Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 3/1986)
- First Published: March 1986

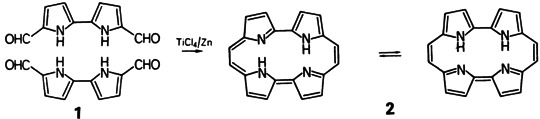
The cover page shows the skeleton (white) of porphycene, a novel aromatic isomer of porphin (gray) with effective D2h symmetry, which is determined by extremely rapid NH-tautomerism. This fascinating pyrrolic macrocycle, which dissolves in organic solvents to give blue solutions showing beautiful red-violet fluorescence, is, despite its—in comparison to porphin—much smaller cavity, capabable of forming metalloporphyrin- and metallophthalocyanine-type complexes. In the light of the intensively studied chemistry and biochemistry of the porphyrins it seems remarkable that porphycene and its derivatives, for which a host of interesting applications can be envisaged, could have remained concealed for such a long time. Further details are reported by E. Vogel et al. on page 257ff.
Graphical Abstract (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 3/1986)
- First Published: March 1986
Reviews
Cluster Beam Chemistry—from Atoms to Solids
- Pages: 197-211
- First Published: March 1986
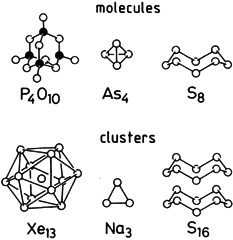
The generation, growth, and properties of homo- and heteronuclear clusters in the vapor phase are a fascinating area of research, where new insights into structure have been gained, especially from mass spectrometric investigations. True, the demarcation of molecules, clusters and microcrystals is important, yet there also exist relationships between clusters in the vapor phase on the one hand and molecules in solution and solids on the other.
New Methods for the Synthesis of Glycosides and Oligosaccharides—Are There Alternatives to the Koenigs-Knorr Method? [New Synthetic Methods (56)]†
- Pages: 212-235
- First Published: March 1986
![New Methods for the Synthesis of Glycosides and Oligosaccharides—Are There Alternatives to the Koenigs-Knorr Method? [New Synthetic Methods (56)]](/cms/asset/b1bbed36-fdb2-4075-a076-63f5199fd566/must001.jpg)
Glycopeptides, glycolipids, and glycophospholipids are of special interest as components of membranes. The oligosaccharide residue is, inter alia, responsible for intercellular recognition and interaction (immuno-reactions). Major advances have been made in the synthesis of oligosaccharide, largely due to 1-O-alkylation, the trichloroacetimidate method, and activation via glycosylsulfonium salts.
3-Chloropropyltrialkoxysilanes—Key Intermediates for the Commercial Production of Organofunctionalized Silanes and Polysiloxanes†
- Pages: 236-252
- First Published: March 1986
The chemical binding of inorganic (particularly siliceous) surfaces to organic polymers is of special importance in the production of composites. Whether this concerns the strengthening of polyester resins with glass fibers for use in boatbuilding, the incorporation of silica as a filter in rubber mixtures for the manufacture of wear-resistant tires, or the immobilization of enzymes on glass spheres—in all cases organofunctionalized silanes guarantee a reliable and permanent union.
Communications
New Products from PCl3, P(NMe2)3, and AlCl3†‡
- Pages: 253-254
- First Published: March 1986
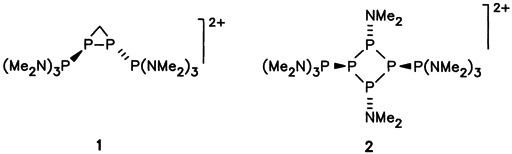
Exploitation of an old and frequently studied reaction (to obtain new compounds) has proven successful with the system PCl3/P(NMe2)3/AlCl3. Depending on the sequence in which the reaction partners are allowed to react with each other, different products are formed. The most interesting new products are the diphosphoniodiphosphirane ion 1 (the CH2 group comes from the solvent CH2Cl2) and the cyclotetraphosphane ion 2.
Synthesis and Structure of the Co3Ti2 Complex [{μ3-[(C5H5)2TiOC]}2{(C5H5)3Co3}]: CO Reduction by Two Different Metal Centers
- Pages: 254-255
- First Published: March 1986
Asymmetric Bromination of Enantiomerically Pure Acetals of Alkyl Aryl Ketones
- Pages: 259-260
- First Published: March 1986
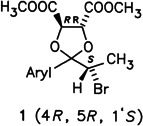
Useful intermediates for the preparation of optically active 2-arylalkanoic acids and aryl-1-bromoethyl ketones, the α-bromoacetal 1 and its 1′R-diastereomer, are formed in the ratio ≥ 90: ⩽ 10 in the title reaction. Compounds of this type are of special interest, among other things, as precursors of antiinflammatory drugs.
Metal Dependence of Cyclometalation and Arene CH Activation in the Photolysis of cis-H2M[P(CH2CH2CH2PMe2)3] (MFe, Ru) in Benzene†
- Pages: 260-261
- First Published: March 1986
![Metal Dependence of Cyclometalation and Arene C<span class='icomoon'></span>H Activation in the Photolysis of cis-H2M[P(CH2CH2CH2PMe2)3] (MFe, Ru) in Benzene](/cms/asset/dd1ee73c-ab45-412e-8281-b20f32aa7c21/must001.jpg)
The metal-dependent transition between intra- and intermolecular CH addition has been studied with the title reaction as example: With cis-H2Fe(pp3), the cyclometalated compound 1 is formed, with cis-H2Ru(pp3) the phenyl hydride 2. A decisive factor might be the difference in size of the metal atoms, which leads to different crowding of the groups and different chelate ring strain ((pp3 = P(CH2)3PMe2)3).
Complex Stabilization of Disulfur Dioxide in the Fragmentation of Thiirane S-Oxide on Bis(triphenylphosphane)platinum(0)†
- Pages: 261-262
- First Published: March 1986
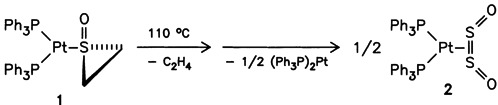
S2O2, the unstable initial product of SO decomposition in the gas phase, has been trapped for the first time by complexation. With the isolation of the surprisingly stable thiirane S-oxide complex 1, it was further demonstrated that C2H4SO first decomposes after coordination to a metal. Ethylene is eliminated from 1 in toluene only at 110°C, whereupon the S2O2 complex 2 is formed.
Synthesis of [Cu3Os3H9(PMe2Ph)9], a Bimetallic Raft, by Reductive Elimination of Alcohol or H2†
- Pages: 262-264
- First Published: March 1986
![Synthesis of [Cu3Os3H9(PMe2Ph)9], a Bimetallic Raft, by Reductive Elimination of Alcohol or H2](/cms/asset/c1c38c24-2443-476f-b198-a47b26271cdc/must001.jpg)
A planar Cu3Os3 framework forms the core of the title compound, which can be synthesized via two routes. Noteworthy is its isolation from [HCuPPh3] and [H4Os(PMe2Ph)3] with elimination of PPh3 and H2. Inspection of the structure of the cluster (Figure on the right, metal atoms hatched), shows that the Os atoms are shielded by the phosphane ligands, but the Cu atoms are accessible through a tunnel of phenyl and methyl groups.
2-(2,4,6-Tri-tert-butylphenyl)-1-arsaethyne—the First Compound Containing an Arsenic–Carbon Triple Bond
- Page: 264
- First Published: March 1986
H3CPCH2: An Ylide with Two-Coordinate Phosphorus?†‡
- Pages: 265-266
- First Published: March 1986
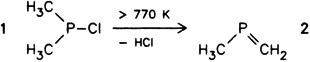
No, but a 2-phosphapropane, is the answer to the question posed in the title. H3CPCH2 1 can be generated by gas-phase pyrolysis from (CH3)2PCl 2 and characterized by PE and mass spectrometry. Whereas the first ionization in the case of normal phosphorus ylides occurs between 5.95 and 6.85 eV, in the case of 2 it first takes place at 9.69 eV. According to an MNDO calculation of the PE spectrum of 1, the answer to the “Hamlet” question “to d or not to d” (i.e. whether d orbitals participate in the PC bonding) is no.
Novel Synthesis of the Angular [3]Phenylene (Terphenylene) by Cobalt-Catalyzed Cyclization of Bis(2-ethynylphenyl)ethyne: a Molecule with an Internal Cyclohexatriene Ring†
- Pages: 266-268
- First Published: March 1986
Hexaethynylbenzene†
- Pages: 268-269
- First Published: March 1986
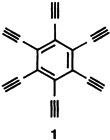
A molecule that doesn't require any introduction, the title compound 1, can be precipitated as a white powder; solutions in polar solvents are stable. 1 forms transition-metal complexes. The ethynyl groups in the precursors with six Me3SiCC groups on the benzene ring are not exactly linear (X-ray structure analysis).
A Simple Access to 2-Epoxy Alcohols: Titanium(IV)-Catalyzed Oxygen Transfer from Allylic Hydroperoxides†
- Pages: 269-270
- First Published: March 1986
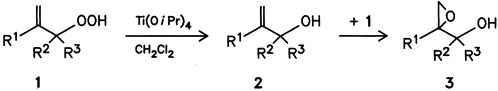
A host of new, synthetically valuable 2-epoxy alcohols 3 should be accessible by the generally applicable title reaction. Oxygen transfer from 1 does not proceed intramolecularly; the first step is the formation of the allylic alcohol 2, which is epoxidized in a rapid secondary step by 1 to the product 3. At the same time, compound 2 is reformed.
Tris(pentacarbonylrhenium)-sulfonium, -selenonium, and -telluronium Ions: Synthesis and Structure of[{(OC)5Re}3E]⊕BF (ES, Se, Te)†‡
(ES, Se, Te)†‡
- Pages: 270-272
- First Published: March 1986
![Tris(pentacarbonylrhenium)-sulfonium, -selenonium, and -telluronium Ions: Synthesis and Structure of[{(OC)5Re}3E]⊕BF (ES, Se, Te)](/cms/asset/200989fc-c906-4ba5-bf4e-3a1d58ef786a/must001.jpg)
A further analogy between inorganic and organic chemistry is found in the reaction of the rhenium complex 1 with alkali metal chalcogenides, which leads to the compounds 2 to 4. These were characterized by an X-ray structure analysis. This reaction corresponds to the alkylation of chalcogenides. Re(CO)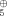 (16e) and carbenium ions R3C⊕ are isolobal.
(16e) and carbenium ions R3C⊕ are isolobal.
[Re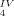 S22]4−, a Highly Symmetrical Metal-Sulfur Cluster with Six S
S22]4−, a Highly Symmetrical Metal-Sulfur Cluster with Six S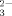 Ligands†
Ligands†
- Pages: 272-273
- First Published: March 1986
![[ReS22]4−, a Highly Symmetrical Metal-Sulfur Cluster with Six S Ligands](/cms/asset/eb9d8cbb-a0e8-46f1-9bc9-d067699c75fe/must001.jpg)
Re-S compounds should be even better catalysts for the desulfurization of crude oil than the long proven MoS compounds. The first step in the development of a catalyst, the synthesis of a discrete ReS cluster anion, has now been accomplished. Reaction of a perrhenate solution reduced with NH2OH·HCl with an aqueous polysulfide solution yielded an NH4-salt of the cluster anion [Re4S22]4− 1.
[Bi2IIIS34]4−, the Hitherto Sulfur-Richest Complex
- Page: 273
- First Published: March 1986
Sulfur complexes are always full of surprises: Reaction of BiCl3 with a polysulfide solution in acetonitrile furnishes the complex anion [Bi2S24]4− in which the Bi atoms are coupled by an S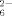 ligand. In each case two bidentate S
ligand. In each case two bidentate S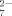 ligands complete the square-pyramidal coordination of the two Bi atoms. Neither a complex with coupled S
ligands complete the square-pyramidal coordination of the two Bi atoms. Neither a complex with coupled S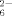 ligands nor one with bidentate S
ligands nor one with bidentate S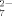 ligands was previously known.
ligands was previously known.
Asymmetric Double-Bond Isomerization of 4,7-Dihydro- to 4,5-Dihydro-1,3-dioxepins
- Page: 274
- First Published: March 1986
Palladium(II) and Platinum(II) Complexes of 1,4,7,10,13,16-Hexathiacyclooctadecane†
- Pages: 274-276
- First Published: March 1986
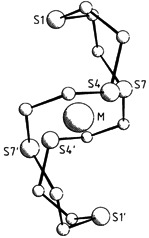
A new form of coordination of the versatile ligand hexathia[18]crown-6 is found in the title compounds: Pd or Pt is coordinated to four S atoms in a square planar fashion; only long range weak axial interactions are observed with the two remaining S atoms of the macrocycle. That is, the macrocycle does not behave like a crown ether.
Ethylene Oxide—X-Ray Structure Analysis (at 150 K) and ab initio Calculations†‡
- Pages: 276-277
- First Published: March 1986
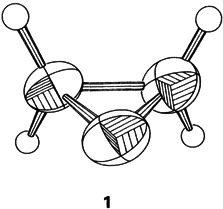
Carrying out an X-ray structure analysis of a substance melting at −112°C is no easy task. However, the effort put into accomplishing such an analysis of ethylene oxide has been worthwhile, since the result is surprising: In the crystalline state the carbon atoms and the oxygen atoms in ethylene oxide 1 form an almost equilateral triangle with CC and CO bond lengths of ca. 143 pm. This is other than what was found in earlier investigations of ethylene oxide in the liquid and gaseous states.
Synthesis of N-(1-Carboxy-5-aminopentyl)dipeptides as Inhibitors of Angiotensin Converting Enzyme†
- Pages: 277-278
- First Published: March 1986
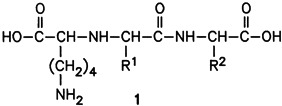
Excellent ligands for an affinity chromatography of angiotensin converting enzyme have been found, namely the new inhibitors of this enzyme such as 1, R1, R2H, alkyl. They were prepared from Nε-Boc-L-lysine methyl ester and α;-trifluoromethanesulfonyloxycarboxylic esters. Inhibitors of this enzyme are of pharmaceutical importance.
Thin Layer Chromatographic Separation of Stereoisomeric Dipeptides
- Pages: 278-279
- First Published: March 1986
Reversible Interconversion of CC and CN Multiple Bond Systems on Clusters†
- Pages: 279-280
- First Published: March 1986
Cluster moieties can be so conditioned by metal exchange that they support one and the same reaction in the region of the organic ligands both in the forward and reverse direction. A spontaneous alkylidyne-vinylidene transformation has been observed for the first time within the sequences of the type shown below.
2-Dewar Phosphinines—a New Class of Compounds Containing Two-Coordinate Phosphorus†‡
- Pages: 280-282
- First Published: March 1986
Hydroxyacetylene: Generation and Characterization of the Neutral Molecule, Radical Cation and Dication in the Gas Phase†‡
- Pages: 282-284
- First Published: March 1986
The simplest ynol, the title compound 2, like the singly and doubly positively charged species 3 and 4, respectively, could be generated in the mass spectrometer. Cleavage of CO from 1 furnished the radical cation 3, which on neutralization with Xe affords the neutral ynol 2. The radical cation 3 can be converted into the dication 4 by charge stripping.
Influence of External Negative Charges on the Absorption Maxima of Symmetrical Cyanines. A Study with Model Compounds and Artificial Bacteriorhodopsin Pigments†
- Pages: 284-286
- First Published: March 1986
Remarkable Ease of Ring Oxidation in Cerium(IV) Bisporphyrinates with Double-Decker Structure†‡
- Pages: 286-287
- First Published: March 1986
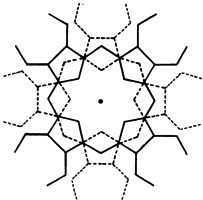
The “special pair” of bacteriochlorophyll molecules in the reaction center of bacterial photosynthesis is immediately recalled to mind by two properties of the title compounds (cf. right): (1) The stable radical cation exhibits strong absorption in the near infrared; (2) the redox potential of this oxidation lies well below that of the corresponding magnesium monotetrapyrrole.
Solvent Polarity and the Anomeric Effect†
- Pages: 287-289
- First Published: March 1986
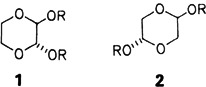
Polar solvents enhance the anomeric effect. This surprising turnabout follows from the NMR data and calculated dipole moments of dioxane derivatives such as 1 and 2. Accordingly, polar solvents stabilize the diaxial conformation in 2, RSiMe3, tBu; in these compounds μeq ≈ μax. Contributions by quadrupole moments etc. Were not taken into account.
Novel Fulvalene Derivatives of Zirconium: A Facile Entry into Organozirconium(III) Chemistry†
- Pages: 289-290
- First Published: March 1986
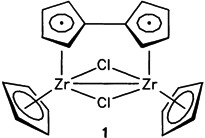
A universally modifiable new starting substance, the fulvalene ZrIII complex 1, is formed upon reaction of Cp2ZrCl2 and sodium amalgam. 1 is highly reactive, but nevertheless it can be isolated. The fulvalene ligand ensures that the secondary products are dinuclear, e.g. [(CpZrCl)2(C5H4−C5H4)O], the oxidation product of 1.
Book Reviews
Book Review: Principles of Nucleic Acid Structure. By W. Saenger
- Pages: 290-291
- First Published: March 1986
Book Review: Bio-inorganic Chemistry. By R. W. Hay
- Page: 291
- First Published: March 1986
Book Review: Methods of Enzymatic Analysis. Vol. 6. Metabolites 1: Carbohydrates. Edited by H. U. Bergmeyer, J. Bergmeyer, and M. Grassl
- Pages: 291-292
- First Published: March 1986
Book Review: Strategies and Tactics in Organic Synthesis. Edited by T. Lindberg
- Pages: 292-293
- First Published: March 1986
Book Review: Bacterial Endotoxin. Chemical, Biological, and Clinical Aspects. Edited by J. Y. Homma, S. Kanegasaki, O. Lüderitz, T. Shiba, and O. Westphal
- Page: 293
- First Published: March 1986
Book Review: Biotransformation von Arzneimitteln. Band 4. By S. Pfeifer. 717 pp., bound, DM 192.00.—ISBN 3-527-25926; Band 5. By S. Pfeifer and H.-H. Borchert. 468 pp., bound, DM 168.00.—ISBN 3-527-26075-7
- Pages: 293-294
- First Published: March 1986
Book Review: Cytochrome P-450. By K. Ruckpaul and H. Rein
- Page: 294
- First Published: March 1986
Book Review: Methoden der Analytischen Chemie. Eine Einführung. Band 2: Nachweis- und Bestimmungsmethoden, Teil 2. By R. Bock
- Pages: 294-295
- First Published: March 1986
Book Review: Reactive Molecules. The Neutral Reactive Intermediates in Organic Chemistry. By C. Wentrup
- Pages: 295-296
- First Published: March 1986
Book Review: Mammalian Semiochemistry. The Investigation of Chemical Signals Between Mammals. By E. S. Albone
- Page: 296
- First Published: March 1986
Book Review: Oligonucleotide Synthesis. A Practical Approach. Edited by N. J. Gait
- Page: 296
- First Published: March 1986




![Synthesis and Structure of the Co3Ti2 Complex [{μ3-[(C5H5)2TiOC]}2{(C5H5)3Co3}]: CO Reduction by Two Different Metal Centers](/cms/asset/6dcf7d09-445f-4dcd-9341-c01f82fb18f2/must001.jpg)
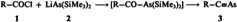
![Novel Synthesis of the Angular [3]Phenylene (Terphenylene) by Cobalt-Catalyzed Cyclization of Bis(2-ethynylphenyl)ethyne: a Molecule with an Internal Cyclohexatriene Ring](/cms/asset/89d68508-e227-4a65-bd30-11496002565d/must001.jpg)