Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Table of Contents
Reduction of Greenhouse Gas Emissions from Gas, Oil, and Coal Power Plants in Pakistan by Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS): A Review
- First Published: 19 August 2020
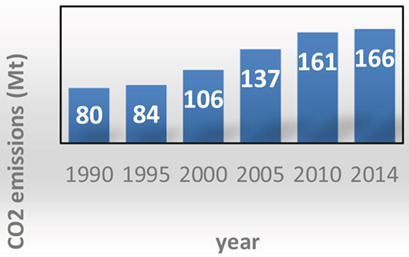
The significance of carbon capture and storage (CCS) from greenhouse gas emission sources of Pakistan is described. Emissions are estimated from coal, oil, and gas power plants. Different sequestration technologies such as mineralization, geological storage, and oceanic storage are suggested. Current CCS running projects in Pakistan and challenges with solutions of CCS implementation are discussed.
Mass Transfer Flux of CO2 into Methyldiethanolamine Solution in a Reactive-Absorption Process
- First Published: 02 August 2020
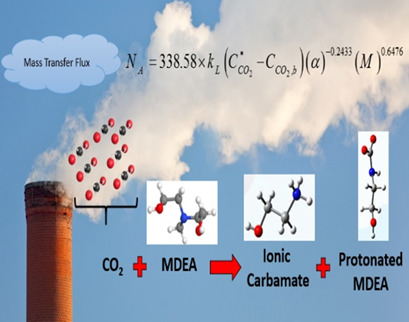
An innovative correlation is proposed based on the Buckingham π theorem for prediction of CO2 mass transfer flux in the reactive-absorption process using methyldiethanolamine solution. Effects of various parameters such as film parameter, CO2 loading, concentration ratio, ratio of partial pressure to total pressure, film thickness ratio, and diffusion ratio are considered in this model.
Activated-Carbon Nanofibers/Graphene Nanocomposites and Their Adsorption Performance Towards Carbon Dioxide
- First Published: 20 July 2020
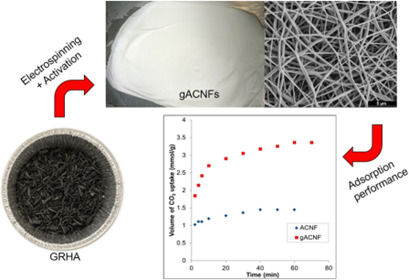
An activated-carbon nanofibers/graphene nanocomposite was developed as adsorbent material with enhanced porous structure and high adsorption performance towards carbon dioxide. The graphene-based material used was synthesized from graphene-derived rice husk ashes, an abundant and cheap agricultural waste, providing an alternative for realizing green technology.
Efficient Removal of Ammonia by Hierarchically Porous Carbons from a CO2 Capture Process
- First Published: 20 July 2020
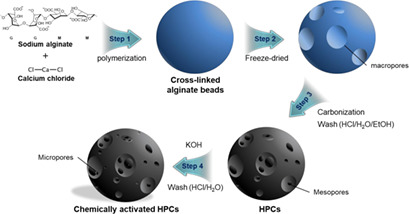
Activated carbon (AC) and hierarchically porous carbon (HPC) preparations were used as adsorbents for the removal of NH3 after an amine-based post-combustion carbon capture process, and their adsorption capacities, adsorption rates, and stabilities were studied. In general, the HPC adsorbents with more mesopores and acid sites showed better performance and stability than the AC ones.
PEBA/PSf Multilayer Composite Membranes for CO2 Separation: Influence of Dip Coating Parameters
- First Published: 09 April 2020
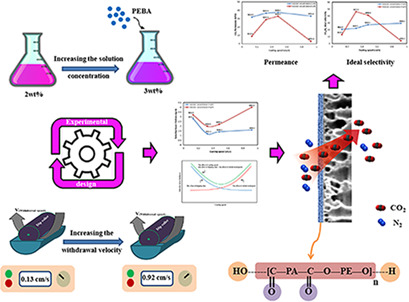
Polyether block amide/polysulfone composite membranes were prepared by the dip coating method and the effects of the coating speed and the solution concentration on the membrane performance were investigated. With increasing coating speed, the increasing withdrawal speed and the decreasing dipping time result in a thin selective layer at the appointed coating speed value.
Compost from Municipal Solid Wastes as a Source of Biochar for CO2 Capture
- First Published: 10 March 2020
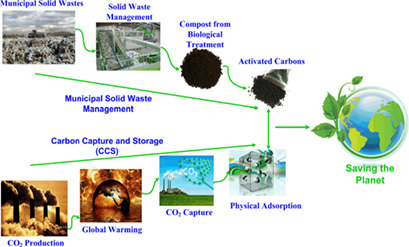
The potential of compost derived from municipal solid wastes as a low-cost source of adsorbents for CO2 capture was investigated. Five different samples were synthesized and screened regarding CO2 uptake. One sample, which was chemically treated by sulfuric acid and thermally activated at 800 °C, had the highest breakthrough time and an adsorption capacity comparable to commercial carbon materials.
Effectiveness of Amine Concentration and Circulation Rate in the CO2 Removal Process
- First Published: 27 January 2020
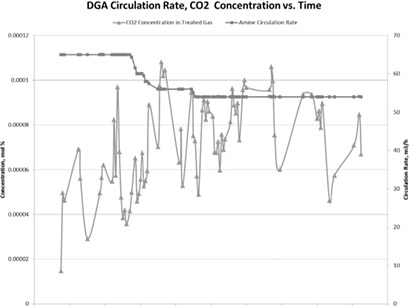
Amine absorption is still considered a state-of-the-art technology for gas industries. A technical analysis of gas-sweetening processes for natural gas with amine absorption has been conducted. An optimal point between amine concentration and circulation rate offers a great potential in this area for reducing the possibility of corrosion and foaming in the CO2 removal system.
Location Planning for the Production of CO2-Based Chemicals Using the Example of Olefin Production
- First Published: 19 December 2019
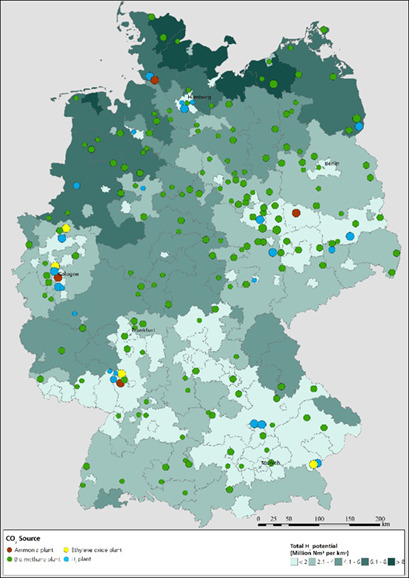
CO2-based chemical production can contribute to climate protection and resource savings. A methodology for deriving suitable locations for CO2-based chemical production in Germany, taking into account the local availability of CO2 and renewable energy sources, is proposed. The location factors for a CO2-based chemical production taking the example of olefin production are evaluated.
Membranes for CO2 /CH4 and CO2/N2 Gas Separation
- First Published: 05 November 2019
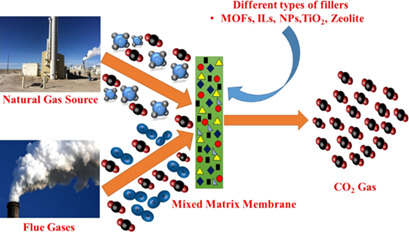
Membrane-based techniques emerged as the most effective option for the separation and/or capture of CO2. Different types of membranes are reviewed with the main emphasis placed on mixed-matrix membranes with various types of fillers. Such membranes combine the advantages of both polymeric and inorganic membranes and exhibit the best performance for CO2 separation from natural gas and other flue gases.
Combined Decarbonization of Electrical Energy Generation and Production of Synthetic Fuels by Renewable Energies and Fossil Fuels
- First Published: 25 September 2019
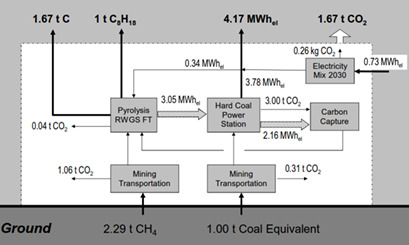
The idea is to interconnect energy generation from renewable energies (RE) with fossil energy from stations with low CO2 footprints. These stations are capable of both base load operation and compensation for RE volatility and would produce both electricity and fuel, resulting in an improved overall efficiency from the combined energy production mix. The concept has a high degree of flexibility.
Various Techniques for Preparation of Thin-Film Composite Mixed-Matrix Membranes for CO2 Separation
- First Published: 03 September 2019
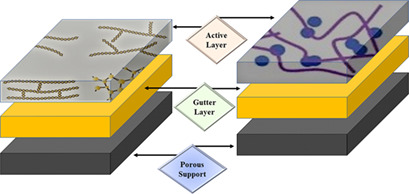
Thin-film composite mixed-matrix membranes are considered as an efficient separation technology for gas separation, fabricated as enhanced versions of mixed-matrix membranes. Recent advancements in these membranes are reviewed by comparing their performance in terms of permeability and selectivity. Various preparation techniques and their effect on the gas separation performance are described.
Effect of Empty Fruit Bunch in Calcium Oxide for Cyclic CO2 Capture
- First Published: 15 July 2019
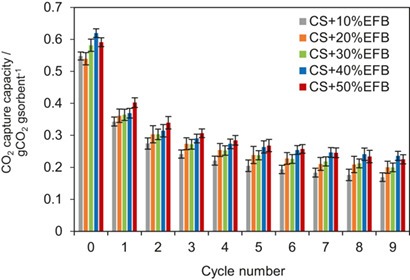
Empty fruit bunch (EFB) is utilized to increase the CO2 capture capacity and enhance the cyclic stability of calcium oxide as an adsorbent prepared from waste cockle shells. The improvement of CaO as an adsorbent for cyclic CO2 capture is explored by adding metal oxides from EFB. The average sorption decay could be also decreased due to the metal elements contained in the EFB.
Stabilized Performance of Al-Decorated and Al/Mg Co-Decorated Spray-Dried CaO-Based CO2 Sorbents
- First Published: 04 April 2019
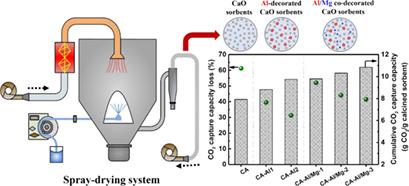
An easily scaled-up spray-drying method was adopted to prepare Al-decorated and Al/Mg co-decorated CaO-based sorbents. Such spray-dried sorbents exhibit enhanced CO2 capture performance. The stabilized performance is mainly attributed to the formation of Ca12Al14O33, MgAl2O4, and MgO acting as skeleton structures to mitigate the sintering of CaCO3 during carbonation/calcination cycles.
Simulation of Post-Combustion CO2 Capture, a Comparison among Absorption, Adsorption and Membranes
- First Published: 23 January 2019
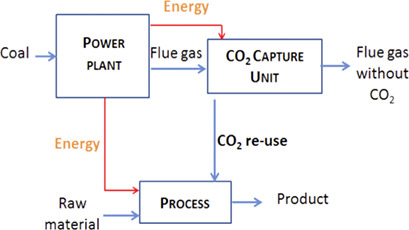
Based on systems modeling, three post-combustion CO2 capture processes – membrane, absorption, and adsorption – were compared regarding energy consumption, design, and efficiency. The membrane process is revealed as the most efficient one in terms of energy consumption, but reaches lower recovery rates than the other two processes and a significantly smaller CO2 purity than the absorption process.
Biomass and Lipid Productivity of Neochloris oleoabundans for CO2 Biofixation and Biodiesel Application
- First Published: 20 August 2018

Photosynthesis-based microalgal-mediated carbon dioxide capture and usage is a promising approach to reduce the amount of CO2 in the atmosphere and provide a long-term and sustainable solution to global warming. To this end, freshwater microalgae Neochloris oleoabundans was cultured and the biomass and lipid productivity and lipid contents under different conditions were investigated.
Facile CO2 Separation in Composite Membranes
- First Published: 31 July 2018
Membrane technology is considered as an efficient, environmentally friendly, and inexpensive technology for CO2 separation. Various approaches to improve membrane performance are reviewed with the focus on permeability and selectivity parameters. Polymer-inorganic nanocomposite membranes, metal organic frameworks, and ionic liquid mixed-matrix membranes are also discussed and evaluated.
Acidification Optimization and Granulation of a Steel-Slag-Derived Sorbent for CO2 Capture
- First Published: 29 June 2018
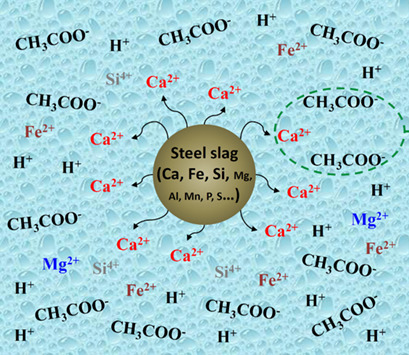
Steel slag is a cheap and abundant raw material for preparing CaO-based sorbents for CO2 capture by acidification. Orthogonal experiments were performed to optimize the acidification process to produce highly efficient CaO-based CO2 sorbents with more stable sorption performance than natural limestone. Attrition-resistant sorbent pellets were produced by extrusion of sorbent powders.
Synthesis of High-Performance Pebax®-1074/DD3R Mixed-Matrix Membranes for CO2/CH4 Separation
- First Published: 27 June 2018
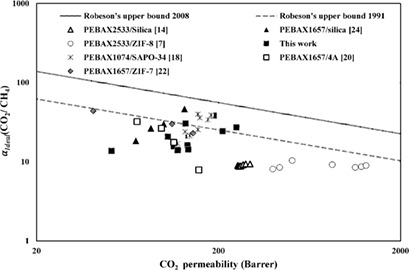
Before natural gas can be transported and used, it is essential to remove impurities such as CO2. In this work, polymer/zeolite (Pebax®-1074/DD3R) mixed-matrix membranes (MMMs) were fabricated for gas-separation applications. The performances of the MMMs were studied at different operating conditions and DD3R loadings. The separation performance of Pebax®-1074 was improved by using DD3R as a filler.
Separation of Methane and Carbon Dioxide Gas Mixtures Using Activated Carbon Modified with 2-Methylimidazole
- First Published: 06 July 2018
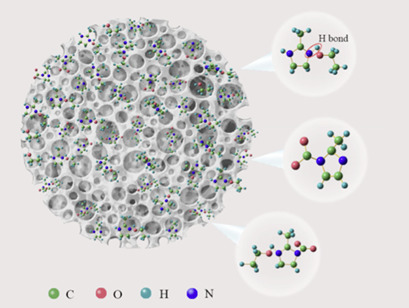
2-Methylimidazole, ethanol, and glycol are proposed for the modification of activated carbon for use in the separation of CH4+CO2 gas mixtures. The selectivity coefficient of the modified activated carbon was about five times higher than that of the fresh activated carbon. The CO2 capture mechanism of 2-methylimidazole and glycol is outlined.
CO2 Capture Performance of Portland Cement-Based Carbide Slag and the Enhancement of Its CO2 Capture Capacity
- First Published: 22 May 2018

Commercial Portland cement (PC) was used as cheap binder to produce PC carbide slag (CS) pellets with enhanced mechanical strength. The carbonation conversion of the CS declined with the addition of PC, but the ability to resist sintering was improved. Extending the hydration time improved the CO2 capture performance of the PCCS during pelletization.









