Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Histidine triad nucleotide-binding protein 2 attenuates doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity through restoring lysosomal function and promoting autophagy in mice
- First Published: 17 February 2025
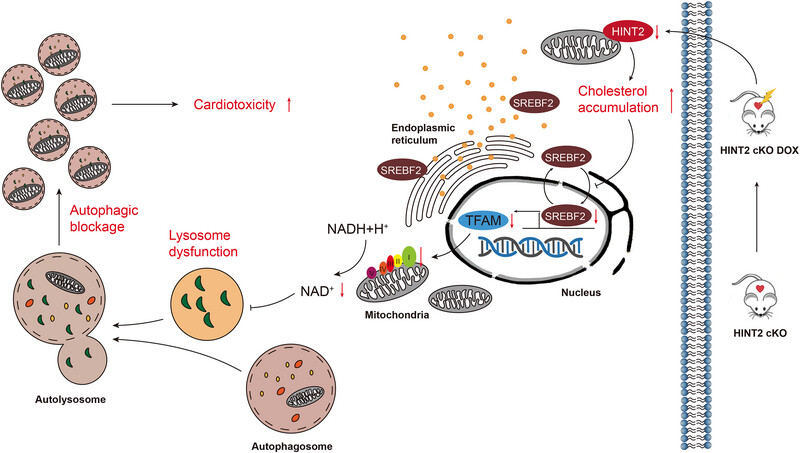
Proposed model of how HINT2 deficiency aggravates DOX-induced cardiotoxicity
Hint2 cKO causes cholesterol accumulation and subsequently inhibits the transcriptional activity of SREBF2, which downregulates TFAM expression. The decrease in TFAM expression reduces both the expression and activity of OXPHOS complex Ι, and lowers the NAD+/NADH ratio, leading to lysosome dysfunction. This impaired lysosome function results in the accumulation of autolysosomes and dysfunction in autolysosomes acidification, which subsequently increases cardiotoxicity.
REVIEW
Exosomes: a double-edged sword in cancer immunotherapy
- First Published: 17 February 2025
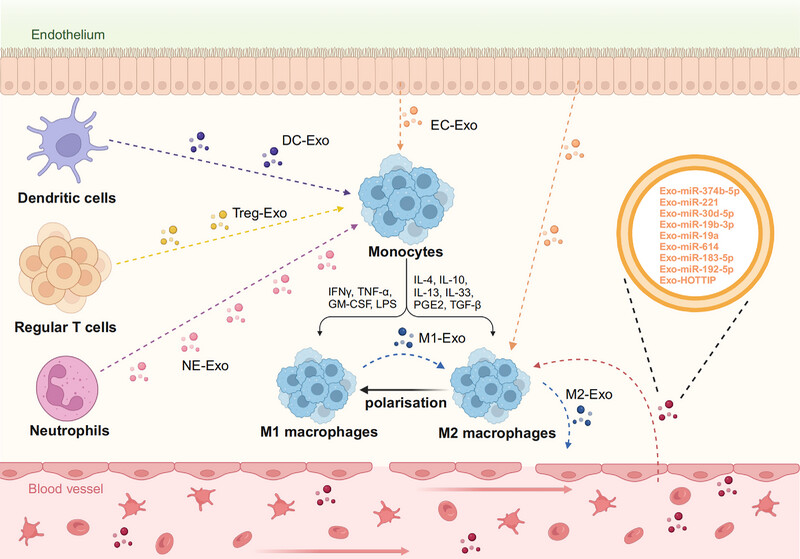
Immunotherapy has emerged as a potent strategy for overcoming the limitations associated with conventional cancer therapies. The use of extracellular vesicles, particularly exosomes which carry cargoes capable of regulating the immune response, has been widely discussed as a potentially therapeutic approach in cancer immunotherapy. Exosomes can transport their cargo to target cells, thereby influencing their phenotype and immunomodulatory functions. They exhibit either immunosuppressive or immune-activating characteristics depending on their internal contents. These exosomes originate from diverse cell sources and their internal contents differ, providing an initial indication that there may be a fine line between immune suppression and stimulation when using them for immunotherapy. This review aims to delineate the roles of exosomes of various origins in cancer development and summarize their mechanisms of action.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
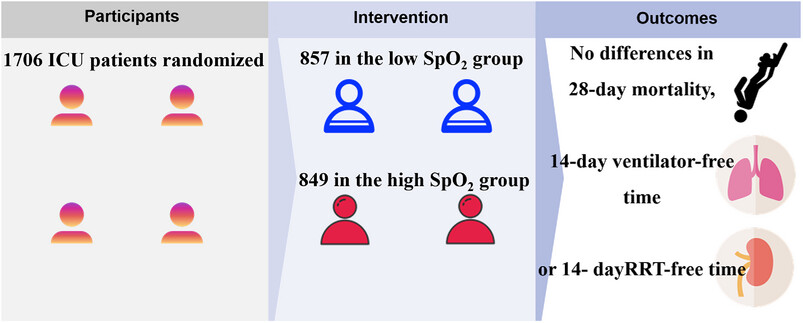
Low versus high peripheral oxygen saturation directed oxygen therapy in critically ill patients: a multicenter randomized controlled trial
- First Published: 17 February 2025
Phase I clinical trial to assess safety and efficacy of Oraxol, a novel oral paclitaxel chemotherapy agent, in patients with previously treated metastatic breast cancer
- First Published: 17 February 2025
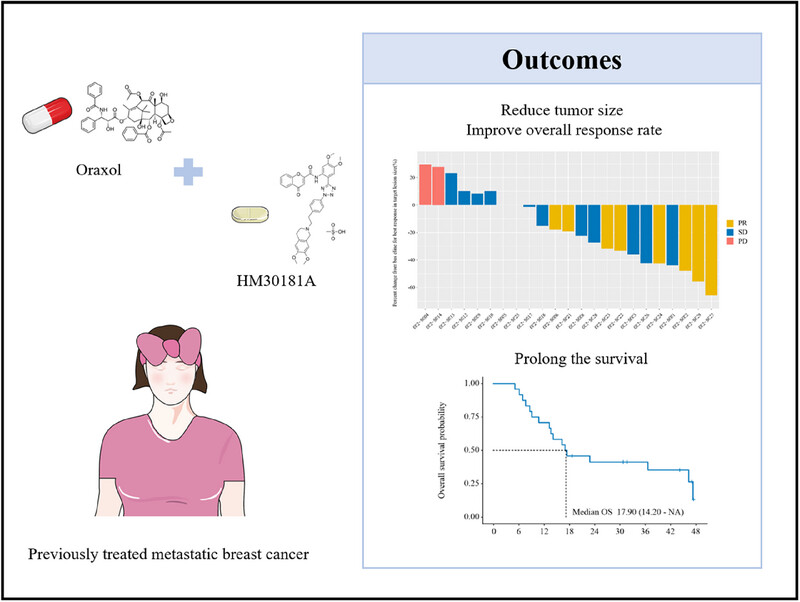
This phase I clinical trial demonstrates the safety, efficacy, and survival of Oraxol. They analyze the correlation between metabolites and Oraxol. The study provides valuable evidence supporting the promising antitumor activity and manageable safety profile of Oraxol in patients with metastatic breast cancer, including those with TNBC.
Controlled release of MIF siRNA and GDNF protein from a photocurable scaffold efficiently repairs spinal cord injury
- First Published: 17 February 2025
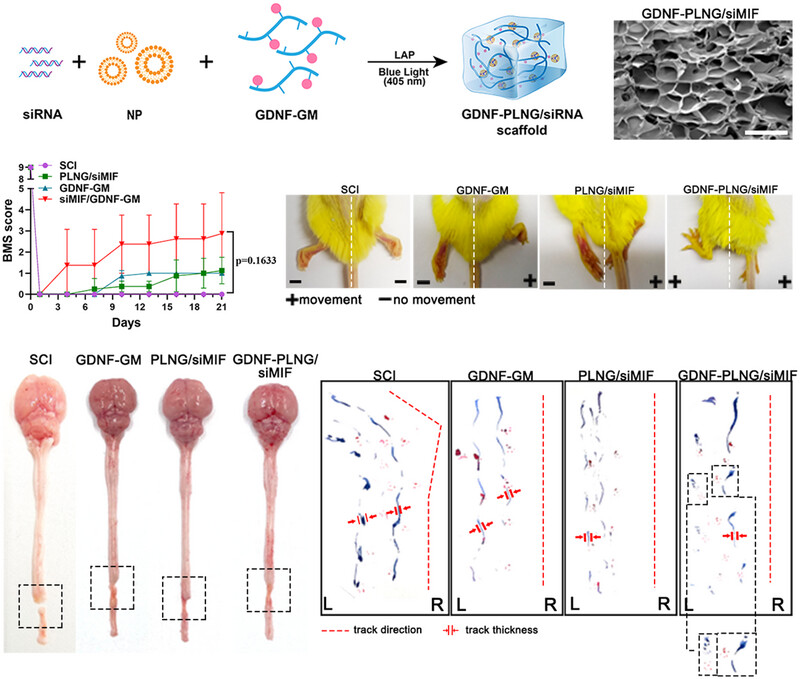
We developed an injectable and photocurable controlled-release scaffold PLNG for MIF siRNA and co-delivery of GDNF protein at the SCI wound site. After treatment with only three doses, GDNF-PLNG/siMIF scaffold successfully regulated the activities of neurons, microglia, and macrophages, thus promoting neuron axon regeneration, re-myelination, and inhibiting neuroinflammatory.
LETTER
Avelumab mediates antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity against monocyte-derived dendritic cells through natural killer cells
- First Published: 18 February 2025
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Changes in L-phenylalanine concentration reflect and predict response to anti-PD-1 treatment combined with chemotherapy in patients with non-small cell lung cancer
- First Published: 17 February 2025
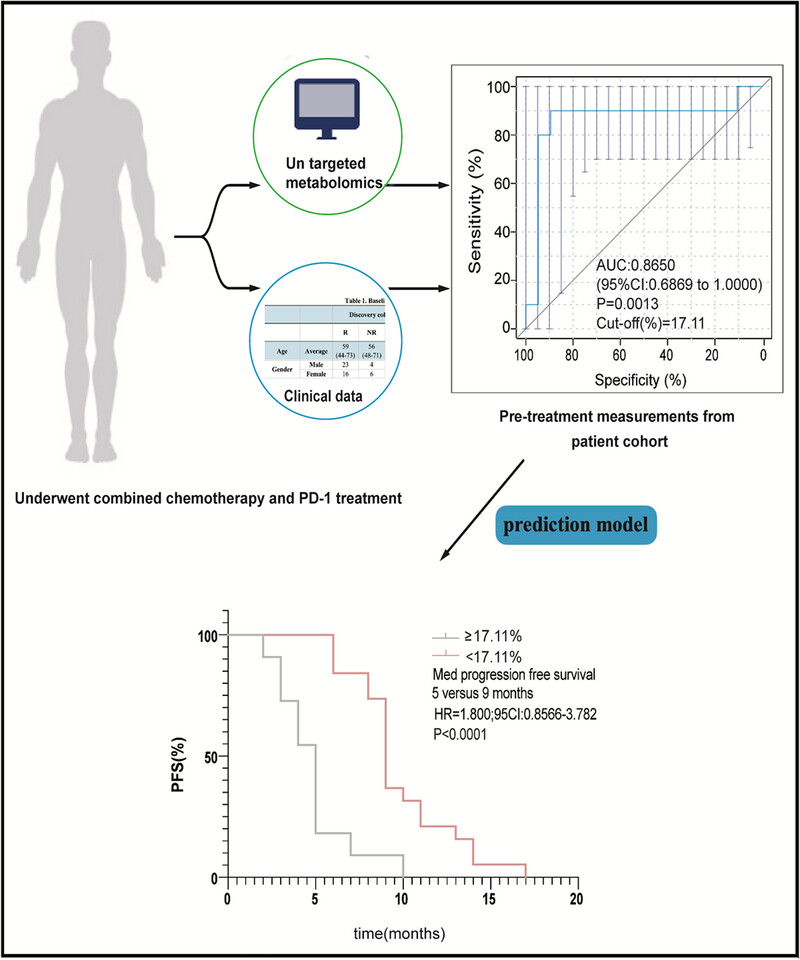
Liu et al. studied serum from patients with non-small cell lung cancer before, during, and after treatment with anti-programmed cell death protein-1 plus chemotherapy, and revealed the metabolic heterogeneity of responders and non-responders. The combination of clinical data profiling and change of L-phenylalanine concentration collected pre- and post-treatment presented a strong predictor for response to immunotherapy in a minimally invasive manner.
Addition of anti-PD-1 immunotherapy to BRAF inhibitor-based targeted therapy improves real-world survival and delays brain metastases in patients with BRAFV600-mutant advanced melanoma: a multicenter cohort study
- First Published: 17 February 2025
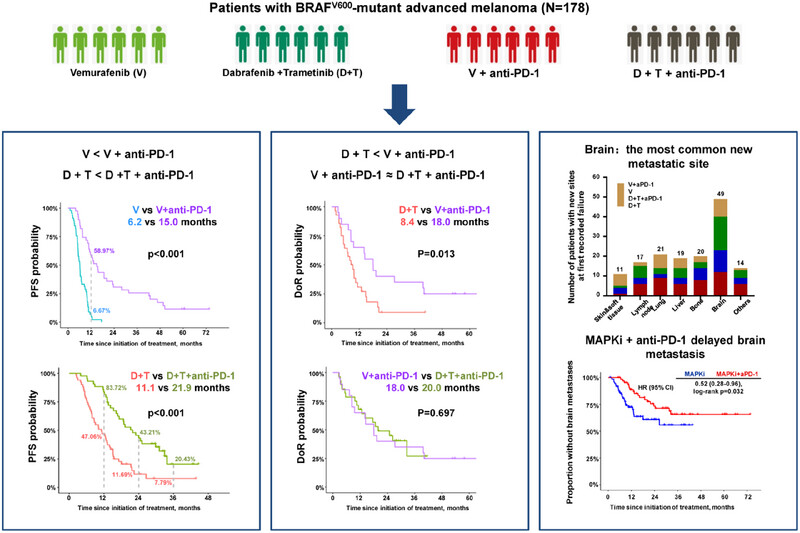
- Addition of anti-PD-1 to BRAF inhibitor-based targeted therapy improved survival.
- Vemurafenib combined with anti-PD-1 antibody seemed to be an effective alternative treatment.
- Brain was the most common new metastatic site at first recorded failure.
- Addition of anti-PD-1 antibody to BRAF inhibitor-based targeted therapy delayed brain metastases.
Targeting CDK4/6 suppresses colorectal cancer by destabilizing YAP1
- First Published: 17 February 2025
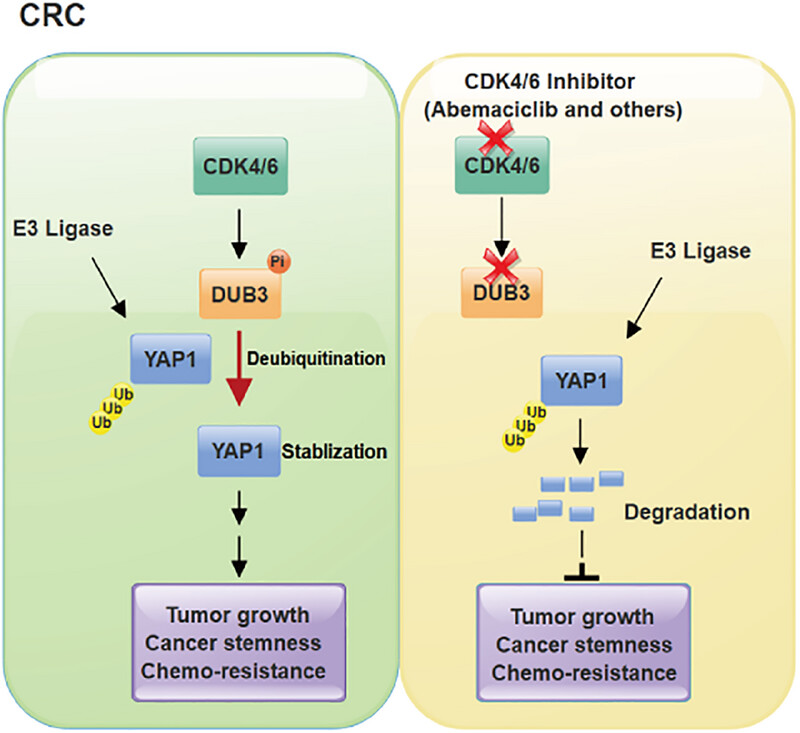
Our findings reveal a pivotal role of the cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6–deubiquitinating enzyme 3 (CDK4/6–DUB3) axis in promoting the stabilization and tumor-promoting function of Yes-associated protein 1 (YAP1) and provide the preclinical evidence that CDK4/6 inhibitors might be an appealing therapeutic strategy for the treatment of colorectal cancer with aberrantly upregulated DUB3 and YAP1.
Early-life antibiotic exposure aggravates hepatic steatosis through enhanced endotoxemia and lipotoxic effects driven by gut Parabacteroides
- First Published: 17 February 2025

Early-life antibiotic exposure caused the overblooming of gut Parabacteroides and hepatic accumulation of cytotoxic lysophosphatidyl cholines (LPCs), which acted in conjunction with LPS derived from Parabacteroides distasonis (LPS_PA) to induce cholesterol accumulation, endoplasmic reticulum stress and apoptosis through ATF6 pathway. Excessive LPS_PA increased the group X secretory Phospholipase A2s, which is associated with enhanced glycerophospholipid hydrolysis and LPC production. Icons were made using BioRender.
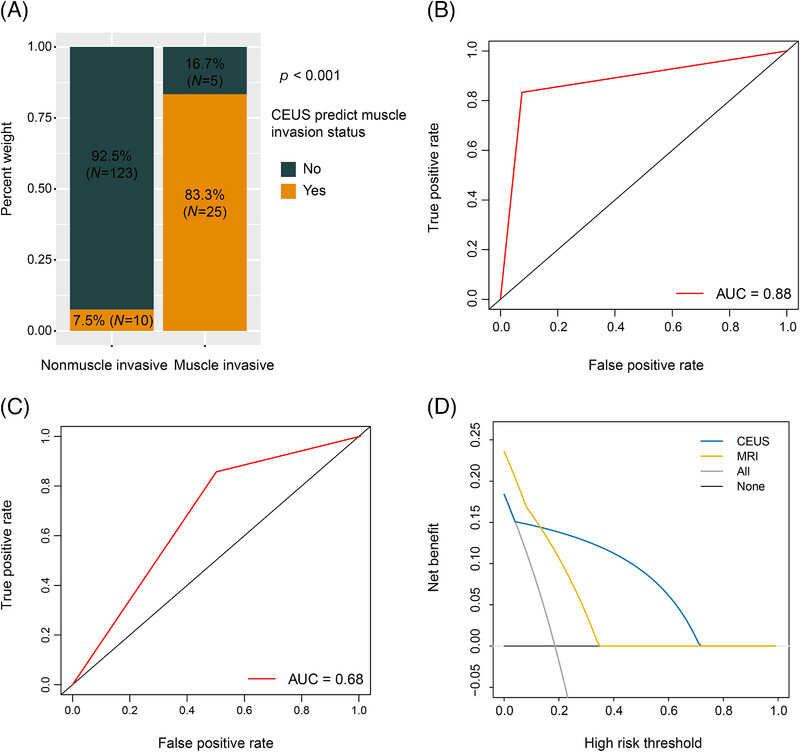
Contrast-enhanced ultrasound enables precision diagnosis of preoperative muscle invasion in bladder cancer: a prospective study
- First Published: 17 February 2025
Differential expression of the MYC-Notch axis drives divergent responses to the front-line therapy in central and peripheral extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer
- First Published: 18 February 2025
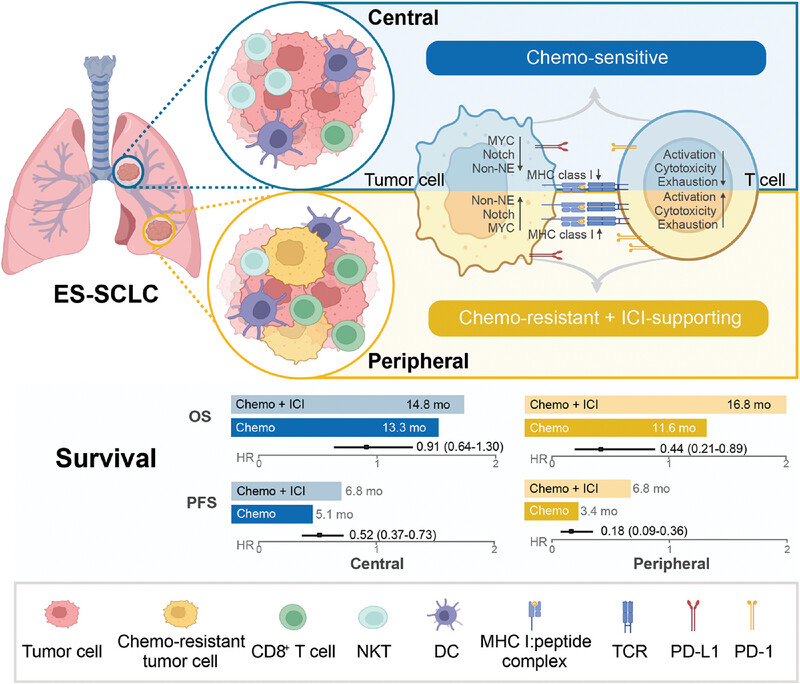
This study found that peripheral ES-SCLC was more chemo-resistant and ICI-responsive in the front-line setting compared with the central type. The activation of the MYC-Notch axis and downregulation of the inhibitory Notch signaling ligand DLL3 in the peripheral type may explain the response differences.
TDP-43/ALKBH5-mediated m6A modification of CDC25A mRNA promotes glioblastoma growth by facilitating G1/S cell cycle transition
- First Published: 18 February 2025
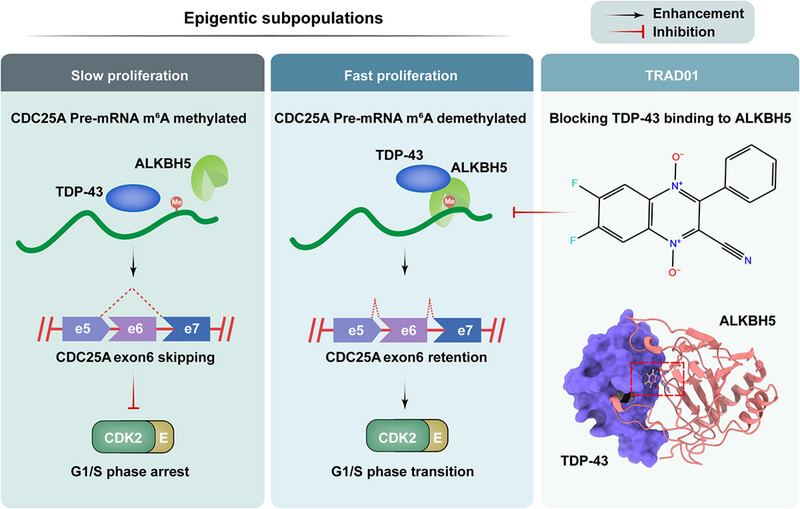
In this study, TDP-43 interacts with ALKBH5 and promotes its binding to CDC25A pre-mRNA in fast-growing GBM cells. TDP-43/ALKBH5 complex demethylates CDC25A pre-mRNA, inhibiting its exon 6 skipping and preserving the expression of the oncogenic isoform CDC25A-1, thereby promoting G1/S phase transition and growth of GBM cells. TRAD01 targeted the interaction between TDP-43 and ALKBH5, leading to significant antitumor effects. Therefore, targeting the TDP-43/ALKBH5 axis might be a promising therapeutic strategy for GBM patients.
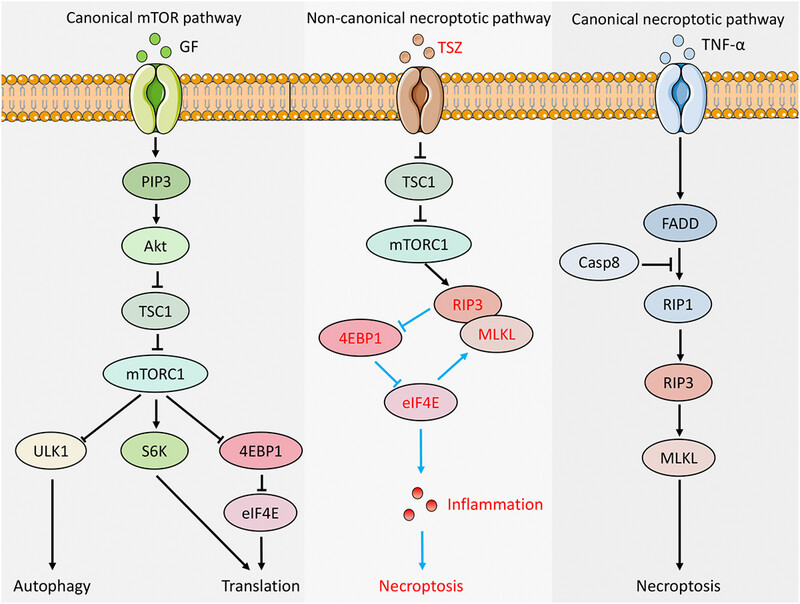
Noncanonical feedback loop between “RIP3–MLKL” and “4EBP1–eIF4E” promotes neuronal necroptosis
- First Published: 18 February 2025
REVIEW
Epigenetic modifications in early stage lung cancer: pathogenesis, biomarkers, and early diagnosis
- First Published: 21 February 2025
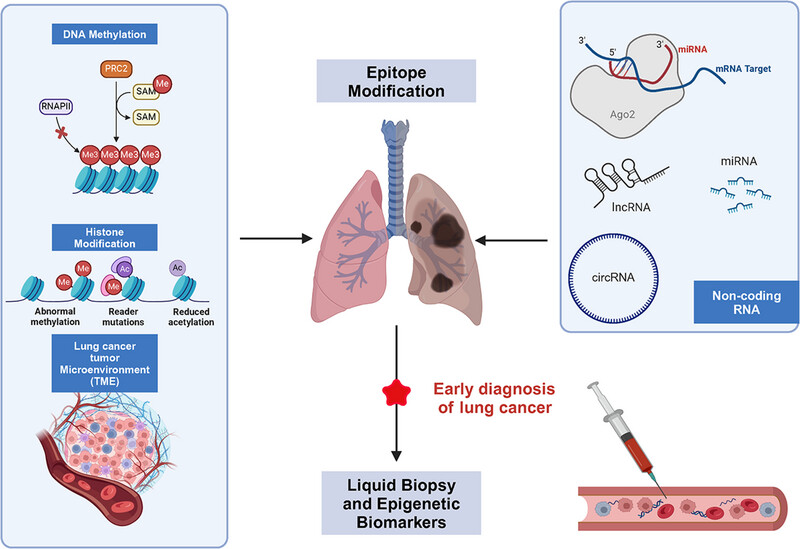
Epigenetic changes like DNA methylation and histone modifications, key from atypical adenomatous hyperplasia to stage I lung cancer, precede genetic mutations and contribute to tissue dysplasia. Along with mRNA, noncoding RNA, and tumor microenvironment regulation, these markers, enhanced by liquid biopsy, are promising for early lung cancer diagnosis.
Protein palmitoylation: biological functions, disease, and therapeutic targets
- First Published: 21 February 2025
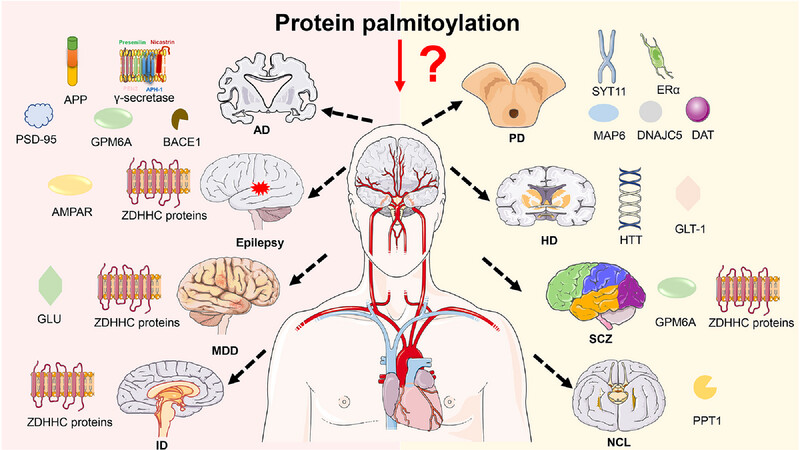
This review focuses on the role of protein palmitoylation in neurological disorders, with an emphasis on biological function and therapeutic targets. ZDHHC protein mediated palmitoylation is strongly implicated in epilepsy, MDD, ID, and SCZ, and in addition, enzymes that mediate palmitoylation may be novel targets in the treatment of neurological diseases.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
The SUMOylated RREB1 interacts with KDM1A to induce 5-fluorouracil resistance via upregulating thymidylate synthase and activating DNA damage response pathway in colorectal cancer
- First Published: 21 February 2025
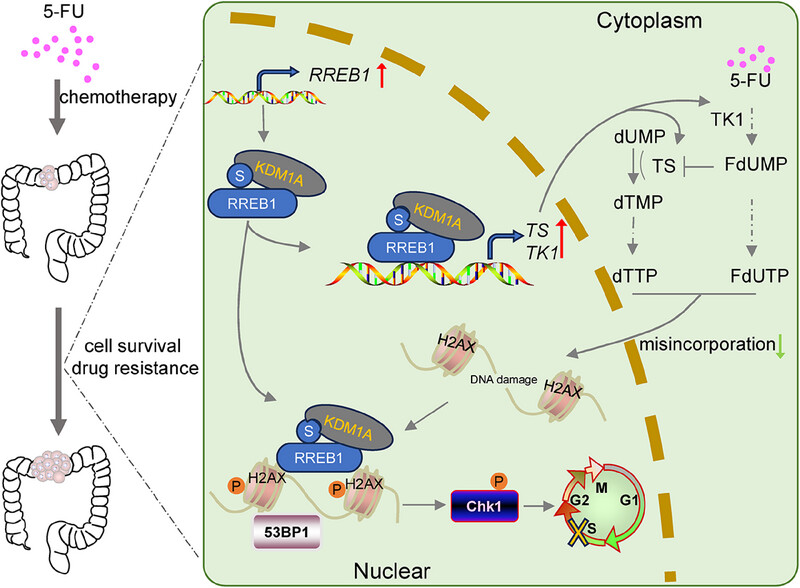
5-Fluorouracil (5-FU) treatment triggers the Ras-responsive element binding protein 1 (RREB1) expression and the formation of RREB1 and lysine demethylase 1A (KDM1A) complex which binds to the promoter of thymidylate synthase (TS) and thymidine kinase (TK1), and be recruited to phosphorylated H2AX foci, contributing to reduced DNA damage and enhanced DNA damage response.
REVIEW
Sepsis: the evolution of molecular pathogenesis concepts and clinical management
- First Published: 23 February 2025
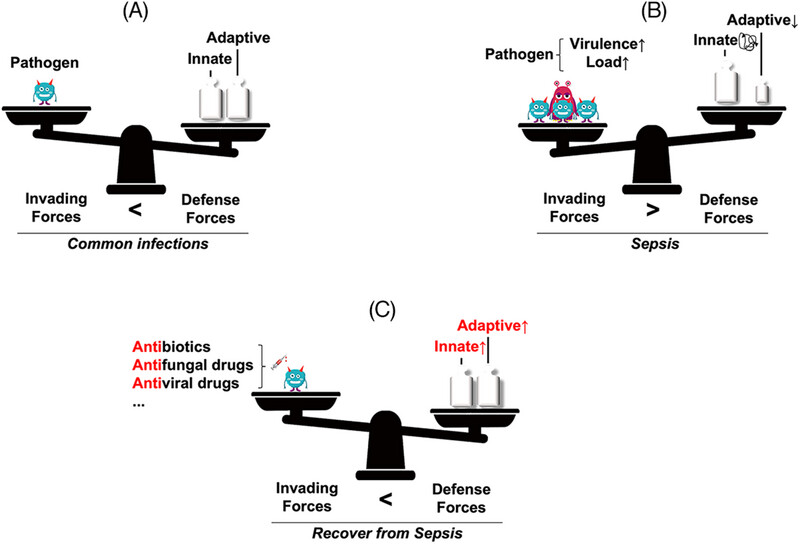
(A) The innate and adaptive immune responses established during long-term evolution can eliminate most invading microorganisms. (B) Sepsis only occurs when the balance is disrupted and the pathogen force overwhelms the host's defense force. (C) Only when the superposition of external forces (sensitive antimicrobial drugs) and internal forces (activation of the host immunity) overpowers invading pathogens can sepsis be cured.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Hypoxia-Induced O-GlcNAcylation of GATA3 Leads to Excessive Testosterone Production in Preeclamptic Placentas
- First Published: 23 February 2025
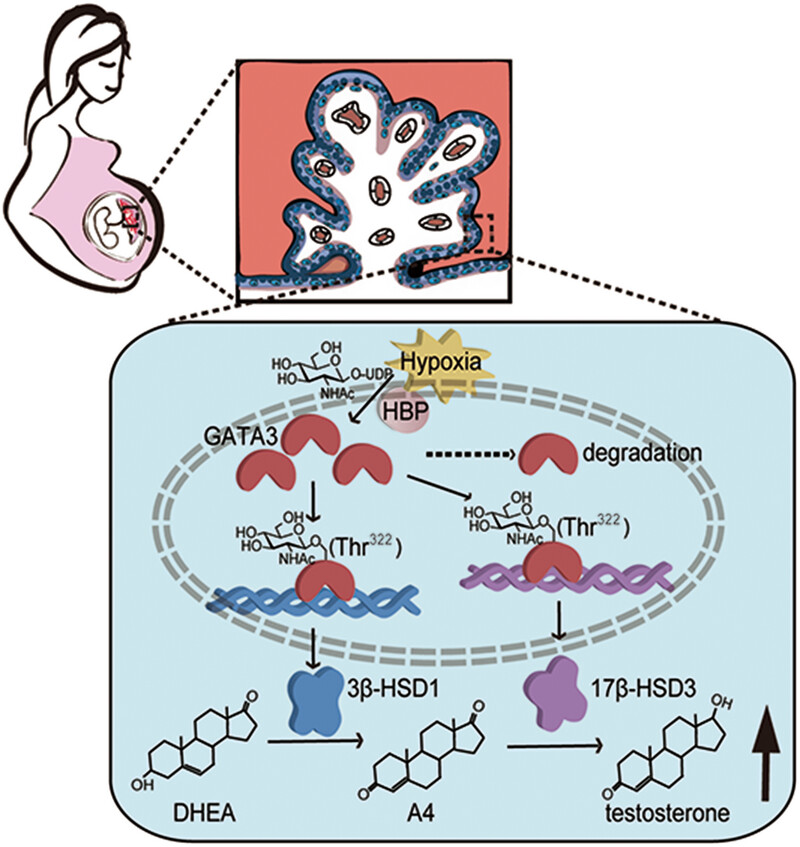
Hypoxia at the maternal–fetal interface of early-onset preeclamptic placentas triggers global O-GlcNAcylation. This process stabilizes the protein through O-GlcNAcylation of GATA3 at Thr322 and transcriptionally induces the expression of 3β-HSD1 and 17β-HSD3, key androgen synthetases. Consequently, this accelerates the production of testosterone, thereby exacerbating the imbalance in the steroid hormones of patients with early-onset preeclampsia.
REVIEW
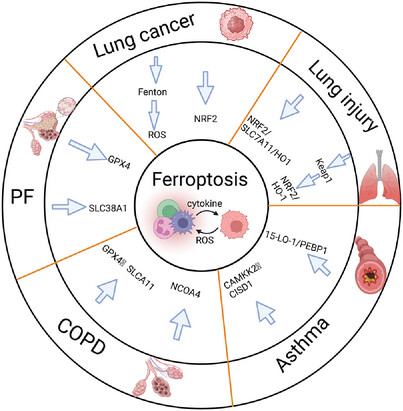
Ferroptosis in Pulmonary Disease and Lung Cancer: Molecular Mechanisms, Crosstalk Regulation, and Therapeutic Strategies
- First Published: 23 February 2025
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Brachytherapy of Yttrium-90 Implantation Into Pancreas: A Dose-Escalation Pilot Study
- First Published: 24 February 2025
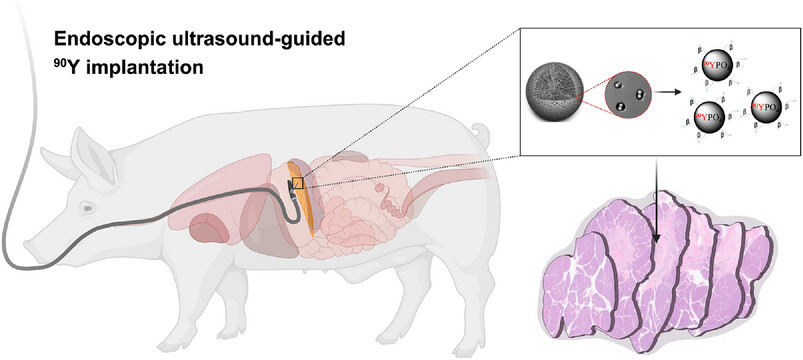
Under EUS guidance, the splenic lobe was located and 90Y-loaded carbon microspheres were implanted into the pancreas of the Bama miniature pigs. Positron emission imaging/computer tomography (PET/CT) imaging was used to check the occurrence of particle displacement and radioactivity postoperatively. All pigs were euthanatized after 15 days postoperative. The pancreas and adjacent organs were excised for histological examination and residue radiation detection.
SIRT1 Alleviates Mitochondrial Fission and Necroptosis in Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury via SIRT1–RIP1 Signaling Pathway
- First Published: 24 February 2025
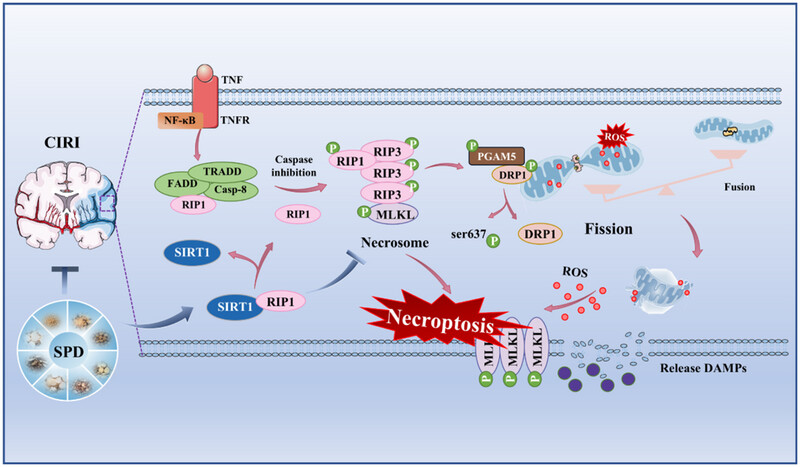
SIRT1, a NAD+-dependent protein deacetylase, is widely distributed in brain tissue. When cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury (CIRI) occurs, downregulation of SIRT1 weakens its interaction with RIP1, facilitating necrosomes formation, and thus exacerbates necroptosis. Additionally, the downstream target PGAM5 dephosphorylates DRP1 at Ser637, worsening mitochondrial fission and dysfunction, and further aggravates CIRI. Sanpian Decoction (SPD), a Chinese herbal formula, serves as a SIRT1 activator, protects against CIRI via the SIRT1–RIP1 pathway .
REVIEW
Liver Metastasis in Cancer: Molecular Mechanisms and Management
- First Published: 27 February 2025
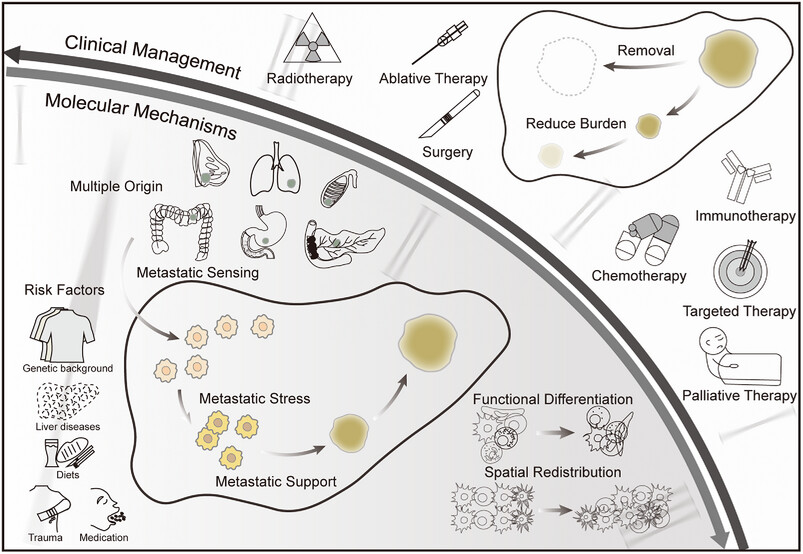
This review focuses on the molecular mechanisms and clinical management of tumor liver metastasis. Liver metastasis is a primary manifestation of the aggressive dissemination of several extrahepatic tumors. Many risk factors, such as individual genetic background, liver diseases, diet, trauma, and medication, may accelerate this process. In terms of temporal trajectory, liver metastasis can be mainly divided into three continuous yet distinct phases, accompanied by the functional differentiation and spatial remodeling of resident and recruited cells. Achieving effective control and even cure of liver metastasis by removing tumors or reducing the tumor burden is the ultimate goal of current preclinical animal experiments and clinical explorations (“turning back the clock”). Despite many challenges, comprehensive clinical management of patients with liver metastasis under multidisciplinary treatment models remains a promising option.2
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Noninvasive Quantification of Hepatic Steatosis Using Ultrasound-Derived Fat Fraction (CHESS2303): A Prospective Multicenter Study
- First Published: 27 February 2025
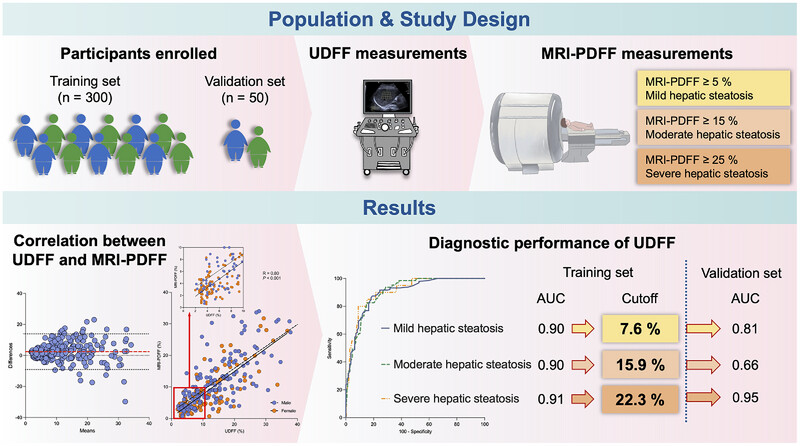
In this prospective multicenter study, UDFF values were positively correlated with MRI-PDFF (R = 0.80). Taking MRI-PDFF ≥ 5%, ≥ 15%, and ≥ 25% as the reference for diagnosing mild, moderate, and severe hepatic steatosis, the cutoff values of UDFF were 7.6%, 15.9%, and 22.3% in the training set (AUC = 0.90–0.91), respectively. UDFF achieved comparable AUCs in the validation set.
Targeting WDPF domain of Hsp27 achieves a broad spectrum of antiviral
- First Published: 26 February 2025
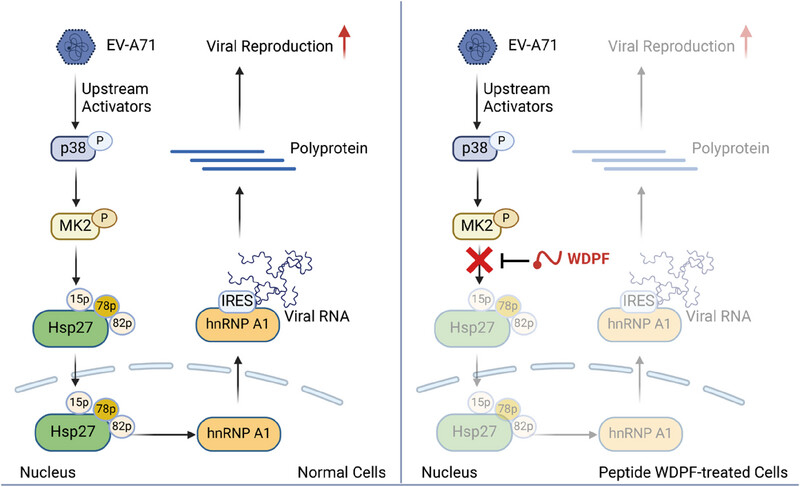
Ser78 phosphorylation of Hsp27 plays an important role in Hsp27 nuclear translocation, which induces hnRNP A1 cytosol relocation and further enhances the IRES activity and viral replication mediated by EV-A71 2Apro. Hsp27-derived WDPF peptide competitively inhibited Hsp27 phosphorylation on serine 78 to block Hsp27/hnRNP A1 translocation and further IRES-dependent viral reproduction.
REVIEW
Metabolic reprogramming in cancer and senescence
- First Published: 04 March 2025
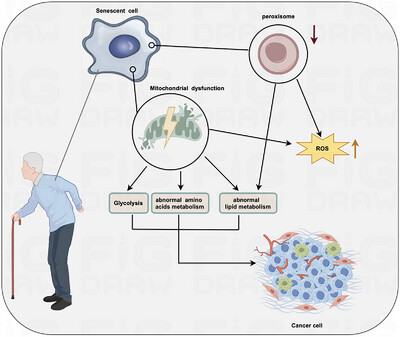
Cancer incidence and mortality rates increase significantly with age, and this rising trend seems to indicate a strong link between aging and cancer. However, despite the commonality between nutrient-sensing disorders, which are a feature of aging, and metabolic reprogramming, which is a feature of tumors, the specific regulatory relationship between the two is not clear. Organismal metabolism includes gluconeogenesis, lipid metabolism, protein/amino acid metabolism, nucleotide/nucleic acid metabolism, and other nutrient metabolism. Among them, glucose metabolism, lipid metabolism, and amino acid metabolism are the main modes of energy supply for tumor cells, and they are also altered in senescent cells. Therefore, this review will focus on these three modes of metabolism in order to provide us with a deeper understanding of the metabolic associations between aging and tumors. It will also summarize drugs that have been used in clinical trials to target aging and tumor signaling pathways, as well as targeting materials that are in the research phase, and conclude with appropriate dietary recommendations. This will provide new perspectives and ideas for antiaging and tumor prevention research .
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Cholesterol-27α-hydroxylase inhibitor nilvadipine can effectively treat cholestatic liver injury in adult offspring induced by prenatal dexamethasone exposure
- First Published: 04 March 2025
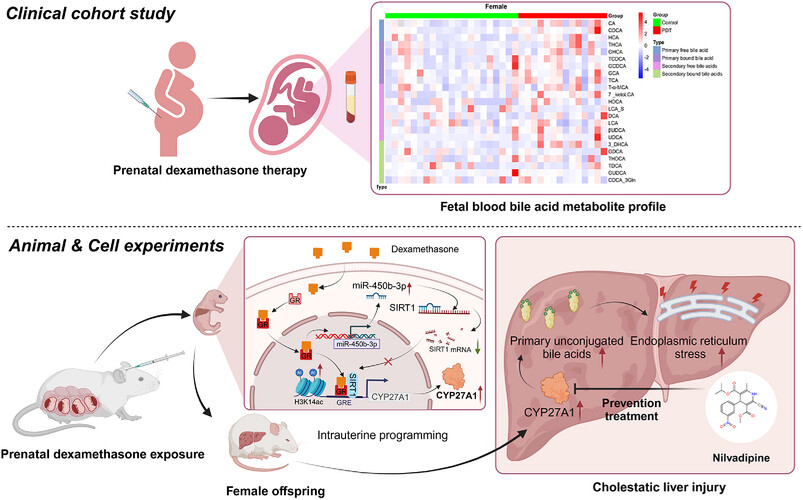
Dexamethasone enhanced CYP27A1 promoter H3K14ac level and expression through the GR/miR-450b-3p/SIRT1 pathway during pregnancy. The elevated CYP27A1 persists until birth, which elevates primary unconjugated bile acids and endoplasmic reticulum stress, causing cholestatic liver injury in adult female offspring. CYP27A1 and nilvadipine are first proposed as early intervention targets and effective drugs against fetal-originated cholestatic liver injury.
HIGHLIGHT
Combining JAK Inhibitors with Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: Overcoming Resistance in Cancer Treatment
- First Published: 04 March 2025
REVIEW
The emerging role of neutrophil extracellular traps in autoimmune and autoinflammatory diseases
- First Published: 06 March 2025
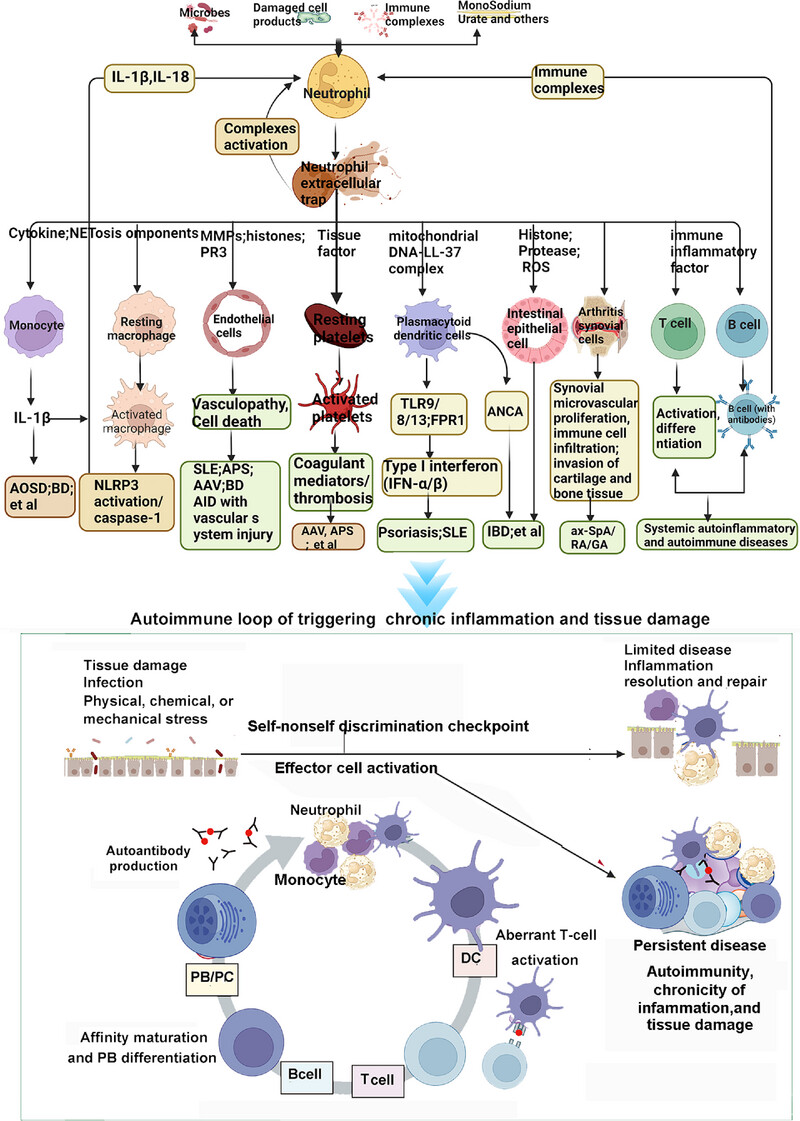
Neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) released by neutrophils in response to pathogens exhibit dual anti-inflammatory and proinflammatory effects. While effective in pathogen capture and inflammation resolution, imbalanced NET formation can lead to tissue damage and exacerbate inflammatory responses in autoimmune diseases. NETs also serve as self-antigens, triggering immune activation and influencing adaptive responses in diseases like rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus, underscoring their critical role in autoimmune pathogenesis.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
PD-1/PD-L1 Inhibitors Plus Chemotherapy Versus Chemotherapy Alone as First-Line Therapy for Patients With Unfavorable Cancer of Unknown Primary: A Multicenter, Retrospective Cohort Study
- First Published: 06 March 2025
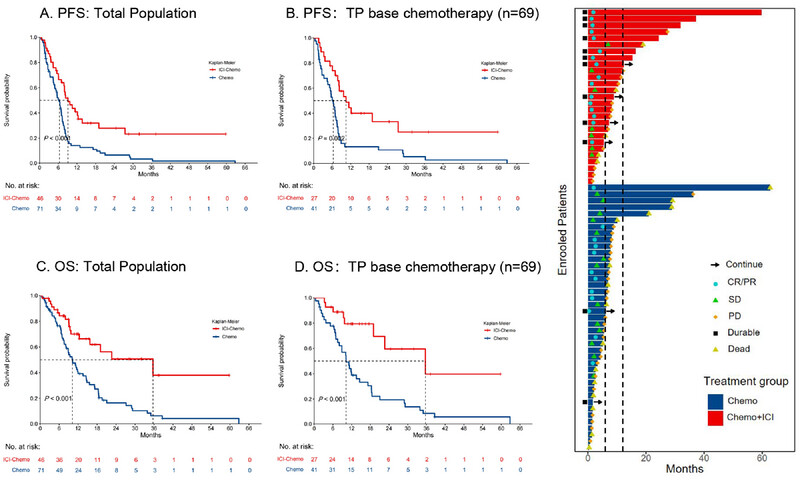
We assessed the efficacy and safety of PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors plus chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone for patients with cancer of unknown primary (CUP) in the first-line setting. In this cohort study of 117 patients, PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors plus chemotherapy delivered progression-free survival and overall survival advantages, along with a higher objective response rate, when compared to chemotherapy. The findings indicated that PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors plus chemotherapy could be the preferred first-line approach for patients with unfavorable CUP.
REVIEW
Colorectal Cancer: Pathogenesis and Targeted Therapy
- First Published: 06 March 2025
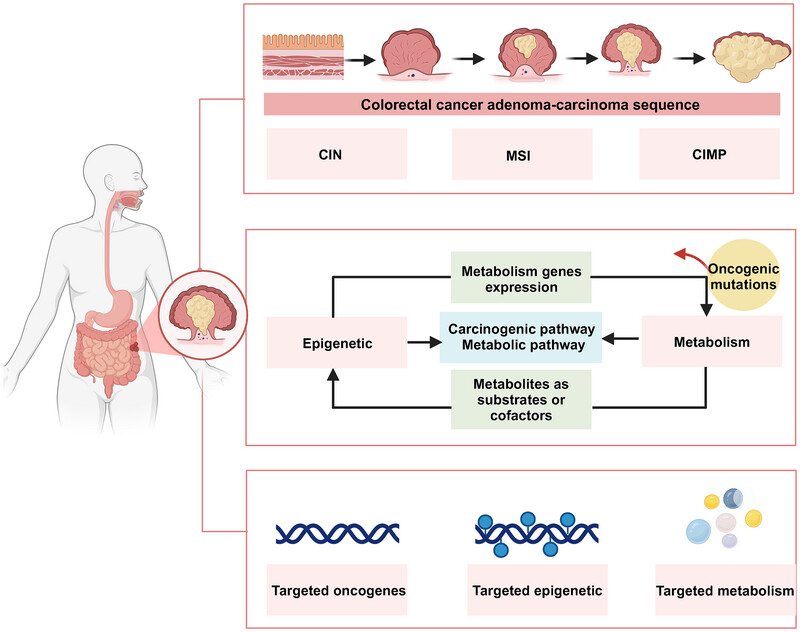
Chromosomal instability, microsatellite instability, and the CpG island methylator phenotype are key pathogenic pathways in the adenoma–carcinoma sequence of CRC. Epigenetic remodeling and metabolic reprogramming are two major hallmarks of tumor cells, demonstrating bidirectional regulatory mechanisms across various cancers, including CRC. Researchers are developing drugs that target critical elements within these pathogenic and metabolic pathways to enhance treatment strategies for colorectal cancer. Abbreviations: CIN, chromosomal instability; MSI, microsatellite instability; CIMP, CpG island methylator phenotype.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Heat Shock Protein Family A Member 1A Attenuates Apoptosis and Oxidative Stress via ERK/JNK Pathway in Hyperplastic Prostate
- First Published: 10 March 2025
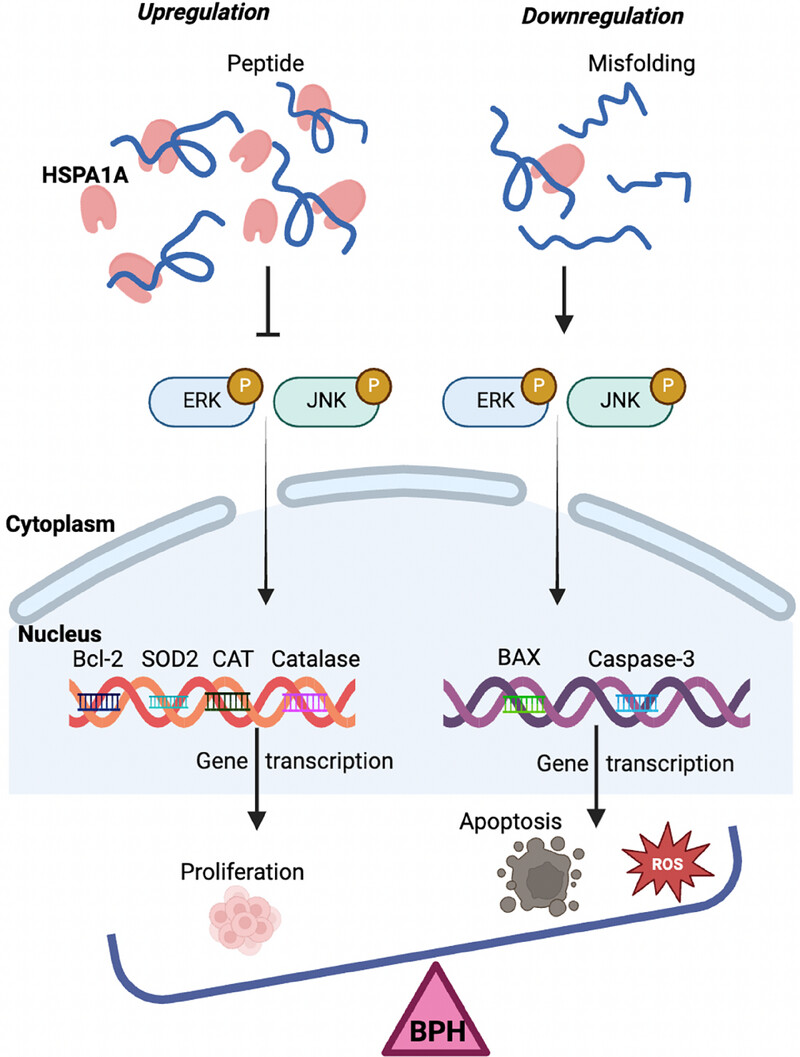
Upregulation of HSPA1A increased the level of Bcl-2 and antioxidants by suppressing the phosphorylation of the ERK/JNK cascade, thereby enhancing cell proliferation. However, the reduction of HSPA1A associated with misfolding of peptides promoted the transcription of BAX and Caspase-3 via activating ERK/JNK, leading to cell apoptosis and ROS accumulation. Consequently, the imbalance between cell proliferation and cell apoptosis and ROS induced by the HSPA1A–ERK/JNK cascade contributed to the development of BPH.
Clinical Utility of 18Fluorine-Fibroblast Activation Protein Inhibitor-04 Positron Emission Tomography/Computed Tomography in the Evaluation of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma: Comparison With 18Fluorine-Fluorodeoxyglucose Positron Emission Tomography/Computed Tomography
- First Published: 10 March 2025
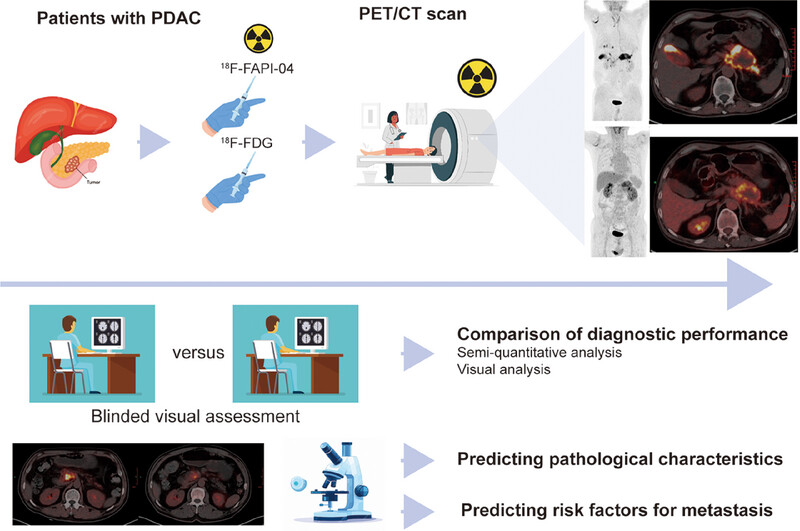
In this study, 67 patients with PDAC completed 18F-FAPI-04 PET/CT and 18F-FDG PET/CT examination within 1 week, respectively. Semi-quantitative analysis and visual inspection were used to evaluate the diagnostic efficacy of the two examination modes in identifying metastasis and predicting pathological characteristics and risk factors of metastasis .
REVIEW
The Malignant Transformation of Viral Hepatitis to Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Mechanisms and Interventions
- First Published: 08 March 2025
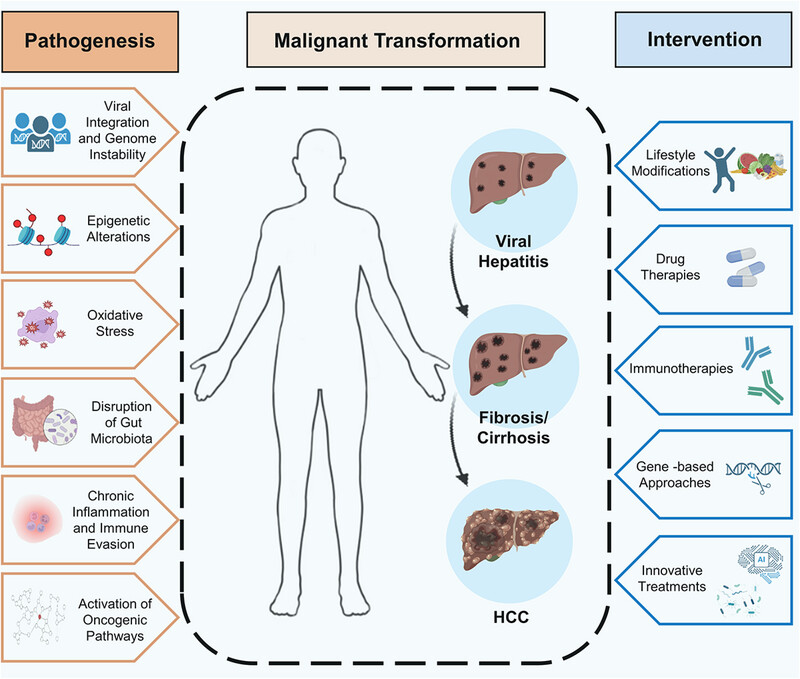
The malignant transformation from chronic viral hepatitis to hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) involves intricate interactions among viral, host, and environmental factors. Key drivers of this transformation include viral integration, genomic instability, epigenetic modifications, oxidative stress, gut microbiota dysbiosis, chronic inflammation, immune evasion, and abnormal signaling pathways. Intervention strategies range from lifestyle modifications and drug therapies to immunotherapies, gene-based approaches, and innovative treatments.
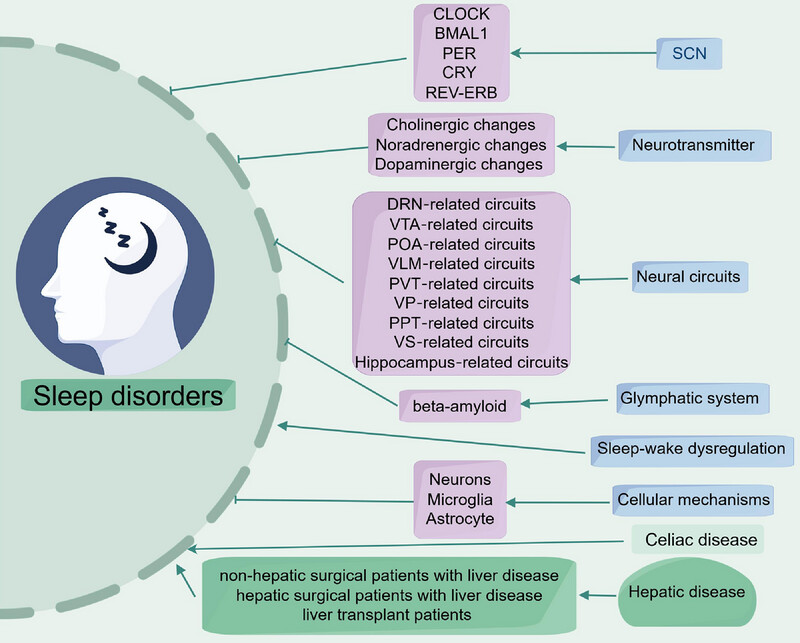
Sleep Disorders: Pathogenesis and Therapeutic Interventions
- First Published: 10 March 2025
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Depletion of Acetyl-CoA Carboxylase 1 Facilitates Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Prostate Cancer Cells by Activating the MAPK/ERK Pathway
- First Published: 10 March 2025
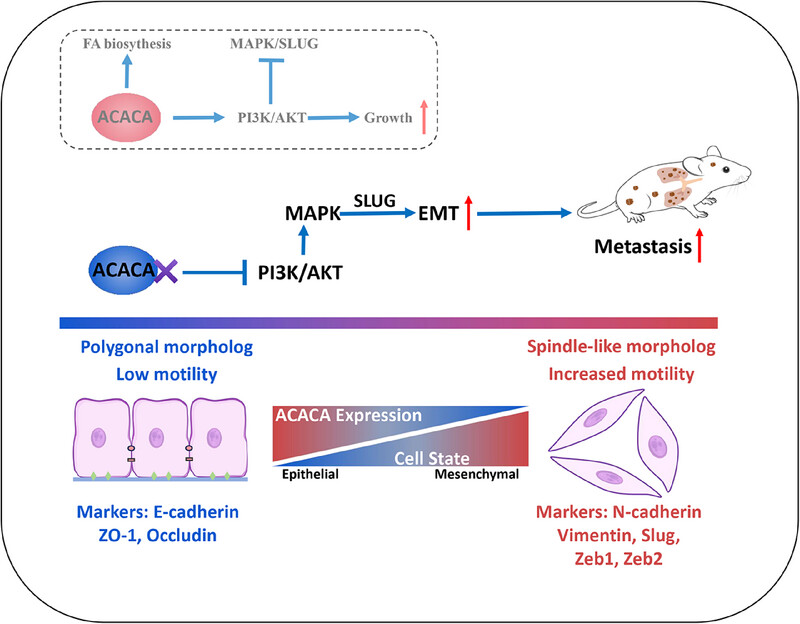
Depletion of ACACA in prostate cancer cells inhibits the PI3K-AKT pathway, leading to negative feedback activation of the MAPK pathway. This activation increases expression of EMT transcription factors, particularly SLUG, resulting in upregulation of mesenchymal biomarkers and down-regulation of epithelial biomarkers. Consequently, cancer cells exhibit morphological changes and enhanced motility, promoting metastasis. These findings highlight the role of ACACA depletion in driving EMT and metastasis via MAPK pathway activation.
REVIEW
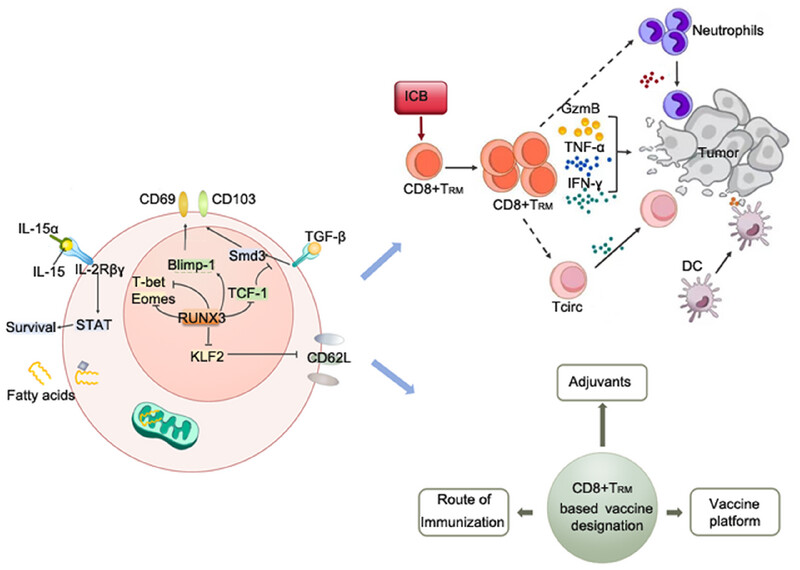
Tissue-Resident Memory CD8+ T Cells: Differentiation, Phenotypic Heterogeneity, Biological Function, Disease, and Therapy
- First Published: 10 March 2025
Pulmonary Hypertension: Molecular Mechanisms and Clinical Studies
- First Published: 10 March 2025
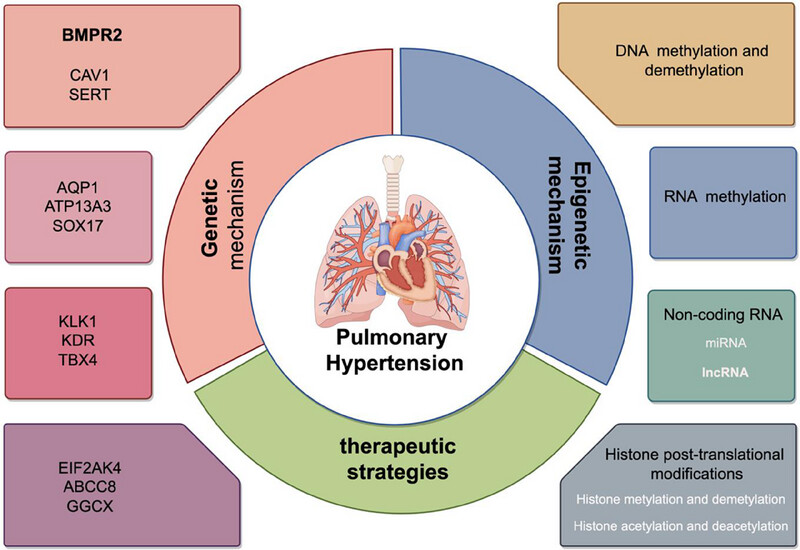
The figure highlights the interplay of genetic and epigenetic mechanisms in pulmonary hypertension (PH) and their implications for therapeutic strategies. The genetic mechanism section features key genes implicated in PH pathogenesis. The epigenetic mechanism encompasses DNA methylation, RNA methylation, noncoding RNAs (miRNA, lncRNA), and histone modifications. These insights inform targeted therapeutic strategies to address PH.
RNA Modification in Metabolism
- First Published: 10 March 2025
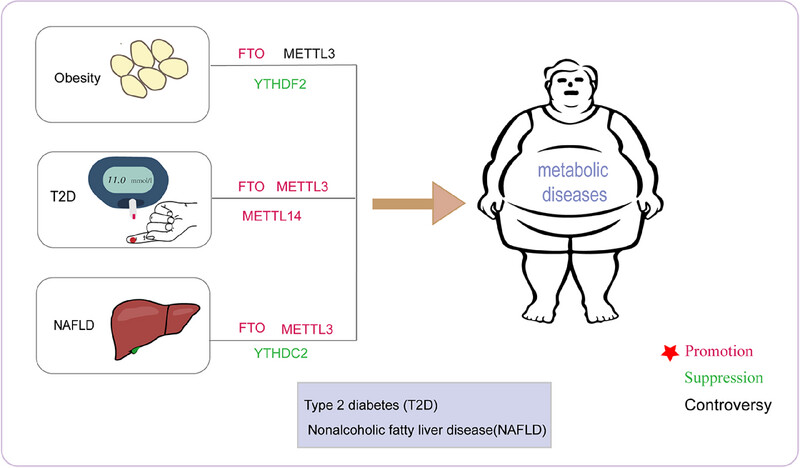
Role of m6A methylation in human metabolic diseases. A series of methylases are involved in the development of metabolic diseases; among them, FTO was found to play a pivotal role in promoting disease, YTHDC2 was believed to suppress disease development, while the role of METTL3 and METTL14 in metabolic disease still needs to be further investigated.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Fusobacterium nucleatum Promotes the Growth and Metastasis of Colorectal Cancer by Activating E-Cadherin/Krüppel-Like Factor 4/Integrin α5 Signaling in a Calcium-Dependent Manner
- First Published: 10 March 2025

Our findings reveal that Fusobacterium nucleatum increases intracellular Ca2+ concentration, which promotes interaction between E-cadherin and KLF4, resulting in KLF4 phosphorylation and translocation in the nucleus. The phosphorylated KLF4 induces ITGA5 transcription and activated FAK/PI3K/Akt1 signaling, finally promoting the growth, invasion, and migration of colorectal cells.
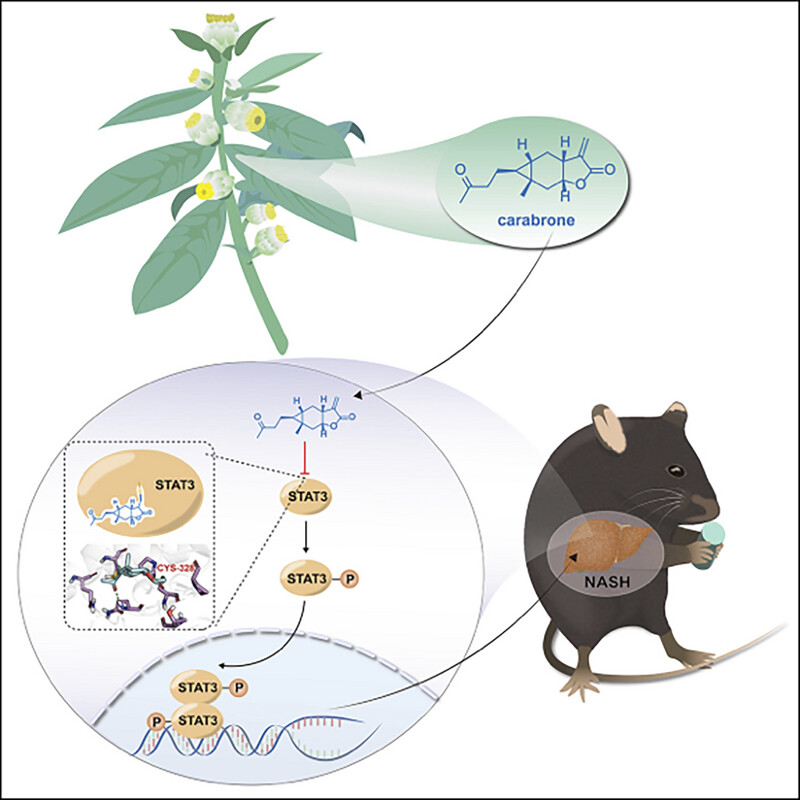
Carabrone Attenuates Metabolic Dysfunction–Associated Steatohepatitis by Targeting STAT3 in Mice
- First Published: 10 March 2025
REVIEW
The Role of Yes-Associated Protein in Inflammatory Diseases and Cancer
- First Published: 10 March 2025
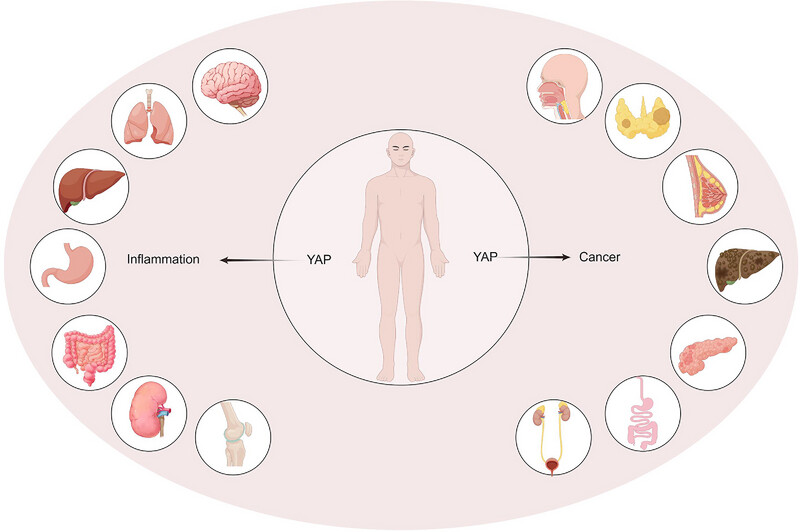
The activation and malfunction of Yes-associated protein (YAP) play a role in enhancing the release of inflammation and inflammatory mediators in respiratory, cardiovascular, and digestive inflammatory disorders. In cancer, YAP drives the growth and differentiation of tumor cells in head and neck, digestive system, and urinary system cancers, influencing the tumor immune microenvironment and facilitating tumor metastasis and advancement.