drug delivery, removal of pathogenic bacteria, and in vivo tracking. A comprehensive review is provided on the newly emerging synthetic approaches, shell functionalization, applications of core-shell structured MNMs. In addition, future research directions and challenges in terms of synthesis, functions, propulsions, and applications are discussed.
Electronic Structure Regulation of Single-Atom Catalysts for Electrochemical Oxygen Reduction to H2O2
- First Published: 02 November 2021
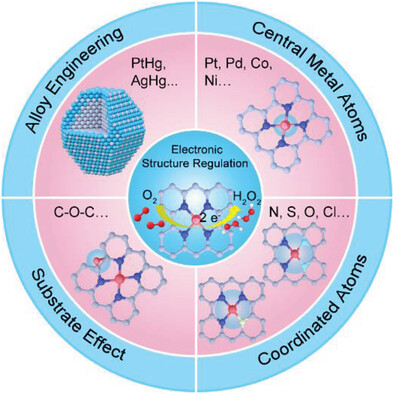
In this review, the recent advances regarding the strategies for regulating the electronic structure of single-atom catalysts for 2-electron oxygen reduction reaction, including the altering of the central metal atoms, the regulation of the coordinated atoms, substrate effect, and alloy engineering, are summarized.
Research Articles
Bone Tumor Suppression in Rabbits by Hyperthermia below the Clinical Safety Limit Using Aligned Magnetic Bone Cement
- First Published: 04 December 2021
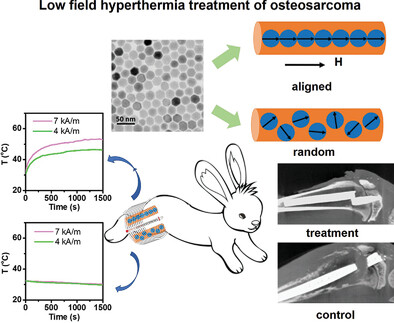
A record high specific loss power of 327 W g-1metal and intrinsic loss power of 47 nHm2 kg-1 are achieved under an alternating current field of 4 kA m-1 and 430 kHz, under the clinical safety limit, in magnetic bone cement incorporating a low concentration of field-aligned Zn0.3Fe2.7O4 nanoparticles. Hyperthermia suppression of osteosarcoma and significant enhancement of survival rate in rabbits are demonstrated.
Intaglio Contact Printing of Versatile Carbon Nanotube Composites and Its Applications for Miniaturizing High-Performance Devices
- First Published: 08 December 2021
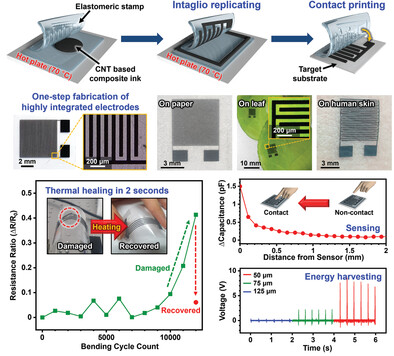
An intaglio contact printing method is presented for realizing highly integrated electrodes based on carbon nanotube composites without restrictions on the substrate. This method facilitates the printing of high-resolution patterned electrodes onto various substrates in a controlled manner. The printed electrodes exhibit high durability and thermal healing abilities. Miniaturized sensing and energy-harvesting applications are also demonstrated with high performances.
3D Carbiyne Nanospheres Boosting Excellent Lithium and Sodium Storage Performance
- First Published: 06 December 2021
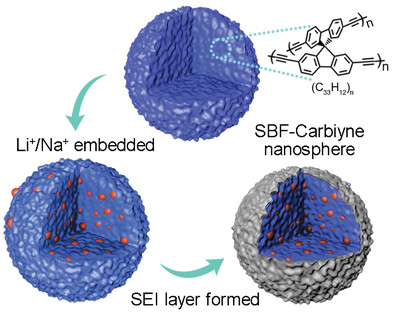
SBF-Carbiyne nanosphere (SBFCY-NS) is a synthesized solid carbon nanosphere containing abundant micropores. Enough space inside of sphere can realize efficient Li+/Na+ storage, suitable micropores enable the SEI layer only formed surround the surface of nanosphere, ending up with boosting Li+/Na+ storage performance.
Highly Conductive Strong Healable Nanocomposites via Diels–Alder Reaction and Filler-Polymer Covalent Bifunctionalization
- First Published: 10 November 2021

A highly conductive strong healable nanocomposite is realized by designing multiple covalent bonding between conductive filler and polymer matrix. This together with in situ formed Ag nanosatellite particles provide the nanocomposite with superior conductivity, high mechanical strength, and healability resulting in figure of merit of 1.78 T Pa S m−1, which is orders of magnitude higher than those reported in literature.
A Tumor-Targeting Metal-Organic Nanoparticle Constructed by Dynamic Combinatorial Chemistry toward Accurately Redressing Carcinogenic Wnt Cascade
- First Published: 05 November 2021
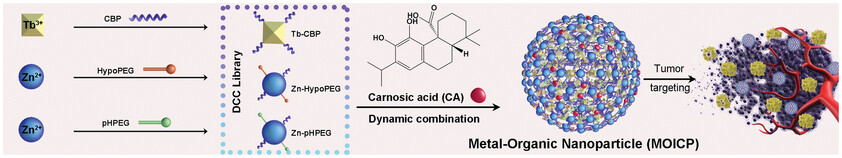
A “one-pot” self-assembled strategy based on dynamic combinatorial chemistry principle is designed to construct a tumor-targeting metal-organic nanoparticle (MOICP) through a spontaneous co-assembling among three metal-organic coordination polymers tuned by a Wnt-inhibitor carnosic acid. Responding to the acidic and hypoxic tumor microenvironment, MOICP presents an optimized tumor-preferential accumulation and the satisfactory biosafety.
Probing Insulin Sensitivity with Metabolically Competent Human Stem Cell-Derived White Adipose Tissue Microphysiological Systems
- First Published: 10 November 2021
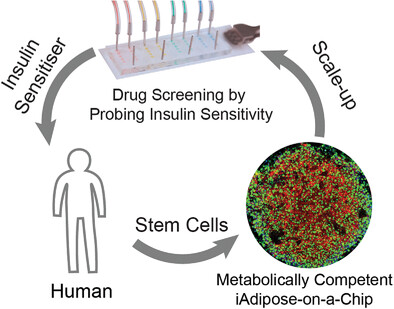
This study uses human stem cells to derive metabolically functional 3D adipose tissue in a microphysiological system. Through concomitant optimization, the adipose system shows mostly unilocular and significantly larger lipid droplets, increased insulin responsiveness of glucose uptake, fatty acid uptake, and suppressing of stimulated lipolysis compared to 2D culture, providing a good dynamic range to identify insulin sensitizers and desensitizers.
Noble Metal (Pt, Rh, Pd, Ir) Doped Ru/CNT Ultra-Small Alloy for Acidic Hydrogen Evolution at High Current Density
- First Published: 21 November 2021
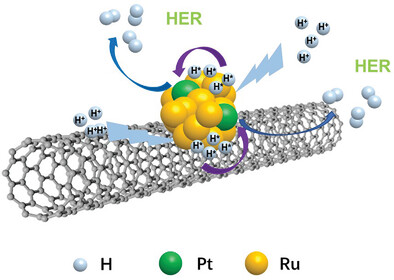
M-Ru/CNT (M = Pt, Rh, Pd, Ir) are synthesized by ultrafast solvent-free microwave method for the first time and used for boosting acidic hydrogen evolution reaction. Strong metal-support interaction improves stability. DFT shows that noble metal doping, especially Pt doping, can significantly promote the H+ adsorption on the Ru surface, promote the release of H2 on the Pt surface, and optimize ΔGH*.
Multiplexing Nanodrug Ameliorates Liver Fibrosis via ROS Elimination and Inflammation Suppression
- First Published: 10 November 2021
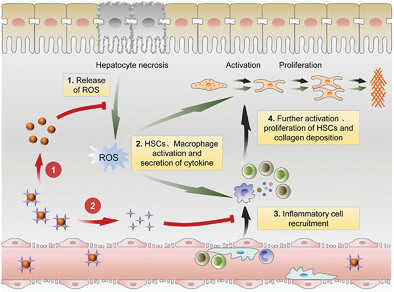
Carbon quantum dot-dexamethasone effectively prevents fibrosis progression by inhibiting the activation of Kupffer cells and the infiltration of inflammatory cells, including monocyte-derived macrophages, T cells, and B cells. This multiplexing nanodrug with reactive oxygen species elimination and inflammation suppression abilities presents an innovative strategy for effective antifibrotic therapy.
Tracking Confined Reaction Based on Host–Guest Interaction Using Single-Molecule Conductance Measurement
- First Published: 19 November 2021
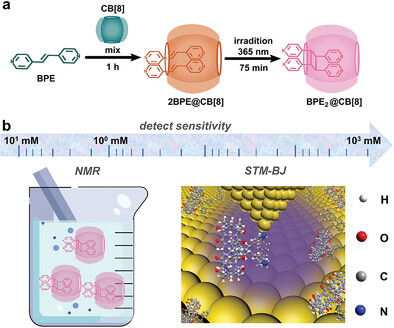
The confined reaction based on host–guest interaction is tracked via scanning tunneling microscope-break junction technique. And the electrical signals of the reactants with a concentration as low as 5 × 10−6 m can be clearly detected. However, the characteristic signal is undetectable when the concentration of reactants is less than 0.5 × 10−3 m in nuclear magnetic resonance measurements.
Epitaxial Growth of 2D Ultrathin Metastable γ-Bi2O3 Flakes for High Performance Ultraviolet Photodetection
- First Published: 05 November 2021
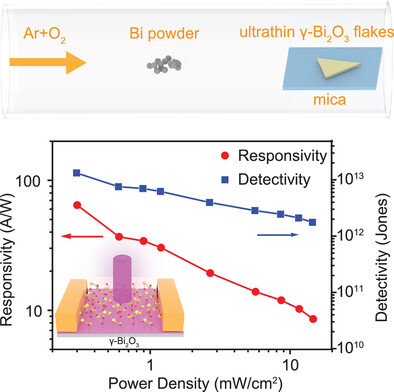
This work presents the synthesis of 2D ultrathin metastable γ-Bi2O3 flakes via a van der Waals epitaxy method. The UV photodetectors based on the as-synthesized γ-Bi2O3 flakes exhibit excellent performance, where the responsivity is 64.5 A W−1, specific detectivity is 1.3 × 1013 Jones, and response time is 290 µs under 365 nm laser illumination.
Temperature-Responsive Nanoparticles Enable Specific Binding of Apolipoproteins from Human Plasma
- First Published: 10 November 2021
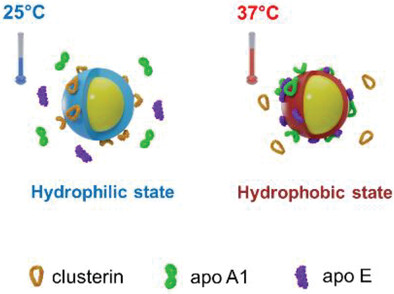
Apolipoproteins are proteins in human plasma which provide stealth effect to nanoparticles, resulting in less unspecific cellular uptake and prolonged blood circulation time. Herein, the specific binding of apolipoproteins around temperature-responsive nanoparticles when incubating the nanoparticles in human plasma is observed. The stealth properties of these nanocarriers can be simply controlled by varying incubation temperature.
Microbial Lipopeptide Supramolecular Self-Assemblies as a Methuosis-Like Cell Death Inducer with In Vivo Antitumor Activity
- First Published: 11 November 2021
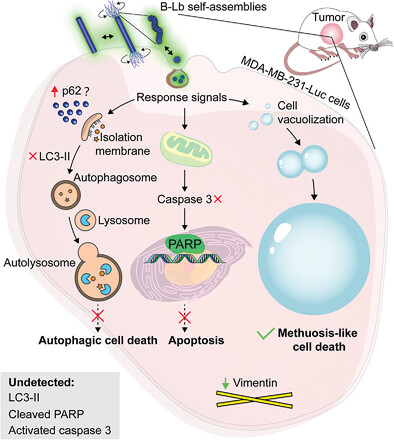
Microbial lipopeptide bacillimycin Lb (B-Lb) can self-assemble into various supramolecular structures in a multilevel and cross-scale manner. B-Lb self-assemblies can induce cytoplasmic vacuolation of human triple-negative breast cancer cells, resulting in methuosis-like cell death in vivo and in vitro. Long fatty acid chain in B-Lb is the key to maintain its self-assembled form and bioactivity.
The Multiweek Thermal Stability of Medical-Grade Poly(ε-caprolactone) During Melt Electrowriting
- First Published: 05 November 2021
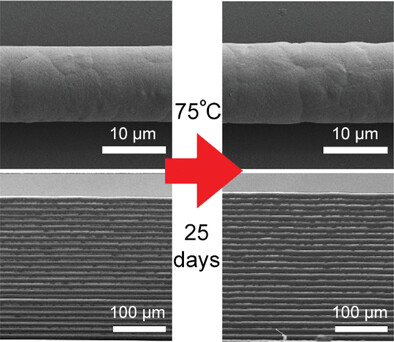
This study pushes the limits of melt electrowriting, by printing daily for a total of 25 d using the same, continuously heated, polymer. The automated generation of samples for various analysis shows that, at the lowest temperature, there was no detectable change in fiber diameter, elastic modulus, or crystallinity of the polymer.
A New Hybrid Lead-Free Metal Halide Piezoelectric for Energy Harvesting and Human Motion Sensing
- First Published: 25 November 2021
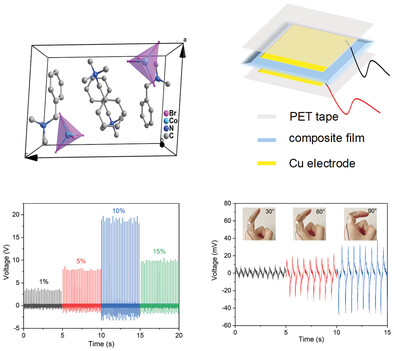
A hybrid lead-free metal halide, (BTMA)2CoBr4 (BTMA, benzyltrimethylammonium), is demonstrated to exhibit significant piezoelectricity and soft elastic properties. Moreover, (BTMA)2CoBr4-based composite films are fabricated for energy harvesting and human body motion sensing with attractive performance. This work broadens the landscape of molecular piezoelectric materials by paying more attention to the non-perovskite-type and lead-free hybrid organic-inorganic systems.
Growth of 1D Nanorod Perovskite for Surface Passivation in FAPbI3 Perovskite Solar Cells
- First Published: 05 November 2021
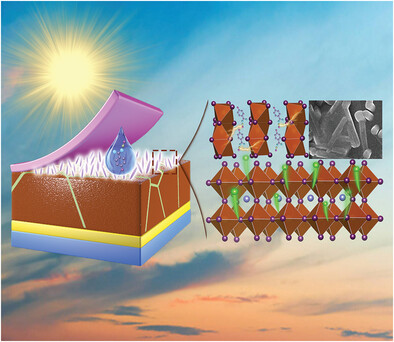
4-Chlorobenzamidine hydrochloride is developed as spacer to form orientationally crystallized nanorod-like 1D perovskite on the top surface of 3D perovskite for surface passivation of FAPbI3 perovskite. The coexistence of 1D–3D hybrid perovskite regulates the crystallization and morphology effectively and assists in promoting charge extraction, and suppressing charge recombination and exhibits a boosted power conversion efficiency of 21.95%.
Optoionic Sensing
- First Published: 01 December 2021
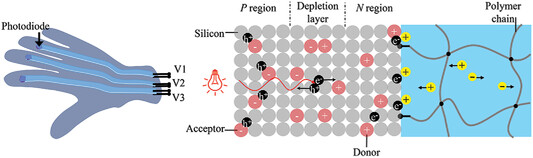
The physics of optoionic transduction in photodiode-hydrogel hybrids is explored. Optoionic sensors are used for mimicking biological functions such as optoionic transduction, photosensitive skin, and light-triggered actuation. Potential applications of optoionic sensing include wearable and implantable devices, as well as soft robots.
Quench-Induced Surface Engineering Boosts Alkaline Freshwater and Seawater Oxygen Evolution Reaction of Porous NiCo2O4 Nanowires
- First Published: 04 December 2021
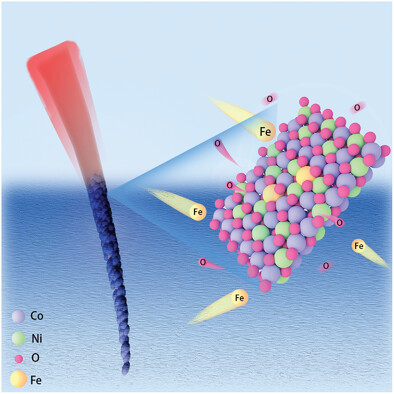
Quenching in FeSO4 solution enables NiCo2O4@CC electrocatalysts with Fe doping and oxygen vacancies generated on the surface. The quench-derived electrocatalysts are highly active and stable in both alkaline freshwater and seawater oxygen evolution reactions, arising from the large surface area, rich active sites, and modulated electronic structure.
Blending Donors with Different Molecular Weights: An Efficient Strategy to Resolve the Conflict between Coherence Length and Intermixed Phase in Polymer/Nonfullerene Solar Cells
- First Published: 25 November 2021
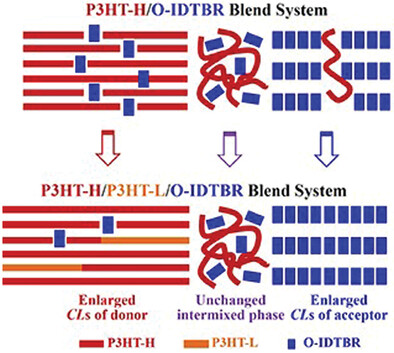
Here, blending polymers of different molecular weights as donors, to solve the conflict between coherence lengths and intermixed phase is proposed. This strategy fully utilizes the individual advantages of polymers of different molecular weights, which may reduce or eliminate trial-and-error approaches to match donor and accepter materials in regulating the microstructure of polymer/nonfullerene as acceptors solar cells.
Highly Flexible Freestanding BaTiO3-CoFe2O4 Heteroepitaxial Nanostructure Self-Assembled with Room-Temperature Multiferroicity
- First Published: 23 November 2021
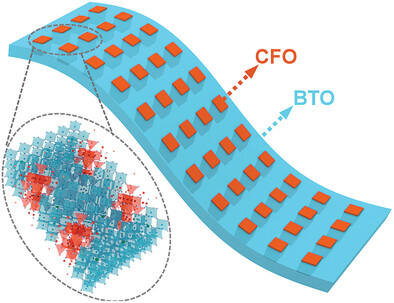
High quality heteroepitaxial freestanding 1D–3D type multiferroics of self-assembled BaTiO3-CoFe2O4 (BTO-CFO) nanostructure with CFO pillars embedded in BTO matrix is prepared based on a water-dissolvable Sr3Al2O6 sacrificial layer. The freestanding BTO-CFO nanostructure enjoys super flexibility and mechanical integrity, and clear piezoelectric and magnetic responses confirming its robust multiferroic properties at room temperature.
Single Crystal Halide Perovskite Film for Nonlinear Resistive Memory with Ultrahigh Switching Ratio
- First Published: 23 November 2021
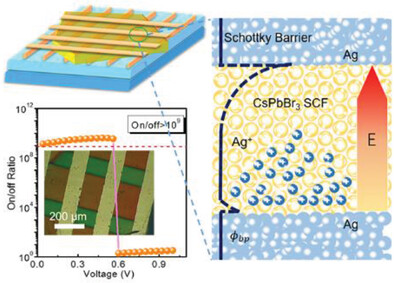
All-inorganic halide perovskite CsPbBr3 single crystal film (SCF) is introduced in resistive memory. An ultrahigh switching ratio over 109 and fast switching speed (1.8 µs) are achieved by Ag/CsPbBr3/Ag structure due to high Schottky barrier height and remarkable interface contact. The memory provides the halide perovskite SCF with potential as an alternative in future computing systems.
Facile Synthesis of Pd and PdPtNi Trimetallic Nanosheets as Enhanced Oxygen Reduction Electrocatalysts
- First Published: 01 December 2021
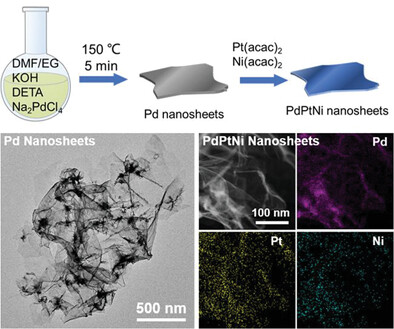
Pd nanosheets with sizes about 1–2 µm and thickness around 3 nm are synthesized with a mild wet chemical method. A comprehensive mechanism study reveals the decomposition of the solvent plays a crucial role in the 2D growth. Further deposition on the existing nanosheets yields trimetallic PdPtNi nanosheets, which exhibit enhanced activity and stability in the oxygen reduction reaction.
Electrical Propulsion and Cargo Transport of Microbowl Shaped Janus Particles
- First Published: 10 November 2021
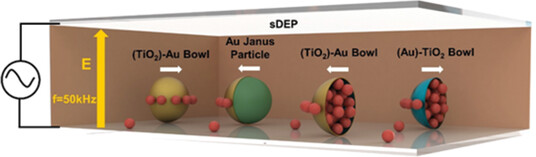
Microbowl-shaped Janus particles (JPs) are made by deposition of Au and Ti layers onto sacrificial spherical polystyrene particles, followed by oxidation of the Ti to TiO2. The dual broken symmetry of both geometrical and electrical properties of the microbowl renders a strong dependence of its mobility and cargo loading on the order of the layering of Au and TiO2.
In Situ Magnetic Alignment of a Slurry of Tandem Semiconductor Microwires Using a Ni Catalyst
- First Published: 30 November 2021
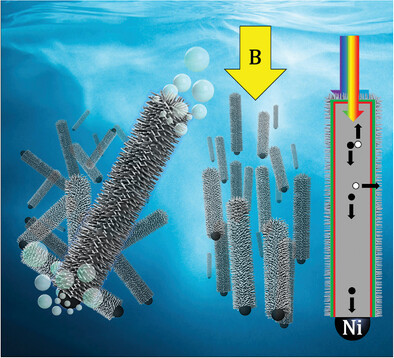
Tandem semiconductor microwires capable of unassisted solar water-splitting are magnetically aligned under operational conditions with active dispersion using an external magnetic field acting on a ferromagnetic nickel-hydrogen evolution catalyst. Aligned microwire slurries may help future tandem systems maintain current matching from a balance of photon absorption between the subcell regions.
A Bioinspired Hemostatic Powder Derived from the Skin Secretion of Andrias davidianus for Rapid Hemostasis and Intraoral Wound Healing
- First Published: 23 November 2021
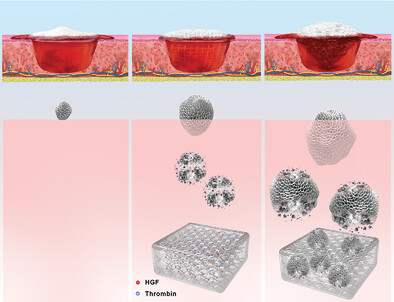
Hemostatic powders derived from the skin secretion of Andrias davidianus (SSAD) with controllable particle sizes are prepared, inducing blood-absorption in a particle size-dependent manner. Featuring favorable hemostatic and simultaneous regenerative effects, along with degradability and good biocompatibility, the SSAD hemostatic powder can be a potential candidate as a new class of inexpensive and natural hemostatic and wound-dressing agent.
Imaging the Single-Electron Ln–Ln Bonding Orbital in a Dimetallofullerene Molecular Magnet
- First Published: 04 December 2021
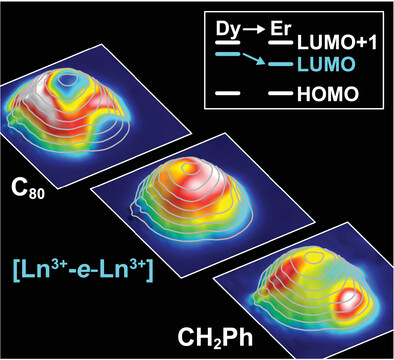
The single-electron bond in lanthanide (Ln) dimetallofullerene molecular magnets mediates the ferromagnetic exchange between both Ln ions, leading to exceptional high blocking temperatures. Using scanning tunneling spectroscopy, this work demonstrates electronic transport through its unoccupied component in individual Ln2@C80(CH2Ph) complexes. The results pave the way for the investigation of the spin system of individual dimetallofullerene molecular magnets.
Interfacial Covalent Bonding Endowing Ti3C2-Sb2S3 Composites High Sodium Storage Performance
- First Published: 05 November 2021
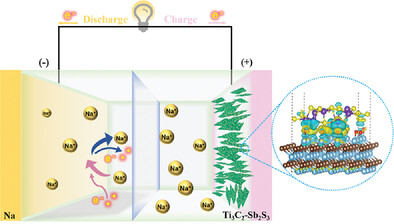
This study constructs covalent chemical linkage to anchor antimony sulfide on flexible 2D conductive materials. Ti3C2Tx MXene serves as both charge storage contributor and flexible conductive buffer to sustain the structural integrity of the Ti3C2-Sb2S3 electrode. This strategy is expected to shed more light on interfacial chemical linkage toward rational design of advanced materials for SIBs.
Hierarchical Ti3C2Tx MXene/Carbon Nanotubes Hollow Microsphere with Confined Magnetic Nanospheres for Broadband Microwave Absorption
- First Published: 16 December 2021
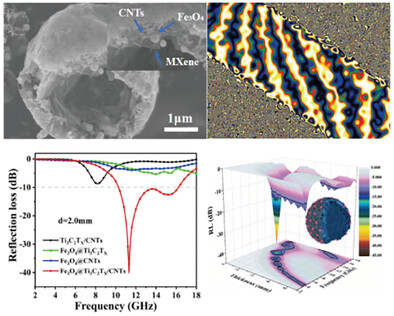
A magnetized strategy of MXene-based microsphere is put forward for the electromagnetic synergy. Within the 3D magnetic confinement architecture, strong interfacial polarization and multiscale magnetic coupling can be triggered, leading to the enhancement of microwave absorption performance. This work may serve as a new idea for the modification of electromagnetic composite.
Oxygen Reduction Activity of B←N-Containing Organic Molecule Affected by Asymmetric Regulation
- First Published: 27 November 2021
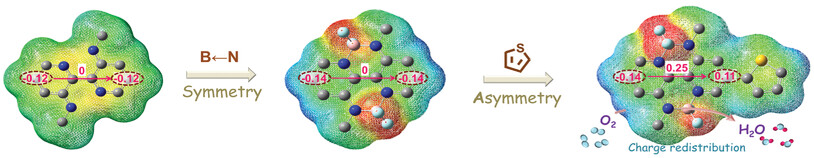
An asymmetrical strategy to design metal-free organic small molecular (OSM) catalysts for the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) is proposed to regulate the electronic distribution of active sites. Both theoretical and experimental results prove and verify the varied active sites and efficient electrocatalytic activity of the asymmetrical OSM system. This work provides an efficient method to design ORR electrocatalysts.
Editor's Choice
Accelerating AFM Characterization via Deep-Learning-Based Image Super-Resolution
- First Published: 27 November 2021

A simple and practical way of accelerating atomic force microscopy (AFM) characterization enabled by a deep-learning-based image super-resolution method combined with the data acquisition and preparation process is developed. Its application to measuring the geometrical and mechanical properties of DNA assemblies reveals that around a tenfold reduction of time in AFM characterization can be achieved without significant loss of accuracy.
Stable Bismuth-Doped Lead Halide Perovskite Core-Shell Nanocrystals by Surface Segregation Effect
- First Published: 27 November 2021
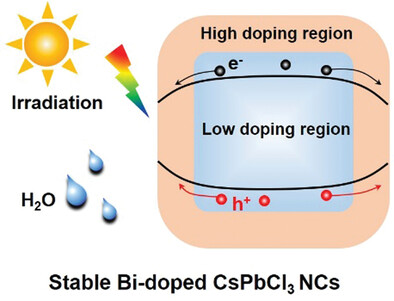
A strategy for stable Bi-doped lead halide perovskite nanocrystals (NCs) with core-shell structure by the surface segregation effect originating from heterovalent doping, which overcomes the obstacles caused by hydrophobic surface of perovskite NCs, is pursued. The Bi-rich shell endows Bi-doped CsPbCl3 NCs superior stability against the strong irradiation, high humidity, CO2, and O2 ambient.
Biomimetic Nanoparticles Enabled by Cascade Cell Membrane Coating for Direct Cross-Priming of T Cells
- First Published: 27 November 2021
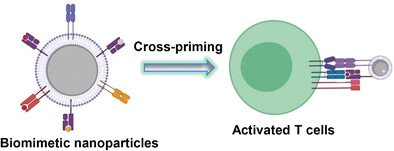
The activation of T lymphocytes by antigen-presenting cells is responsible for eliciting antigen-specific immune responses, which plays a critical role in immunotherapy. Here, the manipulation of cross-priming of T cells using biomimetic nanoparticles enabled by cascade cell membrane coating, which provides a unique yet modulate platform for boosting an effective adaptive immunity for immunotherapy, is described.
Efficient Organic Solar Cells Enabled by Simple Non-Fused Electron Donors with Low Synthetic Complexity
- First Published: 27 November 2021
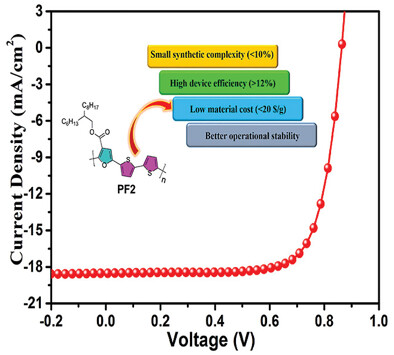
A simple structure non-fused-ring electron donor PF2 alternately consisting of furan-3-carboxylate and 2,2′-bithiophene presents very small synthetic complexity of 9.7% as well as low material cost of ≈19.0 $ g−1. More importantly, PF2 delivers a high efficiency of 12.4% coupled with strong operational stability.
Lithiophilic Carbon Nanofiber/Graphene Nanosheet Composite Scaffold Prepared by a Scalable and Controllable Biofabrication Method for Ultrastable Dendrite-Free Lithium-Metal Anodes
- First Published: 27 November 2021
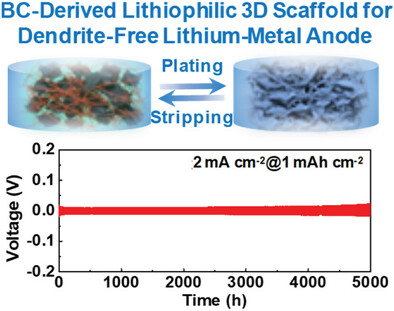
Lithiophilic carbon nanofiber@reduced graphene oxide nanosheet composite scaffolds are fabricated through an in situ biofabrication method. The abundant lithiophilic functional groups and conductive 3D network can effectively regulate uniform Li nucleation and deposition, realizing exceptional Li plating/stripping, and full cell cycling performance. The findings provide a promising material fabrication strategy for realizing high performance Li metal batteries.
Nitrogen-Enriched Conjugated Polymer Enabled Metal-Free Carbon Nanozymes with Efficient Oxidase-Like Activity
- First Published: 27 November 2021
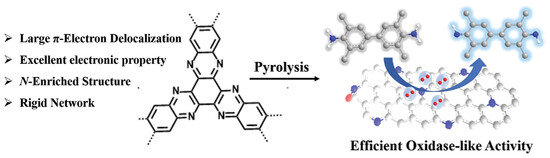
Nitrogen-rich conjugated polymer is first utilized as precursor to construct metal-free N-doped carbon nanozymes QAU-Z1, which is almost the best performance among the current metal-free oxidase-like nanozymes. The inherent mechanism can be attributed to the zeta potential variation between negative nanozyme and positively-charged TMB molecules, as well as the capacity of QAU-Z1 to decrease the overpotential of O2 reduction.
Boosting Oxygen Reduction Activity of Manganese Oxide Through Strain Effect Caused By Ion Insertion
- First Published: 27 November 2021
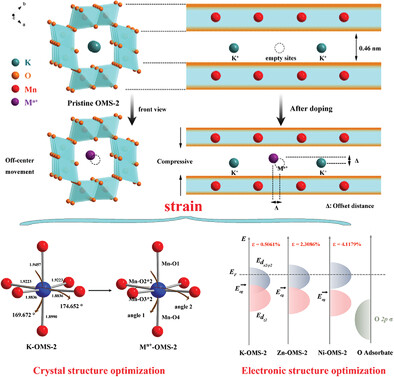
The tunnel structure is skillfully used to adjust the strain of manganese oxide octahedral molecular sieves, enduing OMS-2 with unprecedented catalytic activity. Furthermore, the effect of pure strain on covalency and eg band center is also discussed. The higher compression strain increases the covalence of MnO6 octahedral configuration and moves down the eg band center, thereby benefiting the interaction between active substance and oxygen intermediates.
Engineering pH-Sensitive Stable Nanovesicles for Delivery of MicroRNA Therapeutics
- First Published: 16 November 2021
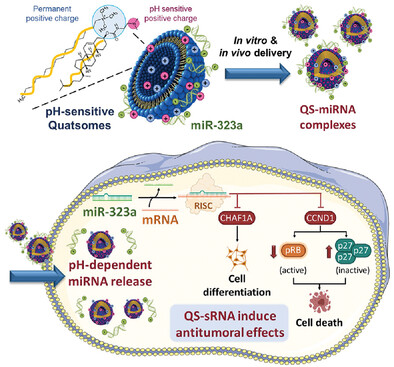
Here is reported the engineering of non-liposomal lipid nanovesicles, named quatsomes, for the effective delivery of miRNAs and other small RNAs into the citosol of tumor cells, triggering a tumor-suppressive response. These stable nanovesicles with tunnable pH sensitiveness constitute an attractive platform for the delivery of nucleic acids with therapeutic activity and their exploitation in the clinics.