Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Titelbild
Titelbild: PI by NMR: Probing CH–π Interactions in Protein–Ligand Complexes by NMR Spectroscopy (Angew. Chem. 35/2020)
- Page: 14805
- First Published: 20 July 2020

Die CH-π-Wechselwirkungen zwischen den CH-Donorgruppen von Trp81-ζ und Trp81-η mit den aromatischen π-Systemen von Ligand 3 (dargestellt in blau bzw. grün) werden im Titelbild illustriert. Der Hintergrund zeigt eine Skala der chemischen Verschiebung, in welche die CH-Kreuzpeaks von Trp81 eingezeichnet sind. In komplexierter Form werden die CH-Gruppen um bis zu 2.3 ppm verschoben, da sie von den aromatischen Ringsystemen des Liganden abgeschirmt werden. Wie G. Platzer, M. Mayer et al. in ihrem Forschungsartikel auf S. 14971 erläutern, zeigen die Hochfeldverschiebungen günstige CH-π-Wechselwirkungen an, die mit anderen Methoden in Lösung schwer nachweisbar sind.
Innentitelbild: Comprehensive and High-Throughput Exploration of Chemical Space Using Broadband 19F NMR-Based Screening (Angew. Chem. 35/2020)
- Page: 14806
- First Published: 04 August 2020

19F-NMR-basiertes Fragmentscreening ist ein effektiver Ansatz in der pharmazeutischen Forschung zur Untersuchung des chemischen Substanzraums für spezifische Target-Ligand-Wechselwirkungen. In ihrem Forschungsartikel auf S. 14919 berichten A. Lingel, A. O. Frank et al. über die Entwicklung von NMR-Pulsen, die das gesamte Spektrum der Fluor-chemischen Verschiebung in einem einzelnen Experiment abdecken. Die neue Methode erlaubt den effizienten Aufbau diversifizierter Fragmentbibliotheken, die innerhalb weniger Tage auf qualitativ hochwertige Treffer gescreent werden können.
Innenrücktitelbild: Reversible Luminescent Switching in an Organic Cocrystal: Multi-Stimuli-Induced Crystal-to-Crystal Phase Transformation (Angew. Chem. 35/2020)
- Page: 15379
- First Published: 20 July 2020

Die Kristall-zu-Kristall-Phasenumwandlung organischer Kokristalle unter verschiedenen externen Stimuli – wie Lösungsmitteldampf und Erwärmen – wird von einer reversiblen Lumineszenzänderung begleitet, wie B. Xu et al. in ihrer Zuschrift auf S. 15210 demonstrieren. Die Ergebnisse zeigen, dass die Lumineszenzänderung auf die einzigartige Umlagerung einer durch Wasserstoff-/Halogenbrücken erzeugten Stapelung zu einer von π-π-Wechselwirkungen abhängigen Stapelung als Antwort auf einen externen Stimulus zurückgeht.
Rücktitelbild: Hydrothermale Synthese von konjugierten Polymeren am Beispiel von Pyrronpolymeren und Polybenzimidazolen (Angew. Chem. 35/2020)
- Page: 15380
- First Published: 20 July 2020

Ein Wechsel der Perspektive kann überraschende Einblicke bieten. Wasser wird ein effektives Medium für die Synthese von hoch aromatischen Verbindungen, wenn man es auf hohe Temperaturen erhitzt. In ihrem Forschungsartikel auf S. 15160 berichten M. M. Unterlass et al. über die hydrothermale Synthese von zwei Klassen hoch konjugierter organischer Polymere – Polybenzimidazolen und Pyrron-Polymeren. Das Titelbild zeigt eine Abstraktion einer Wasseroberfläche, die aus unterschiedlichen Winkeln und Abständen betrachtet unterschiedlich aussieht; dies illustriert, dass flüssiges Hochtemperaturwasser ein leistungsfähiges Medium für Transformationen wird, die bei Raumtemperatur nicht möglich wären.
Frontispiz
Frontispiz: Revisiting the Polymerization of Diphenylacetylenes with Tungsten(VI) Chloride and Tetraphenyltin: An Alternative Mechanism by a Metathesis Catalytic System
- First Published: 17 August 2020
Polymerisation Die Polymerisation von Diphenylacetylenen mit einem WCl6/Ph4Sn-Katalysatorsystem wird von T. Taniguchi, K. Maeda et al. im Forschungsartikel auf S. 14882 beschrieben. Die Polymerisation wird durch die Addition einer Phenylgruppe von Ph4Sn an Diphenylacetylen initiiert.
Graphisches Inhaltsverzeichnis
Graphisches Inhaltsverzeichnis: Angew. Chem. 35/2020
- Pages: 14809-14831
- First Published: 17 August 2020
Berichtigungen
Berichtigung: Synthesis of Biaryl-Bridged Cyclic Peptides via Catalytic Oxidative Cross-Coupling Reactions
- Page: 14831
- First Published: 17 August 2020
Zurückziehung
Zurückziehung: The Manganese(I)-Catalyzed Asymmetric Transfer Hydrogenation of Ketones: Disclosing the Macrocylic Privilege
- Page: 14831
- First Published: 17 August 2020
Autoren-Profil
Kurzaufsätze
Polymerization
Early Transition Metal Catalysis for Olefin–Polar Monomer Copolymerization
- Pages: 14834-14843
- First Published: 27 January 2020
Catalyst design: This Minireview summarizes the recent progress in early transition metal polymerization catalyst development, categorized by the catalytic metal complex and polar comonomer identity. Advances in the mechanistic understanding of these polymerizations are discussed, focusing on critical challenges and strategies that mitigate them.
Electrocatalysis
Stability and Degradation Mechanisms of Copper-Based Catalysts for Electrochemical CO2 Reduction
- Pages: 14844-14854
- First Published: 18 March 2020
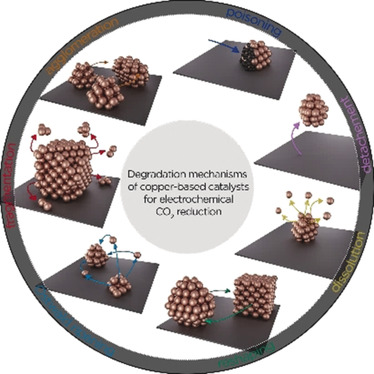
The CO2 electroreduction reaction has recently gained in popularity. Cu is still the only monometallic catalyst that can effectively produce interesting molecules, such as hydrocarbons and alcohols. Many breakthroughs have been on the so-called structure–activity/selectivity relationships. However, the stability of Cu-based electrodes and nanoscale degradation mechanisms are still in their infancy.
Aufsätze
Goldchemie
Excimer- und Exciplex-Bildung in durch aurophile Wechselwirkungen präkonditionierten Gold(I)- Komplexen
- Pages: 14856-14881
- First Published: 05 February 2020
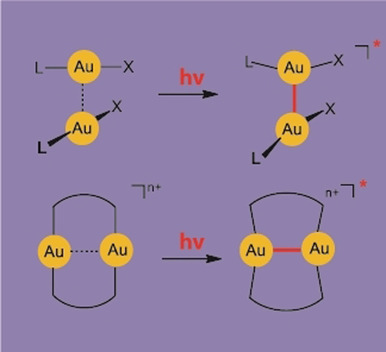
Bindungsbildung im angeregten Zustand: Linear zweifach koordinierte Gold(I)-Komplexe bilden durch seitlich orientierte aurophile Wechselwirkungen Aggregate aus, deren schwache Au-Au-Kontakte durch UV-Bestrahlung verstärkt werden, ersichtlich an einer Verkürzung des Au-Au-Abstands und veränderter Absorptions- und Emissions-Charakteristika. Die veränderten Redoxpotentiale machen die [AuI−AuI]*-Excimere zu reaktiven Intermediaten für die Photoredoxkatalyse.
Forschungsartikel
Polymerization | Very Important Paper
Revisiting the Polymerization of Diphenylacetylenes with Tungsten(VI) Chloride and Tetraphenyltin: An Alternative Mechanism by a Metathesis Catalytic System
- Pages: 14882-14890
- First Published: 25 May 2020
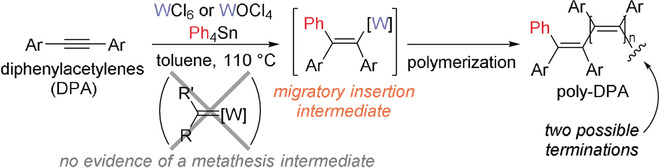
A migratory insertion mechanism has been proposed for the polymerization of diphenylacetylenes by a classic metathesis catalytic system composed of tungsten(VI) chloride (WCl6 or WOCl4) and Ph4Sn. The polymerization is initiated by addition of a phenyl group coming from Ph4Sn to diphenylacetylene monomers and has two possible termination processes.
Functional Materials
Three-Step Spin State Transition and Hysteretic Proton Transfer in the Crystal of an Iron(II) Hydrazone Complex
- Pages: 14891-14897
- First Published: 25 May 2020
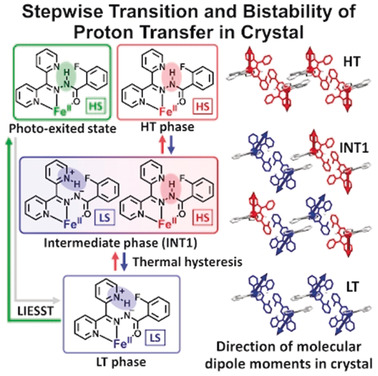
Coupled complex: A novel crystalline proton–electron coupling system was developed using an iron(II) hydrazone complex. The complex exhibits a thermally and photoinduced proton-transfer-coupled spin transition. The intermediate phase has two types of iron(II) complexes with distinct spin states and proton positions. The proton transfer in one of the two ligands changes the direction and magnitude of the molecular dipole moment.
Structural Biology | Hot Paper
Haruspex: A Neural Network for the Automatic Identification of Oligonucleotides and Protein Secondary Structure in Cryo-Electron Microscopy Maps
- Pages: 14898-14905
- First Published: 18 March 2020
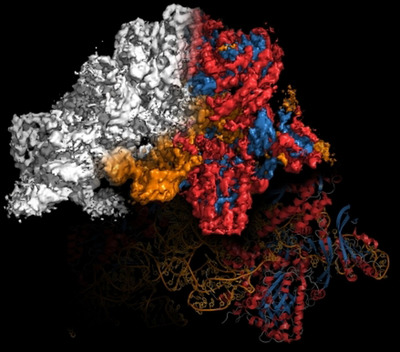
Haruspex is a new tool to identify secondary structure and RNA/DNA in cryo-EM reconstruction maps. It uses a neural network which has been trained on a carefully curated set of 293 experimentally derived reconstructions and can be straightforwardly applied to newly reconstructed maps to support model building and validation.
Chemical Protein Synthesis
Efficient Chemical Protein Synthesis using Fmoc-Masked N-Terminal Cysteine in Peptide Thioester Segments
- Pages: 14906-14911
- First Published: 25 April 2020
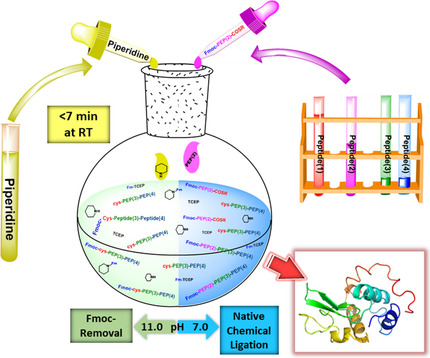
All in one: Highly efficient multisegment native chemical ligation (NCL) has been developed by exploiting the Fmoc group to temporarily mask the N-terminal Cys of the peptide thioester fragments. Fmoc removal and NCL are achieved in the same reaction mixture through pH adjustments in presence of 20 % piperidine. The simplicity and inherent robustness of this method make it an attractive approach for the high-yielding total synthesis of proteins.
Solar Water Splitting
A Stable Integrated Photoelectrochemical Reactor for H2 Production from Water Attains a Solar-to-Hydrogen Efficiency of 18 % at 15 Suns and 13 % at 207 Suns
- Pages: 14912-14918
- First Published: 25 May 2020
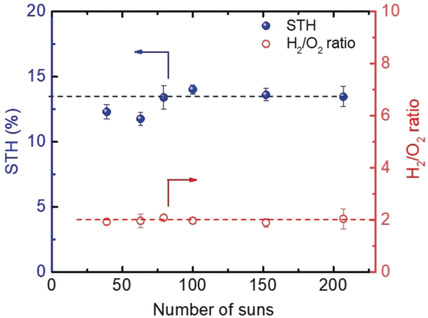
A photoelectrochemical reactor comprised of a III-V-based photovoltaic cell integrated with nickel foil as an O2 evolving catalyst achieves a solar-to-hydrogen (STH) efficiency of 18.3 % at low light concentration without optical lenses. An STH efficiency of 13 % is attained at high light concentration with optical lenses. A 100 hour test at 100–200 suns showed no degradation or deviation from product stoichiometry (H2/O2=2).
NMR Spectroscopy | Hot Paper
Comprehensive and High-Throughput Exploration of Chemical Space Using Broadband 19F NMR-Based Screening
- Pages: 14919-14927
- First Published: 03 May 2020
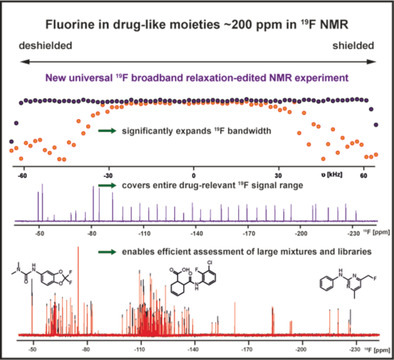
A new, universal 19F broadband relaxation-edited NMR experiment enables fast screening of the entire drug-relevant fluorine chemical shift range for distinct hit molecules in a single measurement. It further facilitates the efficient generation and evaluation of large, chemically diverse compound libraries and expedites the ligandability assessment of any macromolecular target.
Photocatalysis
Homogeneous Molecular Iron Catalysts for Direct Photocatalytic Conversion of Formic Acid to Syngas (CO+H2)
- Pages: 14928-14934
- First Published: 06 May 2020
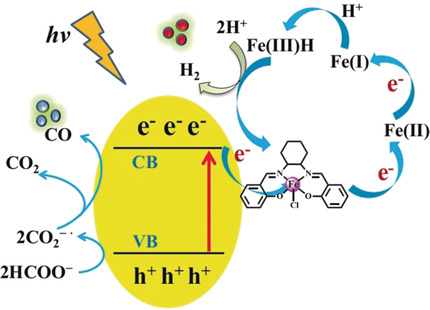
Photocatalytic syngas production: The use of homogeneous molecular iron catalysts combined with a CdS nanorods (NRs) semiconductor creates a novel photocatalytic system for direct conversion of formic acid to syngas at room temperature and atmospheric pressure. These catalysts demonstrate remarkable enhancement in CO evolution with robust stability.
Rotaxanes
Precision Molecular Threading/Dethreading
- Pages: 14935-14944
- First Published: 12 May 2020
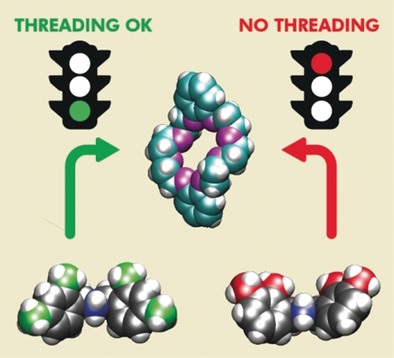
Fine mechanics: A systematic experimental and computational study explains why tiny structural changes in the extremities of a molecular axle can allow or prevent its insertion in the cavity of a macrocycle. These results provide guidelines to design interlocked molecules with predetermined dynamic features, that can be used to make nanostructured machines, motors and materials.
Heterogeneous Catalysis | Hot Paper
A Physical Model for Understanding the Activation of MoS2 Basal-Plane Sulfur Atoms for the Hydrogen Evolution Reaction
- Pages: 14945-14951
- First Published: 18 May 2020
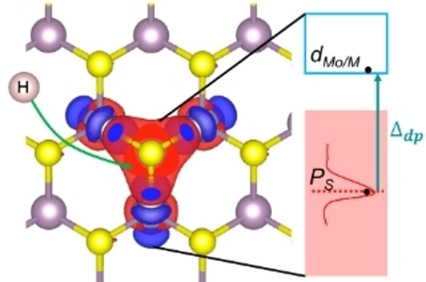
That′s dope! The energy cost of moving an electron from sulfur to its neighboring metal atoms can predict the trend in hydrogen-binding strengths in MoS2 and its doped variants. An electronic-structure-based descriptor for the hydrogen-binding strength allows to understand these trends: Δdp, the local interband energy separation between the lowest empty d-states on the dopant metal atoms and occupied p-states on sulfur.
Adoptive Immunotherapy | Hot Paper
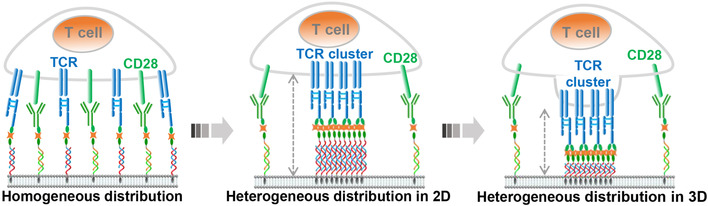
DNA-Edited Ligand Positioning on Red Blood Cells to Enable Optimized T Cell Activation for Adoptive Immunotherapy
- Pages: 14952-14963
- First Published: 12 May 2020
Macrocycles | Hot Paper
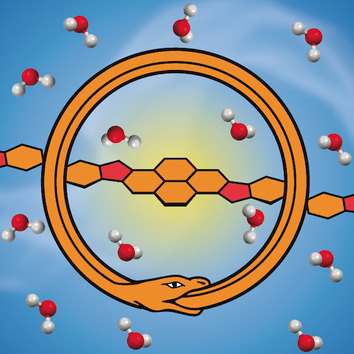
Toward Möbius and Tubular Cyclopolyarene Nanorings via Arylbutadiyne Macrocycles
- Pages: 14964-14970
- First Published: 20 May 2020
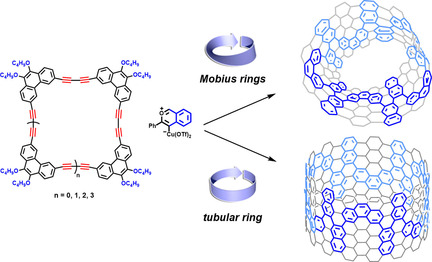
Round round get around: A highly efficient metal-catalyzed tandem cycloaddition reaction enables benzannulation to access cyclopolyarene nanorings of varied sizes from poly(arylene-butadiynylene) macrocyclic precursors. Unique Möbius topology is manifested by the cyclopolyarene nanorings composed of an odd number of repeat units, whereas cylindrical tubular structures with radial conjugation are formed with an even number of repeat units.
NMR Spectroscopy | Hot Paper
PI by NMR: Probing CH–π Interactions in Protein–Ligand Complexes by NMR Spectroscopy
- Pages: 14971-14978
- First Published: 18 May 2020
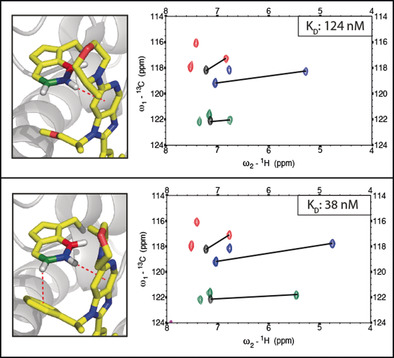
CH–π interactions are crucial determinants for the affinity of arguably every drug molecule. PI by NMR can differentiate the strength of protein–ligand CH–π interactions in solution. By combining selective amino-acid side-chain labeling with 1H-13C NMR, CH–π interactions can be identified based solely on 1H chemical shift values. This information serves as a proxy for the strength of each individual CH–π interaction.
Lithium Metal Batteries
Fluorinated Aromatic Diluent for High-Performance Lithium Metal Batteries
- Pages: 14979-14986
- First Published: 19 May 2020
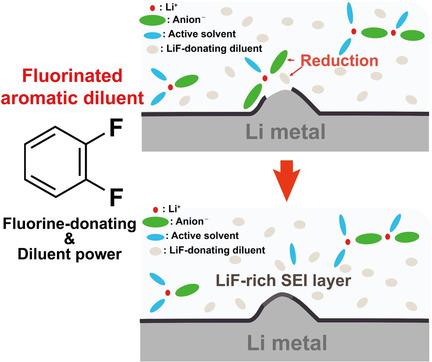
1,2-Difluorobenzene serves as an electrolyte diluent to realize the high-concentration effect in lithium metal batteries even at a bulk salt concentration near 2 m. The incorporation of this diluent also induces an anion-associated lithium solvation structure to passivate lithium metal with a LiF-rich solid-electrolyte-interphase (SEI) layer, thereby resulting in superior cyclability.
Gas Purification | Very Important Paper
Molecularly Engineered 6FDA-Based Polyimide Membranes for Sour Natural Gas Separation
- Pages: 14987-14993
- First Published: 04 May 2020
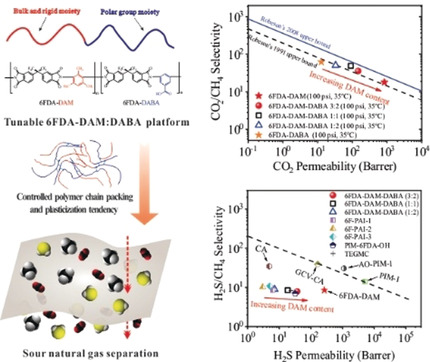
No need to be sour: CO2/CH4 and H2S/CH4 separation performance of glassy polyimide membranes can be tailored by finely tuning the DAM:DABA ratio in the 6FDA-DAM:DABA polyimide backbone. This facile tunability is attractive for their applications for challenging sour gas separation (that is, methane contaminated with undesirable acid gases (CO2 and H2S)) across a spectrum of feed compositions.
Olefin Polymerization
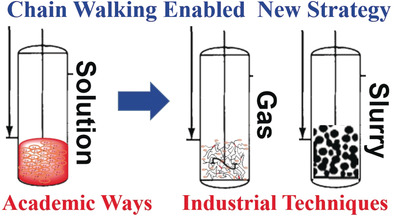
A Self-Supporting Strategy for Gas-Phase and Slurry-Phase Ethylene Polymerization using Late-Transition-Metal Catalysts
- Pages: 14994-15000
- First Published: 17 May 2020
Polycycles
Unveiling 79-Year-Old Ixene and Its BN-Doped Derivative
- Pages: 15001-15005
- First Published: 14 May 2020
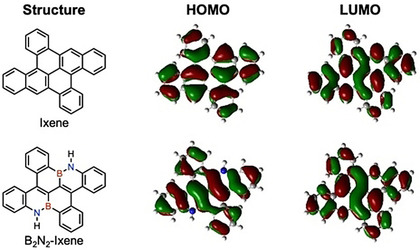
A forgotten curiosity: Ixene, a compound that was previously named but never prepared, and its BN-doped derivative (B2N2-ixene) were synthesized in two steps from simple intermediates. The effect of BN-doping, or substitution of carbon–carbon bonds with isoelectronic boron–nitrogen bonds, was elucidated both experimentally and theoretically.
X-Ray Detection | Hot Paper
Centimeter-Sized Single Crystal of Two-Dimensional Halide Perovskites Incorporating Straight-Chain Symmetric Diammonium Ion for X-Ray Detection
- Pages: 15006-15012
- First Published: 20 May 2020
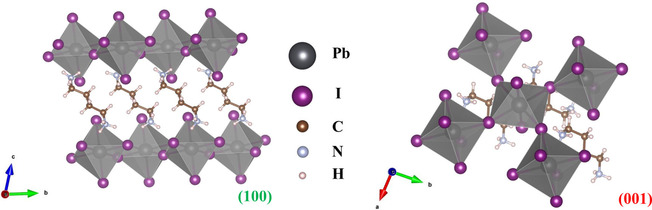
Crystal clear: Reported here is the synthesis of a centimeter-sized AA′n−1MnX3n+1 type perovskite, BDAPbI4 (BDA=NH3C4H8NH3), single crystal and its charge-transport properties under X-ray excitation. The crystal shows a staggered configuration of the [PbI6]4− layers, a band gap of 2.37 eV, and a low trap density of 3.1×109 cm−3. These crystals are promising candidates for the next generation of optoelectronic devices.
Aggregation-Induced Emission
Direct Observation of Aggregation-Induced Emission Mechanism
- Pages: 15013-15019
- First Published: 22 May 2020
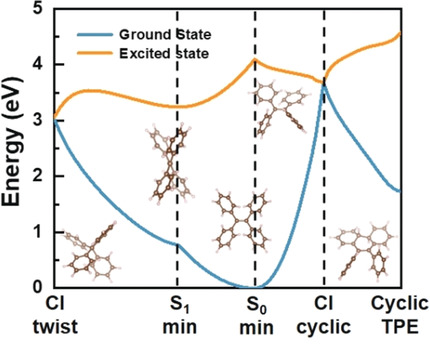
The mechanism of aggregation-induced emission is revealed by monitoring real time structural evolution and dynamics of the electronic excited state. The formation of Woodward–Hoffmann cyclic intermediates as nonradiative relaxation pathway is observed in dilute solutions of tetraphenylethylene upon ultraviolet excitation. In solid state, the electronic excitation is preserved, and the molecule fluoresces efficiently.
Radical Polymerization | Hot Paper
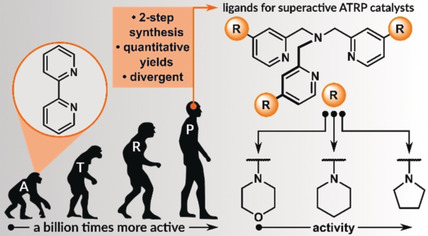
p-Substituted Tris(2-pyridylmethyl)amines as Ligands for Highly Active ATRP Catalysts: Facile Synthesis and Characterization
- Pages: 15020-15030
- First Published: 16 May 2020
C−H Activation
Fluctuating Storage of the Active Phase in a Mn-Na2WO4/SiO2 Catalyst for the Oxidative Coupling of Methane
- Pages: 15031-15036
- First Published: 04 May 2020
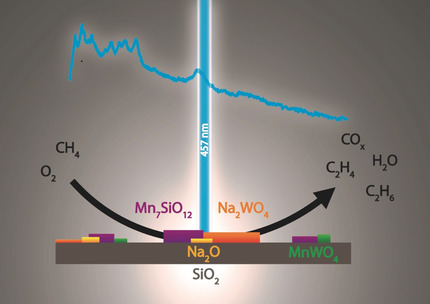
Give and take: Operando Raman spectroscopy in combination with in situ XRD and thermal analysis was applied to study a Mn-Na2WO4/SiO2 catalyst at work during the oxidative coupling of methane. Melting of Na2WO4 and Mn7SiO12-MnWO4 redox chemistry occur simultaneously, thereby enabling the transient release and storage of active sodium oxide species. Coupling of these processes is essential to avoid catalyst deactivation.
Dyes
Perylene-Fused, Aggregation-Free Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons for Solution-Processed Distributed Feedback Lasers
- Pages: 15037-15044
- First Published: 25 May 2020
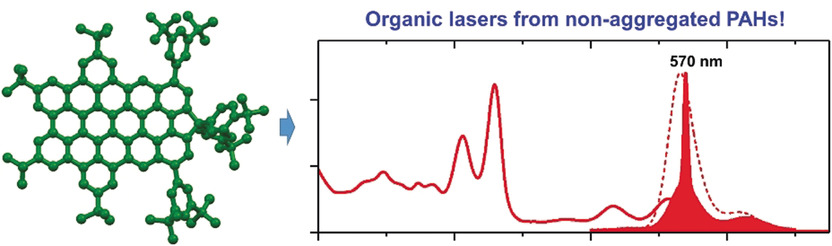
Novel organic lasers were fashioned from large, aggregation-free polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs. Several new perylene-based PAHs were prepared that show perylene-like electronic properties with moderate fluorescence quantum yields. Two of them show amplified spontaneous emission, and solution-processed distributed feedback lasers were successfully fabricated.
Surface Analysis | Hot Paper
Synergistic Dual-Additive Electrolyte Enables Practical Lithium-Metal Batteries
- Pages: 15045-15051
- First Published: 15 May 2020
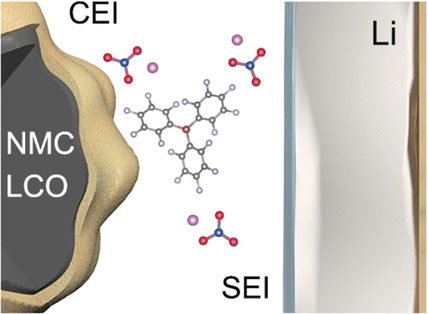
It's electric: An advanced dual-additive electrolyte containing a unique solvation structure comprising tris(pentafluorophenyl)-based additives and LiNO3 in a carbonate-based electrolyte is reported. It can generate a robust outer Li2O solid electrolyte interface (SEI) and a F- and B-containing conformal cathode electrolyte interphase (CEI), thus realizing a stable cell operation when E/C and the N/P ratio decrease to 3.4 g Ah−1 and 2.28, respectively.
Nanotechnology | Hot Paper
Rapid Capillary-Assisted Solution Printing of Perovskite Nanowire Arrays Enables Scalable Production of Photodetectors
- Pages: 15052-15059
- First Published: 11 May 2020
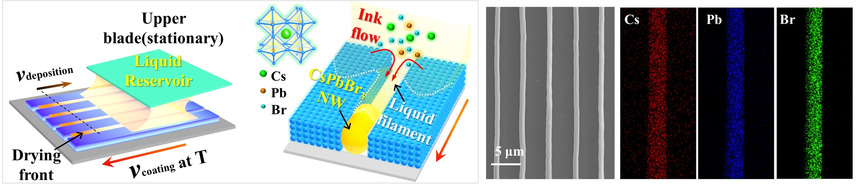
Down to the nanowire: A convenient, rapid, and robust capillary-assisted solution printing (CASP) strategy, which combines nanochannel-enabled, capillary-guided assembly with moving substrate-facilitated printing, yields a perovskite nanowire array with excellent optoelectronic properties for photodetectors.
Methyltransferases
Engineering Orthogonal Methyltransferases to Create Alternative Bioalkylation Pathways
- Pages: 15060-15066
- First Published: 13 May 2020
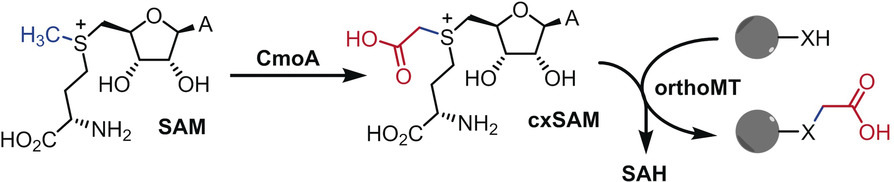
Methyltransferase enzymes (MTs) selectively deliver methyl substituents to an array of molecules, thereby controlling gene expression or modulating the bioactivity of therapeutically important natural products. A MT was engineered for selective carboxy(m)ethylation to give an orthogonal MT that was combined with the SAM-derivatising enzyme CmoA to create new carboxymethylation pathways.
Protein Delivery
Protein and mRNA Delivery Enabled by Cholesteryl-Based Biodegradable Lipidoid Nanoparticles
- Pages: 15067-15074
- First Published: 21 May 2020
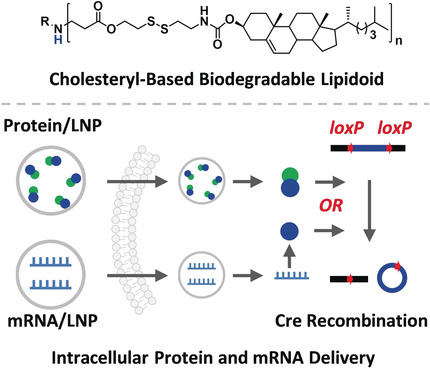
Intracellular delivery: a new combinatorial library of cholesteryl-based and reduction-responsive lipidoid nanoparticles can deliver genome engineering protein and mRNA molecules in vitro and in vivo. Using adult Ai14 mouse model, successful Cre-mediated gene recombination events were observed in skeletal muscle, brain, lung, and spleen through the local and systemic administrations.
Drug Discovery | Hot Paper
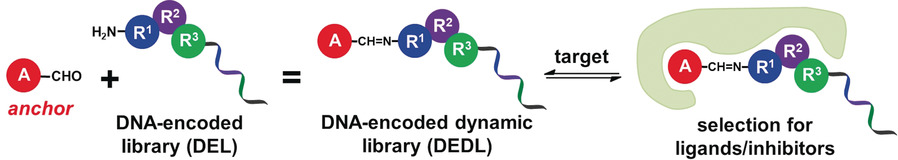
Selection of DNA-Encoded Dynamic Chemical Libraries for Direct Inhibitor Discovery
- Pages: 15075-15082
- First Published: 20 May 2020
DNA Nanotechnology
Harnessing Effective Molarity to Design an Electrochemical DNA-based Platform for Clinically Relevant Antibody Detection
- Pages: 15083-15088
- First Published: 11 May 2020
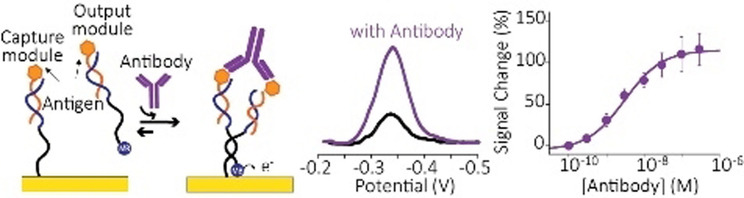
Sensing in close quarters: A nucleic acid-based electrochemical platform able to measure levels of immunoglobulins of type G and E (IgG and IgE) directly in blood serum and other bodily fluids was developed. The antibody detection exploits effective molarity effects that are induced by the spatial confinement of electrochemically active DNA-based sensing modules at the nanoscale.
DNA Nanotechnology | Hot Paper
Fuzzy DNA Strand Displacement: A Strategy to Decrease the Complexity of DNA Network Design
- Pages: 15089-15095
- First Published: 12 May 2020
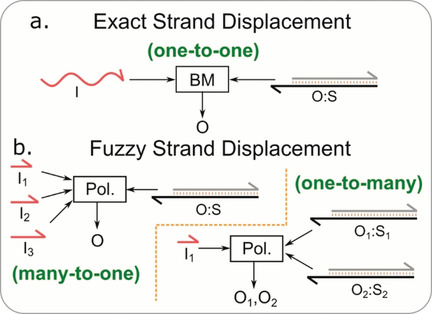
Less is more: Toehold-mediated strand displacement has been used to produce dynamic DNA nanostructures and networks; however, the complexity of sequence design dramatically increases as the size and complexity of the DNA network increases. Fuzzy strand displacement allows a single input strand to displace multiple substrate strands and multiple input strands to displace a single substrate strand, reducing the complexity of DNA-sequence design.
Photocatalysis
Photocatalytic α-Tertiary Amine Synthesis via C−H Alkylation of Unmasked Primary Amines
- Pages: 15096-15101
- First Published: 11 May 2020
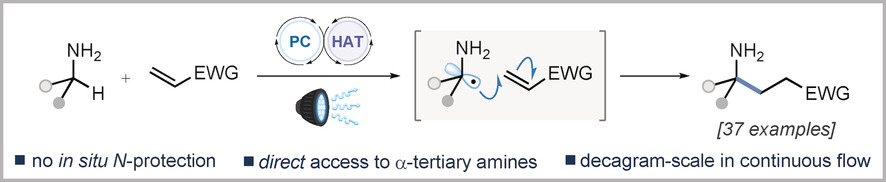
Catalytic strategies for the α-C−H functionalisation of primary amines are a major challenge in organic synthesis. A photocatalytic protocol for the α-C−H alkylation of unprotected primary amines that is amenable to the direct synthesis of α-tertiary primary amines is reported. This process is readily scalable in continuous flow to provide access to decagram quantities of valuable γ-lactams and azaspirocycles, for application in drug discovery.
Predictive Models
A Predictive Model Towards Site-Selective Metalations of Functionalized Heterocycles, Arenes, Olefins, and Alkanes using TMPZnCl⋅LiCl
- Pages: 15102-15109
- First Published: 12 May 2020
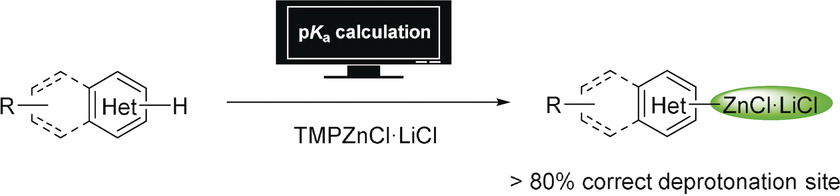
Metalation site prediction: The use of simple pKa calculations allowed a reliable prediction of metalation sites in various heterocycles, arenes, olefins, and alkanes, employing the mild base TMPZnCl⋅LiCl. Using this predictive model, also unexplored N-heterocycles were investigated, and the obtained deprotonation sites rationalized readily.
Photocatalysis
A Blinking Mesoporous TiO2−x Composed of Nanosized Anatase with Unusually Long-Lived Trapped Charge Carriers
- Pages: 15110-15117
- First Published: 22 May 2020
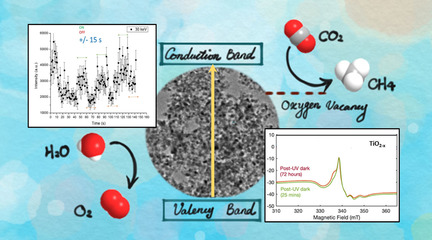
A blinking mesoporous TiO2−x is composed of small, crystalline, vacancy-rich anatase nanoparticles. It shows unique optical, thermal, electronic, and photocatalytic properties. The nanoparticles continuously light up and fade away for an extended period of time under an electron beam. They also show long-lived charge carriers (trapped electrons and holes) at room temperature in the dark, even long (30 min) after UV irradiation.
Fullerenes
Studying Natural Buckyballs and Buckybowls in Fossil Materials
- Pages: 15118-15123
- First Published: 19 May 2020
The big bucks: A wide range of fullerenes (buckyballs; C30–C114) and their building blocks (buckybowls with a stoichiometry of C10xH10) were detected in heavy crude oil by ultrahigh-resolution mass spectrometry. Structural findings are supported by high-level calculations at the DLPNO-CCSD(T) level of theory, revealing for the first time the presence of fullerenes in low-energy fossil materials on a molecular level.
Electrocatalysis
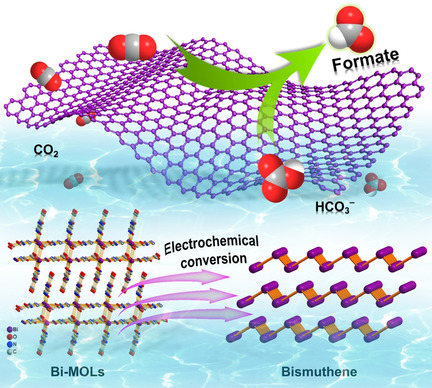
Metal–Organic Layers Leading to Atomically Thin Bismuthene for Efficient Carbon Dioxide Electroreduction to Liquid Fuel
- Pages: 15124-15130
- First Published: 18 May 2020
Olefin Functionalization | Hot Paper
Photoinduced Olefin Diamination with Alkylamines
- Pages: 15131-15138
- First Published: 20 May 2020
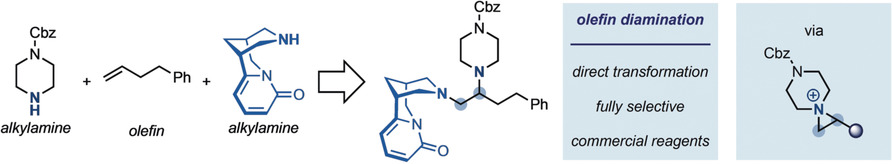
All in one: Direct olefin diamination with alkylamines was achieved by using a photoinduced radical-to-polar crossover strategy. This approach enables the programmable and sequential addition of complex amine building blocks across olefins in a single chemical transformation. This operationally simple process has broad functional-group compatibility and enables the use of advanced building blocks for the preparation of drug-like small molecules.
Enzymatic Release
Magnetic Micromotors for Multiple Motile Sperm Cells Capture, Transport, and Enzymatic Release
- Pages: 15139-15147
- First Published: 11 May 2020
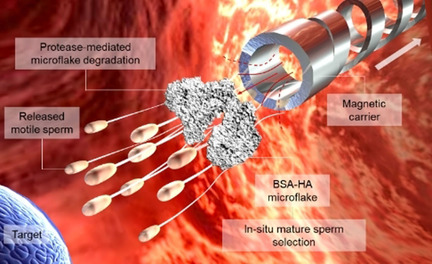
A cluster of motile and mature sperm previously immobilized on the BSA-HA microflake is transported by a magnetically-driven microhelix, which delivers the sperm-loaded microflake close to the area of interest. Due to the presence of local proteases, the microflake is then hydrolyzed allowing the sperm release to finally reach the target location.
DNA Nanotechnology
DNA-Based Adaptive Plasmonic Logic Gates
- Pages: 15148-15152
- First Published: 14 May 2020
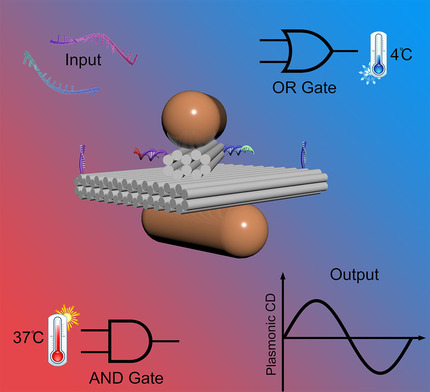
Logic gates that read DNA molecules and return plasmonic chiroptical signals are presented. They are achieved on a DNA-based platform that can direct the conformation of two gold nanorods. With delicate designs, the logic gates can operate in an adaptive manner, namely, they perform as AND gates at body temperature while as OR gates at cold storage temperature.
Organic Solar Cells
Triplet Acceptors with a D-A Structure and Twisted Conformation for Efficient Organic Solar Cells
- Pages: 15153-15159
- First Published: 08 May 2020

Triplet materials are designed by introducing heavy atoms to enhance spin–orbit coupling or constructing donor and acceptor units with a twisted conformation to reduce ΔEST. However, the twisted materials have not been applied in solar cells due to weak absorption and low charge-transport mobilities. Now two nonplanar acceptors with large π-conjugated core were constructed that achieved over 15 % efficiency.
Polymerchemie
Hydrothermale Synthese von konjugierten Polymeren am Beispiel von Pyrronpolymeren und Polybenzimidazolen
- Pages: 15160-15171
- First Published: 07 April 2020
Photokatalyse | Hot Paper
Kalium-Polyheptazinimid: Ein übergangsmetallfreier Festkörper-Triplett-Sensibilisator in Kaskadenenergietransfer und [3+2]-Cycloadditionen
- Pages: 15172-15180
- First Published: 15 May 2020
![Kalium-Polyheptazinimid: Ein übergangsmetallfreier Festkörper-Triplett-Sensibilisator in Kaskadenenergietransfer und [3+2]-Cycloadditionen](/cms/asset/686f08b9-4dda-4e6b-a8c1-960895ad873d/ange202004747-toc-0001-m.jpg)
Die angeregten Triplett-Zustände in einem neuen heterogenen Triplett-Sensibilisator, Kalium-Polyheptazinimid (K-PHI), können genutzt werden, um eine Kaskade von Energieübertragungsreaktionen auszulösen und z. B. Singulett-Sauerstoff (1O2), als Ausgangspunkt für die Synthese von N-reichen Heterozyklen, zu sensibilisieren. Auf diese Weise werden Aldoxime unter Bestrahlung mit sichtbarem Licht in Oxadiazole-1,2,4 umgewandelt.
Organokatalyse | Very Important Paper
Enantioselektive Synthese von 3-Fluorchromanen durch Iod(I)/Iod(III)-Katalyse
- Pages: 15181-15187
- First Published: 29 April 2020
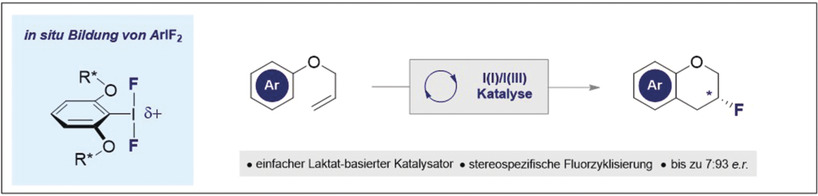
Eine Iod(I)/Iod(III)-katalysierte Strategie für den Zugang zu enantiomerenangereicherten 3-Fluorchromanen wird gezeigt. Die In-situ-Erzeugung von ArIF2 ermöglicht die direkte Fluorzyklisierung von Allylphenylethern, um neue Molekülgerüste aufzubauen, die den stereoelektronischen gauche-Effekt manifestieren. Mechanistische Untersuchungen mit deuterierten Substraten bestätigen einen stereospezifischen Prozess, der mit dem Reaktionsweg des Typs IIinv übereinstimmt.
Zuschriften
Elektrosynthese | Hot Paper
Rhodiumkatalysierte elektrooxidative C-H-Olefinierung von Benzamiden
- Pages: 15188-15192
- First Published: 29 April 2020
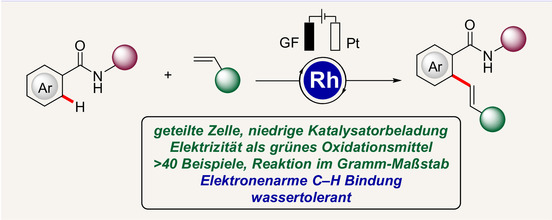
Die elektrooxidative C-H-Olefinierung von Amiden wird durch Rhodiumkatalyse ermöglicht. Die Olefinierung elektronenarmer Benzamide wurde unter elektrochemischen Bedingungen entwickelt und verläuft nach einem dehydrierenden Mechanismus mit H2 als einzigem Koppelprodukt. Die stöchiometrische Verwendung von chemischen Oxidationsmitteln wird dabei vermieden.
Energieumwandlung
Effiziente Umwandlung von Licht in chemische Energie: Gerichtete, chirale Photoschalter mit sehr hohen Quantenausbeuten
- Pages: 15193-15198
- First Published: 29 April 2020
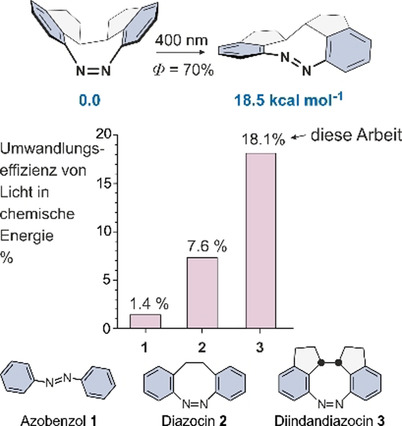
Lockdown von Azobenzol: Photoisomerisierbare Moleküle wie Azobenzol wandeln Licht direkt in chemische Energie, jedoch mit einer geringen Energieeffizienz um. Durch systematische Reduktion der konformationellen Flexibilität von Azobenzol und somit der Verhinderung von unproduktiven Reaktionspfaden wurde die Energieumwandlungseffizienz von 1.4 % auf 18.1 % erhöht. Dies ist die höchste bisher bekannte Effizienz aller photochromen Verbindungen.
Diradikaloide
Bildung Stabiler All-Silicium Varianten von 1,3-Cyclobutandiyl im Gleichgewicht
- Pages: 15199-15204
- First Published: 14 May 2020
Stabile homonukleare Tetrasila-1,3-cyclobutandiyl-Analoga wurden aus den Gleichgewichtsreaktionen eines Cyclotrisilens und gesättigter N-heterocyclischer Silylene (c-[(CR2CH2)(NtBu)2]Si: (R=H, Me)) erhalten. Festkörperstrukturen zeigen im Wesentlichen planare viergliedrige Si4-Ringsysteme. Trotz der großen Entfernung zwischen den formalen Radikalzentren deuten Berechnungen auf eine nicht unterstützte π-Bindung.
Cyclisierungen
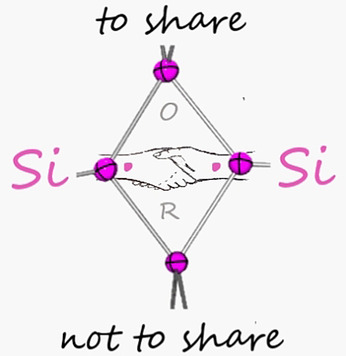
Polyether Natural Product Inspired Cascade Cyclizations: Autocatalysis on π-Acidic Aromatic Surfaces
- Pages: 15205-15209
- First Published: 17 March 2020
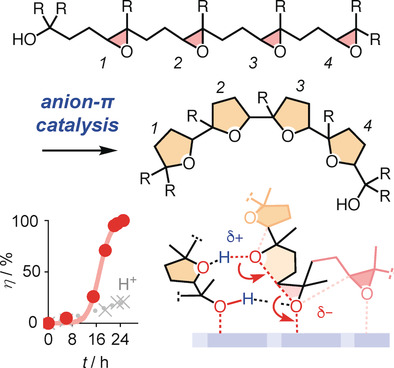
Der Traum von einer anionischen Version der Kation-π-katalysierten Steroidcyclisierung wird mit den Epoxidöffnungs-Ethercyclisierungen von Oligomeren realisiert. Verglichen mit konventionellen Katalysatoren erweist sich die Anion-π-Autokatalyse als schnell (Reaktionsbeschleunigung >104 m−1) und mechanistisch ausschlaggebend (Goldilocks-Profile) und bietet faszinierende Perspektiven.
Supramolecular Interactions | Hot Paper
Reversible Luminescent Switching in an Organic Cocrystal: Multi-Stimuli-Induced Crystal-to-Crystal Phase Transformation
- Pages: 15210-15215
- First Published: 14 April 2020
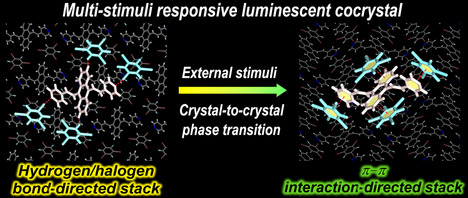
A luminescent cocrystal exhibits reversible luminescent switching, responding to THF-vapor/thermal stimuli and mechanical grinding. The crystal-to-crystal phase transition between two different cocrystal polymorphs under the external stimuli was demonstrated, enabling an in-depth understanding of the luminescent switching of organic luminescent materials.
Self-Assembly
Gas-Constructed Vesicles with Gas-Moldable Membrane Architectures
- Pages: 15216-15220
- First Published: 28 June 2019

Cooking with gas: CO2 gas and frustrated Lewis pair monomers can polymerize to form vesicles. Changing the gas used results in the formation of vesicles with distinct components, architectures, and morphologies. This introduces the use of gases to form nanomaterials and could be used to recycle industrial waste gases.
Electrochemistry | Hot Paper
Cycling a Lithium Metal Anode at 90 °C in a Liquid Electrolyte
- Pages: 15221-15225
- First Published: 19 May 2020
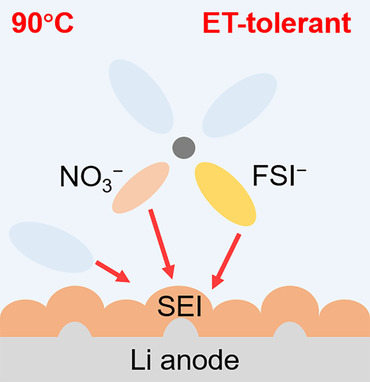
A Li metal anode working at 90 °C is demonstrated in a thermotolerant liquid electrolyte. The anode undergoes 100 cycles in a Li|LiFePO4 battery at 90 °C (10 cycles in a practical carbonate electrolyte). High operation temperature promotes independent and incomplete decomposition of Li salts and solvents to form a distinctive solid electrolyte interphase.
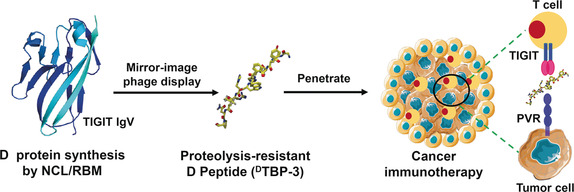
Immunotherapy | Very Important Paper
A Novel d-Peptide Identified by Mirror-Image Phage Display Blocks TIGIT/PVR for Cancer Immunotherapy
- Pages: 15226-15230
- First Published: 09 May 2020
Crystal Growth | Very Important Paper
Synthesis of NiO Crystals Exposing Stable High-Index Facets
- Pages: 15231-15235
- First Published: 17 April 2020
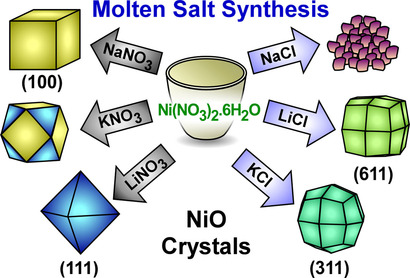
Getting into shape: The role of chloride, nitrate, and alkali ions during metal-oxide crystallization via molten salt routes has been thoroughly explored. It is shown that various ion combinations direct the NiO crystal morphology with nitrates acting as oxygen donors. Findings reveal the generation of unique high-index {311} facets in media containing Cl− and K+ ions.
Host–Guest Systems | Hot Paper
A Macrocycle Based on a Heptagon-Containing Hexa-peri-hexabenzocoronene
- Pages: 15236-15240
- First Published: 19 May 2020
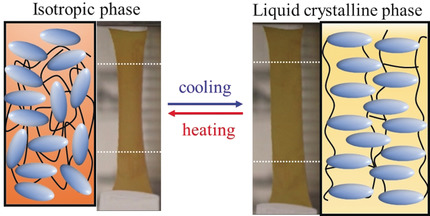
Shape Memory
A Novel Side-Chain Liquid Crystal Elastomer Exhibiting Anomalous Reversible Shape Change
- Pages: 15241-15246
- First Published: 25 May 2020
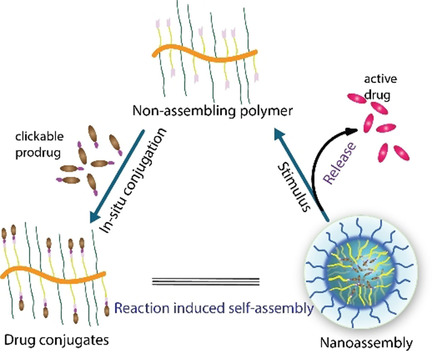
Drug Delivery
In Situ Formation of Polymeric Nanoassemblies Using an Efficient Reversible Click Reaction
- Pages: 15247-15252
- First Published: 14 May 2020
Crystal Growth
Precise Control Over Kinetics of Molecular Assembly: Production of Particles with Tunable Sizes and Crystalline Forms
- Pages: 15253-15258
- First Published: 20 May 2020
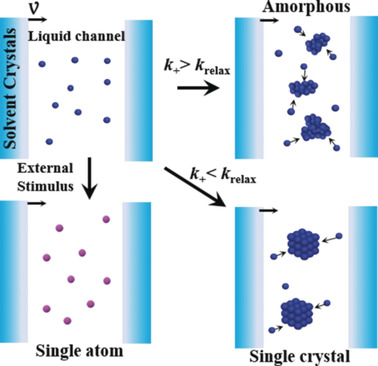
In control: Solute molecules are assembled in the microchannel between solvent crystal grains driven by solvent recrystallization. Benefitting from separate and adjustable assembly kinetics and thermodynamics of the solvent recrystallization, various molecules can be assembled into monodisperse amorphous and crystalline particles with precisely controlled sizes, down to that of single atoms.
Fluorescent Probes
A Diselenide Turn-On Fluorescent Probe for the Detection of Thioredoxin Reductase
- Pages: 15259-15263
- First Published: 24 May 2020
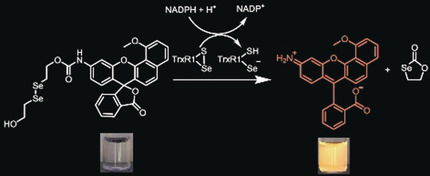
A reductive approach: A diselenide-based probe for the detection of thioredoxin reductase 1 (TrxR1) was designed and synthesized. The non-fluorescent probe switched on in the presence of TrxR1 and had minimal interference from other biological reducing species. The diselenide probe was successfully used in imaging TrxR1 in human lung cancer cells and showed greater fluorescence compared to a disulfide-based analogue.
Real-Time In Vivo Detection of Cellular Senescence through the Controlled Release of the NIR Fluorescent Dye Nile Blue
- Pages: 15264-15268
- First Published: 16 May 2020
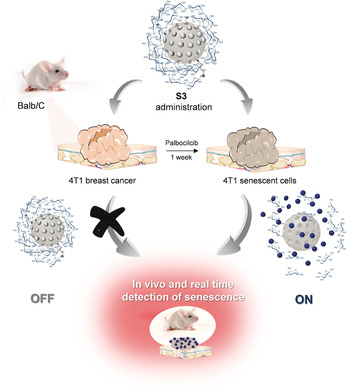
I got the Nile blues: Mesoporous silica nanoparticles loaded with Nile blue and capped with a galacto-hexasaccharide are used for in vivo imaging of cellular senescence. Fluorescence dye emission is quenched inside nanoparticles, yet a remarkable fluorescence is observed upon cap hydrolysis by β-galactosidase. The probe detects cellular senescence in vitro and in vivo in palbociclib-treated BALB/cByJ mice bearing breast tumors.
Photoelectrochemistry | Hot Paper
Luminescence Amplification at BiVO4 Photoanodes by Photoinduced Electrochemiluminescence
- Pages: 15269-15272
- First Published: 28 April 2020
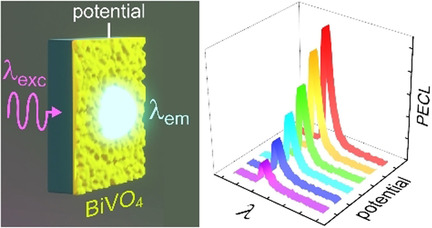
Light triggers: Photoinduced electrochemiluminescence (PECL) can be induced at BiVO4 photoanodes in an aqueous electrolyte containing a luminol derivative (L-012), at a record potential of −0.4 V. Here, the incident light simultaneously triggers L-012 fluorescence and PECL. The latter process considerably amplifies the luminescence and the potential control allows fine tuning of the overall luminescence.
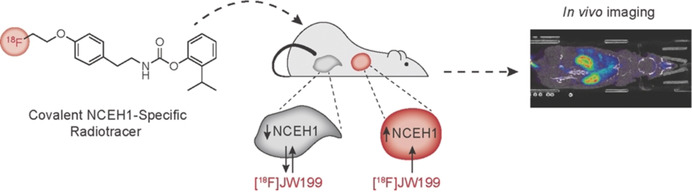
Radiopharmaceuticals
In Vivo Imaging of the Tumor-Associated Enzyme NCEH1 with a Covalent PET Probe
- Pages: 15273-15277
- First Published: 16 May 2020
Organic Semiconductors | Very Important Paper
A Three-Dimensional Porous Organic Semiconductor Based on Fully sp2-Hybridized Graphitic Polymer
- Pages: 15278-15282
- First Published: 12 May 2020
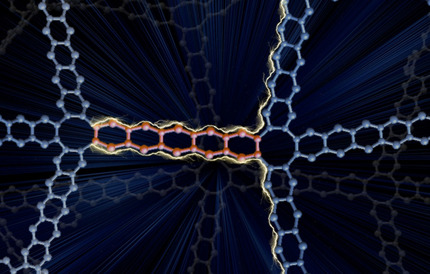
3D p-POP! A 3D π-conjugated porous organic polymer incorporating in situ formed pentacene linkers was synthesized through a catalyst-free Diels–Alder cycloaddition polymerization and an acid-promoted aromatization reaction. The resulting polymer shows high electrical conductivity and is the first member of a class of permanently porous 3D organic semiconductors.
Umpolung Reactions | Hot Paper
Direct Umpolung Morita–Baylis–Hillman like α-Functionalization of Enones via Enolonium Species
- Pages: 15283-15287
- First Published: 12 May 2020
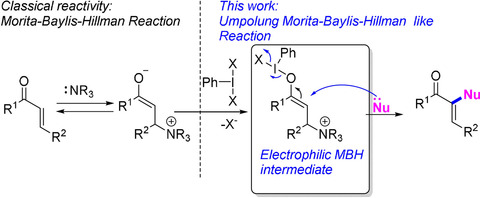
The hypervalent iodine reagent PIDA in combination with a nucleophilic amine (DABCO or pyridine) induces α-functionalization of enones with three different nucleophiles. The reaction is proposed to proceed through the umpolung of Morita–Baylis–Hillman type intermediates. The proposed mechanism is supported by spectroscopic studies that details the conversion of several reaction intermediates into products.
Hetero-liposomes | Hot Paper
Construction of Liposomes Mimicking Cell Membrane Structure through Frame-Guided Assembly
- Pages: 15288-15292
- First Published: 19 May 2020
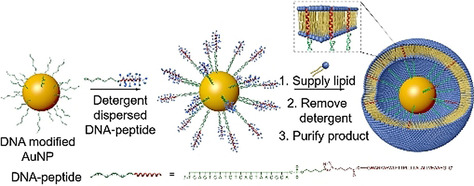
Hetero-liposomes with a structural composition similar to that of eukaryotic cells were prepared by constructing transmembrane peptide frames that mimicked the cell cytoskeleton structure. The conformation and transmembrane mode of the peptides played dominant roles during the frame-guided assembly (FGA) process. FGA liposomes were formed with excellent stability and could be utilized as a drug delivery platform.
Polymers | Hot Paper
High-Performance All-Polymer Solar Cells: Synthesis of Polymer Acceptor by a Random Ternary Copolymerization Strategy
- Pages: 15293-15297
- First Published: 19 May 2020
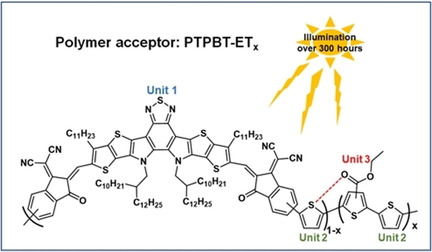
All-polymer solar cells (all-PSCs) are composed of polymer donors and acceptors, which hold potentially superior morphological stability and mechanical flexibility. In this work, a new random ternary copolymerization strategy was adopted to synthesize new polymer acceptors with high performance. The all-PSCs based on the new polymer acceptor shows high power conversion efficiency of over 12.5 % and high photostability capable of withstanding long-term illumination stress.
Microporous Materials | Hot Paper
Site-Specific Iron Substitution in STA-28, a Large Pore Aluminophosphate Zeotype Prepared by Using 1,10-Phenanthrolines as Framework-Bound Templates
- Pages: 15298-15302
- First Published: 20 May 2020
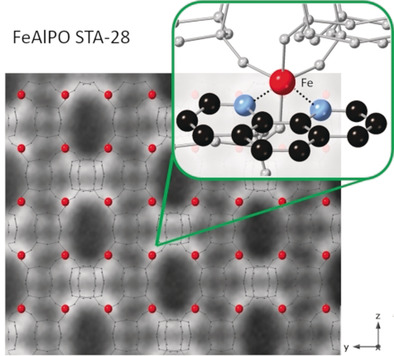
The aromatic diamine 1,10-phenanthroline acts as a framework-bound template for the large-pore aluminophosphate zeotype STA-28 and can be used to introduce Fe for Al at a single crystallographic site, as verified by Rietveld refinement and annular dark field scanning transmission electron microscopy. Removal of the template leaves a crystalline microporous solid with accessible iron cations.
Perovskites
Lead-Free Halide Double Perovskite Cs2AgBiBr6 with Decreased Band Gap
- Pages: 15303-15306
- First Published: 15 May 2020
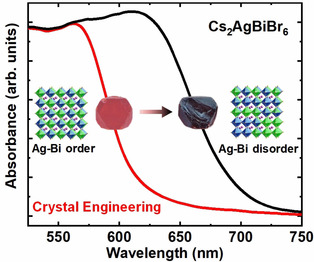
Disorderly conduct: A crystal-engineering strategy has been introduced to narrow the band gap of benchmark double perovskite Cs2AgBiBr6. The band gap of Cs2AgBiBr6 crystals can be reduced from 1.98 eV to 1.72 eV, reaching the smallest reported band gap for Cs2AgBiBr6 under ambient conditions. DFT calculations indicate that Ag–Bi disorder in the crystal structure could lead to band-gap narrowing.
Natural Product Synthesis | Hot Paper
Total Synthesis of (−)-Glaucocalyxin A
- Pages: 15307-15310
- First Published: 20 May 2020
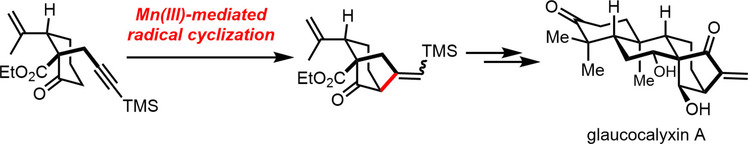
Ringing the changes: A practically useful method for the formation of the highly oxygenated bicyclo[3.2.1]octane ring system through Mn(OAc)3-mediated radical cyclization of alkynyl ketones was developed, which opens up a new avenue for the total synthesis of a number of highly oxidized diterpenoids. Application of this method enabled the first total synthesis of the ent-kaurene diterpenoid(−)-glaucocalyxin A.
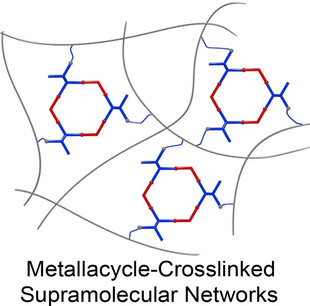
Supramolecular Chemistry
Emissive Metallacycle-Crosslinked Supramolecular Networks with Tunable Crosslinking Densities for Bacterial Imaging and Killing
- Pages: 15311-15315
- First Published: 18 May 2020
Glycosylation | Very Important Paper
Stereoselective Electro-2-deoxyglycosylation from Glycals
- Pages: 15316-15320
- First Published: 11 May 2020
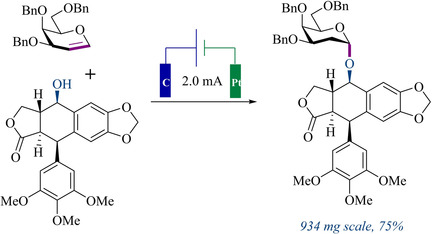
Sweet dreams are made of this: A highly stereoselective electro-2-deoxyglycosylation from glycals was developed. This method features excellent stereoselectivity, scope, and functional-group tolerance, and can also be applied to the modification of a wide range of natural products and drugs. Furthermore, a scalable synthesis of glycosylated podophyllotoxin and a one-pot trisaccharide synthesis through iterative electroglycosylations were achieved.
Radio-photoluminescence | Hot Paper
Emergence of a Radical-Stabilizing Metal–Organic Framework as a Radio-photoluminescence Dosimeter
- Pages: 15321-15326
- First Published: 20 May 2020
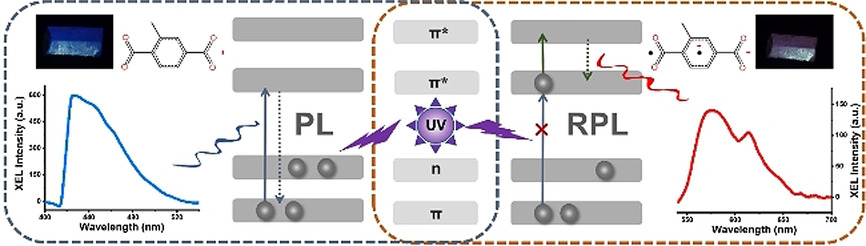
Radio-photoluminescence in MOFs: The first metal–organic framework (MOF) to display radio-photoluminescence (RPL) may lead to a new generation of RPL dosimeters showing advantages in terms of detection sensitivity, detection range, reusability, stability, and energy threshold over the existing commercial materials.
N−H Bond Formation
N−H Bond Formation at a Diiron Bridging Nitride
- Pages: 15327-15331
- First Published: 22 May 2020
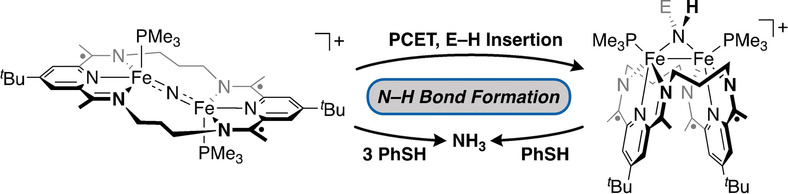
A diiron bridging nitride complex supported by a geometrically flexible, redox-active macrocycle was synthesized and characterized by X-ray crystallography and Mössbauer spectroscopy. Treatment of the electrophilic nitride with PhSH afforded NH3 in high yield through a reaction that engages the redox-activity of the ligand during proton-coupled electron transfer followed by protonolysis.
Aurophilicity | Very Important Paper
Gold Complexes with Difunctional Perfluoroalkyl Chains: Quantifying the Energy of Aurophilic Interactions in Flexible Open-Chain Complexes
- Pages: 15332-15337
- First Published: 19 May 2020
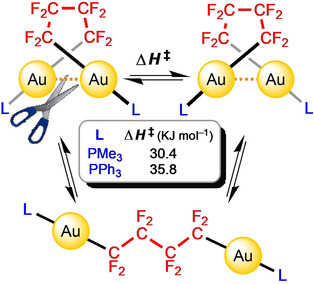
Cycles and chains: The first perfluorinated auracycles and complexes containing Au(CF2)nAu chains are prepared. LAu(CF2)4AuL complexes adopt folded conformations stabilized by an aurophilic interaction depending on the auxiliary ligand L. The study of their dynamic behaviour in solution has allowed the energy associated with an aurophilic interaction to be determined.
Chirality
Enantiomeric Discrimination by Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering–Chiral Anisotropy of Chiral Nanostructured Gold Films
- Pages: 15338-15343
- First Published: 18 May 2020
Absolution by SERS: A surface-enhanced Raman scattering chiral anisotropy effect is presented that combines chiral discrimination and surface Raman scattering enhancement on chiral nanostructured Au films. It is applied in the normal Raman scattering system to identify the absolute configuration and composition of enantiomers, overcoming disadvantages of polarimeter systems and chromatography.
Hydrogen Evolution Reaction
Identifying the Transfer Kinetics of Adsorbed Hydroxyl as a Descriptor of Alkaline Hydrogen Evolution Reaction
- Pages: 15344-15349
- First Published: 13 May 2020
Polycyclic Heteroaromatic Compounds | Hot Paper
Electrochemical Oxidative [4+2] Annulation for the π-Extension of Unfunctionalized Heterobiaryl Compounds
- Pages: 15350-15355
- First Published: 10 May 2020
![Electrochemical Oxidative [4+2] Annulation for the π-Extension of Unfunctionalized Heterobiaryl Compounds](/cms/asset/9b33da17-882e-4213-b985-8197f4b1d7a8/ange202003656-toc-0001-m.jpg)
The straightforward π-extension of unfunctionalized heterobiaryl compounds is achieved by electrochemical oxidative [4+2] annulation reactions with alkynes or alkenes. The anodic oxidation of heterobiaryl compounds generates heteroarene radical cations, and the selective nucleophilic attack proceeds with good regioselectivity under mild conditions.
Synthetic Methods
Synthesis of Spirocyclic 1-Pyrrolines from Nitrones and Arynes through a Dearomative [3,3′]-Sigmatropic Rearrangement
- Pages: 15356-15360
- First Published: 06 May 2020
![Synthesis of Spirocyclic 1-Pyrrolines from Nitrones and Arynes through a Dearomative [3,3′]-Sigmatropic Rearrangement](/cms/asset/0e42cc21-f294-4ec7-8fc1-6dab71cec3d0/ange202004652-toc-0001-m.jpg)
A cascade reaction has been designed for the synthesis of spirocyclic pyrrolines from nitrones and arynes. A key feature of this transformation is an unusual dearomative [3,3′]-sigmatropic rearrangement of a heterocyclic intermediate that results in a spirocyclization. This modular approach provides access to three-dimensionally-defined pyrrolines and pyrrolidines with opportunities for divergent derivatization.
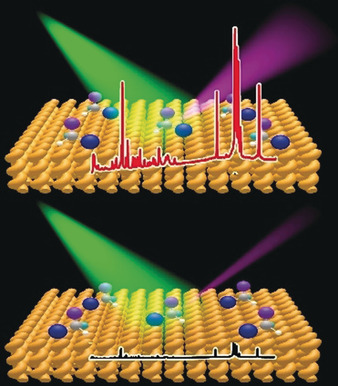
Cyclization
Catalytic Dehydrogenative Cyclization of o-Teraryls under pH-Neutral and Oxidant-Free Conditions
- Pages: 15361-15365
- First Published: 18 May 2020
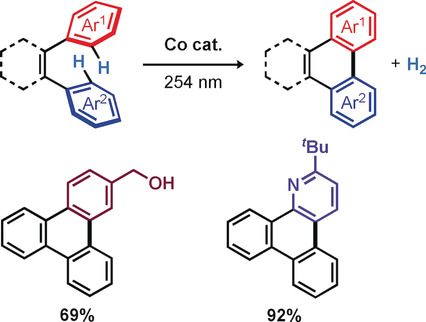
Come full circle: A highly chemoselective cobaloxime-catalyzed acceptorless dehydrogenative cyclization of o-teraryls was developed. Due to the acid- and oxidant-free conditions, diverse substrates with various electronic properties and sensitive functional groups, including electron-poor arenes and electron-rich heterocycles, are tolerated.
Cross-Coupling Reactions | Hot Paper
CuII/TEMPO-Catalyzed Enantioselective C(sp3)–H Alkynylation of Tertiary Cyclic Amines through Shono-Type Oxidation
- Pages: 15366-15371
- First Published: 11 May 2020
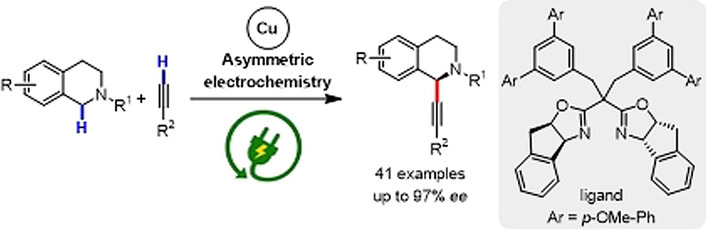
An asymmetric Shono-type oxidative cross-coupling to give C1-alkynylated tetrahydroisoquinolines with good to excellent enantioselectivity was developed by merging copper catalysis and electrochemistry. The use of TEMPO as a co-catalytic redox mediator is crucial for oxidizing a tetrahydroisoquinoline to an iminium ion species and for decreasing the oxidation potential of the reaction.
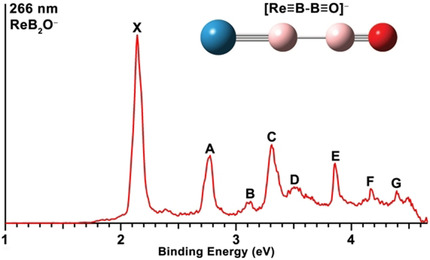
Photoelectron Spectroscopy
Observation of Transition-Metal–Boron Triple Bonds in IrB2O− and ReB2O−
- Pages: 15372-15377
- First Published: 18 May 2020