Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
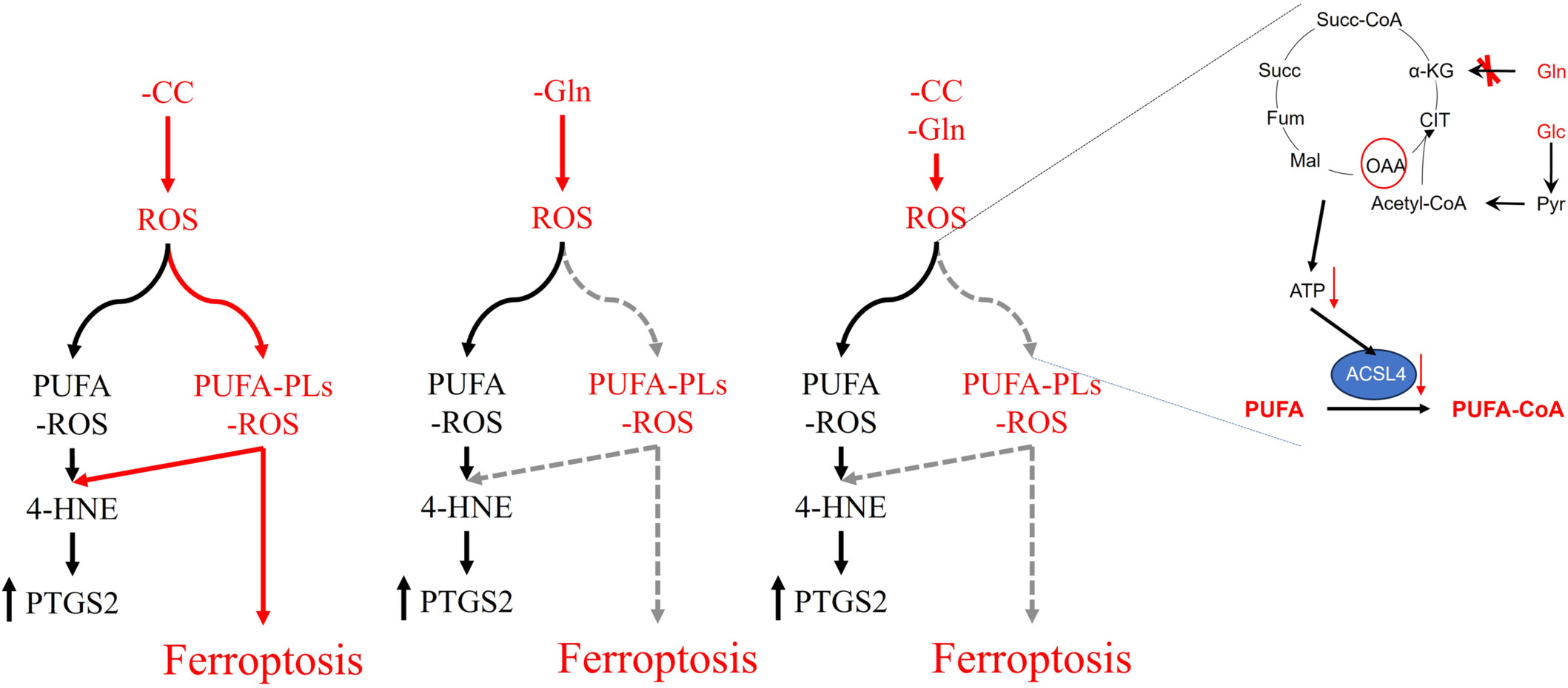
Mitochondria ATP Pro-Ferroptosis by Adjusting the Conversion of PUFA to PUFA-PLs
- First Published: 24 July 2025
REVIEW ARTICLE
Targeting Immune Checkpoints: Basic Signaling Pathways and Clinical Translation in Cancer Therapeutics
- First Published: 07 July 2025
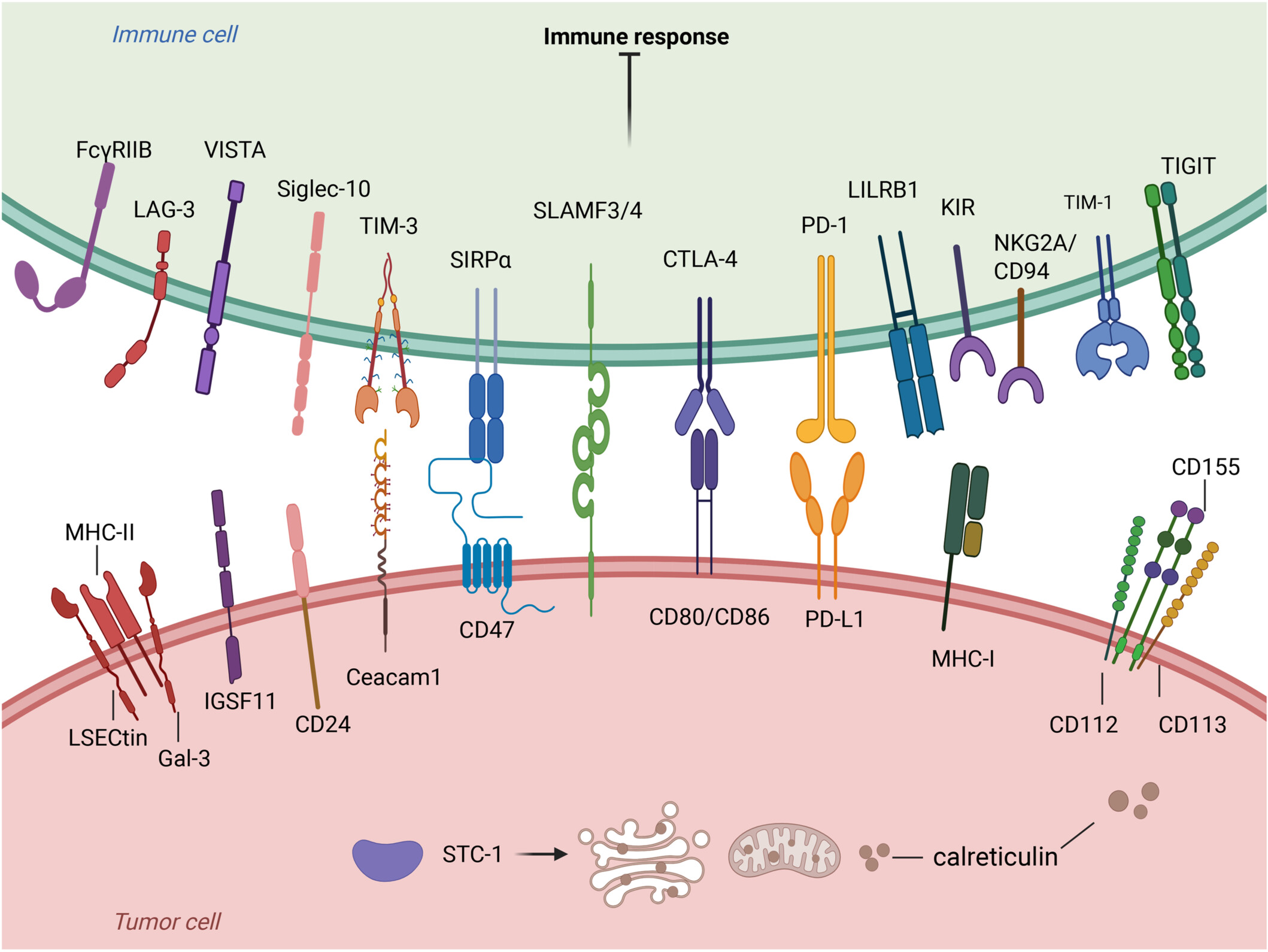
Immune checkpoints in tumor immunotherapy. Ligand binding to the receptor inhibits immune cell function, promotes tumor cell immune escape, and suppresses the immune response. The pathways of action are VISTA-IGSF11, TIM-3-Ceacam1, CD47-SIRPα, CTLA-4-CD80/CD86, PD-L1-PD-1, MHC-1-LILRB, and CD24 - Siglec -10. There are also other immune checkpoints such as FcγRIIB, LAG-3, SLAMF3/SLAMF4, KIR, NKG2A/CD94, TIGIT, and STC-1.
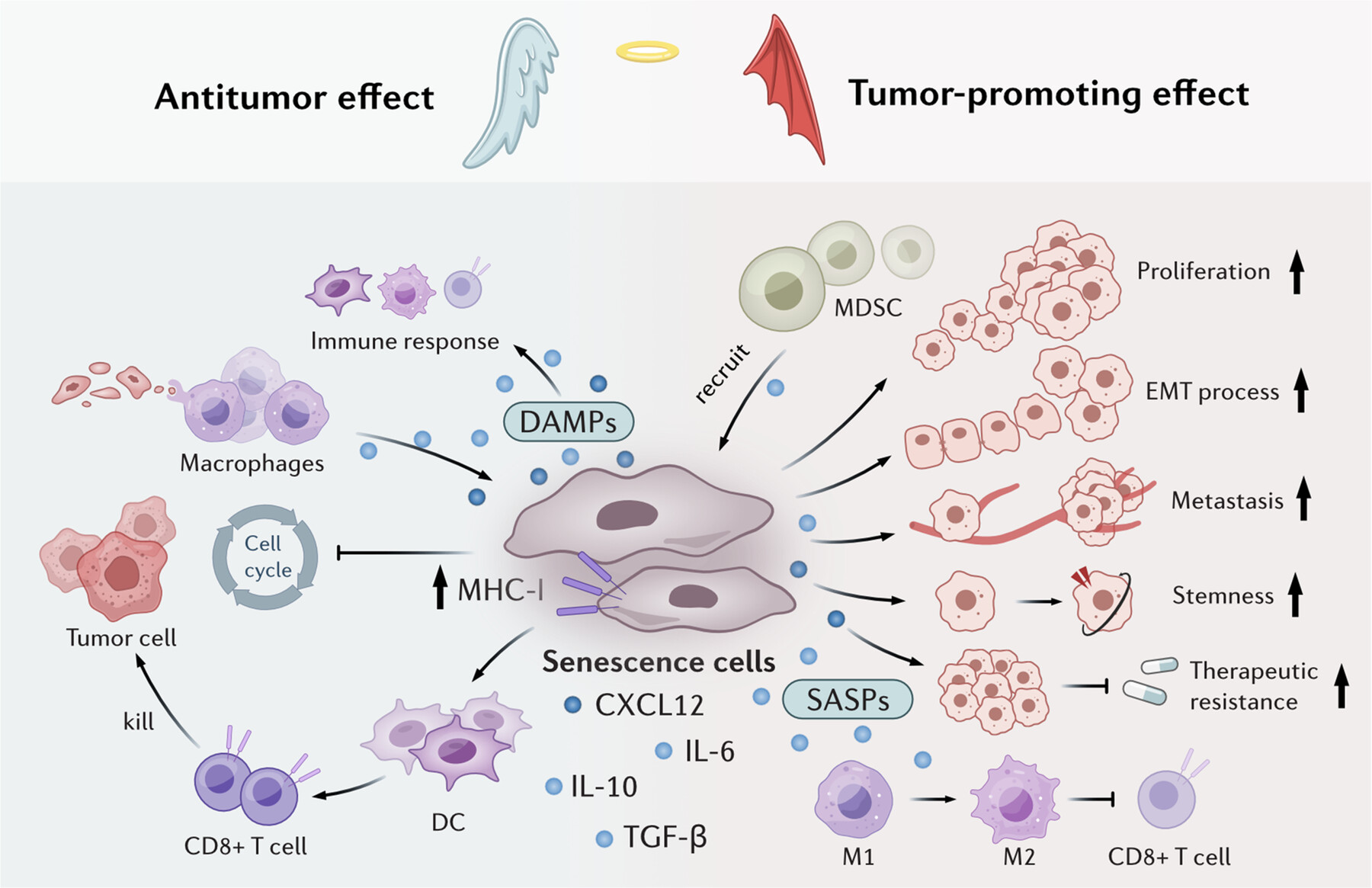
Cellular Senescence in Cancer: Mechanisms, Roles in Tumor Progression, and Therapeutic Implications
- First Published: 07 July 2025
Transforming Growth Factor-Beta Signaling in Cancer: Therapeutic Implications, Challenges, and Pathways to Progress
- First Published: 14 July 2025
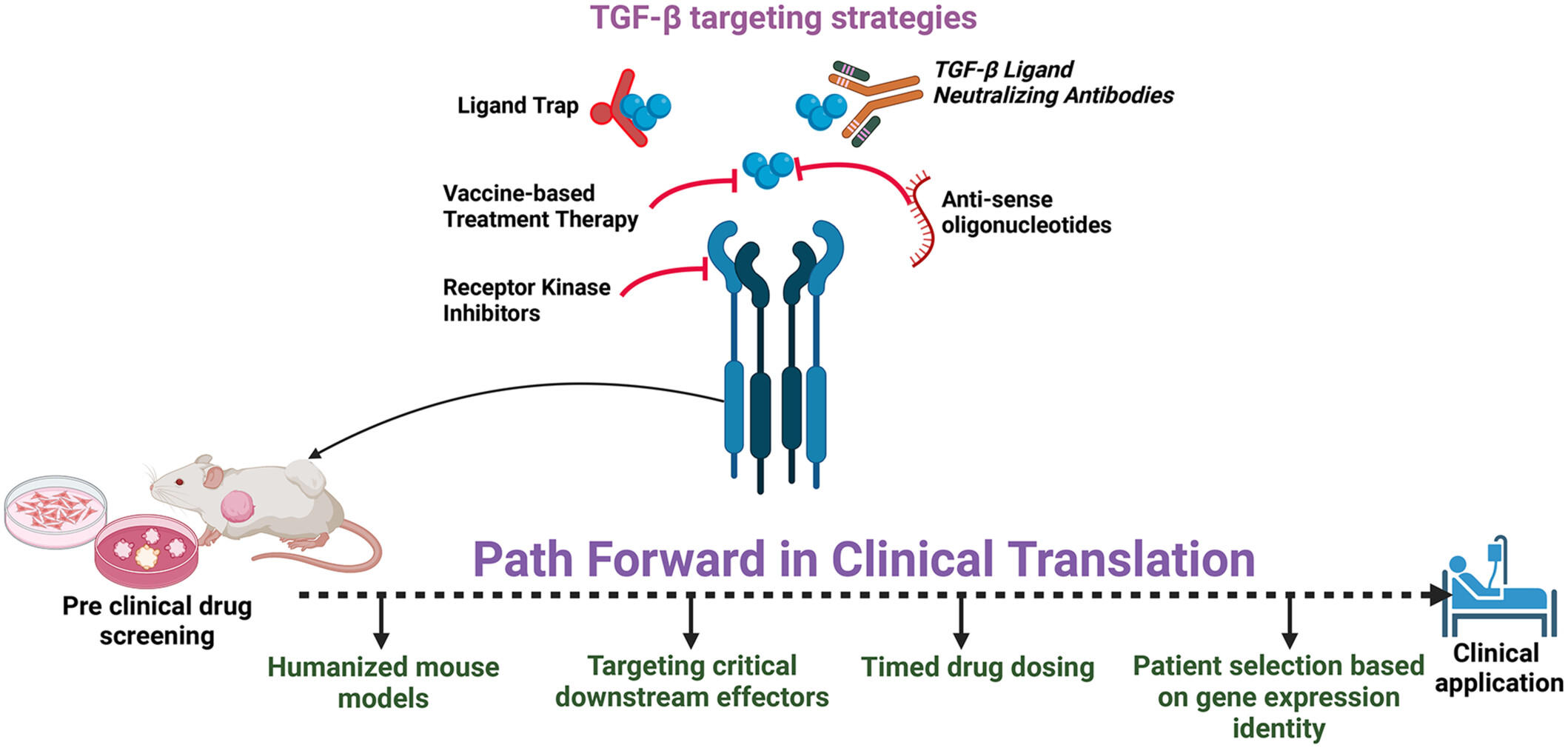
TGF-β inhibition is emerging as a promising cancer therapy, yet translating laboratory success to bedside implementation has suffered significant setbacks. The associated challenges include adverse drug reactions, inadequate predictive models, and activation of alternative signaling pathways. To bolster the therapeutic efficacy of TGF-β blockade, strategies such as optimized dosing regimens, adoption of humanized mouse models that better replicate human disease, and refined patient selection based on genetic profiles are crucial. These approaches aim to address current limitations and improve the translation of TGF-β inhibition from preclinical promise to clinical reality.
LETTER
Using Period Analysis to Timely Provide Serial Data on Long-Term Survival for Gastric Cancer Patients From Taizhou, Eastern China
- First Published: 24 July 2025