Journal list menu
Health Systems, Policies, and Ethical Considerations
The equity group: Supporting Cochrane's social responsibility of improving health equity
Who is the ‘standard’ patient?
- Medical Education
- 503-505
- 10.1111/medu.15074
Abstract
The authors describe the harm, to patients and professionals alike, of medical education's tendency to assume the white cisgendered man to be the "normal" from which all other patient identities are deviations.
Epistemic injustice: The silenced voices
Challenges facing standardised patients representing equity‐deserving groups: Insights from health care educators
- Medical Education
- 516-522
- 10.1111/medu.15085
Abstract
The authors explore healthcare educator insights into how safety for Standardized Patient work related to equity-deserving groups requires unique focus to avoid the educational process itself being oppressive.
If we do not count it, it does not count: ethnicity in allogeneic haemopoietic stem cell transplant in Australia
- Internal Medicine Journal
- 2155-2158
- 10.1111/imj.16232
Understanding experiences of Aboriginal and/or Torres Strait Islander patients at the emergency departments in Australia
It's a little bit like prison, but not that much: Aboriginal women's experiences of an acute mental health inpatient unit.
Examining emergency department inequities in Aotearoa New Zealand: Findings from a national retrospective observational study examining Indigenous emergency care outcomes
Graphical Abstract
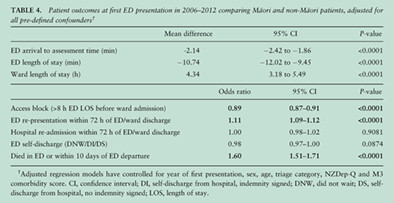
This retrospective observational study used a Kaupapa Māori framework to investigate ED admissions into 18/20 District Health Boards in Aotearoa New Zealand (2006–2012). Despite some ED process measures being positive for Māori, for example arrival to assessment time and access block, others showed no difference, for example self-discharge. Despite this, Māori mortality and ED re-presentation were higher than non-Māori. Our findings reinforce the need to investigate health professional bias and institutional racism within an acute care context.
Impact of educational policies on access to health care in Brazil: A cross‐sectional study
- Medical Education
- 587-594
- 10.1111/medu.15012
Abstract
Workforce patterns are analyzed to demonstrate that educational policies aimed at expanding access to medical education for underrepresented groups increases the number of physicians in underserved areas and primary care.
Community Health: Innovations and Interventions
Experiences of conditional and unconditional cash transfers intended for improving health outcomes and health service use: a qualitative evidence synthesis
Clara A Yoshinoa, Kristi Sidney-Annerstedta, Tom Wingfield, Beatrice Kirubi, Kerri Viney, Delia BocciaSalla Atkins
Version published: 31 March 2023
Reaching under‐screened/never‐screened indigenous peoples with human papilloma virus self‐testing: A community‐based cluster randomised controlled trial
Interventions to improve sanitation for preventing diarrhoea
Valerie Bauza, Wenlu Ye, Jiawen Liao, Fiona Majorin, Thomas Clasen
Version published: 25 January 2023
Empowering workplace allies for lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender employees to prevent and minimize psychological distress: A scoping review
Systematic review of quantitative studies assessing the relationship between environment and mental health in rural areas
Artificial intelligence and digital health in improving primary health care service delivery in LMICs: A systematic review
Evidence for the routine collection and clinical utilisation of patient‐reported outcomes is compelling: It is time to jump on the bandwagon
Graphical Abstract
A study in patient satisfaction regarding telemedicine consultations in radiation oncology
Graphical Abstract
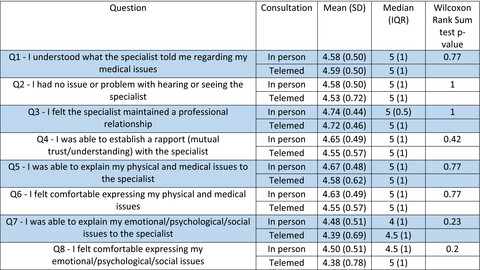
Telemedicine consultations can be a cost effective and convenient method of communication particularly with patients living in remote areas. Given the dearth of patient reported satisfaction data with this form of consultation in Radiation Oncology, we surveyed patients to assess this in our department.
Improved metabolic parameters of people with diabetes attending an Aboriginal health service in regional Victoria
Evidence-based Clinical Approaches and Research
Advances in breast cancer screening modalities and status of global screening programs
Key points
Mammography is the most widely used and most effective technique; other complementary techniques include ultrasound, clinical breast examination, and magnetic resonance imaging. Globally, the implementation status of breast cancer screening programs is uneven, which is reflected by differences in screening modes, techniques, and examination coverage. Combining effective risk prediction models and advanced screening techniques for risk-stratified screening strategies may be the future direction.
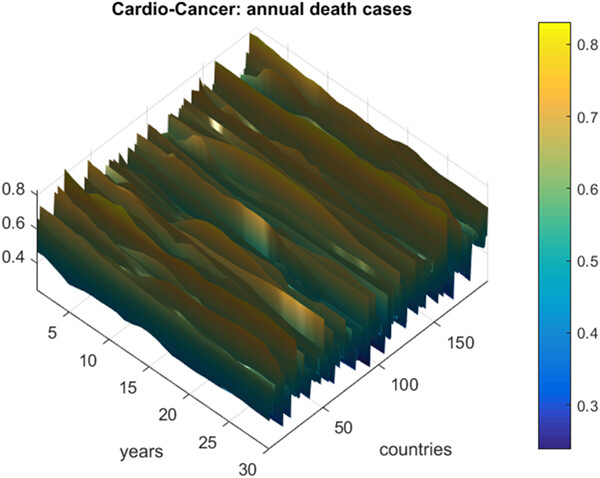
Prediction of death rates for cardiovascular diseases and cancers
- Cancer Innovation
- 140-147
- 10.1002/cai2.47
Glucocorticoid‐induced osteonecrosis in systemic lupus erythematosus patients
Graphical Abstract
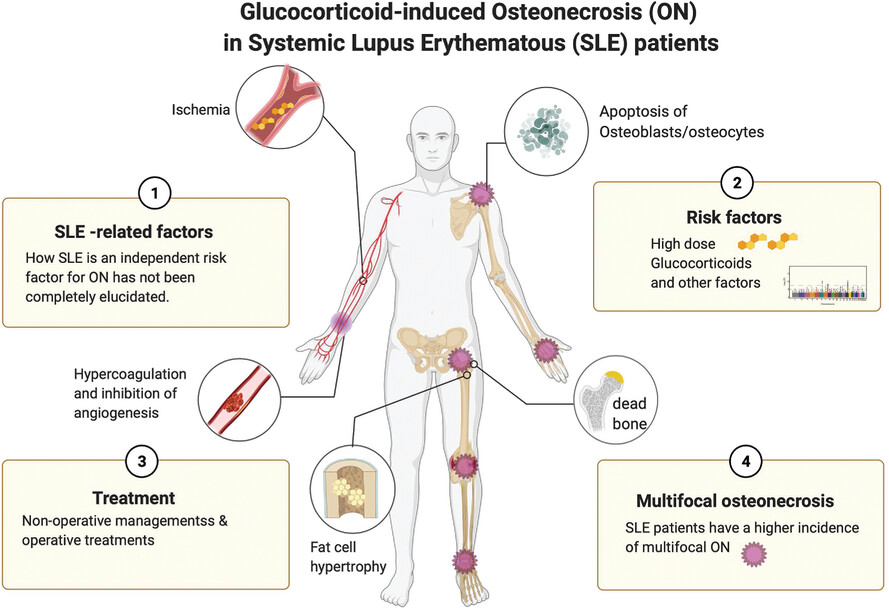
ON is a complex and multifactorial complication of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE). However, the pathophysiology and risk factors for ON in patients with SLE have not been fully determined yet. Here, we review the epidemiology, risk factors, diagnosis, and treatment options for glucocorticoid-induced ON, with a specific focus on patients with SLE
Management of macular oedema due to retinal vein occlusion: An evidence‐based systematic review and meta‐analysis
Perspectives of vitamin C upregulating regulatory T cells in the era of thrombopoietin receptor agonists for immune thrombocytopenia
Graphical Abstract
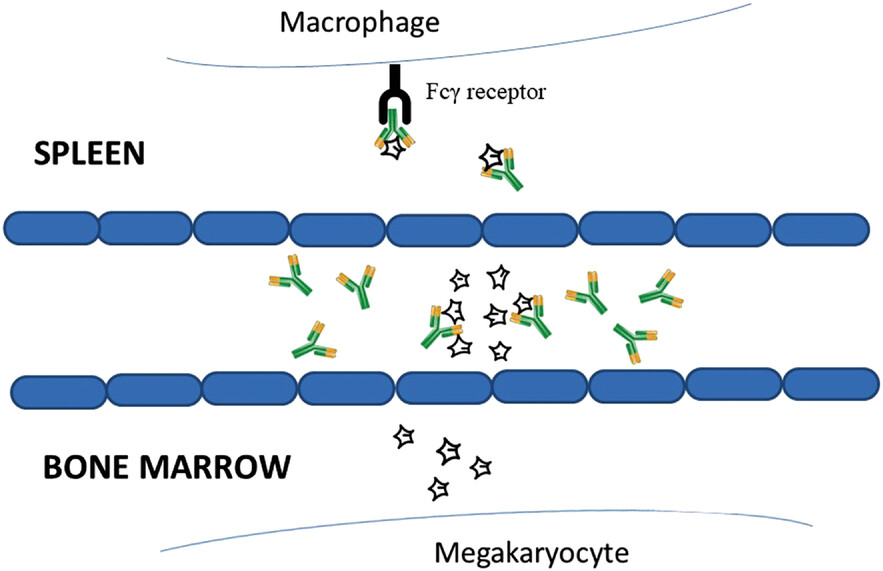
Gross platelet deficiency marks idiopathic thrombocytopenia's pathophysiology: normalization of the regulatory T cells (Tregs) through demethylation may well reverse the abnormal DNA methylation. Despite thrombopoietic receptor agonists’ recognized effectiveness, strongly demethylating (yet safe and affordable) ascorbate (e.g. with a plasma level of >1 mM several hours/week) could prevent their undesirable “rebound phenomenon” upon routine discontinuation, especially if abruptly mandated by refusal/adverse effects. [In Figure 1, star-shaped objects are platelets; Y-shaped objects are autoantibodies; in Figure 2, pro-inflammatory T helper 17 (Th17) cells are characterized by RORγt: a transcription factor (encoded by the gene Rorc) of the retinoic acid-receptor (RAR)-related orphan receptor (ROR) family. In ITP, Tregs expressing forkhead box P3 (Foxp3) are crucial for controlling ITP: in Figure 3, TET: ten-eleven translocation enzymes; 5mC; 5hmc: 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (the initiating step of active DNA demethylation. A cofactor fostering this process is vitamin C which acts synergistically with retinoic acid (RA)].
Development and validation of a prognostic model incorporating tumor thrombus grading for nonmetastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma with tumor thrombus: A multicohort study
Graphical Abstract
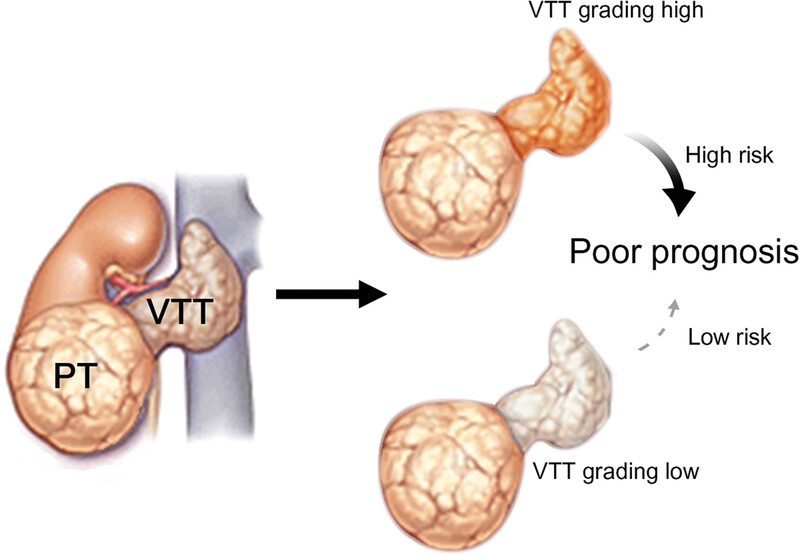
Inspired by the metastasis-seeding potential of VTT in ccRCC, we identified for the first time that pathological grading of VTT could serve as an unheeded prognostic factor. By incorporating VTT grading, TT-GPS score was constructed, displaying superior discriminatory ability for risk stratification in nonmetastatic ccRCC patients with VTT. This study highlights the significance of introducing VTT grading or TT-GPS score into routine pathological reports to improve the efficacy of risk assessment.
Toric intraocular lenses: Evidence‐based use
New era for emerging therapeutic targeting human epidermal growth factor receptor 3 (HER 3) in advanced nonsmall cell lung cancer and metastatic breast cancer
Graphical Abstract
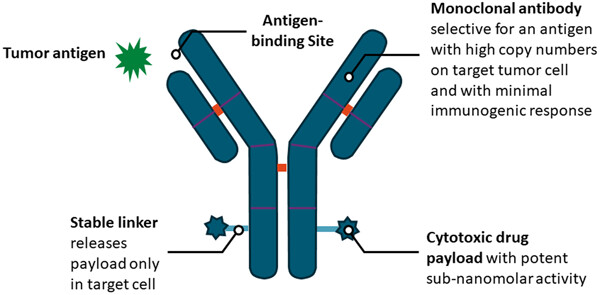
Human epidermal growth factor receptor 3 (HER3) overexpression represents a negative prognostic biomarker associated with poor survival. Targeting HER3 has shown some promise in early phase trials in both nonsmall cell lung cancer and metastatic breast cancer in heavily pretreated patients with varying degrees of response. Identifying a predictive biomarker will aid to better select patients that will respond to treatment.
Nonviral vector system for cancer immunogene therapy
Graphical Abstract
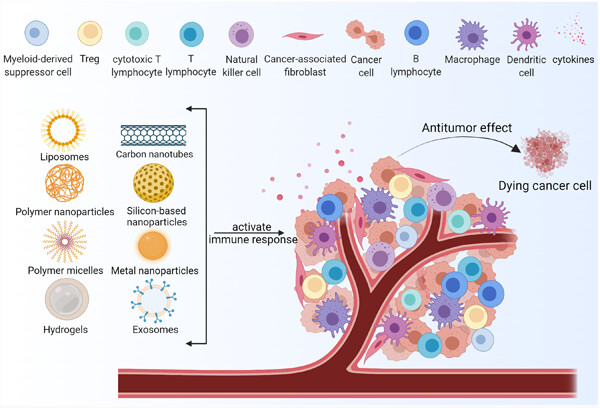
Immunogene therapy has become an effective and significant clinical strategy for cancer therapy. Enhancing the response rate to immunogene therapy is significant to controlling side effects and improving efficacy. Improved nonviral vectors combined with immunogene therapy efficiently deliver genes to the desired tumor cells and activate immune response to fight tumors while alleviating adverse reactions, which is a promising treatment approach for cancer.
Chemoimmunotherapy for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma—Summary and discussion of recent clinical trials
Graphical Abstract
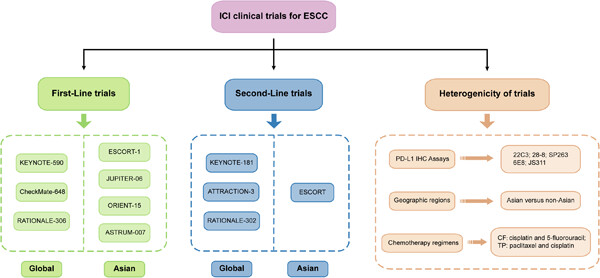
A large majority of clinical trials demonstrate the promising results of the addition of immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) to the existing treatment strategy for patients with advanced or metastatic esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC). Therefore, this article aims to discuss the results of these trials and to highlight the changes and future of ESCC treatment.
Zinc supplementation for preventing mortality, morbidity, and growth failure in children aged 6 months to 12 years
Aamer Imdad, Jaimie Rogner, Rida N Sherwani, Jasleen Sidhu, Allison Regan, Maya R Haykal, Olivia Tsistinas, Abigail Smith, Xin Hui S Chan, Evan Mayo-Wilson, Zulfiqar A Bhutta
Version published: 30 March 2023