Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
REVIEW ARTICLE
Unlocking T-Cell Plasticity in the Tumor Microenvironment: Implications for Cancer Progression and Therapeutic Strategies
- First Published: 24 May 2025
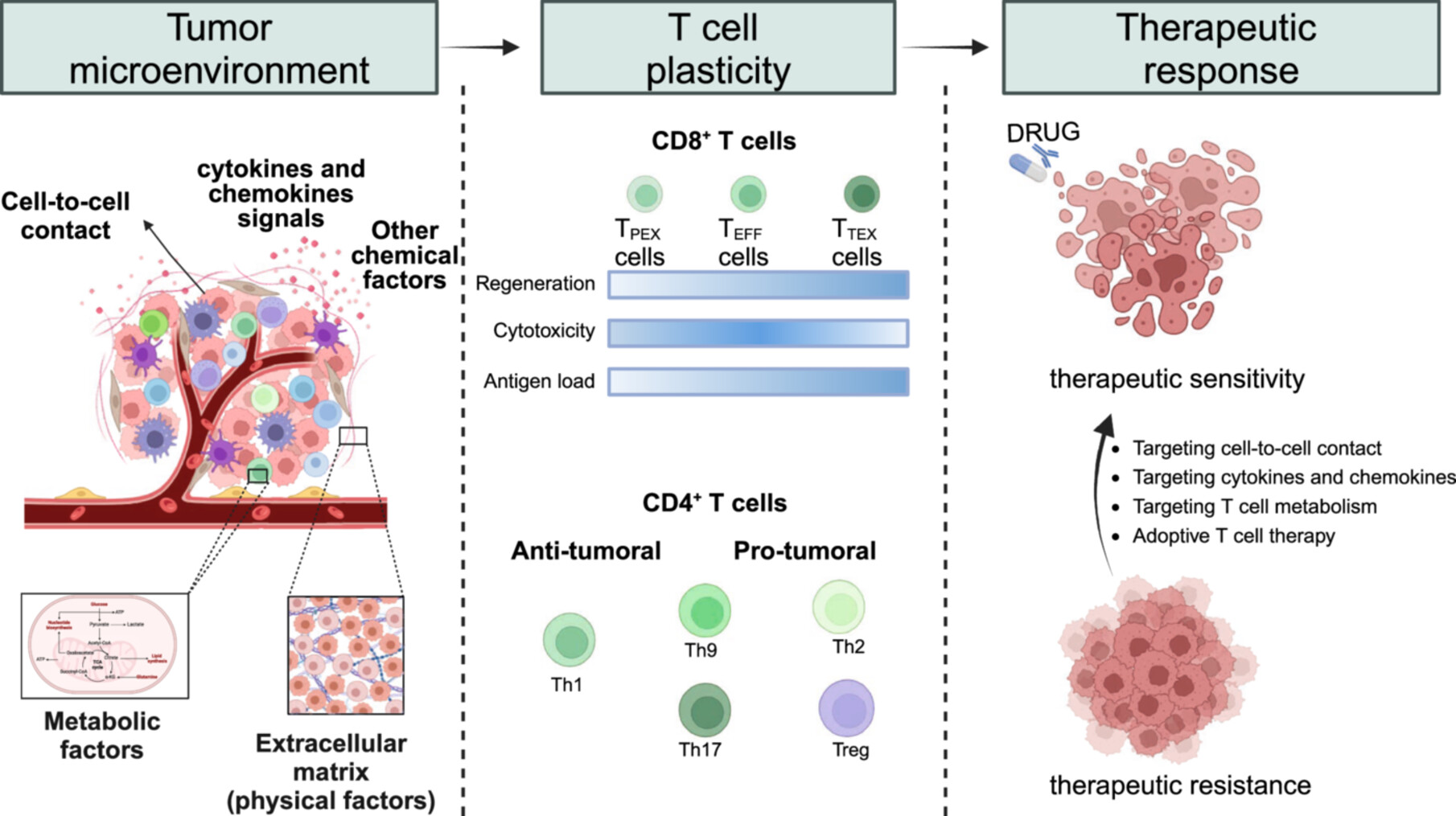
The tumor microenvironment (TME) shapes T-cell plasticity, influencing cancer progression and therapeutic outcomes. Here, we summarize the phenotypic transitions and spatial distribution of T cells within the TME, highlighting their dual roles in therapeutic efficacy and resistance. Novel strategies leveraging T-cell plasticity offer the potential for optimizing cancer treatment.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Fexofenadine Overcomes Osimertinib Resistance by Inhibiting c-Met in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
- First Published: 14 April 2025
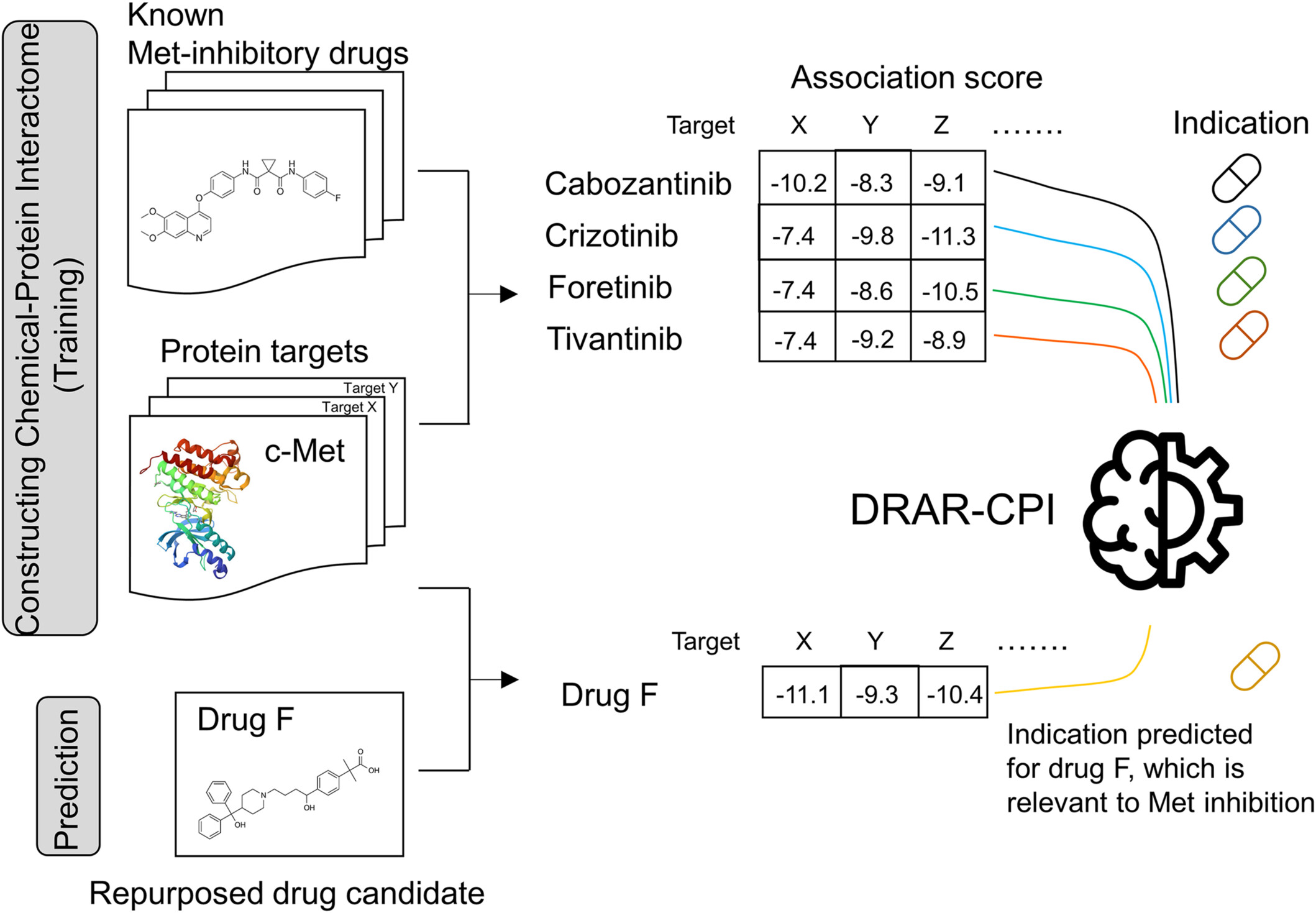
Fexofenadine was identified as a new Met inhibitory drug by a computational drug repurposing tool called “DRAR-CPI” via chemical-protein interactome analysis of known Met inhibitors. It was shown to overcome osimertinib resistance in non-small cell lung cancer by inhibiting Met in vitro and in vivo.
HIGHLIGHT
Intercellular Mitochondrial Transfer Enhances the Antitumor Immunity of CD8+ T Cells
- First Published: 04 April 2025
REVIEW ARTICLE
Phase Separation: A New Dimension to Understanding Tumor Biology and Therapy
- First Published: 05 May 2025
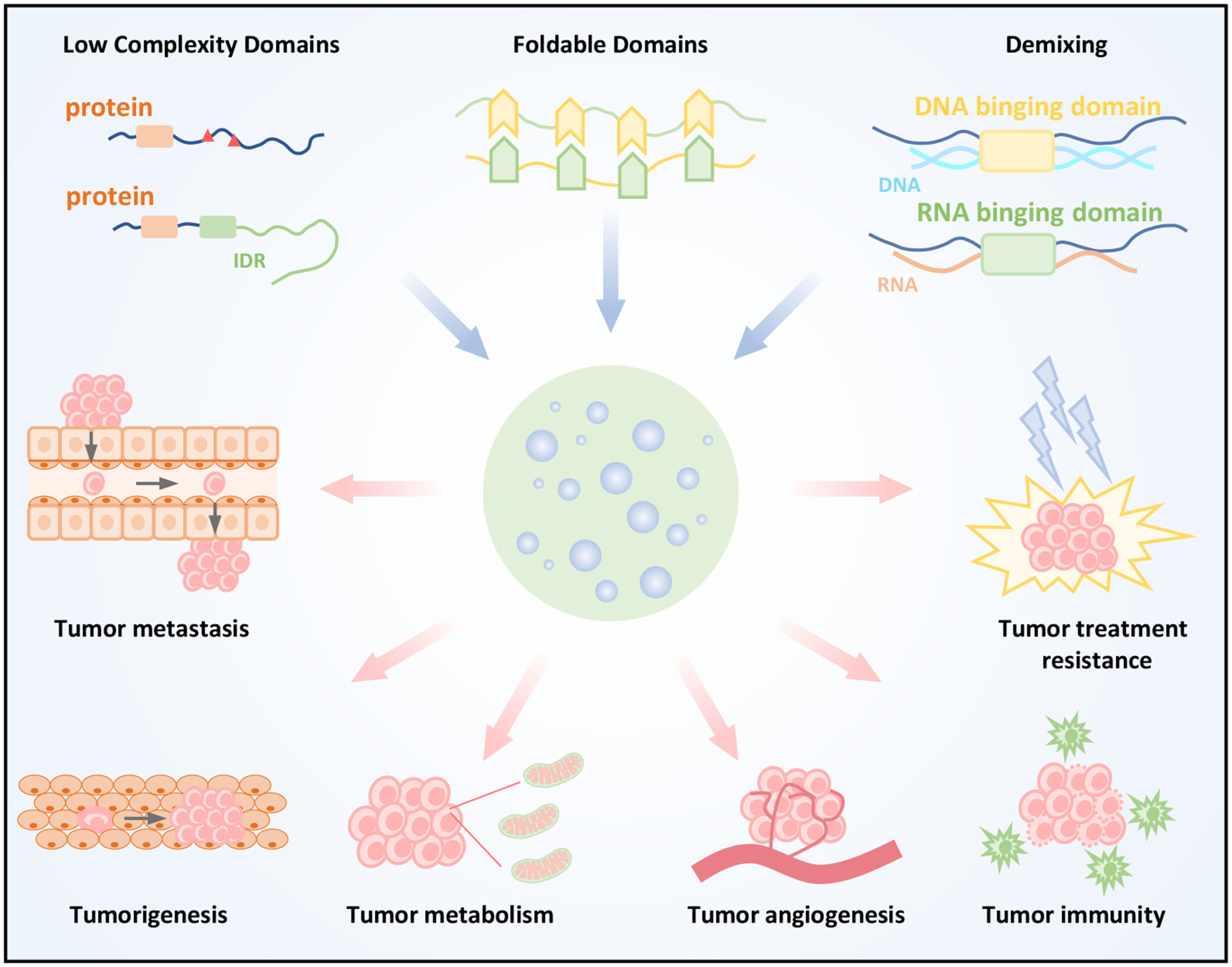
Liquid–liquid phase separation (LLPS) facilitates the assembly of biomolecular condensates by leveraging weak multivalent interactions. The low-complexity domains, foldable domains of proteins, and nucleic acids provide multivalent interaction sites among different molecules and contribute to the formation of condensates. Dysregulation of condensates contributes to cancer hallmarks, including tumorigenesis, metastasis, angiogenesis, metabolism, drug resistance, and tumor immunity. Targeting biomolecular condensates offers new therapeutic opportunities for advancing cancer treatment.
LETTER
A Causal Relationship Between Genetically Proxied Inhibition of HMGCR, NPC1L1, and PCSK9 and Cancers
- First Published: 24 June 2025
REVIEW ARTICLE
Phosphatase Dysregulation in Cancer: Signaling Pathways and Therapeutic Opportunities
- First Published: 24 June 2025
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Activation of Adenosine Phosphate Signaling Promotes Antitumor Immunity in Tumor Microenvironment and Facilitate Immunotherapy
- First Published: 24 May 2025
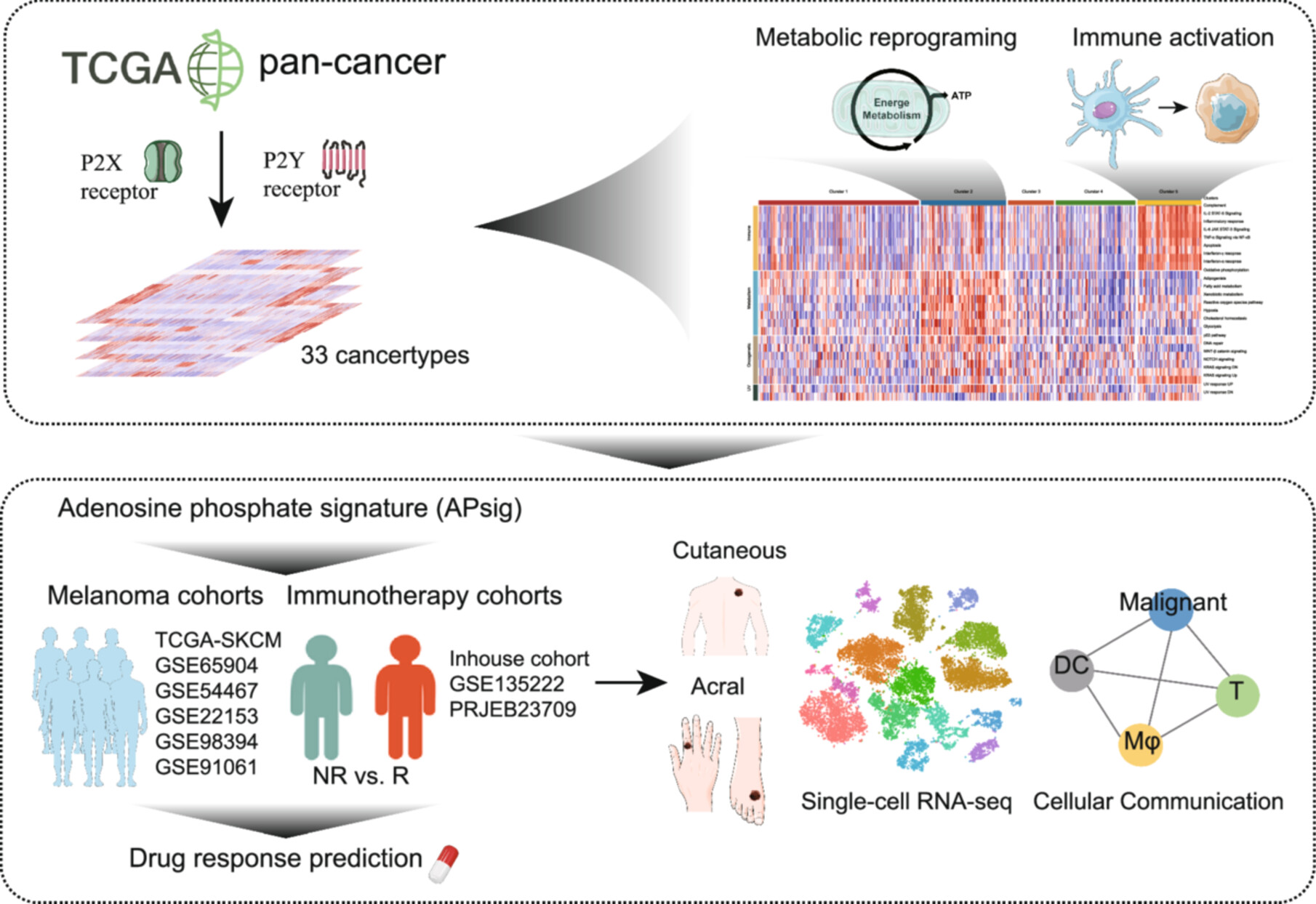
A comprehensive analysis of the purinergic signaling mediated by P2 receptors (P2Rs) was conducted at both bulk, single-cell, and spatial transcriptomic levels, evaluating the prognostic and predictive value of the adenosine signaling pathway in cancer immunotherapy. The results underscore the potential of targeting purinergic P2 signaling in the development of novel anticancer therapies, particularly in combination with immune checkpoint inhibitors.
REVIEW ARTICLE
Oxidative Stress in Antigen Processing and Presentation
- First Published: 14 May 2025
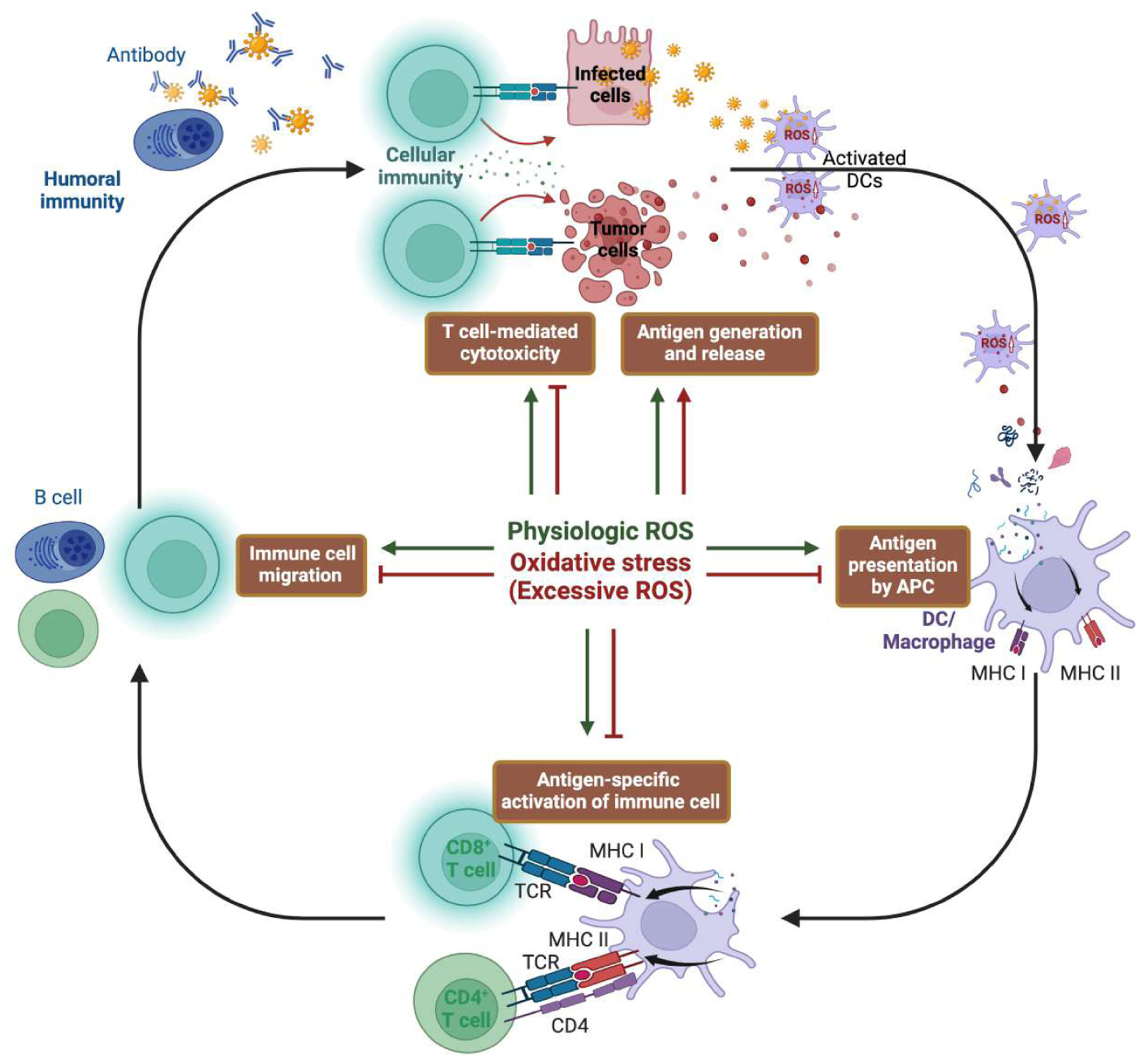
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) play a crucial role in antigen processing and presentation, essential for linking innate and adaptive immunity. While balanced ROS levels promote immune function, excess ROS can disrupt antigen recognition, resulting in immune dysfunction. Targeted therapies to regulate ROS present new avenues for enhancing immunotherapy.
Mitochondrial Ribosomal Protein Family in Cancers: Mechanistic Insights and Therapeutic Implications
- First Published: 14 June 2025
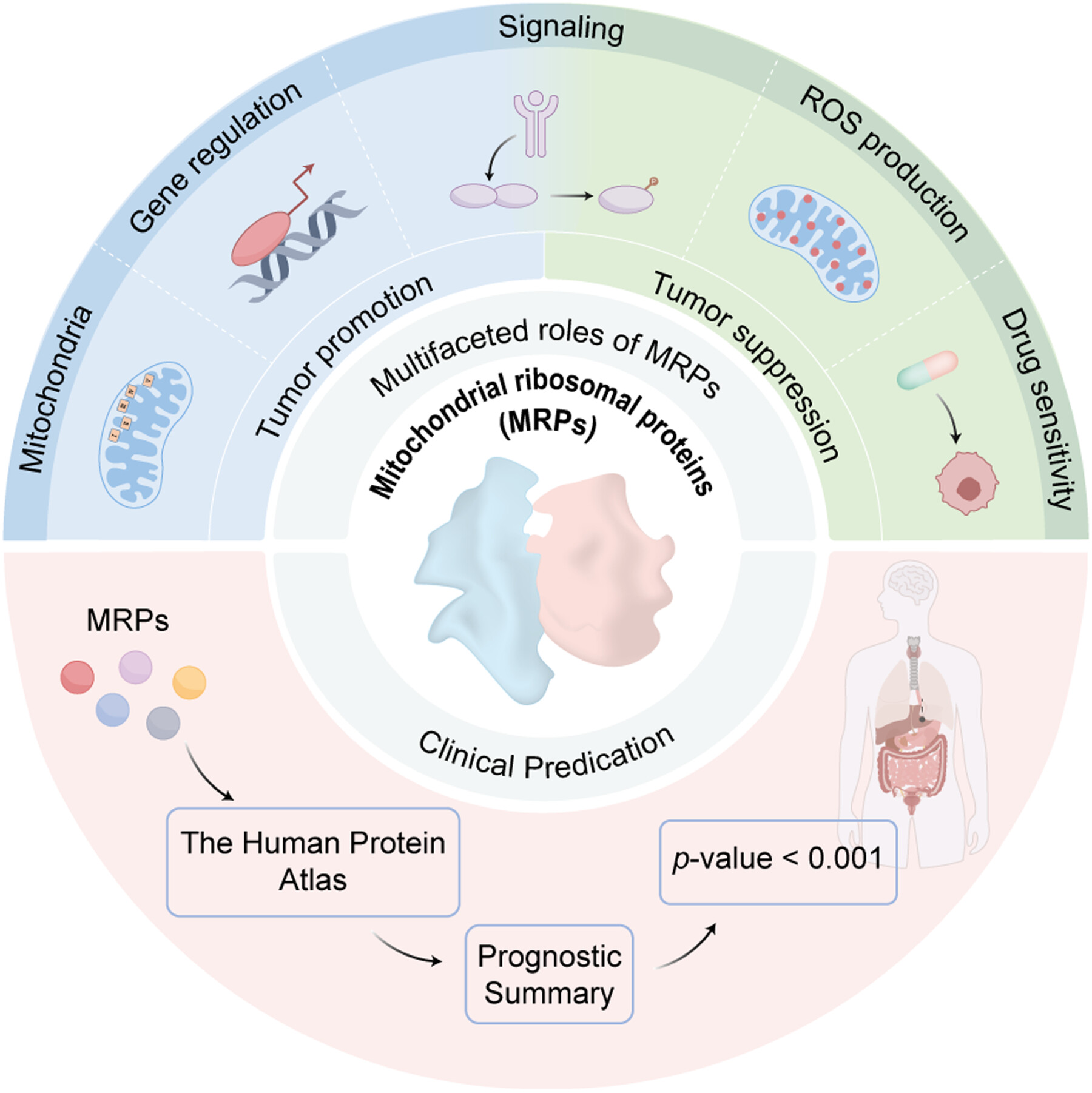
Mitochondrial ribosomal proteins (MRPs) are the important components of mitoribosome. They are aberrantly expressed in various human cancers. In this review, we introduce the roles of MRPs in tumorigenesis and development by regulating OXPHOS and other mechanisms. Furthermore, to confirm the potential of MRPs as biomarkers, we predict the relevance of MRPs family with prognosis and immunotherapy in different cancers.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Alcohol Dehydrogenase 4-Mediated Retinol Metabolism Inhibits Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression Through Inhibiting the Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway
- First Published: 24 April 2025
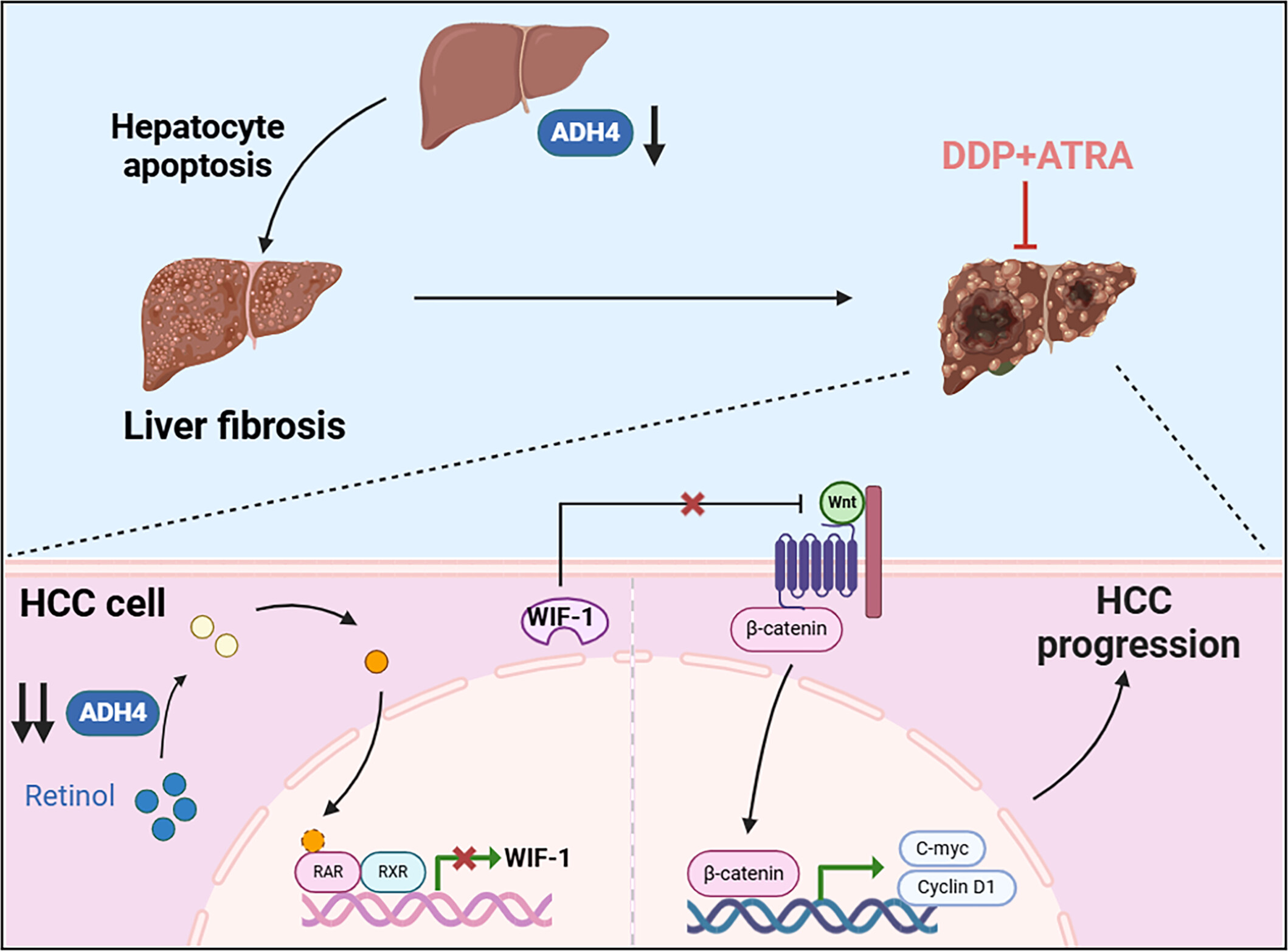
The downregulation of ADH4 expression induces hepatocyte apoptosis, thereby contributing to liver fibrosis and the initiation of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Moreover, sustained suppression of ADH4 in HCC cells disrupts retinoic acid synthesis, leading to reduced expression of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling inhibitor WIF-1 via RARs/RXRs-mediated mechanisms. This disruption fosters the upregulation of oncogenic regulators such as c-Myc and Cyclin D1, thereby accelerating HCC progression. Notably, the combination therapy involving all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA) and cisplatin exhibits a pronounced synergistic antitumor effect.
HIGHLIGHT
Foe to Ally: Oncolytic Virus-Driven Xenorejection Ignites Potent Antitumor Immunity
- First Published: 04 June 2025
REVIEW ARTICLE
Characteristic, Regulation and Targeting Strategies of Cancer Stem Cells and Their Niche in Digestive System Tumors
- First Published: 08 April 2025
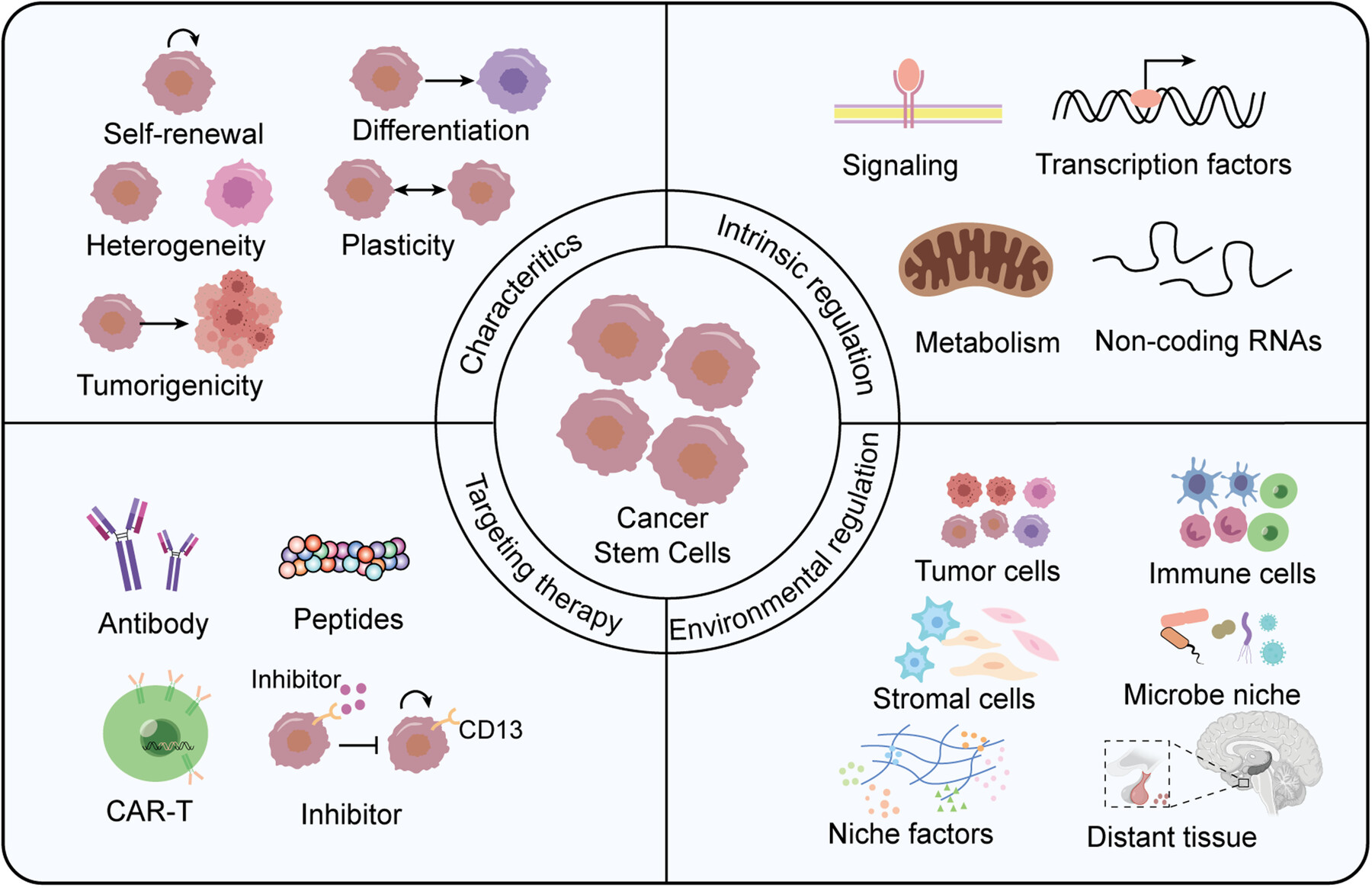
Cancer stem cells, characterized by self-renewal, differentiation, heterogeneity, plasticity and tumorigenicity, are regulated by intrinsic factors such as signaling pathways, transcription factors, metabolism and noncoding RNAs, as well as environmental cells (including tumor cells, immune cells and stromal cells), environmental factors and distant tissues. CSCs and their niche serve as promising target for tumor elimination.