Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
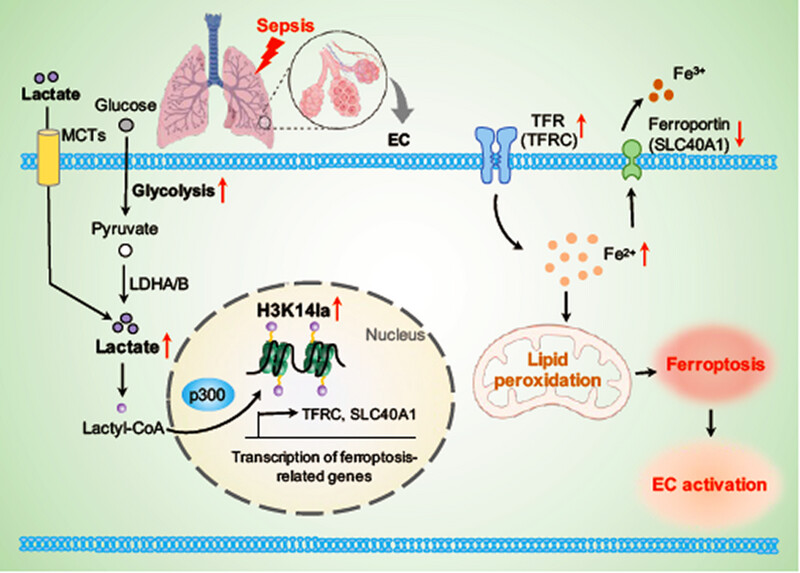
H3K14la drives endothelial dysfunction in sepsis-induced ARDS by promoting SLC40A1/transferrin-mediated ferroptosis
- First Published: 14 January 2025
REVIEW
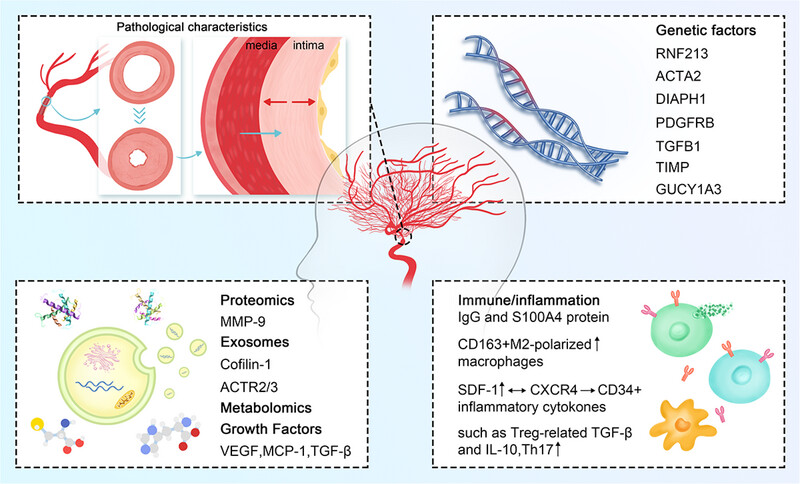
Advances in moyamoya disease: pathogenesis, diagnosis, and therapeutic interventions
- First Published: 14 January 2025
HIGHLIGHT
Transient pre-seizure inhibition of lateral hypothalamic orexin neurons: a novel possibility for seizure control
- First Published: 14 January 2025
REVIEW
Disseminated intravascular coagulation: cause, molecular mechanism, diagnosis, and therapy
- First Published: 14 January 2025
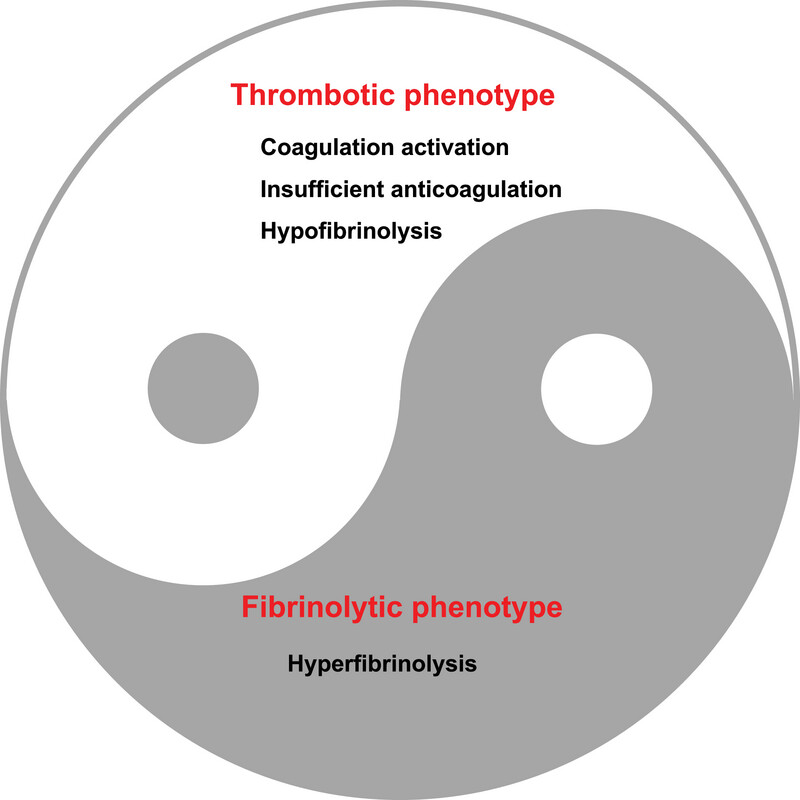
DIC course: imbalance of coagulative system, anticoagulant activity, and fibrinolysis system. DIC includes two phenotypes: thrombotic and fibrinolytic. The thrombotic phenotype includes coagulation activation, insufficient anticoagulation, and hypofibrinolysis, indicating a proclivity for clot formation. Conversely, the fibrinolytic phenotype is characterized by hyperfibrinolysis, which suggests an increased risk of bleeding due to excessive clot breakdown
HIGHLIGHT
A novel innate immunity-mediated senescence mechanism regulated by cGAS–STING–IRF3–pRB
- First Published: 15 January 2025
REVIEW
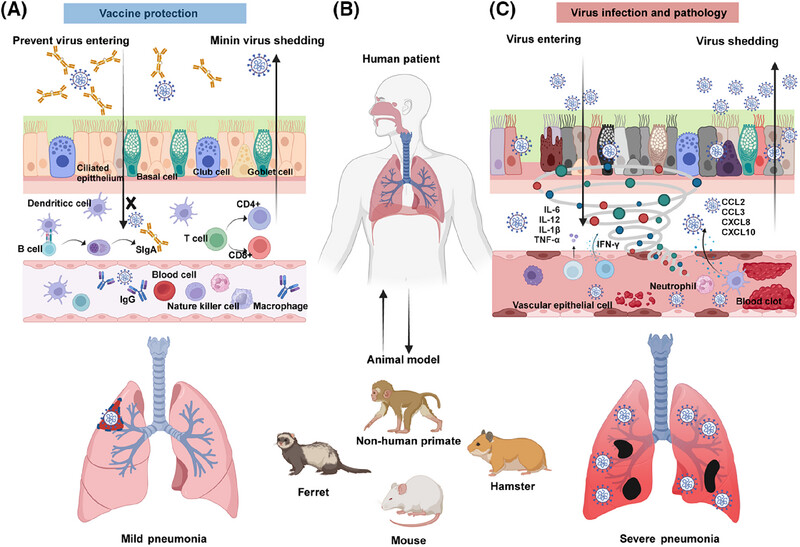
Novel vaccine strategies to induce respiratory mucosal immunity: advances and implications
- First Published: 16 January 2025
Vascular endothelial cell injury: causes, molecular mechanisms, and treatments
- First Published: 16 January 2025
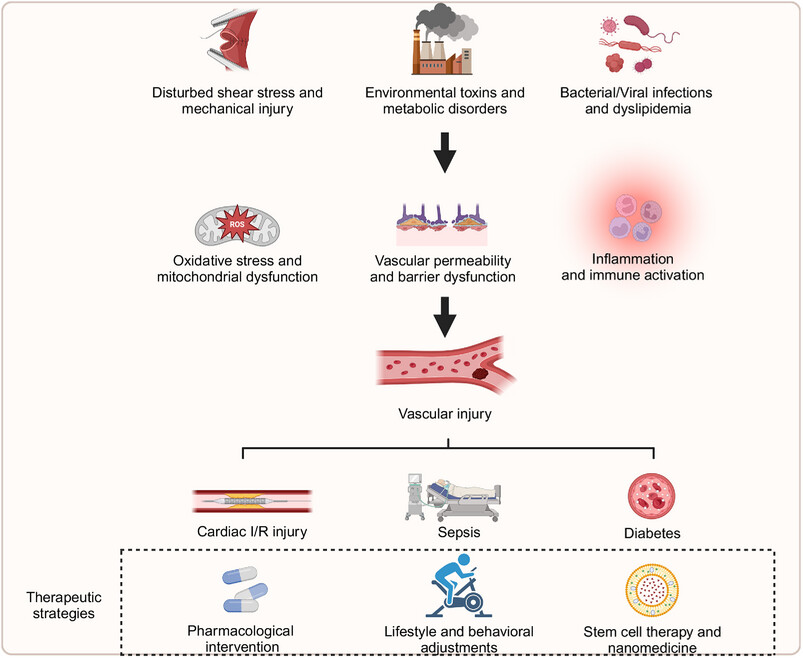
Endothelial cell injury is considered a critical initiating factor in the pathogenesis of various diseases, triggered by multiple factors such as disturbed shear stress and mechanical injury, environmental toxins, metabolic disorders, bacterial/viral infections, and dyslipidemia. These factors significantly compromise vascular integrity and function, lead to mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress, and activate inflammatory responses. This review specifically focuses on endothelial injury in cardiac I/R injury, sepsis, and diabetes. Current treatment strategies include pharmacological interventions, lifestyle modifications, stem cell therapies, and nanoparticle-based treatments, all of which require further optimization.
LETTER
Estimating myocardial fibrosis in aortic stenosis using the serum collagen type I C-terminal telopeptide to matrix metalloproteinase-1 ratio
- First Published: 16 January 2025
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Targeting intracellular cancer proteins with tumor-microenvironment-responsive bispecific nanobody-PROTACs for enhanced therapeutic efficacy
- First Published: 19 January 2025

We engineered a fusion protein integrating nanobodies KN035 and Nb4A, a Furin site, and a degron sequence to selectively degrade intracellular proteins. This construct targets PD-L1 on cancer cells, internalizes, and redirects Nb4A to bind Survivin, promoting its degradation through the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway upon Furin cleavage. Our strategy precisely targets and degrades oncogenic proteins in cancer cells using engineered proteins.
Circulating tumor DNA analysis for prediction of prognosis and molecular insights in patients with resectable gastric cancer: results from a prospective study
- First Published: 19 January 2025
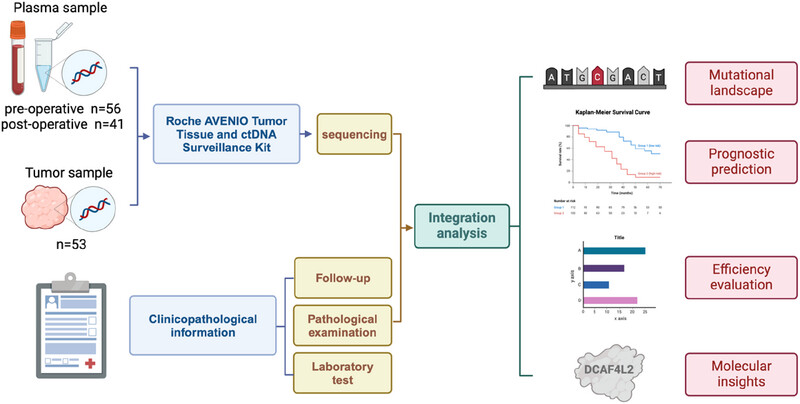
Our study indicated ctDNA level in 1-month post-operative plasma sample effectively predicted prognosis of GC patients. Plasma samples and paired tumor tissue were prospectively collected from patients pre-operatively at baseline and at subsequent time points of post-operative follow-up for ctDNA detection by AVENIO ctDNA Surveillance Kit. Integrated with clinicopathological information, prognostic prediction was conducted in further analysis.
A novel allosteric driver mutation of β-glucuronidase promotes head and neck squamous cell carcinoma progression through STT3B-mediated PD-L1 N-glycosylation
- First Published: 19 January 2025
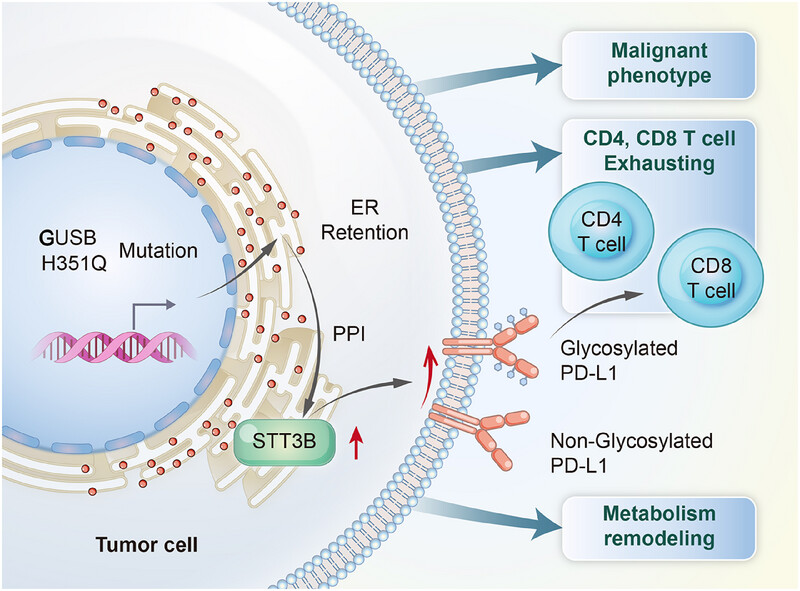
Liu et al. identified the specific mutation H351Q in β-glucuronidase (GUSB) as a novel allosteric driver mutation, which facilitated the aberrant N-glycosylation of PD-L1 through increasing protein stability and mRNA transcripts of the STT3 oligosaccharyltransferase complex catalytic subunit B (STT3B). Moreover, GUSB-H351Q reshaped a more immunosuppressive microenvironment featuring increased infiltration of exhausted CD8+ T cells and remodeled tumor metabolism, characterized by increased activity of the purine metabolism pathways and pyruvic acid accumulation.
REVIEW
Patient-derived xenograft model in cancer: establishment and applications
- First Published: 19 January 2025
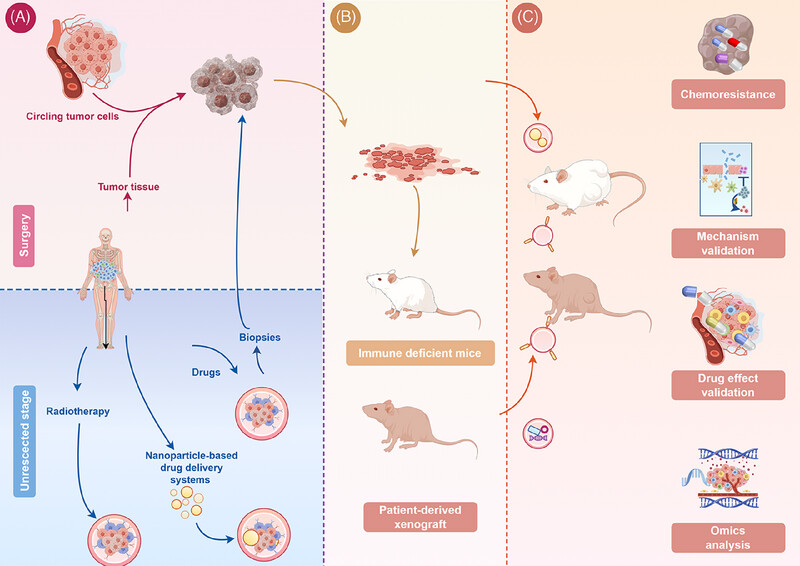
This review presents the establishment and application of patient-derived xenograft (PDX) models, underscoring their extensive application in various therapeutic strategies including chemotherapy, targeted therapy, delivery systems, combination therapy, antibody–drug conjugates, and radiotherapy. Additionally, the integration of PDX models with multiomics and single-cell analysis in cancer research is highlighted. Pertinent clinical studies are further examined and discussed, thereby advancing the development of cancer treatment strategies.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
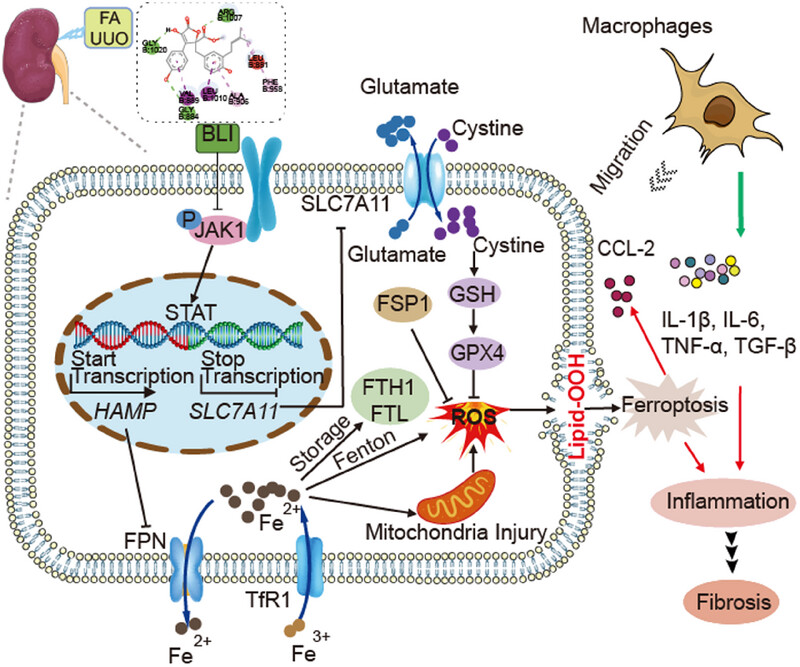
Butyrolactone I blocks the transition of acute kidney injury to chronic kidney disease in mice by targeting JAK1
- First Published: 21 January 2025
REVIEW
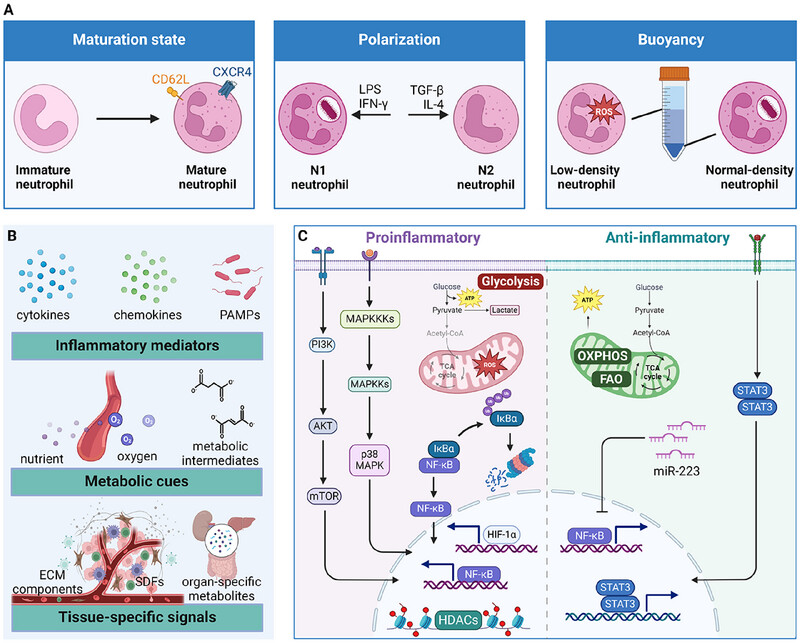
Neutrophil heterogeneity and plasticity: unveiling the multifaceted roles in health and disease
- First Published: 21 January 2025
PERSPECTIVE
The design of retroviral vectors used in the CAR-T products, risk management, and future perspective
- First Published: 24 January 2025
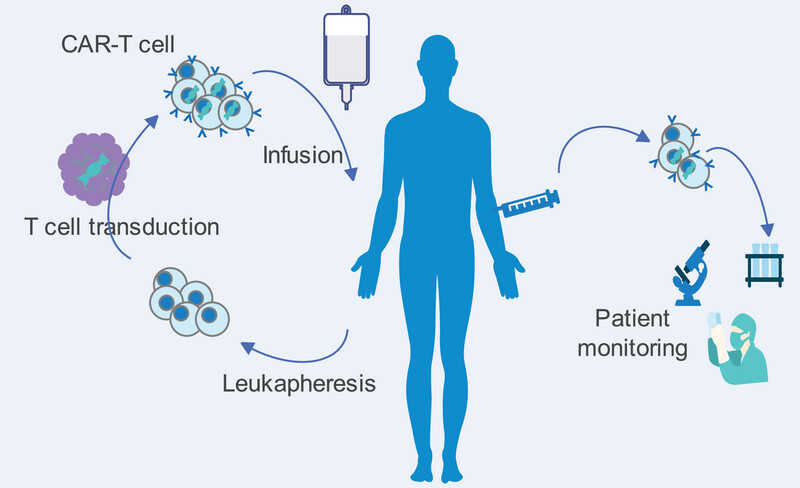
This article compares gamma retroviral and lentiviral vectors, discussing packaging systems and SIN vector design. It also covers risks of secondary malignancies linked to retroviral vectors and strategies to minimize them. The article explores the regulatory framework, safety monitoring, and future safety improvements for CAR-T therapy, emphasizing a balance between innovation and patient safety.
LETTER
WSB2 inhibits apoptosis and autophagy by targeting NOXA for degradation
- First Published: 24 January 2025
REVIEW
At the nucleus of cancer: how the nuclear envelope controls tumor progression
- First Published: 24 January 2025
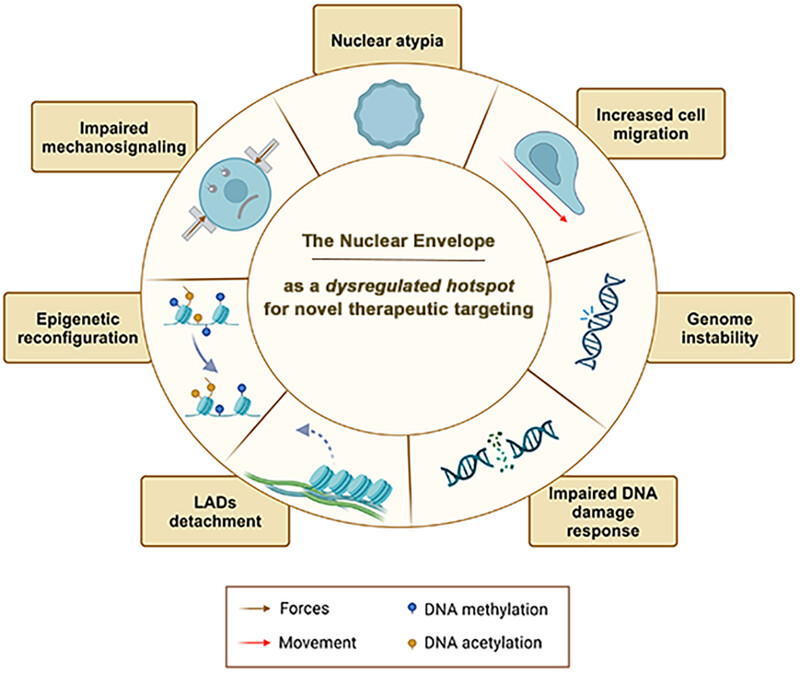
The review is focused on exploring novel intriguing perspectives on the role of the nuclear envelope in tumor progression. Alterations of nuclear envelope proteins result in the dysregulation of cellular pathways and promote tumorigenesis, highlighting that complex regulatory mechanisms lie behind the alterations in nuclear shape in cancer, thus revealing that these mechanisms could potentially open new frontiers for cancer therapies.
Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS): from mechanistic insights to therapeutic strategies
- First Published: 26 January 2025
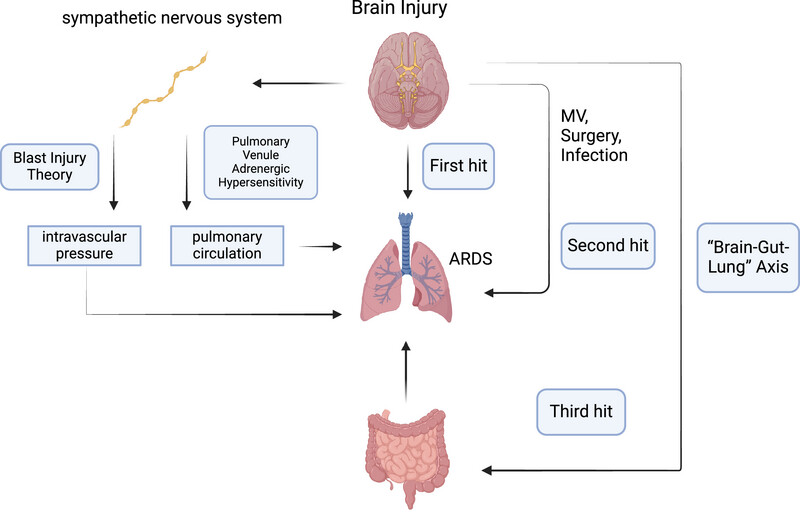
Acute brain injury (ABI), especially severe ABI, may cause dysfunction of peripheral extracranial organs and systems. “Blast injury” is one of the classic theories used to explain ABI-related acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). Sympathetic nervous system activation after brain injury changes the intravascular pressure, which damages the alveolocapillary membrane and causes neurogenic pulmonary edema. The management of ABI-related ARDS patients requires multidisciplinary cooperation to ensure that patients receive the best treatment.
Airway stenosis: classification, pathogenesis, and clinical management
- First Published: 26 January 2025
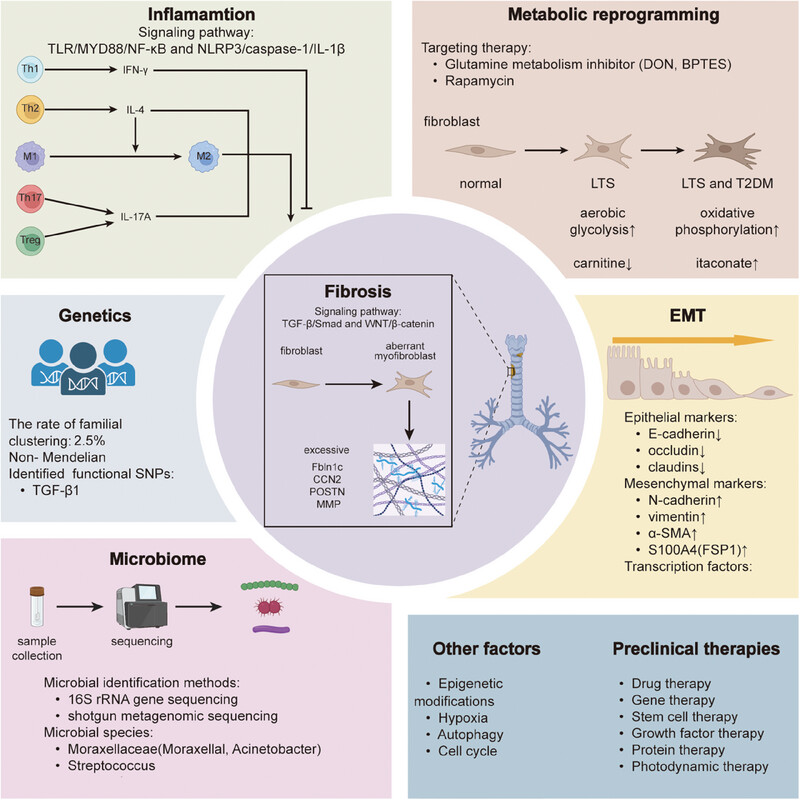
The development of AS can be affected by many factors, and fibrosis is the core process. Inflammation, Epithelial–mesenchymal transition and metabolic reprogramming can accelerate the development of AS by promoting the process of fibrosis. And the rest also show the correlation with AS. Targeting these aberrant signaling pathways and molecular mechanism can lead to development of effective treatment of AS.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
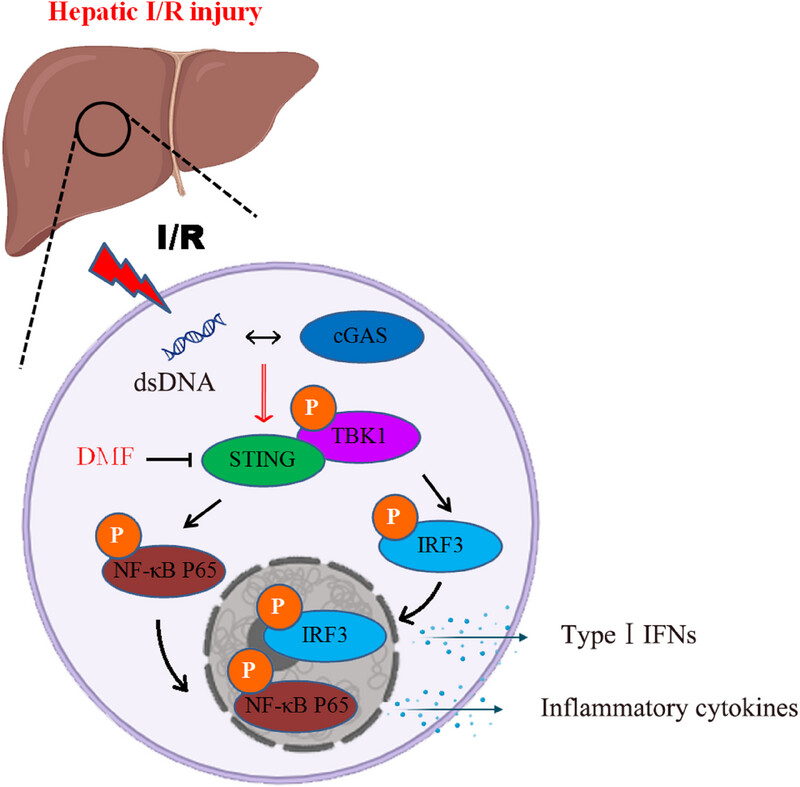
Dimethyl fumarate alleviate hepatic ischemia–reperfusion injury through suppressing cGAS-STING signaling
- First Published: 28 January 2025
Salt-inducible kinase 2 confers radioresistance in colorectal cancer by facilitating homologous recombination repair
- First Published: 28 January 2025
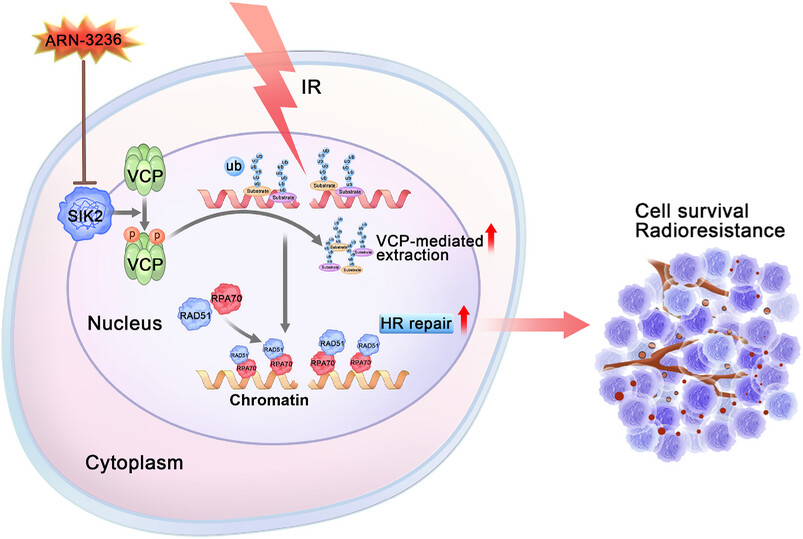
SIK2 promotes hyperphosphorylation of VCP and subsequent extraction of K48–Ub conjugates from DNA damage sites, thereby facilitating homologous recombination and radioresistance. Inhibition of SIK2 with the small molecule ARN-3236, significantly enhances CRC radiosensitivity by arresting HR-mediated DNA repair, suggesting a potential therapeutic strategy for overcoming radioresistance in CRC.
Outer membrane vesicle contributes to the Pseudomonas aeruginosa resistance to antimicrobial peptides in the acidic airway of bronchiectasis patients
- First Published: 30 January 2025
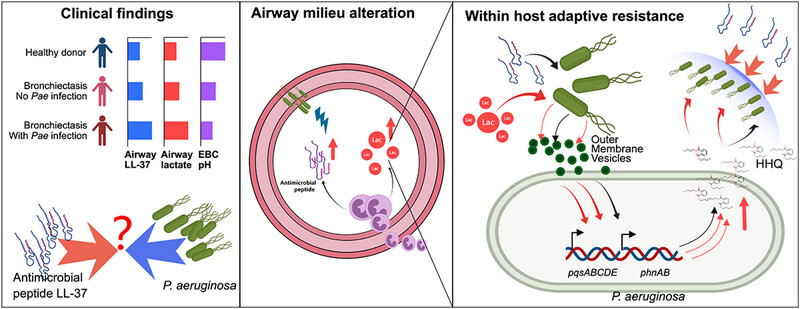
Airway lactate and LL-37 enrich in the P. aeruginosa-infected bronchiectasis patients. Outer membrane vesicles release of P. aeruginosa increases in the acidic environment. OMVs induce the overproduction of 2-heptyl-4-quinolone (HHQ) in P. aeruginosa. HHQ protects P. aeruginosa from LL-37 killing by inhibiting the binding to the membrane.
Antimicrobial peptide DP7 alleviates dextran sulfate sodium (DSS)-induced colitis via modifying gut microbiota and regulating intestinal barrier function
- First Published: 30 January 2025
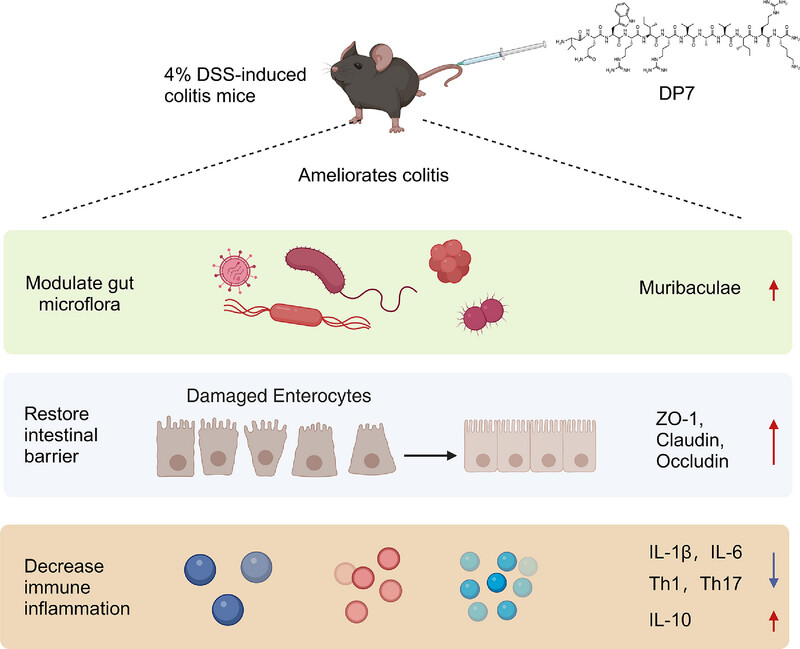
DP7 effectively alleviated dextran sulfate sodium (DSS)-induced colitis in mice. The potential mechanisms include enhancing gut barrier integrity, reducing proinflammatory cytokine secretion, and modulating gut microbiota composition. These findings highlight DP7's therapeutic potential for treating inflammatory bowel diseases by targeting both immune response and microbiota homeostasis.
LETTER
Carbonaceous particle exposure triggered accumulation of Osteopontin/SPP1+ macrophages contributes to emphysema development
- First Published: 28 January 2025
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
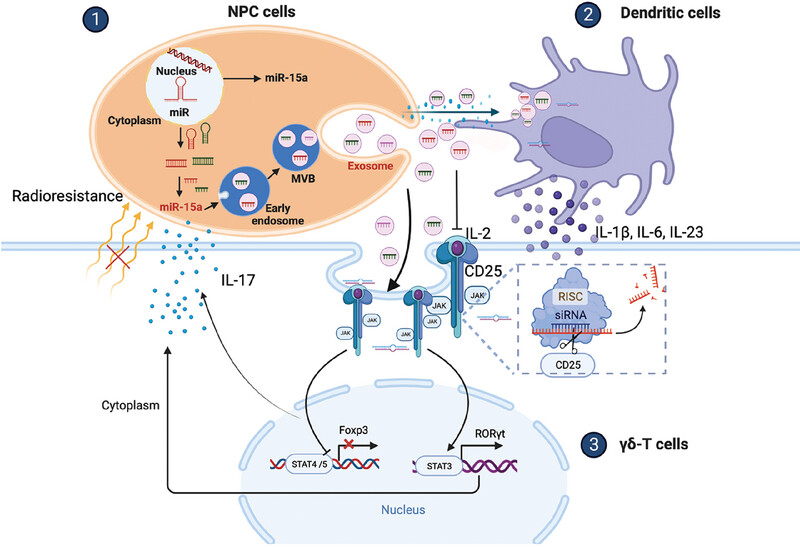
CD25 downregulation by tumor exosomal microRNA-15a promotes interleukin-17-producing γδ-T-cells-mediated radioresistance in nasopharyngeal carcinoma
- First Published: 02 February 2025
REVIEW
Circular RNAs in cancer
- First Published: 02 February 2025
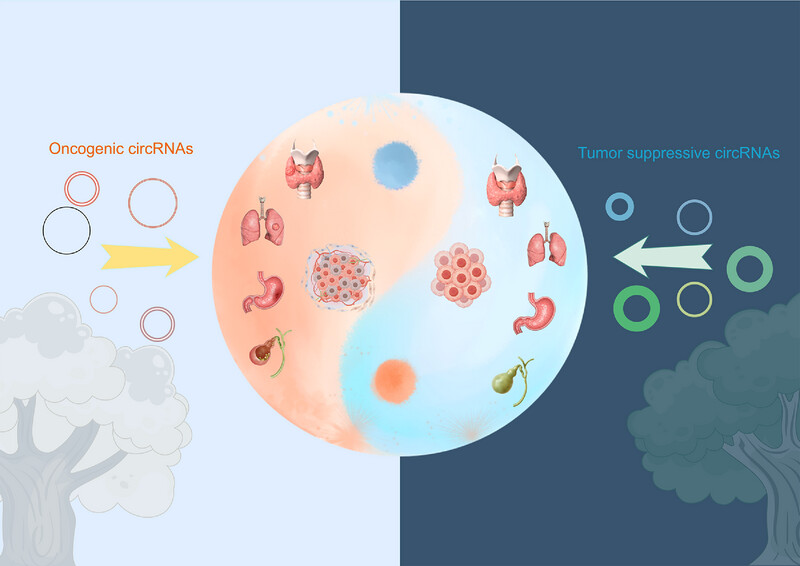
Circular RNAs (circRNAs) play essential roles in hallmarks of cancer, exerting either oncogenic or tumor-suppressive effects, as observed in thyroid cancer. This review presents an extensive review of circRNAs, encompassing their biogenesis, characteristics, functions, and mechanisms of turnover. Additionally, we examine the roles of dysregulated circRNAs in contributing to the hallmarks of cancer, with a particular focus on their involvement in the dynamic regulation of the “Yin-Yang” balance in thyroid cancer. Furthermore, the clinical implications of various circRNAs as biomarkers and therapeutic targets in different cancers are discussed.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Therapeutic potential of nicotinamide and ABT263 in alcohol-associated liver disease through targeting cellular senescence
- First Published: 09 February 2025
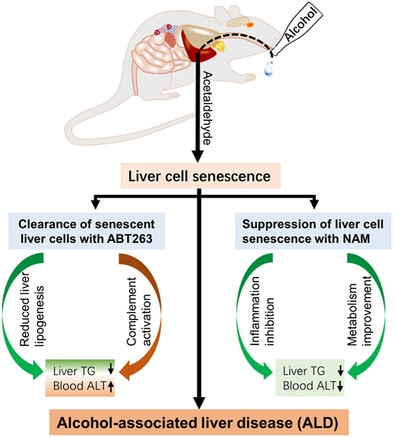
Alcohol metabolite acetaldehyde (ACH) induces senescence in the liver, which is involved in alcohol-associated liver disease (ALD). Clearance of senescent liver cells with ABT263 reduced triglyceride (TG) in the liver, but increased ALT levels possibly via activation of the complement system. In contrast, suppression of senescence with nicotinamide (NAM) mitigates ALD via inhibiting inflammation and improving metabolism in the liver.
Recombinant protein HR212 targeting heptad repeat 2 domain in spike protein S2 subunit elicits broad-spectrum neutralizing antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 and its variants
- First Published: 09 February 2025
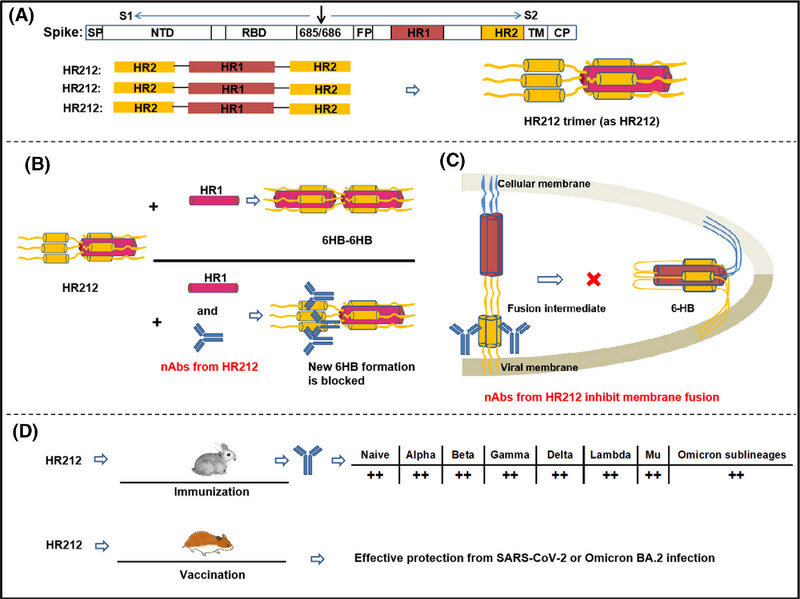
1. HR212 assembles to be a trimer with three HR2s exposed.
2. The nAbs induced by HR212 showed inhibition of HR1 binding with HR212 and the nAbs induced by HR212 would block the S2 conformational rearrangement from “fusion intermediate” to “postfusion” structure (6-HB), thus inhibiting membrane fusion between viral and cellular membranes.
3. Immunization with HR212 evoked highly cross-nAbs against SARS-CoV-2 and its variants.
Prognostic and predictive effects of new steatotic liver disease nomenclatures: a large population-based study
- First Published: 13 February 2025
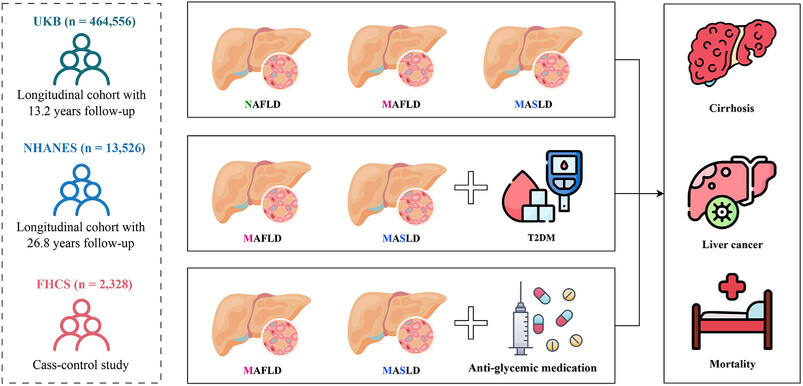
This study analyzed the UK Biobank, NHANES III, and FHCS data to assess the prognostic and associative effects of new steatotic liver disease nomenclatures. It found that MAFLD, MASLD, and MetALD were associated with higher risks of liver-related conditions and mortality, with diabetes and certain antiglycemic medications further heightening these risks .
Endothelial monocarboxylate transporter 1 drives atherosclerosis via a lactate/NADH/CtBP-mediated transrepression pathway
- First Published: 13 February 2025
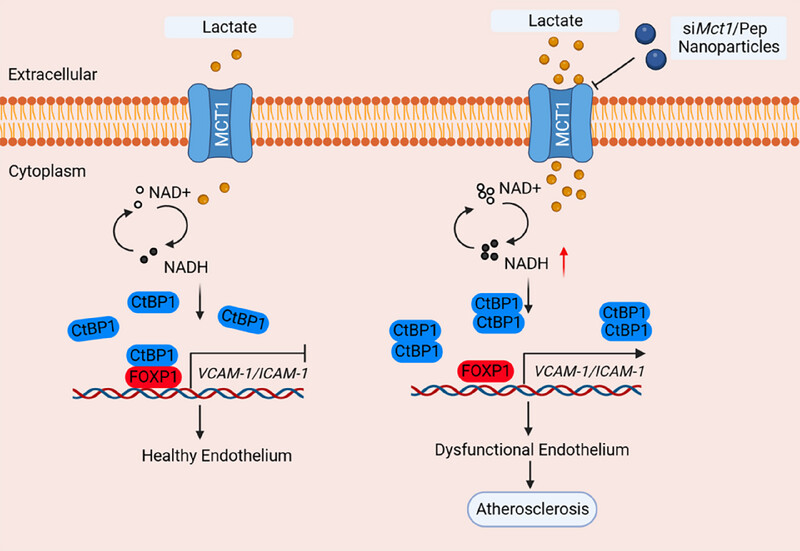
In this study, we identified the buildup of lactate within the tissue microenvironment in the context of atherosclerosis. Our findings indicate that MCT1-mediated lactate uptake enhances endothelial activation by modulating FOXP1 transrepressive activity through a CtBP1 oligomerization-dependent mechanism, thereby inducing atherosclerotic lesion formation. Furthermore, the use of endothelial-targeting nanoparticles loaded with siRNA against Mct1 was shown to mitigate endothelial inflammation and atherogenesis in Apoe−/− mice.
Microbiota-derived 3-Methyl-L-histidine mediates the proatherogenic effect of high chicken protein diet
- First Published: 13 February 2025
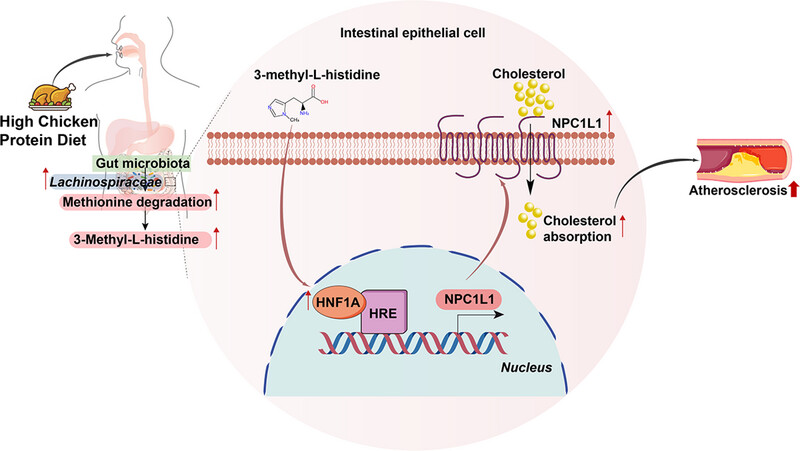
Schematic summary illustrates the potential mechanism, whereby high chicken protein diet promoted the progression of atherosclerosis. Long-term adherence to a diet rich in chicken protein accelerated atherosclerosis through an enhanced microbial production of 3-Methyl-L-histidine, which in turn facilitated NPC1L1-mediated intestinal cholesterol absorption.
SHCBP1 is a novel regulator of PLK1 phosphorylation and promotes prostate cancer bone metastasis
- First Published: 13 February 2025
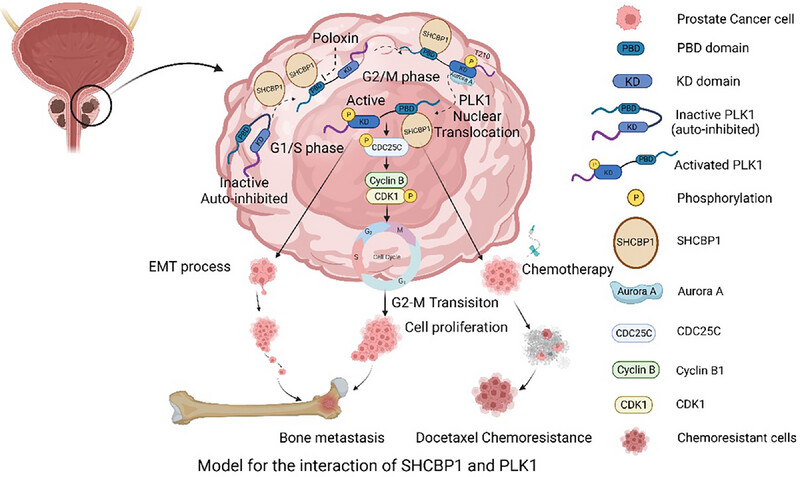
Model for the interaction of SHCBP1 and PLK1. Schematics summarizing the interaction between SHCBP1 and PLK1, which promotes the Aurora A-PLK1 interaction, leading to altered phosphorylation of PLK1 at T210, thus promoting cell mitosis and contributing to tumor development via the SHCBP1-PLK1-CDC25C axis. It also highlights the involvement of SHCBP1 in epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT), facilitating cancer cell metastasis, and docetaxel chemoresistant.
HIGHLIGHT
Redefining DNA cleavage in type I CRISPR systems with the HNH domain
- First Published: 13 February 2025
REVIEW
Gene therapy for genetic diseases: challenges and future directions
- First Published: 13 February 2025
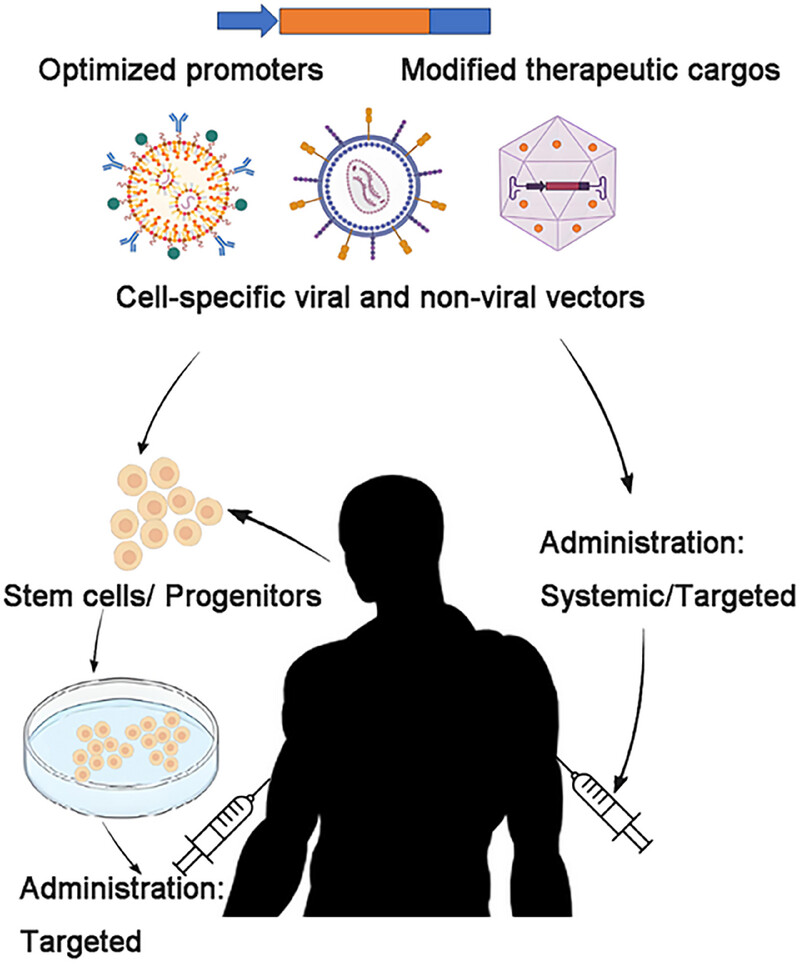
The graphical abstract provides an overview of gene therapy approaches, detailing the components of the therapy and the various delivery routes. Both in vivo and ex vivo strategies facilitate the implementation of gene replacement, gene suppression, gene supplementation, and gene editing. Therapeutic effects have been demonstrated across a spectrum of genetic diseases as well as in various specific degenerative diseases.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Cannabidiol restores hematopoietic stem cell stemness in mouse through Atf2–Lrp6 axis after acute irradiation
- First Published: 13 February 2025
Once-weekly glucagon-like peptide receptor agonist polyethylene glycol loxenatide protects against major adverse cardiovascular events in patients with type 2 diabetes: a multicenter ambispective cohort study (FLYING trial)
- First Published: 13 February 2025
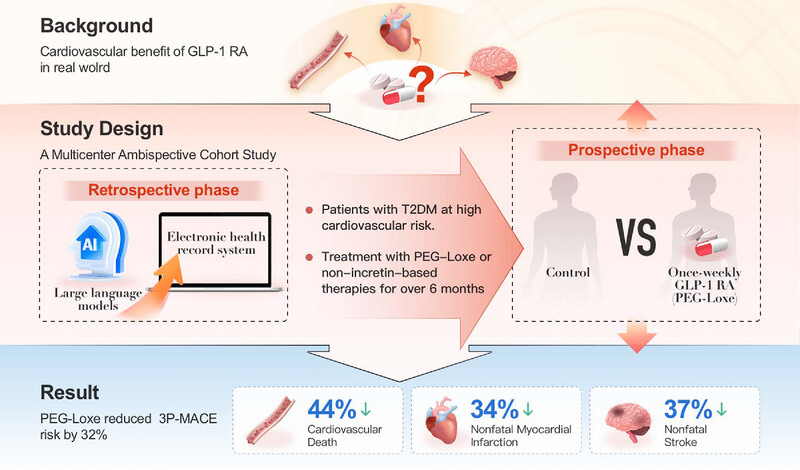
Large language models were used to retrospectively screen and include 12,341 patients with T2DM who had either cardiovascular disease or cardiovascular risk factors. We found a significantly lower incidence of first nonfatal myocardial infarction, nonfatal stroke, or cardiovascular deaths in the PEG-Loxe cohort than the control cohort.