Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture: Multivalency in the Gas Phase: The Study of Dendritic Aggregates by Mass Spectrometry (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 27/2004)
- Page: 3497
- First Published: 29 June 2004
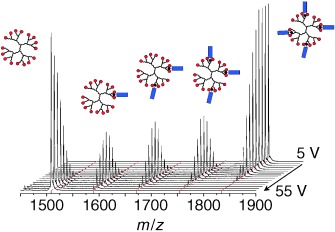
The deconvoluted mass spectrum shown in the cover picture of a third-generation poly(propylene imine) dendrimer to which one to eight guest molecules are bound indicates that the complex with four guest molecules is the most abundant. Each of these aggregates can be selected, and the guests can be removed one by one by collision-induced dissociation (CID). The results provide new insight into the role of important secondary interactions in the gas phase. For more information, see the Communication by E. W. Meijer and co-workers on page 3557 ff.
Molecular Biology in Medicinal Chemistry. (Series: Methods and Principles in Medicinal Chemistry, Vol. 21.) Edited by Theodor Dingermann, Dieter Steinhilber and Gerd Folkers.
- Page: 3510
- First Published: 29 June 2004
Physics and Chemistry of Interfaces. By Hans-Jürgen Butt, Karlheinz Graf, and Michael Kappl.
- Pages: 3510a-3511
- First Published: 29 June 2004
Nanocosm. Nanotechnology and the Big Changes Coming from the Inconceivably Small. By William Illsey Atkinson.
- Pages: 3511-3512
- First Published: 29 June 2004
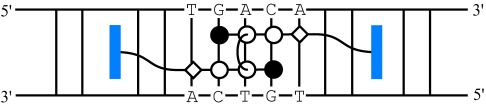
Ozone in Arteriosclerotic Plaques: Searching for the “Smoking Gun”
- Pages: 3514-3515
- First Published: 29 June 2004
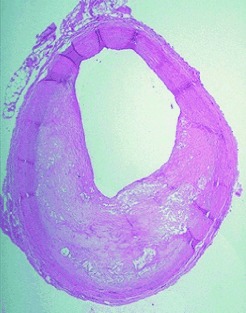
Ozone as an endogenous compound? The discovery of 5,6-secosterol, a characteristic product of the in vitro ozonolysis of cholesterol, in atherosclerotic tissue (see picture) suggests that ozone is formed by biochemical processes. This and other typical products of oxidation may serve as indicators (“biomarkers”) of endogenous ozone.
The Belluš–Claisen Rearrangement
- Pages: 3516-3524
- First Published: 29 June 2004
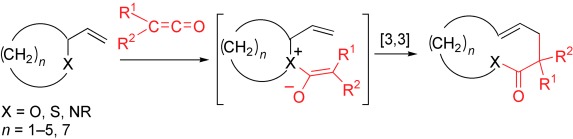
Now a quarter of a century since its serendipitous discovery, the Belluš–Claisen rearrangement of ketenes with allylic ethers, amines, and thioethers has been developed into a simple and reliable [3,3] bond reorganization reaction. This rearrangement, which proceeds via a zwitterionic intermediate, is especially powerful for the ring expansion of cyclic allylic substrates by four carbon atoms (see scheme). R1, R2=alkyl, Cl.
Sulfotransferases: Structure, Mechanism, Biological Activity, Inhibition, and Synthetic Utility
- Pages: 3526-3548
- First Published: 29 June 2004
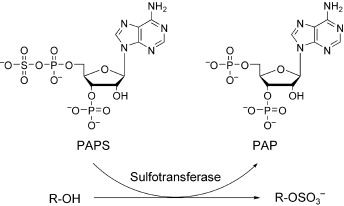
A diverse range of biomolecules, including steroids and glycosaminoglycans, are sulfonated enzymatically by the cosubstrate PAPS in the presence of sulfotransferases (see scheme). As these enzymes have been implicated in several crucial pathophysiological events (regulation of estrogen sulfate synthesis and leukocyte adhesion, viral entry) they have emerged as promising therapeutic targets.
A DNA-Based Machine That Can Cyclically Bind and Release Thrombin†
- Pages: 3550-3553
- First Published: 29 June 2004
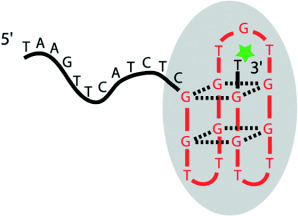
A DNA aptamer structure is the basis of a molecular machine that can be instructed to grab or release the human blood-clotting factor α-thrombin, depending on the operator DNA sequence addressing it. In the picture the aptamer structure, which assumes a conformation characterized by two stacked guanine quadruplex structures, is linked to thrombin (gray ellipse).
An Autonomous DNA Nanomotor Powered by a DNA Enzyme†
- Pages: 3554-3557
- First Published: 29 June 2004
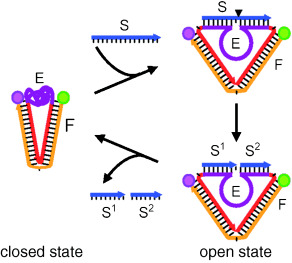
The power of life: An autonomous DNA nanomotor powered by an RNA-cleaving DNA enzyme (see figure) has been constructed that works in the same way as cellular protein motors: it continuously extracts chemical energy from fuel molecules to power mechanical motions. The fuel for the DNA nanomotor is the RNA substrate of the DNA enzyme.
Multivalency in the Gas Phase: The Study of Dendritic Aggregates by Mass Spectrometry†
- Pages: 3557-3562
- First Published: 29 June 2004
New Oxidation States and Defect Chemistry in the Pyrochlore Structure†
- Pages: 3562-3565
- First Published: 29 June 2004
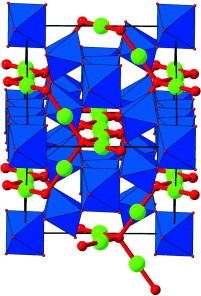
Titanium(III) pyrochlores with TiIII centers at up to 90 % of the B sites of the A2B2O6O′ pyrochlore structure (see picture; blue: BO6, green: A, red: O′), which is well-known for supporting high oxidation states at the octahedral B sites, were obtained by the low-temperature reduction of lanthanide pyrochlores Ln2Ti2O7 with CaH2. This leads to significant rearrangement of the anion sublattice and introduces antisite disorder between the two distinct cation arrays.
Exploiting the Joint Action of Chemical Shielding and Heteronuclear Dipolar Interactions To Probe the Geometries of Strongly Hydrogen-Bonded Silanols†
- Pages: 3565-3568
- First Published: 29 June 2004
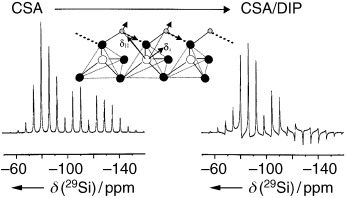
Magic probes: The geometry of strongly hydrogen bonded silanols in octosilicate can be probed by exploiting the 1H NMR distance correlations together with the joint effects of 29Si chemical shielding and dipolar 1H–29Si interactions. Dipolar-modulated, slow magic-angle spinning 29Si NMR spectra allow the determination of Si⋅⋅⋅H distances, the magnitude of the 29Si chemical-shielding tensor, and its orientation in the molecular frame.
The Pristine Oil/Water Interface: Surfactant-Free Hydroxide-Charged Emulsions†
- Pages: 3568-3571
- First Published: 29 June 2004
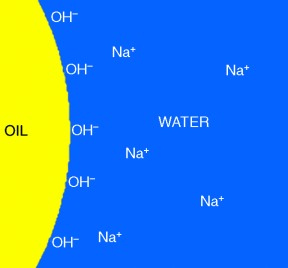
Stable oil-in-water emulsions are obtained in alkaline solution in the absence of any conventional surfactant. The oil droplets are charged by hydroxide ions (see picture). The surface charge density is obtained by measuring the size of the emulsion droplets by electroacoustics and the quantity of NaOH required to keep the pH constant during homogenization.
An Unusual Cyclization in a Bis(cysteinyl-S) Diiron Complex Related to the Active Site of Fe-Only Hydrogenases†
- Pages: 3571-3574
- First Published: 29 June 2004
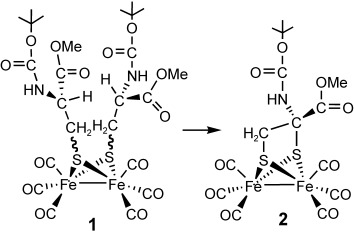
Classical organometallic chemistry was used to prepare the dinuclear iron complex 1 with two protected cysteinyl-S ligands. Oxidative addition of the thiol to [Fe3(CO)12] gave complex 1, which undergoes an unusual intramolecular nucleophilic cyclization with inversion of the configuration to form the chiral carbon-bridged diiron complex 2.
Highly Active, Binary Catalyst Systems for the Alternating Copolymerization of CO2 and Epoxides under Mild Conditions†
- Pages: 3574-3577
- First Published: 29 June 2004
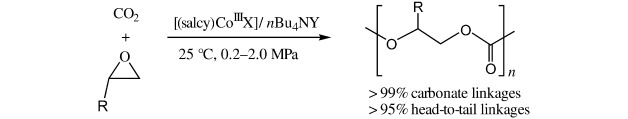
Excellent activity and selectivity in the copolymerization of CO2 with epoxides at extremely mild temperature and pressure are observed in the presence of binary nucleophile–electrophile catalyst systems based on chiral [(salcy)CoIIIX] complexes and quaternary ammonium salts (see scheme). Completely alternating copolymers are obtained with >95 % head-to-tail linkages.
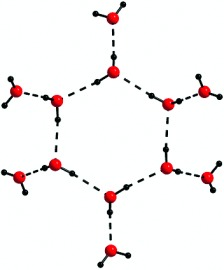
A Dodecameric Water Cluster Built around a Cyclic Quasiplanar Hexameric Core in an Organic Supramolecular Complex of a Cryptand†
- Pages: 3577-3580
- First Published: 29 June 2004
A Straightforward and Mild Synthesis of Functionalized 3-Alkynoates†
- Pages: 3580-3582
- First Published: 29 June 2004
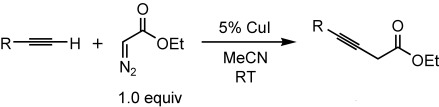
Diazoacetates in coupling reactions: CuI serves as an effective catalyst for coupling terminal alkynes with diazo compounds to generate 3-alkynoates (see scheme). This method is efficient (1:1 ratio of reactants), mild (room temperature), and simple (no additional ligand), and a range of functional groups are tolerated (e.g., CC double bonds, heteroatoms, and hydroxy groups).
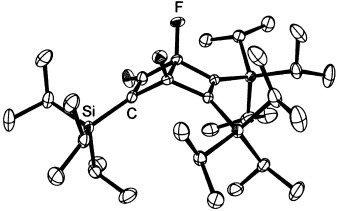
Crystal Structure of a Dewar Benzene Derivative Formed from Fluoro(triisopropylsilyl)acetylene†
- Pages: 3582-3584
- First Published: 29 June 2004
Cyclometalated Ruthenium(II) Complexes as Highly Active Transfer Hydrogenation Catalysts†
- Pages: 3584-3588
- First Published: 29 June 2004
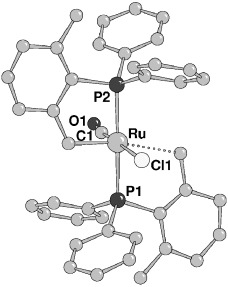
Quantitative conversion: Reaction of the 14-electron complex [RuCl2{(2,6-Me2C6H3)PPh2}2] with CH2O in the presence of NEt3 gave a five-coordinate cyclometalated complex with a δ-agostic interaction of one ortho-methyl group (see X-ray crystal structure). Displacement of one phosphane group with 2-(aminomethyl)pyridine gave a highly active catalyst for the quantitative conversion of ketones into alcohols.
An Unusually Fast Nucleophilic Aromatic Displacement Reaction: The Gas-Phase Reaction of Fluoride Ions with Nitrobenzene†
- Pages: 3588-3590
- First Published: 29 June 2004
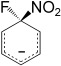
Quick reactions: The gas-phase nucleophilic displacement reaction of fluoride ions with nitrobenzene proceeds with a rate constant close to the collision limit. The calculated energy profile indicates that the reaction proceeds by an out-of-plane attack, with the Meisenheimer complex being the local transition state for the reaction (see picture).
Design of a Sequence-Specific DNA Bisintercalator†
- Pages: 3591-3594
- First Published: 29 June 2004
Preparation and Reactivity of 1,3,5,7-Tetrakis[4-(diacetoxyiodo)phenyl]adamantane, a Recyclable Hypervalent Iodine(III) Reagent†
- Pages: 3595-3598
- First Published: 29 June 2004
![Preparation and Reactivity of 1,3,5,7-Tetrakis[4-(diacetoxyiodo)phenyl]adamantane, a Recyclable Hypervalent Iodine(III) Reagent](/cms/asset/0f2c9472-d607-4665-89c2-189fedd5b6cd/mcontent.jpg)
A wide range of oxidative reactions are mediated by novel, nonpolymeric, and recyclable hypervalent IIII reagents (e.g. 2). In all cases, tetraiodide 1 was recovered nearly quantitatively in pure form after a simple workup. Reoxidation of 1 to 2 with m-chloroperbenzoic acid also proceeded quantitatively, without loss of oxidative activity.
A Novel Tin-Free Procedure for Alkyl Radical Reactions†
- Pages: 3598-3601
- First Published: 29 June 2004
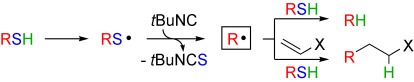
Desulfuration as a source of alkyl radicals: The addition of alkylsulfanyl radicals to isocyanides gives the corresponding alkyl radicals. This methodology can replace the usual tin-mediated radical procedures and allows for the generation of tertiary, secondary, and even nonstabilized primary radicals that can be used efficiently in reductive defunctionalizations and intermolecular additions to electron-rich olefins (see scheme).
Total Synthesis of the Salicylate Enamide Macrolide Oximidine III: Application of Relay Ring-Closing Metathesis†
- Pages: 3601-3605
- First Published: 29 June 2004
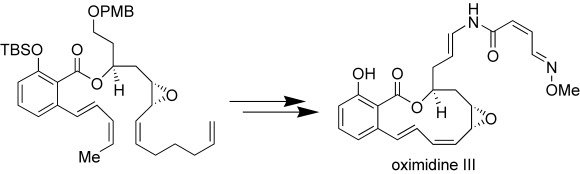
The vacuolar-type (H+)-adenosine triphosphatase inhibitor oximidine III and its enamide and epoxide stereoisomers have been synthesized enantioselectively. A relay ring-closing metathesis (RCM) strategy was employed to facilitate the macrocyclization of a well-defined substrate possessing two differentially functionalized RCM alkene partners (see scheme).
Palladium-Catalyzed Synthesis of N-Aryl Pyrrolidines from γ-(N-Arylamino) Alkenes: Evidence for Chemoselective Alkene Insertion into PdN Bonds†
- Pages: 3605-3608
- First Published: 29 June 2004
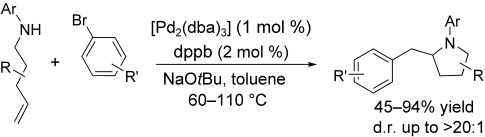
The formation of a CC and a CN bond in a reaction between γ-(N-arylamino) alkenes and aryl bromides results in the stereoselective synthesis of substituted pyrrolidine derivatives (see scheme). Preliminary studies suggest these reactions proceed by intramolecular alkene insertion into the PdN bond of intermediate [Pd(Ar)(amido)] complexes. dba=dibenzylideneacetone, dppb=1,3-bis(diphenylphosphanyl)butane.