Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
A Single-Nucleus Transcriptomic Atlas Reveals Cellular and Genetic Characteristics of Alzheimer's-Like Pathology in Aging Tree Shrews
- First Published: 15 March 2025
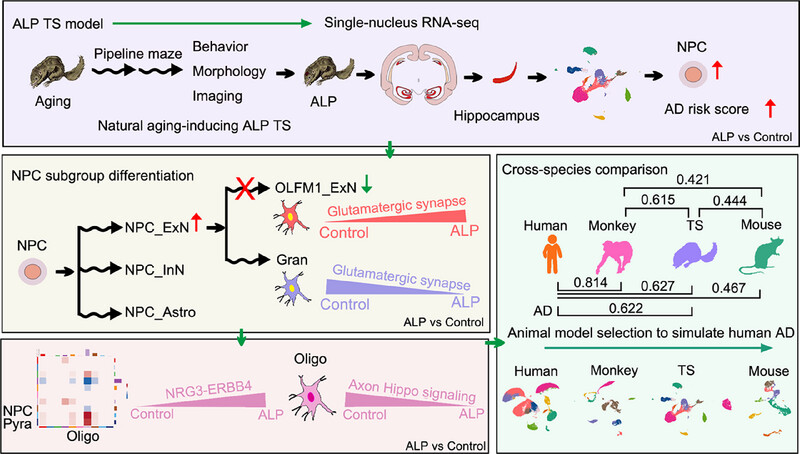
We present a novel Alzheimer's disease (AD) model using naturally aging tree shrews (TSs) that exhibit Alzheimer's-like pathology (ALP), offering unique insights into human AD progression. Through single-nucleus RNA sequencing, we mapped the hippocampal transcriptome, revealing key neural progenitor cell differentiation trajectories linked to AD. Cross-species comparisons demonstrated greater cellular and genetic similarities between TSs and primates than mice, highlighting conserved cell types, synaptic processes, and excitatory/inhibitory imbalances. Cell–cell communication patterns mirrored those in AD human tissue, underscoring the value of TSs as a translational model for AD research.
Mitigating Early Phosphatidylserine Exposure in a Tmem30a-Dependent Way Ameliorates Neuronal Damages After Ischemic Stroke
- First Published: 18 March 2025
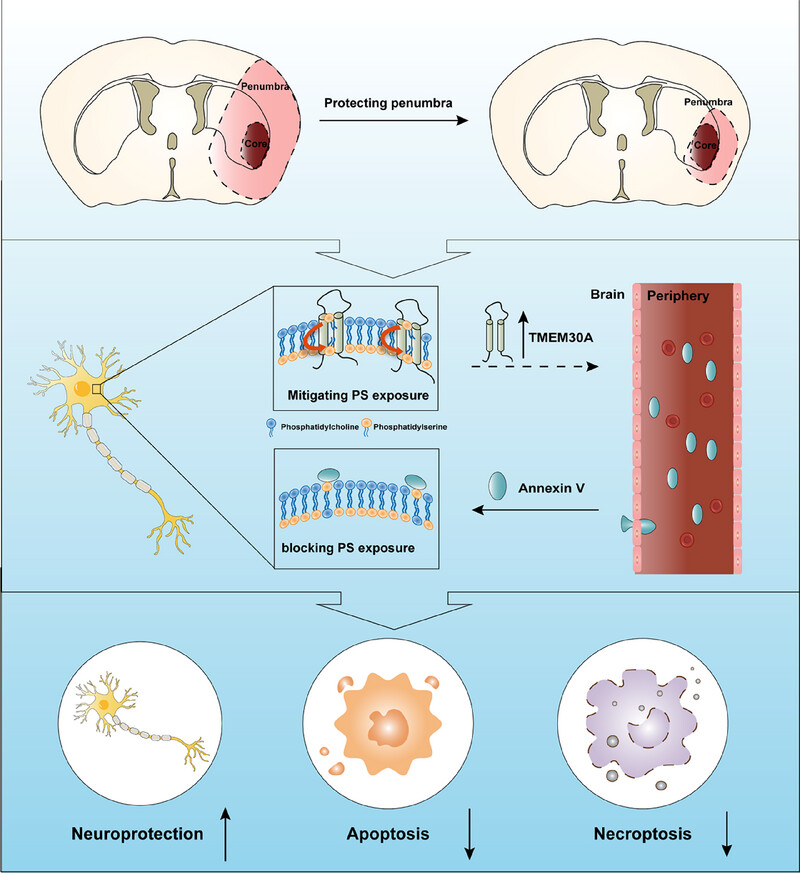
The ischemic penumbra is the hypo-perfused brain tissue at risk of progressing to infarction but is still salvageable if re-perfused. Wu et al. demonstrate increased plasma Annexin V reduced PS exposure in a Tmem30a-dependent way in the penumbra after stroke, consequently leading to a better neurological outcome. Thus, Tmem30a-mediated externalization of PS may be a novel mechanism and target in stroke.
Swimming Exercise Pretreatment Attenuates Postoperative Delirium-Like Behavior in Type 2 Diabetic Rats by Enhancing Mitochondrial Biogenesis Through Activation of SIRT2 Deacetylation
- First Published: 18 March 2025
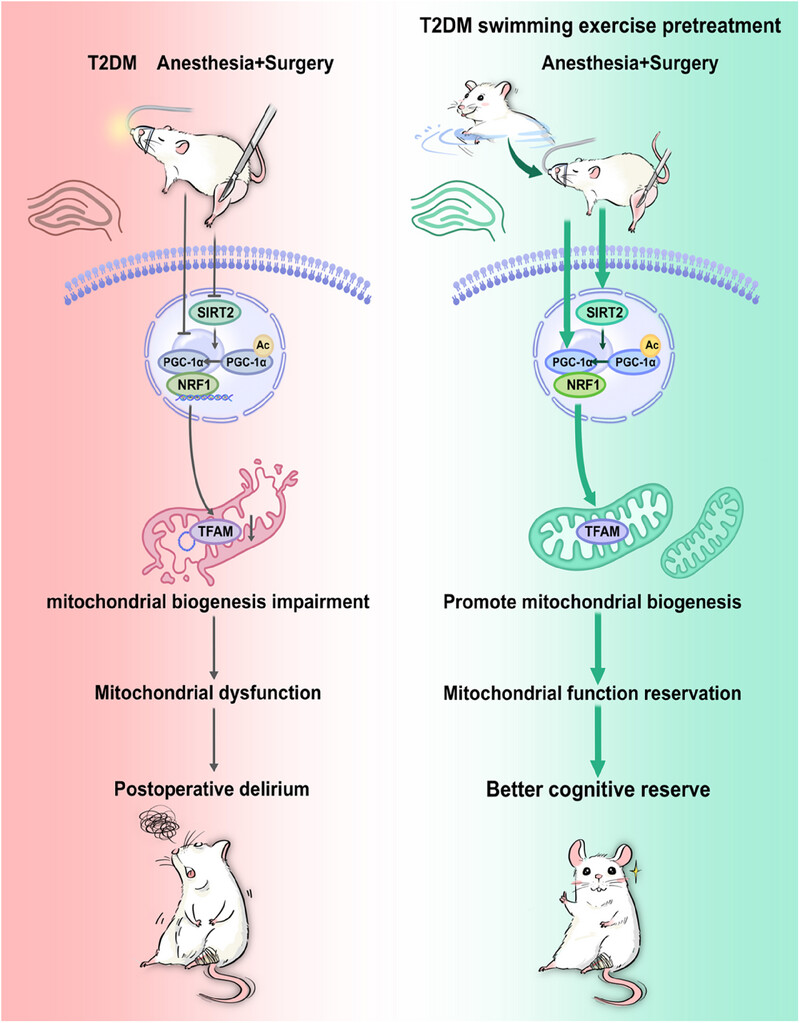
The reduction of SIRT2 following orthopedic surgery in the hippocampus of T2DM rats inhibits the acetylation process of PGC-1α and the subsequent mitochondrial biogenesis process, leading to mitochondrial dysfunction and postoperative delirium-like behavior. Preoperative swimming exercise upregulates SIRT2 and PGC-1α expression in hippocampal neurons, activating mitochondrial biogenesis, preserving mitochondrial function, and improving postoperative cognitive outcomes in T2DM rats.
Subsequent Survival and Loss of Lifetime for Patients With Progression-Free 24 Months After Treatment in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma: A Comprehensive Nationwide Population-Based Analysis
- First Published: 20 March 2025
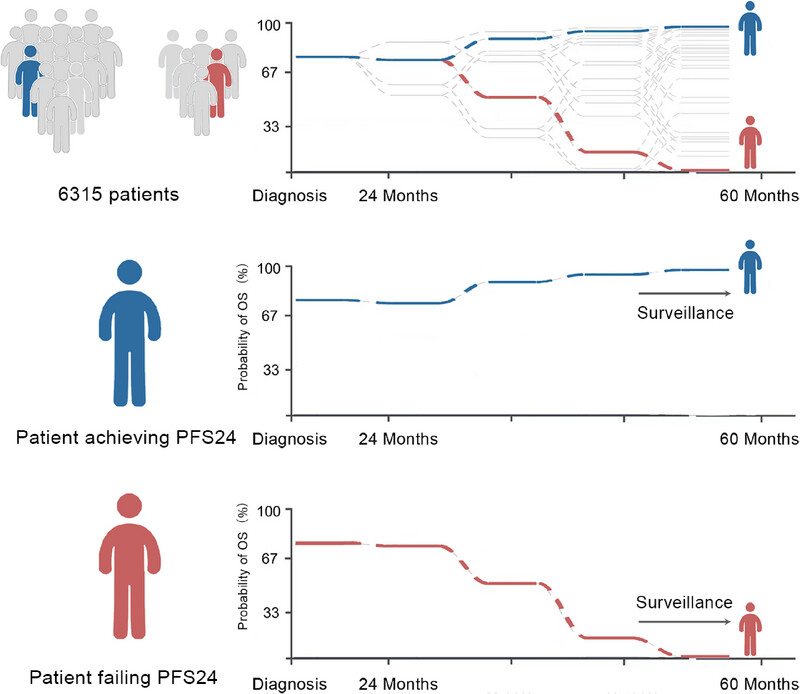
Progression-free survival at 24 months (PFS24) is a valid milestone for risk stratification, patient surveillance, and study design in nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC). Patients achieving PFS24 exhibited a comparable subsequent overall survival (sOS) and loss of lifetime (LoL) with the background population. Patients failing to achieve PFS24 had markedly unfavorable outcomes, with significantly reduced 5-year sOS and higher LoL.
LETTER
Rational Design, Synthesis, and Biological Assessment of Potential Indole-Capped HDAC6 Inhibitors for Gastric Cancer Suppression
- First Published: 20 March 2025
REVIEW
Bioactive hemostatic materials: a new strategy for promoting wound healing and tissue regeneration
- First Published: 22 March 2025
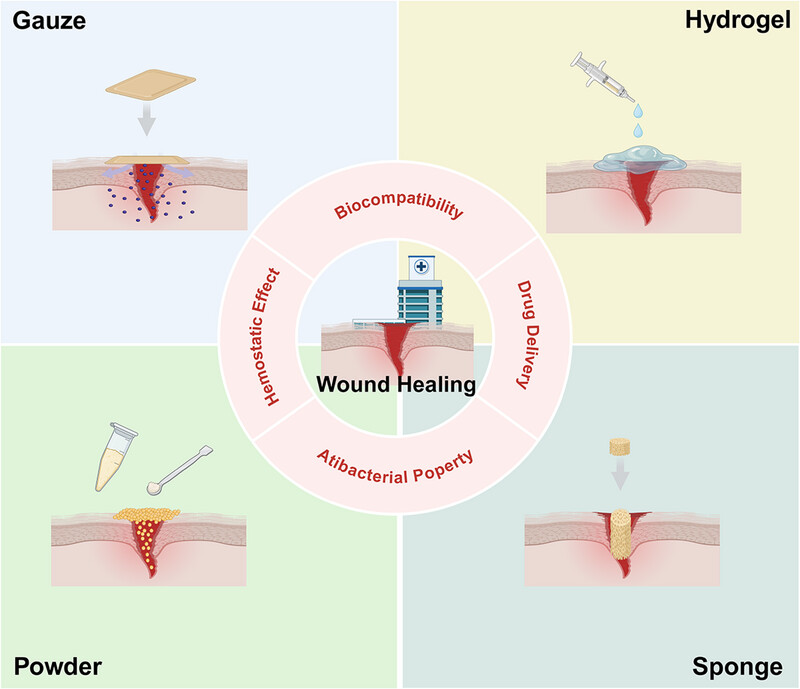
This paper reviews the current status and latest advancements in the field of hemostatic materials, focusing on the mechanism of hemostasis and wound healing, the chemical design principles and physiological mechanisms of hemostatic materials, and the comparison of different active ingredients and dosage forms. In addition, considering the subsequent needs of wound healing posthemostasis, this review also discusses the main challenges and future directions of hemostatic materials for wound healing .
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Integrated Analysis of the Anoikis-Related Signature Identifies Rac Family Small GTPase 3 as a Novel Tumor-Promoter Gene in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- First Published: 22 March 2025
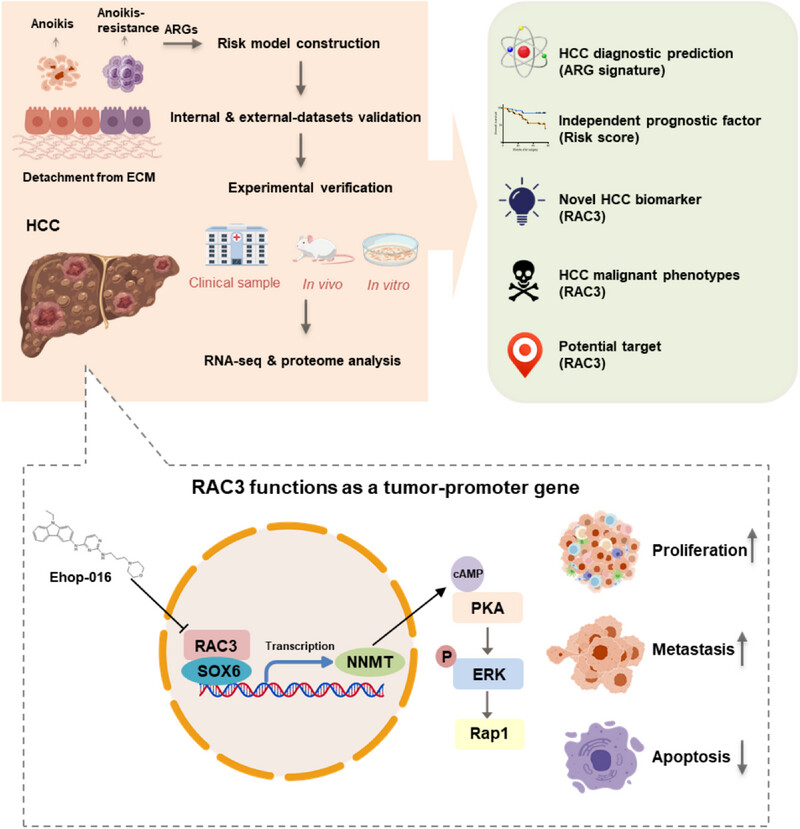
A five-gene risk model is constructed based on anoikis-related genes by internal and external cross-validation. The risk model serves as an independent prognostic factor for HCC. RAC3, a novel anoikis-related oncogene in HCC, promotes cell proliferation and invasion, and inhibits apoptosis. RAC3 interacting with SOX6 accelerates HCC malignant phenotypes via NNMT-mediated cAMP/MAPK/Rap1 signaling activation. Targeting RAC3 by EHop-016 suppresses HCC progression. .
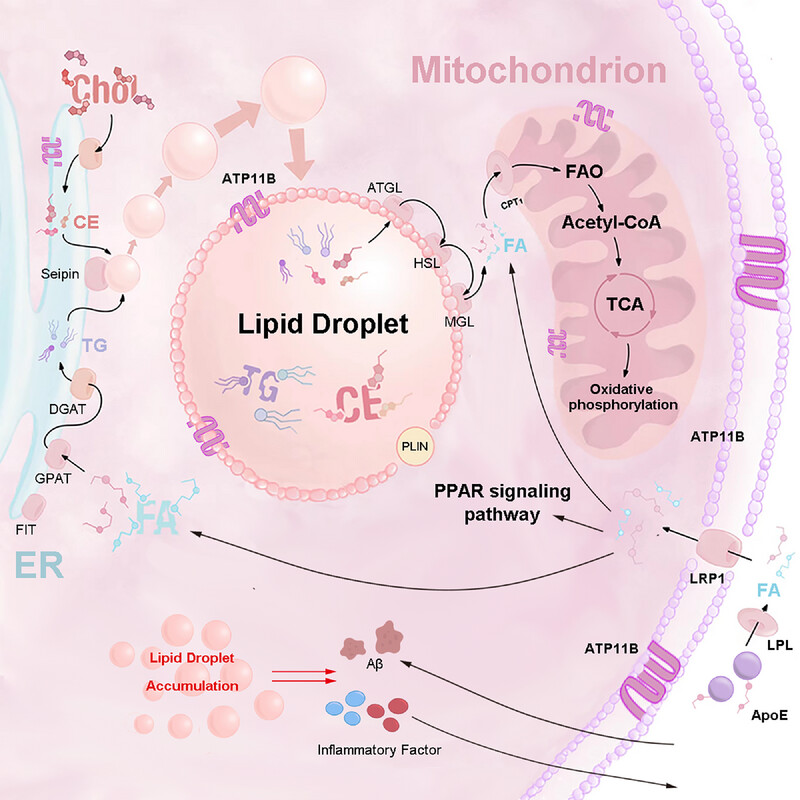
ATP11B Modulates Microglial Lipid Metabolism and Alleviates Alzheimer's Disease Pathology
- First Published: 22 March 2025
REVIEW
The Peptide PROTAC Modality: A New Strategy for Drug Discovery
- First Published: 24 March 2025
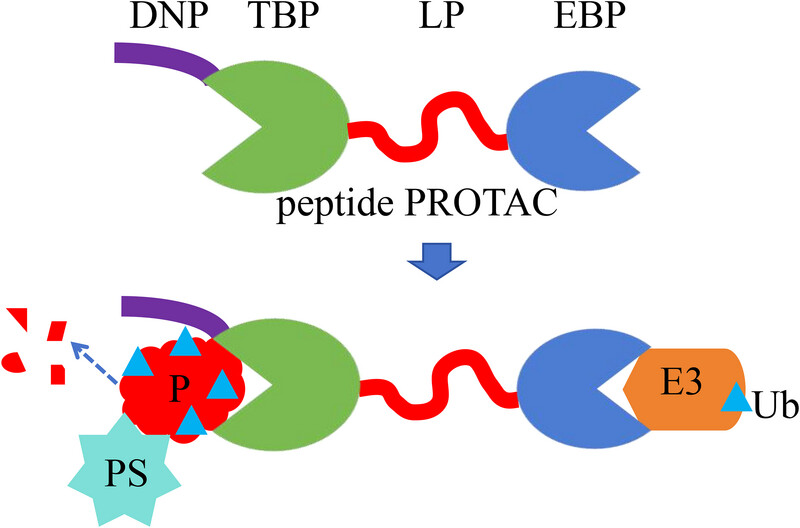
Peptide PROTAC is a bifunctional molecule generally composed of a target protein binding peptide (TBP), a linker peptide (LP), an E3 ligase binding peptide (EBP), and a delivery-enhancing peptide (DEP), which can bind to the target protein (P) and E3 ligase (E3), inducing P to be labeled with ubiquitin (Ub) and subsequently recognized and degraded by the proteasome (PS) .
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
(−)-Epicatechin Rescues Memory Deficits by Activation of Autophagy in a Mouse Model of Tauopathies
- First Published: 24 March 2025
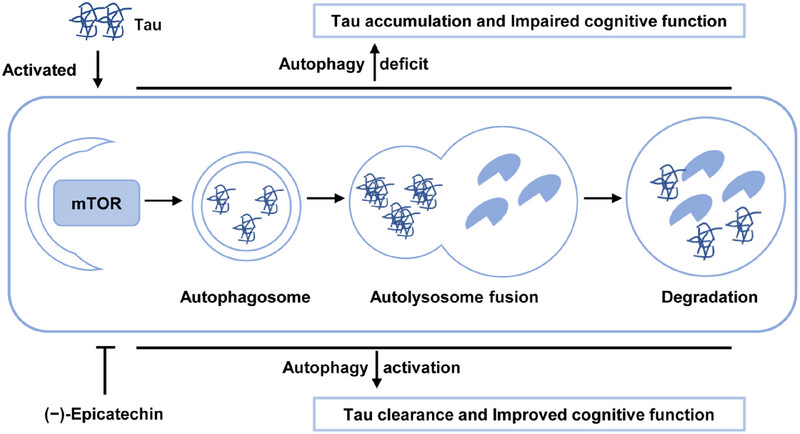
Accumulated tau induces autophagy deficits by activating mTOR. However, (−)-Epicatechin enhanced autophagosome formation, leading to the degradation of aggregated tau proteins via suppressing mTOR activity. This activation of autophagy and subsequent reduction in tau pathology contribute to the observed improvements in synaptic density, reversed neuron loss and attenuated neuroinflammation, and enhanced cognitive function in P301S mice. The graphical abstract image was created using Adobe Photoshop CS3.
Intranasal Inoculation of Cationic Crosslinked Carbon Dots-Adjuvanted Respiratory Syncytial Virus F Subunit Vaccine Elicits Mucosal and Systemic Humoral and Cellular Immunity
- First Published: 24 March 2025
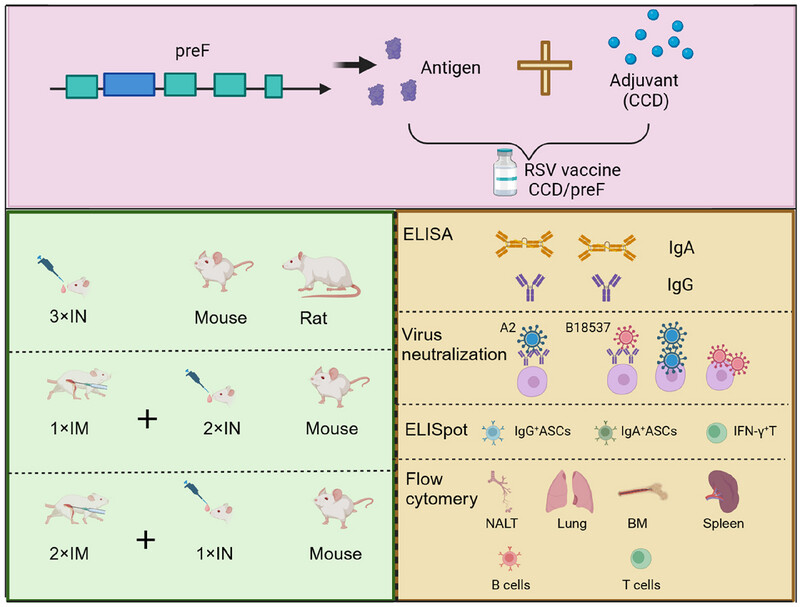
We prepared a CCD-adjuvanted preF vaccine for intranasal delivery against RSV infection. Three-dose intranasal administration of this vaccine induced long-lasting humoral and cellular immunity against RSV F protein at both local sites and systemic immune organs. We then optimized the CCD/preF vaccine by combining IM and IN immunization, which induced stronger systemic and mucosal immunity.
Calpain 2 Isoform-Specific Cleavage of Filamin A Enhances HIF1α Nuclear Translocation, Promoting Metastasis in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
- First Published: 27 March 2025
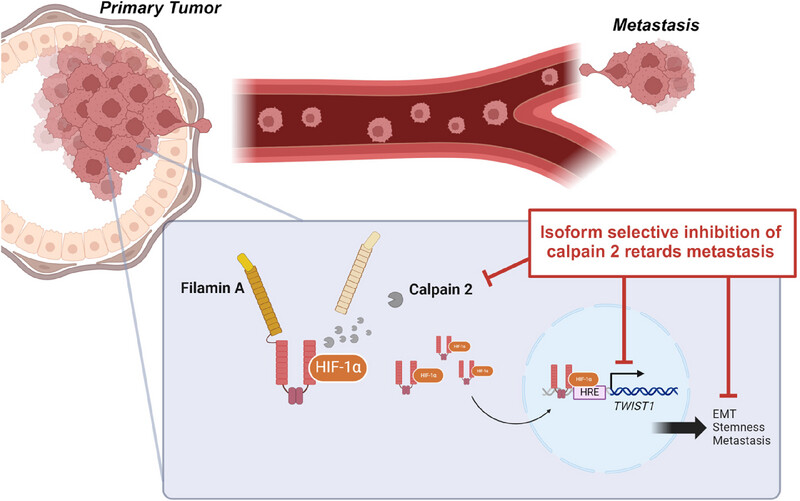
Calpain 2 cleaves Filamin A, leading to the activation of HIF-1α, which translocates to the nucleus and interacts with the hypoxia response element (HRE) on the TWIST1 gene promoter. The promoted expression of TWIST1 results in epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT), stemness, and metastasis. Isoform selective inhibition of calpain 2 specifically halts this cascade, thereby reducing metastasis.
Transforming Growth Factor Beta2 Promotes Migration and Inhibits the Proliferation of Gastric Cancer Cells by Regulating the pSmad2/3-NDRG1 Signaling Pathway
- First Published: 27 March 2025
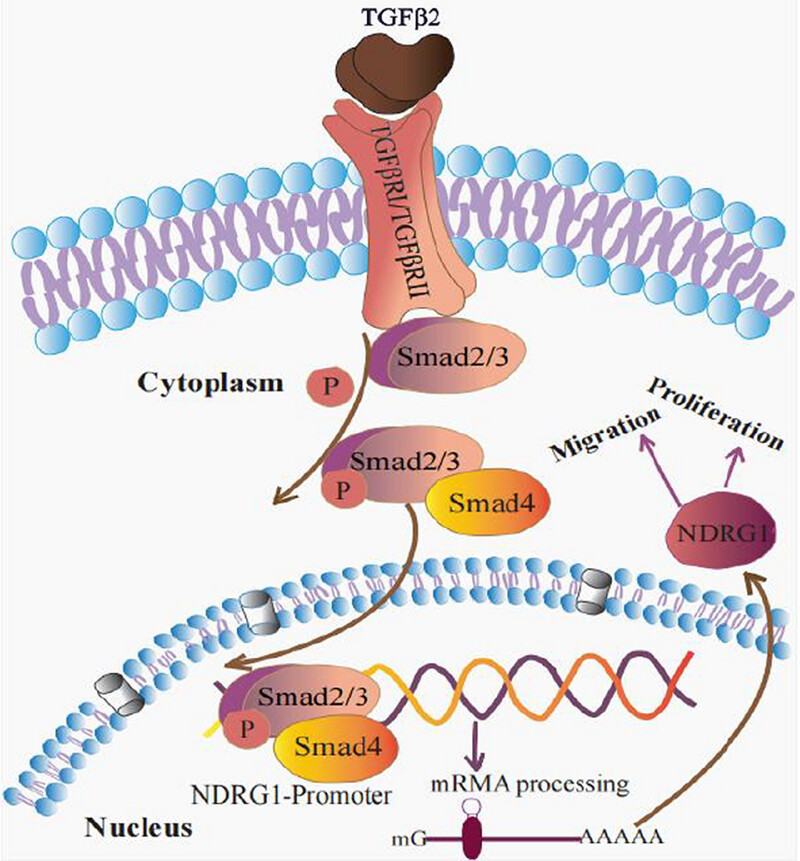
The binding of TGFβ2 to its cognate receptor triggers activation of the Smad2/3 signaling cascade. Following phosphorylation, Smad3 undergoes nuclear translocation where it specifically binds to the NDRG1 promoter region, facilitating transcriptional activation of this target gene. This molecular mechanism ultimately upregulates NDRG1 expression and enhances migratory capacity in gastric cancer(GC) cells.
LETTER
Stable Expressed DNMT3A Mutants Predict a Poor Prognosis in Acute Myeloid Leukemia Patients Without Receiving Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation
- First Published: 27 March 2025
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Identifying the Intergenic ALK Fusion LOC388942-ALK as a Driver of Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer
- First Published: 27 March 2025
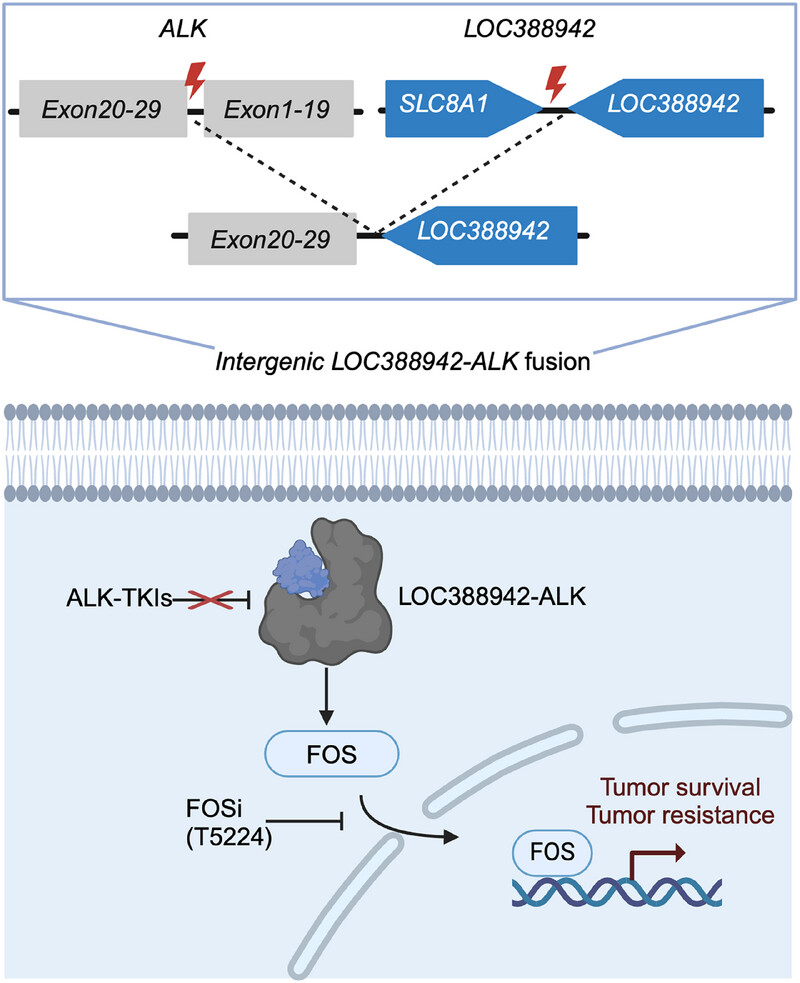
Intergenic breakpoint fusions are generally nonfunctional due to the lack of chimeric full-coding transcripts. However, in this study we demonstrate an intergenic fusions LOC388942-ALK (LA) drives oncogenesis through accelerated tumor growth (in vitro/vivo) and alectinib resistance. Crucially, FOS inhibition sensitizes LA tumors to treatment, establishing LA as a targetable NSCLC driver with therapeutic implications for fusion-positive malignancies.
REVIEW
HIGHLIGHT
Restoration of Transgelin 2 Expression Reverses Immune Escape in Ovarian Cancer: A Dawn for Immunotherapy
- First Published: 30 March 2025
REVIEW
Posttranslational Modification in Bone Homeostasis and Osteoporosis
- First Published: 01 April 2025
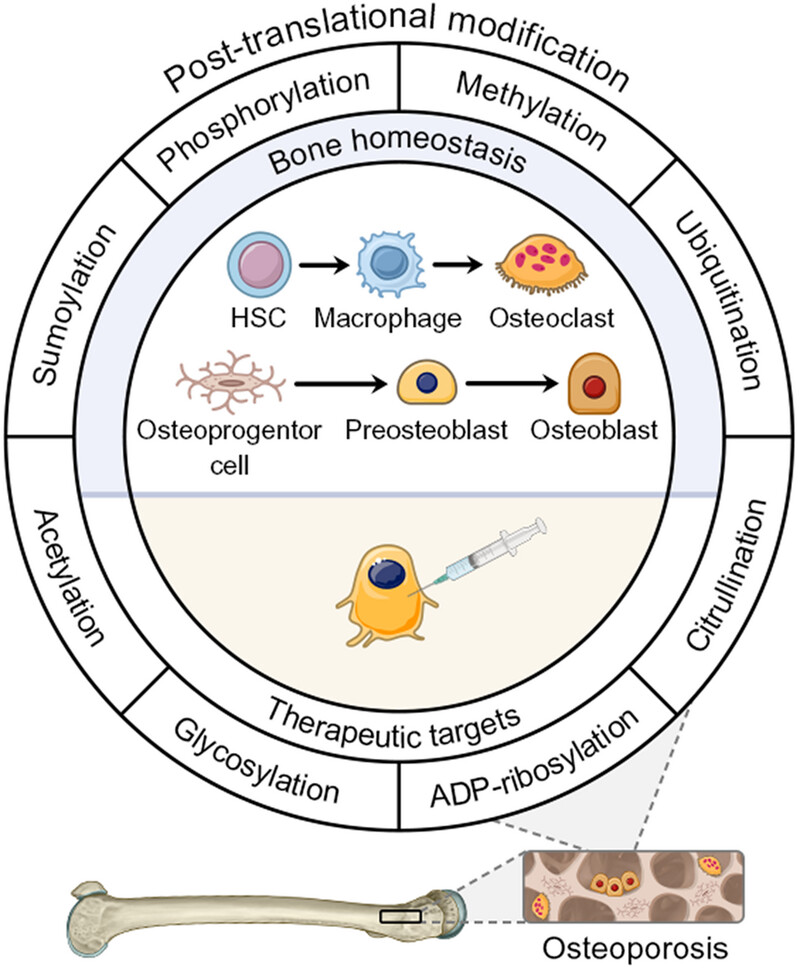
This review summarizes the updating researches concerning bone formation and bone resorption mediated by different types of posttranslational modification. We highlight dysregulated posttranslational modification in osteoblast and osteoclast differentiation. We then emphasize involvement of posttranslational modification in osteoporosis development, so as to elucidate the underlying molecular basis of osteoporosis. We also suggest translational potential of PTMs as therapeutic targets .
HIGHLIGHT
Bending and Scission: When the Membraneless Condensates Meet Endosome Membrane
- First Published: 01 April 2025
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Dynamic Alterations in DNA Methylation of CD4+ T Cells and Macrophages in a Murine Model of Tuberculous Pleural Infection Induced by BCG Vaccination
- First Published: 01 April 2025
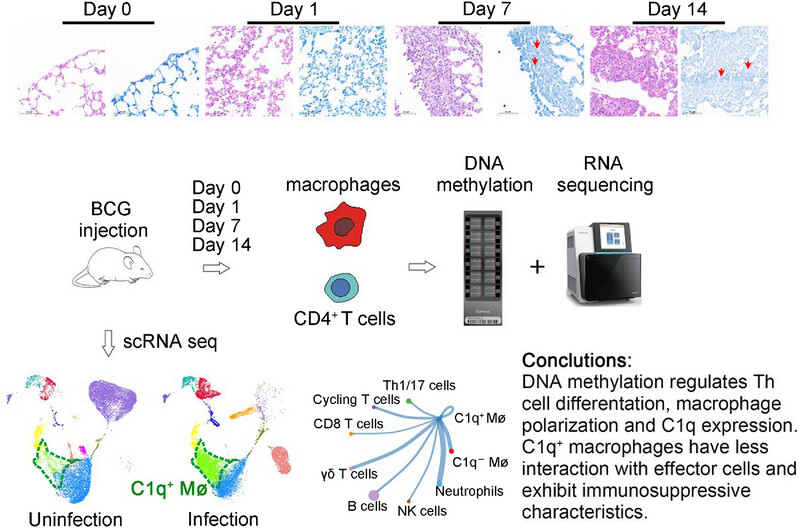
We obtained DNA methylation and transcriptome data of macrophages and CD4+ T cells isolated from pleural lavage fluid of BCG-induced tuberculous pleurisy mouse models at Days 0, 1, 7, and 14. DNA methylation primarily controlled the differentiation of Th1 and Th17 cells, polarization, and increasing C1q expression of macrophages. C1q+ macrophages have less interaction with effector T cells and exhibit immunosuppressive characteristics.
REVIEW
Pancreatic Cancer: Pathogenesis and Clinical Studies
- First Published: 02 April 2025
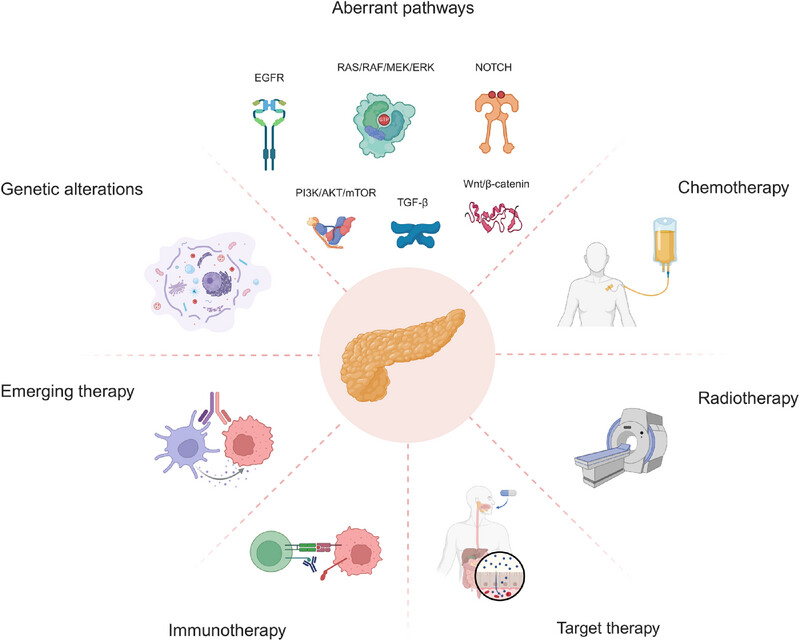
Although the treatment landscape for cancer has evolved rapidly in recent years, progress has stagnated for pancreatic cancer (PC). PC includes multiple types, but pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) accounts for >90% of cases. This review focuses on the molecular pathogenesis and different treatments for PDAC, hoping to propose future directions for optimizing treatment modalities and improving clinical outcomes of PDAC (created with BioRender.com).
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Genomic and Immune Profiling of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Undergoing Neoadjuvant Therapy Versus Upfront Surgery Identifies Novel Immunogenic Cell Death-Based Signatures for Predicting Clinical Outcomes
- First Published: 02 April 2025
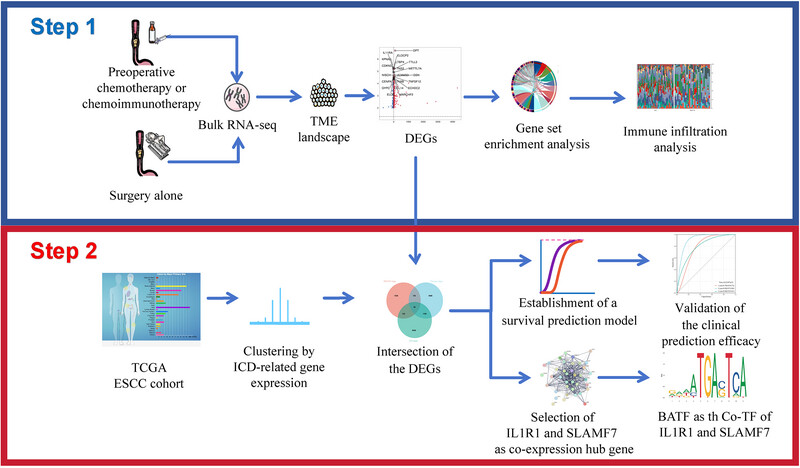
A total of 88 ESCC samples undergoing neoadjuvant therapy plus surgery (NA+S) or surgery alone (SA) were obtained and subjected to bulk RNA sequencing. An external cohort consisting of 95 ESCC undergoing SA was retrieved from The Cancer Genomic Atlas as validation. A five-gene RINscore incorporating ICD-related signature genes with TME-based hub genes was established, with pivotal genes and their co-transcriptional mechanisms elucidated in vitro.