Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Table of Contents
Development of covalent inhibitors: Principle, design, and application in cancer
- First Published: 31 October 2023
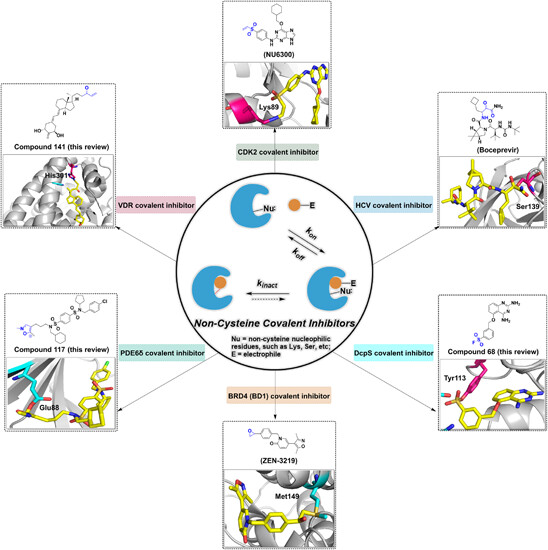
The noncysteine covalent inhibitors are a class of small molecule inhibitors that can bind irreversibly to their target enzymes through covalent bonding with noncysteine residues. They have shown promise as potential therapeutics for a variety of diseases, including cancer, infectious diseases, and autoimmune disorders. Examples of noncysteine covalent inhibitors. The illustration emphasizes the representative noncysteine covalent inhibitors in drug discovery and development.
Fatty acids in cancer: Metabolic functions and potential treatment
- First Published: 10 March 2023
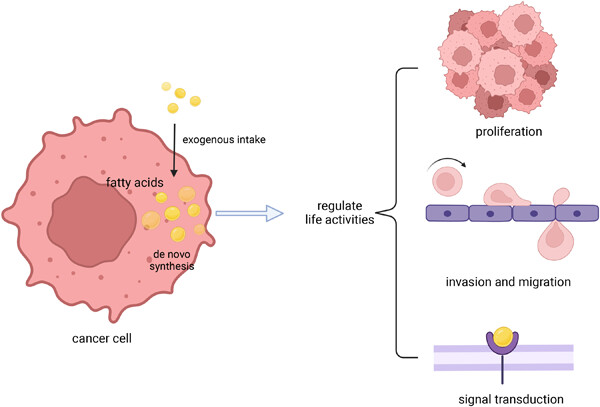
Fatty acids in cancer cells are derived from cellular synthesis and extracellular uptake. Fatty acids are extensively reprogrammed in cancer cells and regulate life activities, including supporting cell growth as energy, influencing cell movement as components of membrane structure, and regulating signal transduction as signaling molecules. Focusing on the role of fatty acids in tumor cells is helpful to find new strategies for tumor treatment.
Microtubule-targeting agents for cancer treatment: Seven binding sites and three strategies
- First Published: 16 August 2023
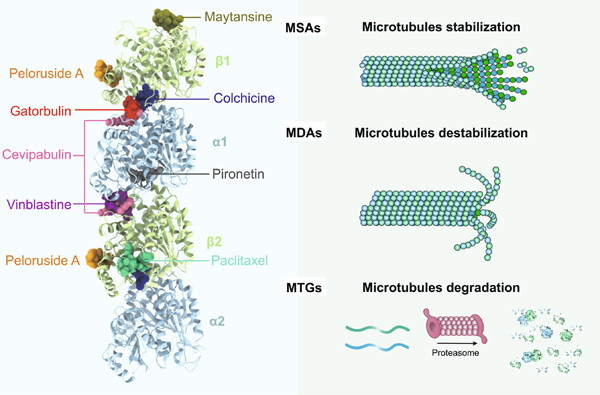
Microtubule-targeting agents (MTAs) are pivotal in the field of cancer treatment. This study presents a comprehensive review of the seven binding sites and three strategies (stabilization, destabilization, and degradation) utilized by MTAs, along with an overview of their current clinical applications and challenges. This review provides insights into the development of new-generation MTAs for cancer therapy.
cGAS-STING signaling in cancer: Regulation and therapeutic targeting
- First Published: 21 August 2023
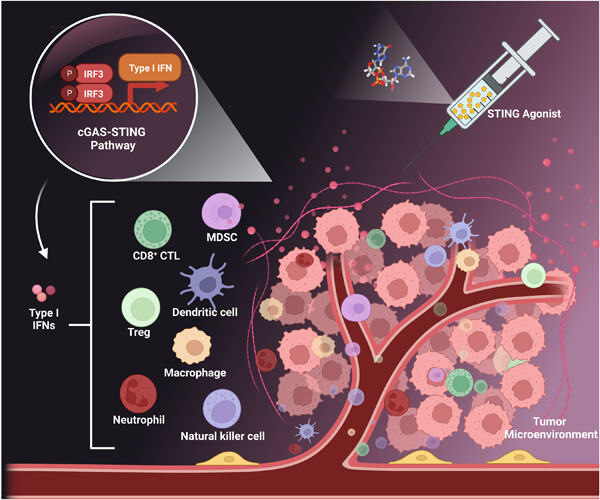
Immunotherapy has revolutionized antitumor therapy, and the study of stimulator of interferon genes (STING) pathway and STING agonists have become a fantastic research area in recent years. The cyclic GMP–AMP synthase (cGAS)-STING pathway influences almost all aspects of tumorigenesis and has great antitumor potential. In this review, we summarize the activation and potential mechanisms of the cGAS-STING pathway, discuss the association of the cGAS-STING pathway with tumors and autoimmune diseases, and highlight research progress, clinical applications, and combination drug strategies for STING agonists.
Delivering CAR-T cells into solid tumors via hydrogels
- First Published: 20 June 2023
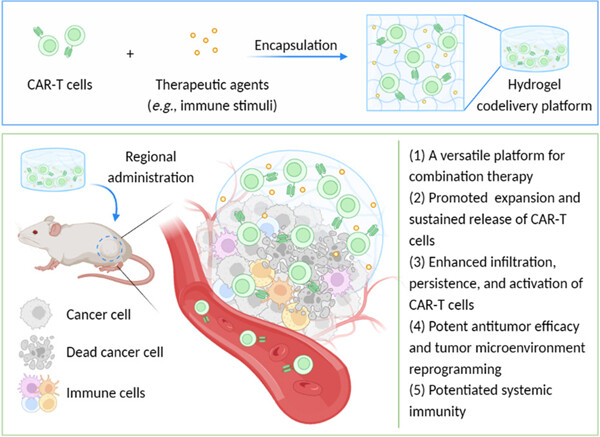
This perspective comments on the regional codelivery of chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-T cells and therapeutic agents via hydrogels for solid tumor treatment. Diverse design strategies of CAR-T cell delivery hydrogel depots are introduced and discussed, with an emphasis on their applications for cancer immunotherapy. The current limitations and future research directions regarding the use of hydrogels for CAR-T cell therapy are also proposed.
Oncolytic virotherapy using neural stem cells as a novel treatment option for glioblastoma multiforme
- First Published: 31 January 2023
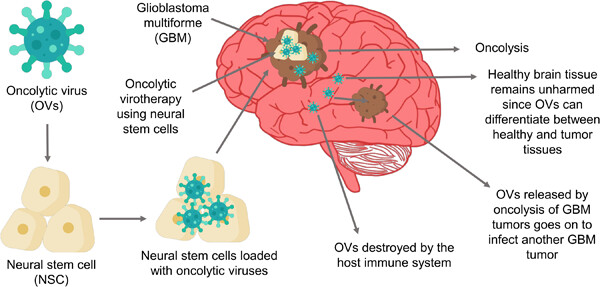
The oncolytic viruses (OVs) are loaded into neural stem cells (NSCs) which acts as a carrier. The NSCs loaded by OVs are then transferred into the brain where the NSCs release the OVs into the precise tumor locations (GBM tumors). The OVs multiply inside the tumor and carries out oncolysis. The OVs gets liberated to infect more GBM tumors.
Viral vector-based cancer treatment and current clinical applications
- First Published: 29 October 2023
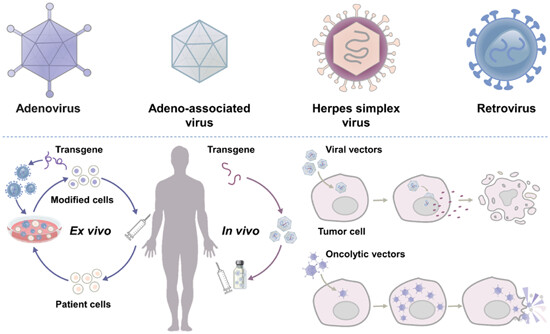
Adenovirus, adeno-associated virus, herpes simplex virus, and retrovirus have been utilized for cancer treatment. Ex vivo treatment: cells isolated from the patients are genetically modified by viral vectors and then transfused back into patients. In vivo treatment: viral vectors display the antitumor effects through expression of transgenes, particularly, oncolytic vectors can replicate in the tumor cells to lyse them.
Big data and single-cell sequencing in acute myeloid leukemia research
- First Published: 28 August 2023
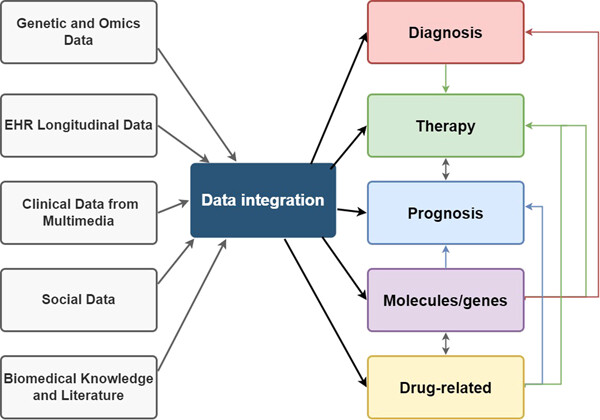
Utilizing numerous amounts of different kinds of data from various sources can contribute to further understanding of acute myelogenous leukemia, playing a positive role in different aspects of research and applications to benefit patients, and the discoveries in different fields can even interact to provide one-way or mutual promotion as well. Among various data sources, single-cell sequencing is an emerging option that is powerful and impressive.
Gasdermin E plasmid DNA/indocyanine green coloaded hybrid nanoparticles with spatiotemporal controllability to induce pyroptosis for colon cancer treatment
- First Published: 02 June 2023
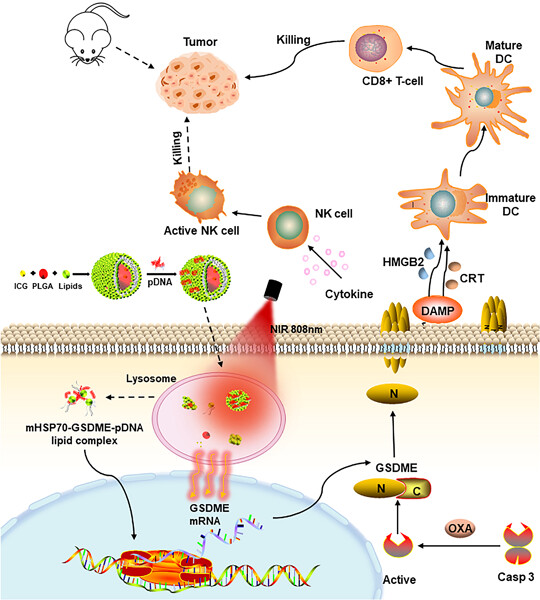
We develop lipid-coated poly(lactide-co-glycolide) nanoparticles coloaded with indocyanine green and Gasdermin E expressing plasmid DNA (GSDME-pDNA) to possess the spatiotemporal controllability of target gene expression induced by a heat-inducible mHSP70 promoter. Oxaliplatin is administered to activate caspase-3 to cleave GSDME to cause pyroptosis, which promotes the release of damage-associated molecular patterns molecules and causes an immunogenic inflammatory response and attendant strong antitumor effect.
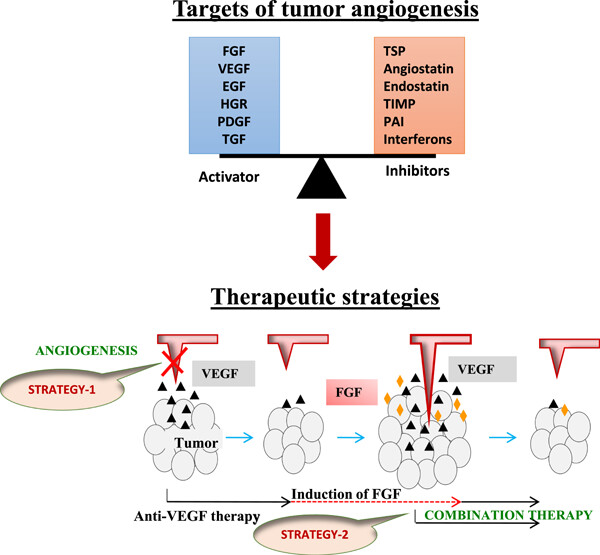
Insight on the cellular and molecular basis of blood vessel formation: A specific focus on tumor targets and therapy
- First Published: 08 February 2023
Immune checkpoint inhibitor-related myocarditis in thymic epithelial tumors: Recent progress and perspectives
- First Published: 17 May 2023
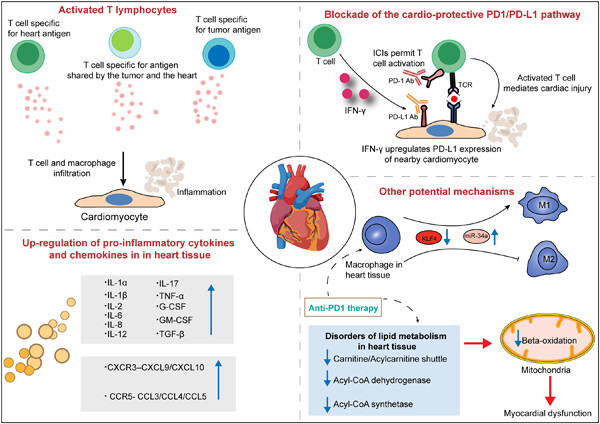
Potential mechanisms driving myocarditis associated with immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) therapy. Insights from studies of ICI-related cardiotoxicity suggest that various mechanisms contribute to the development of myocarditis, which includes activated T lymphocytes, pro-inflammatory cytokine storms in heart tissues, overexpressed chemokine axes, polarization of macrophages and disorders of lipid metabolism in heart tissues and so on.
NKT cells contribute to alleviating lung metastasis in adenoid cystic carcinoma
- First Published: 15 April 2023
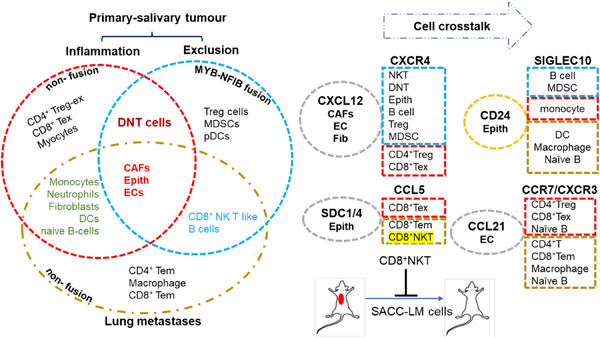
Our single-cell sequencing data reveals significant differences in the composition of immunocytes, intercellular communication, and signaling molecules between primary inflamed and primary excluded tissues, as well as metastatic lung inflamed tissues from salivary adenoid cystic carcinoma (SACC) patients. Furthermore, the analysis of the animal experimental results demonstrates that CD8 + NK cells have therapeutic potential for inhibiting lung metastasis.
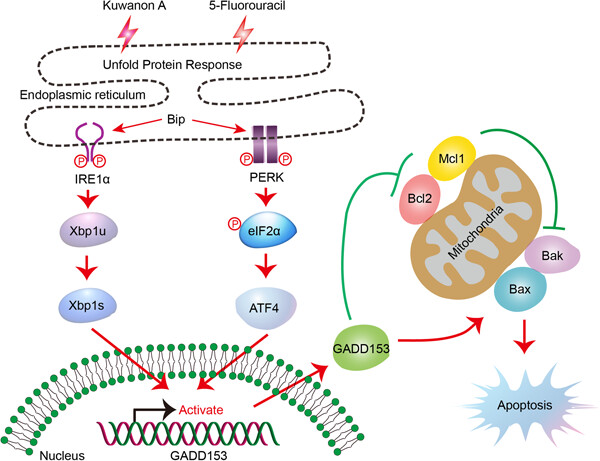
Morus alba derived Kuwanon-A combined with 5-fluorouracil reduce tumor progression via synergistic activation of GADD153 in gastric cancer
- First Published: 19 February 2023
Precision gas therapy by ultrasound-triggered for anticancer therapeutics
- First Published: 20 March 2023
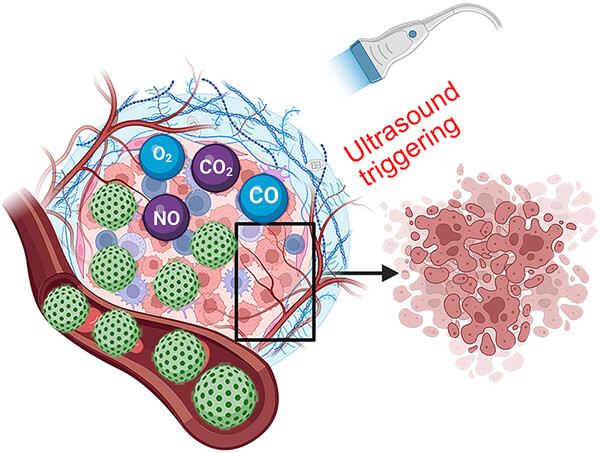
The gas-generating platforms for tumor therapy precisely have been as a green treatment method. We summarized a nice overview on the mechanism, the common gas release pathways of NO, O2, CO, CO2 under ultrasound, and their applications for tumor therapy. We believe this review could represent a new field on antitumor.
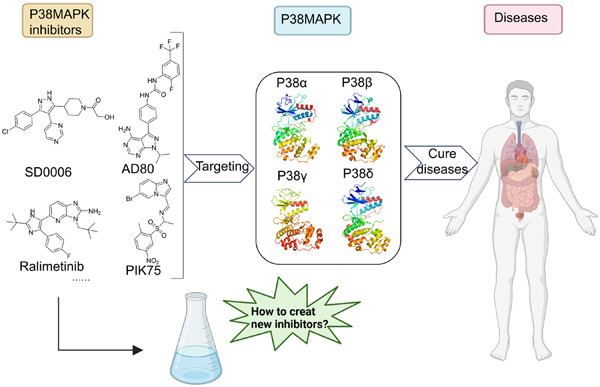
p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase: Functions and targeted therapy in diseases
- First Published: 26 September 2023