Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
REVIEW
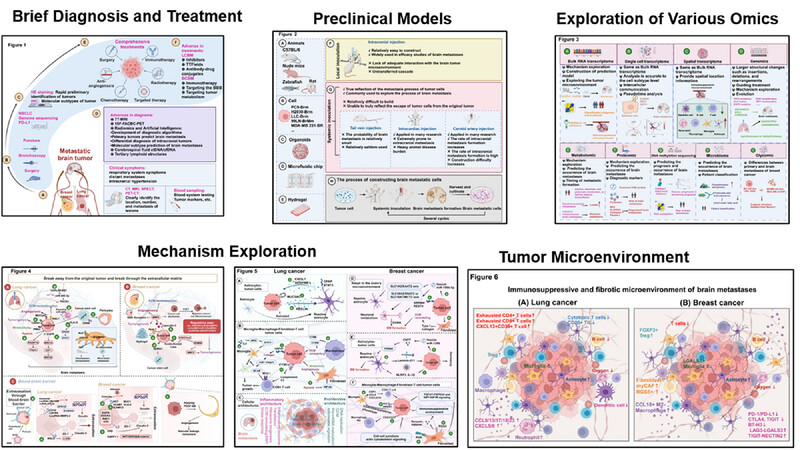
Metastatic brain tumors: from development to cutting-edge treatment
- First Published: 20 December 2024
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Discovery of a non-nucleotide stimulator of interferon genes (STING) agonist with systemic antitumor effect
- First Published: 20 December 2024
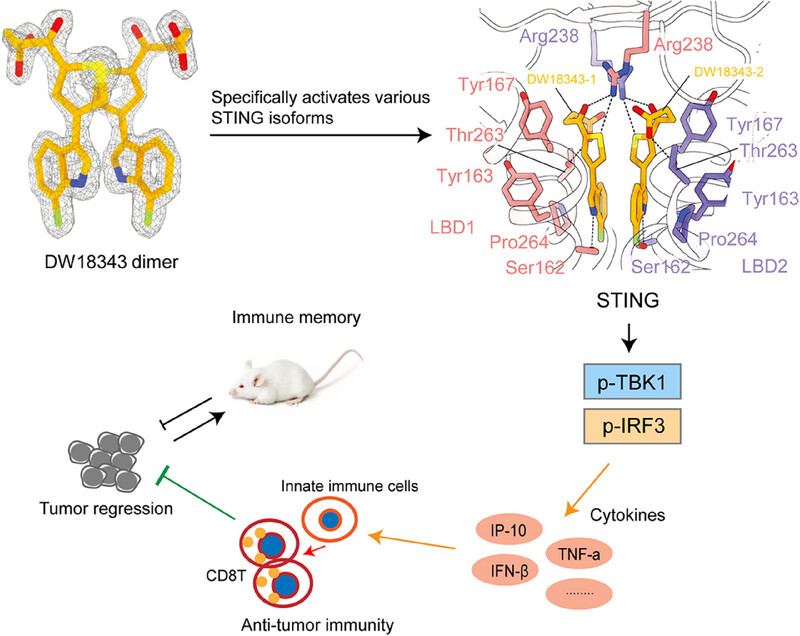
DW18343 specifically binds to various STING isoforms and activates downstream p-TBK1/p-IRF3 signaling.
DW18343 binds more deeply into a pocket formed by the ligand binding domain (LBD) of STING-H232 as compared to other agonists such as MSA-2, SR-717, or cGAMP.
DW18343 demonstrated durable antitumor activity in syngeneic mouse tumor models and induced immune memory, which is associated with the activation of antitumor immunity .
Combined pyrotinib and fulvestrant for hormone receptor-positive and HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer: A multicenter, single-arm, phase II trial
- First Published: 20 December 2024
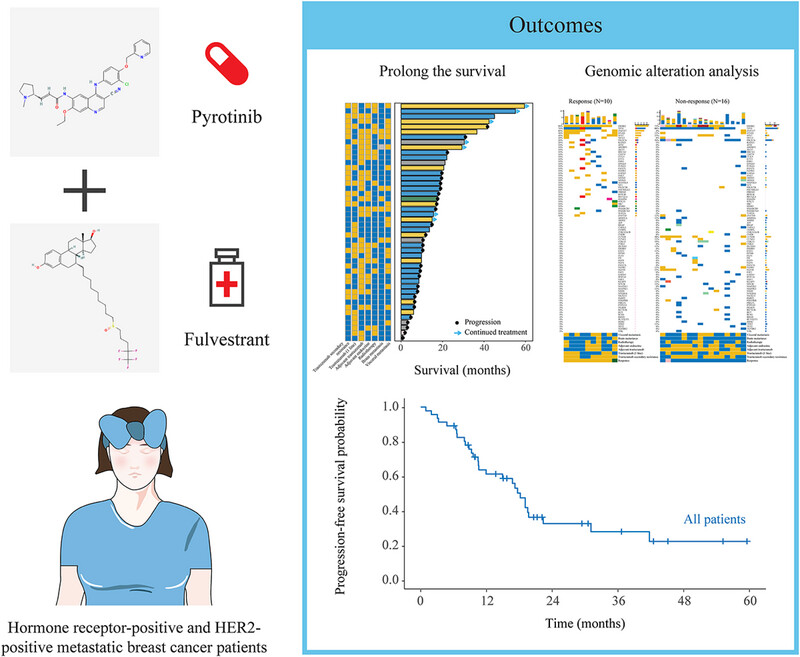
This study suggests that pyrotinib plus fulvestrant might be an efficacious and well-tolerated option in HR-positive/HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer patients who have shown resistance to trastuzumab. This regimen could be a potential first-line treatment and may be considered the preferred option for patients with brain metastases, secondary resistance to trastuzumab, and those who have received adjuvant endocrine therapy. Additionally, responses were observed in patients with low tumor mutation burden and ZNF217 mutation .
A SARS-CoV-2 EG.5 mRNA vaccine induces a broad-spectrum immune response in mice
- First Published: 02 January 2025
Considering that SARS-CoV-2 infection cases continue to appear worldwide, and the continuous mutation of the virus has reduced the protective effectiveness of existing vaccines, this study designed a novel vaccine to provide effective protection against SARS-CoV-2 variant strains. It will provide reference value for the research and development of the next generation of COVID-19 vaccine and other related vaccines .
Impaired network organization in mild age-related hearing loss
- First Published: 02 January 2025
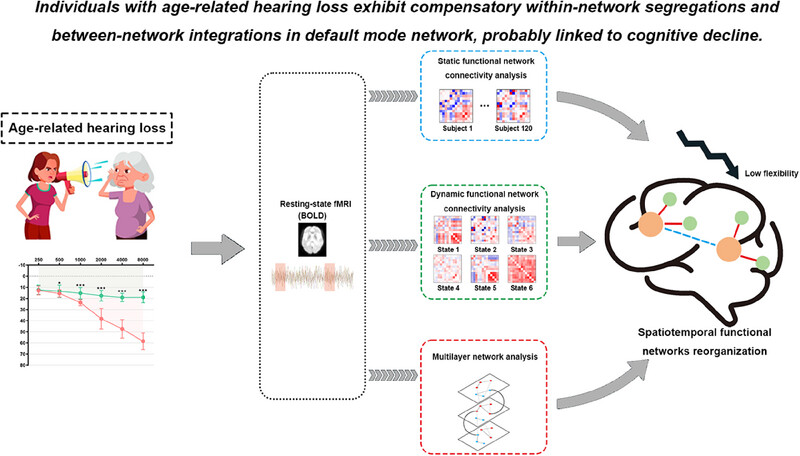
The authors investigated the spatiotemporal characteristics of brain network functional reorganization in patients with age-related hearing loss (ARHL) in terms of static and dynamic functional network connectivity and network switching. Compensatory within-network segregations and between-network integrations as well as low flexibility in default mode network caused by ARHL are probably linked to cognitive decline, offering new insights on how ARHL contributes to age-related cognitive impairment.
REVIEW
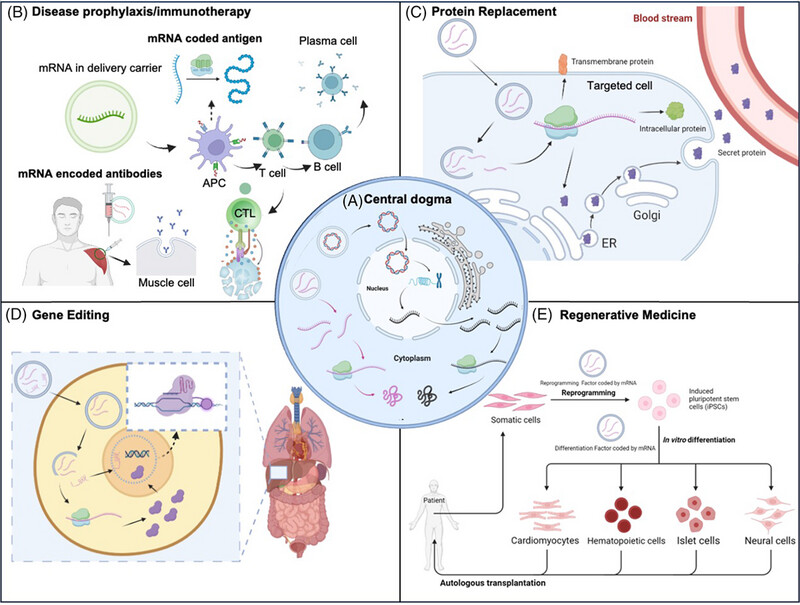
Nonviral targeted mRNA delivery: principles, progresses, and challenges
- First Published: 02 January 2025
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Prolyl 4-hydroxylase α-subunit family regulation of type I collagen deposition and IL17RB/c-Jun activation synergistically mediate choline dehydrogenase promotion of colorectal cancer metastasis
- First Published: 03 January 2025
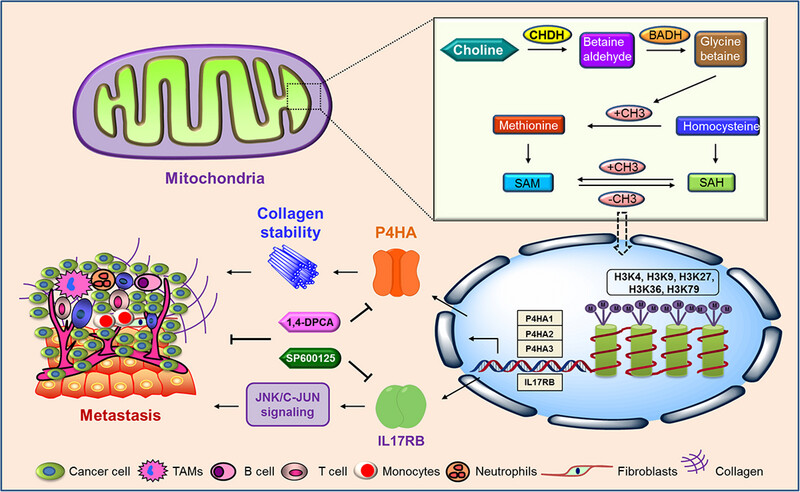
Choline dehydrogenase (CHDH), one of the enzymes involved in methyl donor pathway, affects histone H3 trimethylation, which in turn regulates the expression of the downstream target genes prolyl 4-hydroxylase α-subunits (P4HAs) and IL17RB. The P4HAs stabilize and promotes collagen I expression, and IL17RB promotes downstream c-Jun activation, which together contribute to colorectal cancer (CRC) metastasis. 1,4-Dihydrophenonthrolin-4-one-3-carboxylic acid (1,4-DPCA) targets P4HAs, and SP600125 targets c-Jun, both of which prevent CHDH-mediated CRC metastasis .
Left ventricular trabecular complexity for risk stratification of cancer therapy–related cardiac dysfunction in breast cancer
- First Published: 02 January 2025
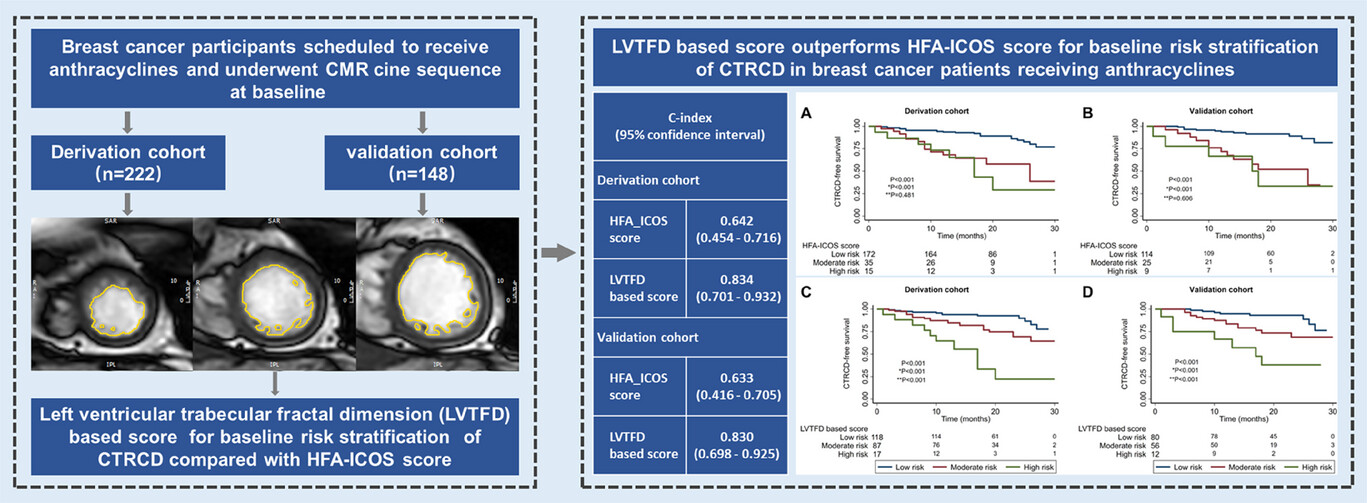
The left ventricular trabecular fractal dimension (LVTFD)-based score integrating age, hypertension, previous cardiovascular disease, and maximal apical FD outperforms Heart Failure Association-International Cardio-Oncology Society (HFA-ICOS) score for stratifying cancer therapy–related cardiac dysfunction (CTRCD) in breast cancer patients receiving anthracycline.
Multiorgan proteomic analysis of infected animal models predict potential host factors for chikungunya virus
- First Published: 03 January 2025
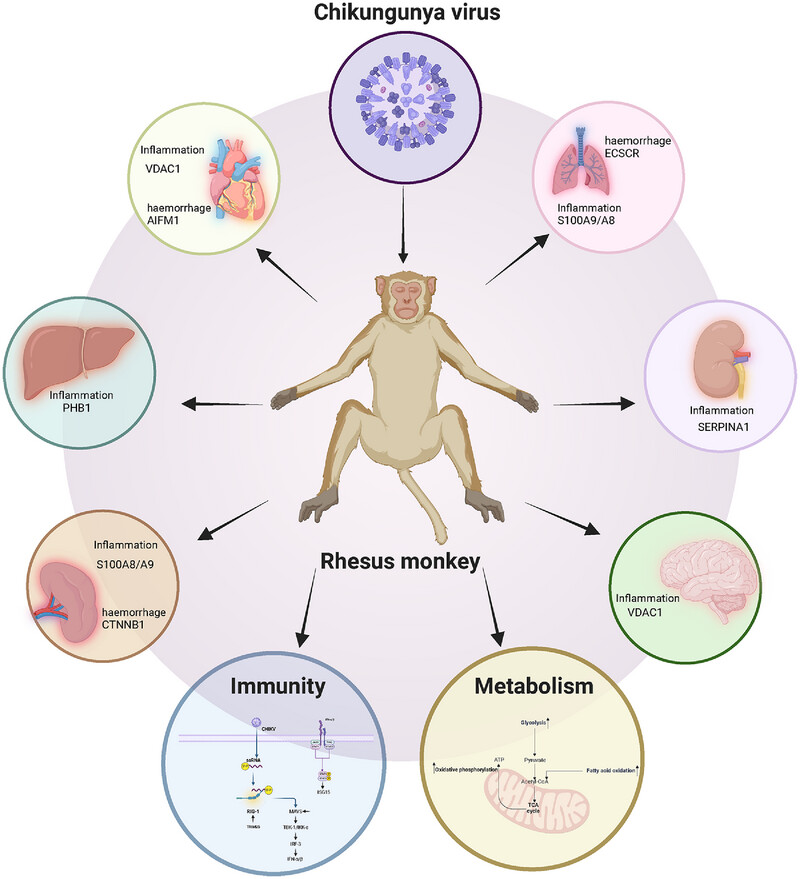
We depicted the multiorgan proteomic landscape in CHIKV-infected animal models, revealing the potential role of the RLR signaling pathway against CHIKV infection and dysregulated metabolism. Moreover, we predicted potential host factors contributing to organ-specific inflammation and hemorrhage in rhesus monkeys through bioinformatic and correlation analyses.
REVIEW
RNA N4-acetylcytidine modification and its role in health and diseases
- First Published: 03 January 2025
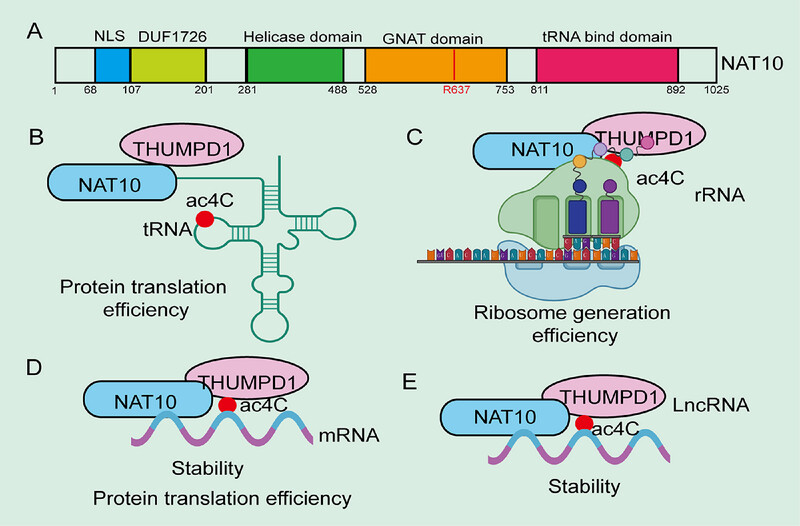
N4-acetylcytidine (ac4C) modification is a crucial RNA modification widely present in eukaryotic RNA. This review first outlines the latest research advancements on the roles and mechanisms of ac4C modification in both health and disease and explores ac4C-targeted therapies with the aim of advancing cancer research and improving patient outcomes .
HIGHLIGHT
Targeting EZH1/2: tackling epigenetic resistance advances cancer therapy
- First Published: 03 January 2025
REVIEW
Sarcopenia and cachexia: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic interventions
- First Published: 05 January 2025
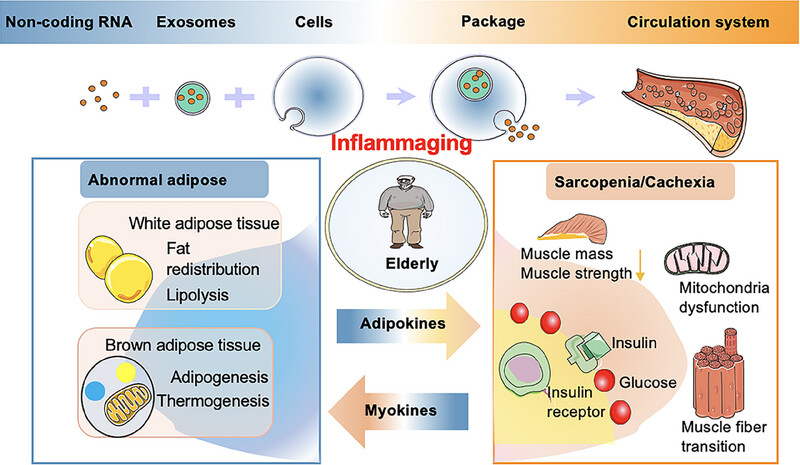
Sarcopenia is defined as a muscle-wasting syndrome that occurs with accelerated aging, while cachexia is a severe wasting syndrome associated with conditions such as cancer and immunodeficiency disorders, which cannot be fully addressed through conventional nutritional supplementation. Sarcopenia can be viewed as a component of cachexia, with bidirectional regulation between adipose tissue and skeletal muscle serving as a potential molecular mechanism for both conditions. However, the underlying mechanisms differ. Despite the development of various therapeutic strategies aimed at reversing or preventing sarcopenia and cachexia, their effectiveness has often been limited. In this review, we discuss the abnormal changes in the muscle microenvironment that contribute to the progression of these conditions. We also highlight recent therapeutic approaches, including lifestyle modifications, small molecular agents, and nutritional interventions targeting sarcopenia and cachexia. Additionally, we explore emerging strategies for muscle wasting, such as gene editing, stem cell therapy, and gut microbiome modulation, along with their potential applications and prospects for improving muscle function. Finally, we address the major challenges and opportunities associated with multimodal interventions. We hope this review provides insights into the pathogenesis and molecular mechanisms of sarcopenia and cachexia, ultimately facilitating new methods, drug discovery, and improved treatment options for these conditions.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Altered zygotic gene expression caused by sperm with Tdrd6 variants disrupts early embryonic development
- First Published: 05 January 2025
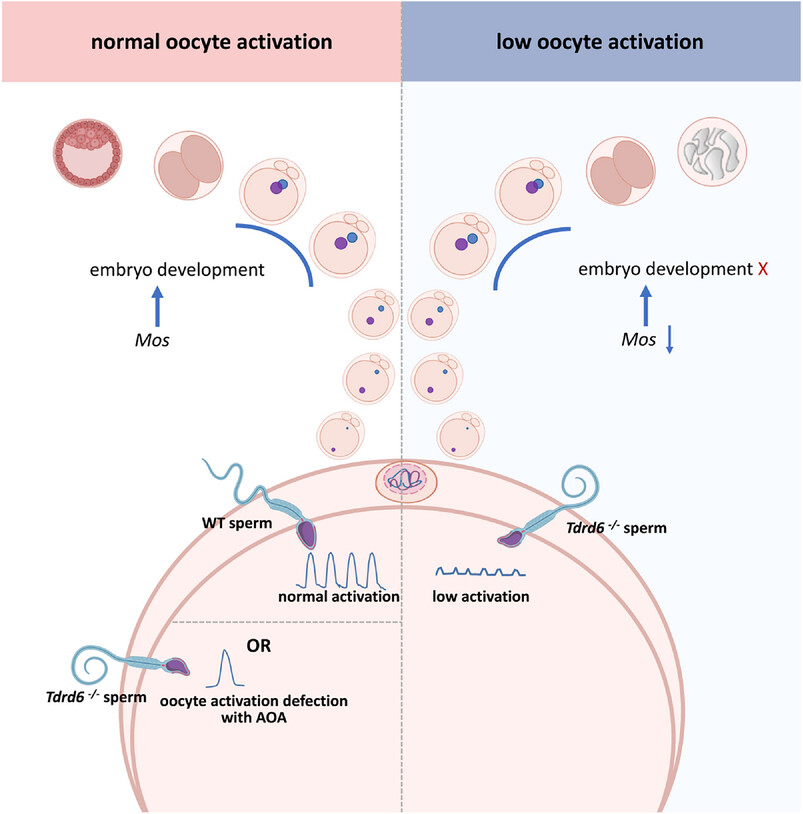
Tdrd6−/− sperm have deficiency in intracellular Ca2+ oscillations and oocyte activation, which affects gene expression in the 2PN stage. The low expression of Mos in PN4 zygotes is the key to early embryonic arrest. AOA can rescue Mos gene expression, overcome male factor-derived embryonic arrest, and achieve live births.
Loading of CAR-T cells with magnetic nanoparticles for controlled targeting suppresses inflammatory cytokine release and switches tumor cell death mechanism
- First Published: 05 January 2025
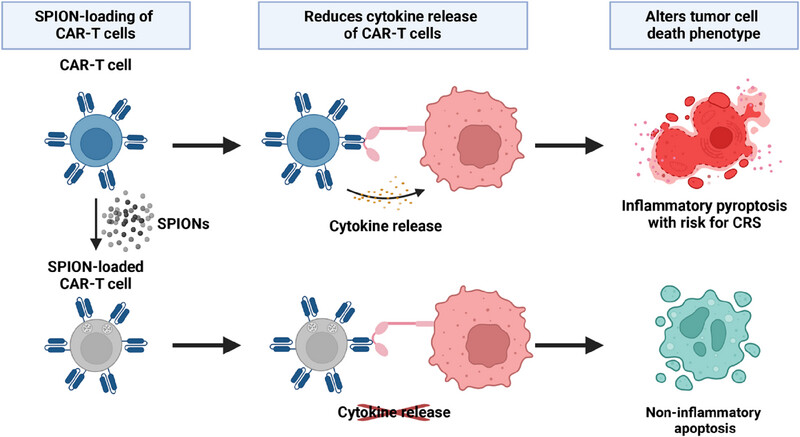
CAR-T cells were functionalized with superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPIONs) to enable site-directed targeting of solid tumors using an external magnetic field. The SPION-loaded CAR-T cells maintained their killing capacity against melanoma cells expressing the CAR-specific antigen chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan (CSPG4). Furthermore, the SPION-loading also suppressed the cytokine release of the CAR-T cells and switched the cell death phenotype of the tumor cells.
Osteoarthritis synovium as a nidus for monosodium urate crystal deposition inducing severe gout studied by label-free stimulated Raman scattering combined with synovial organoids
- First Published: 05 January 2025
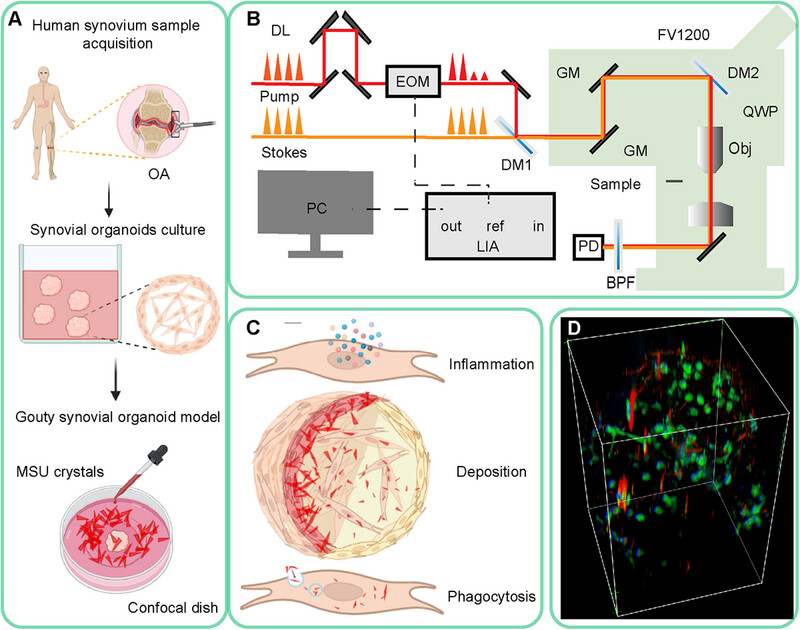
We investigated whether osteoarthritis (OA) synovium acts as a nidus for monosodium urate crystals deposition inducing severe gout using stimulated Raman scattering microscopy combined with synovial organoids. Crystal deposition, cellular phagocytosis, and subsequent inflammation was measured. Results revealed that crystals were more likely to deposit in OA synovium; OA synoviocytes were more capable of phagocytosing crystals; therefore, leading to severe inflammation, expediting gout .
PDPN+ cancer-associated fibroblasts enhance gastric cancer angiogenesis via AKT/NF-κB activation and the CCL2-ACKR1 axis
- First Published: 06 January 2025
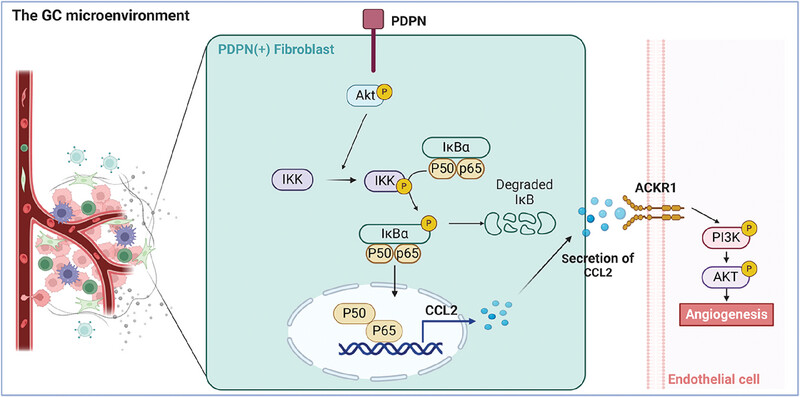
The Akt/NF-κB pathway was significantly activated in podoplanin (PDPN)(+) cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs). P65 directly bind to the chemokine (CC-motif) ligand 2 (CCL2) promoter, thereby increasing the CCL2 transcription and secretion in CAFs; CCL2, which was transcriptional activated by P65 in PDPN(+) CAFs, sustains tumor angiogenesis by interacting with ACKR1 and activating PI3K/AKT signaling in endothelial cells.
Chemical cross-linking facilitates antigen uptake and presentation and provides improved protection from Mpox with a dual-antigen subunit vaccine
- First Published: 08 January 2025
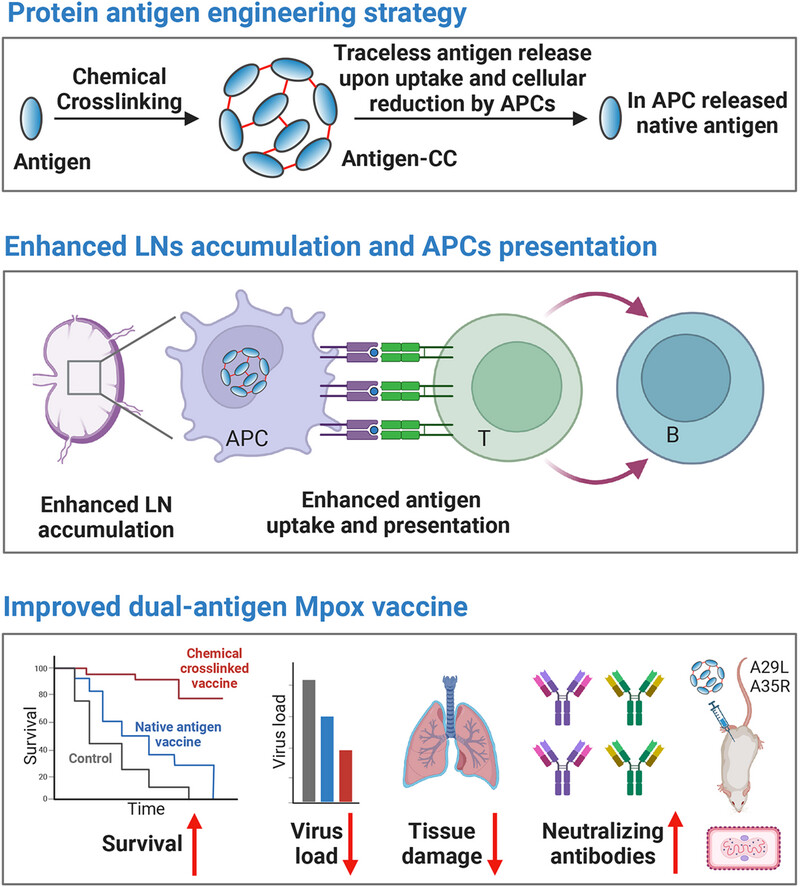
This work presented a reversable chemical cross-linking strategy to improve the accumulation of antigens in lymph node and to increase the uptake and presentation of antigens in antigen-presenting cell (APC). A dual-antigen vaccine was constructed for Mpox using this strategy, which provide enhanced protection against monkeypox virus. This work thus provided universal tools for the fight against future emerging pathogens.
Novel antibiotics against Staphylococcus aureus without detectable resistance by targeting proton motive force and FtsH
- First Published: 08 January 2025
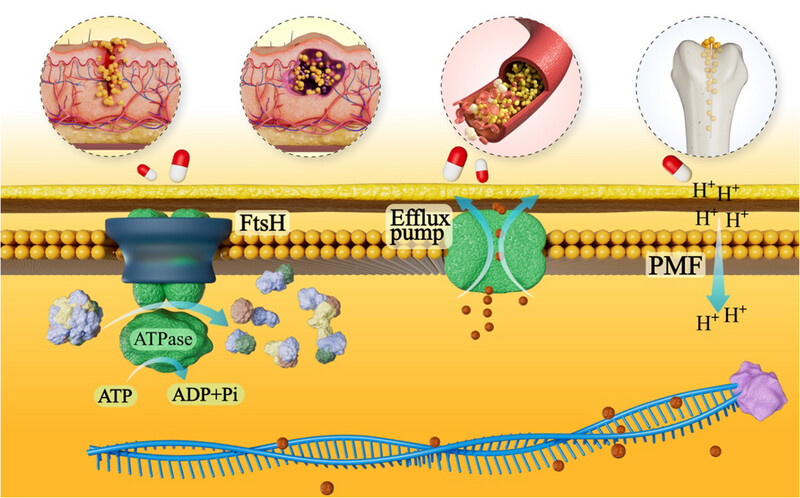
• We identified novel structural molecules C218-0546 and STK848198 that exhibited effective antimicrobial activity without detectable resistance against Staphylococcus aureus.
• The antimicrobial effects of the compounds were mainly mediated by proton motive force disruption and FtsH protein inhibition.
• The pharmacokinetic and toxicological profiles of the compounds are excellent, and STK848198 has great therapeutic potential for S. aureus-related bone implantation infections .
HIGHLIGHT
New advances in noninvasive screening technology for colorectal cancer
- First Published: 08 January 2025
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Serum sodium to chloride ratio and mortality on continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis: a multicenter retrospective study
- First Published: 10 January 2025
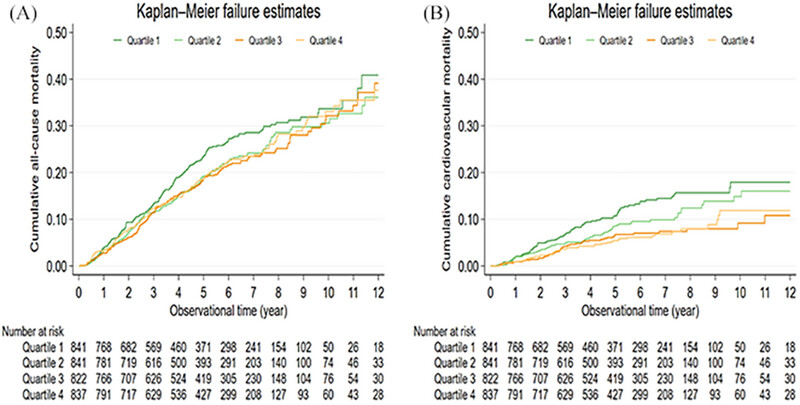
In this study, 3341 patients on peritoneal dialysis between 2005 and 2021 were enrolled and grouped into quartiles according to baseline Na/Cl. After following up for a median of 5.77 years, the results showed that the highest Na/Cl quartile patients were associated with lower all-cause and cardiovascular mortality, compared with that of the lowest quartile patients.
REVIEW
RNA modifications in cancer
- First Published: 10 January 2025
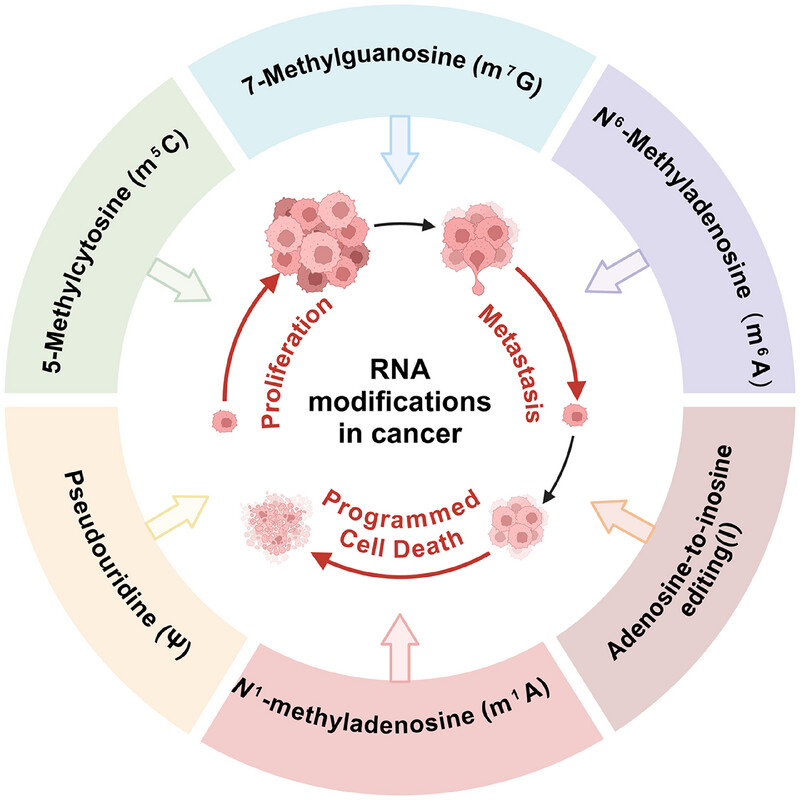
This review highlights the pivotal roles of key RNA modifications (m1A, m5C, m6A, m7G, ψ, and I) in cancer progression. These modifications influence tumor proliferation, metastasis, and programmed cell death, while also affecting the immune microenvironment. Understanding their mechanisms may enhance targeted therapies and improve patient outcomes in cancer treatment.
HIGHLIGHT
HCoV-HKU1 and TMPRSS2 interaction: uncovering mechanisms of viral invasion
- First Published: 10 January 2025
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
LungDiag: Empowering artificial intelligence for respiratory diseases diagnosis based on electronic health records, a multicenter study
- First Published: 12 January 2025
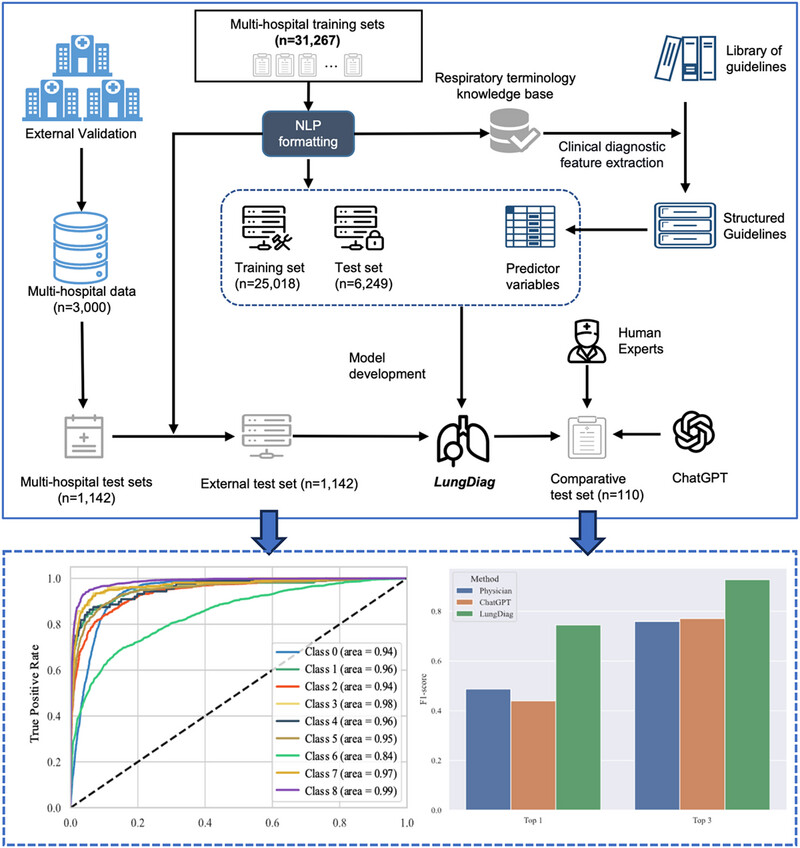
LungDiag is an advanced system for diagnosing respiratory diseases, integrating deep learning-based NLP to accurately extract clinical features at admission. It demonstrated high precision in identifying phenotypic entities and diagnosing respiratory diseases. By standardizing terminology and using detailed semantic modeling, LungDiag supports physicians in managing inpatient records and enhances clinical decision-making amid diagnostic uncertainties.
Comparison of diet and exercise on cardiometabolic factors in young adults with overweight/obesity: multiomics analysis and gut microbiota prediction, a randomized controlled trial
- First Published: 12 January 2025
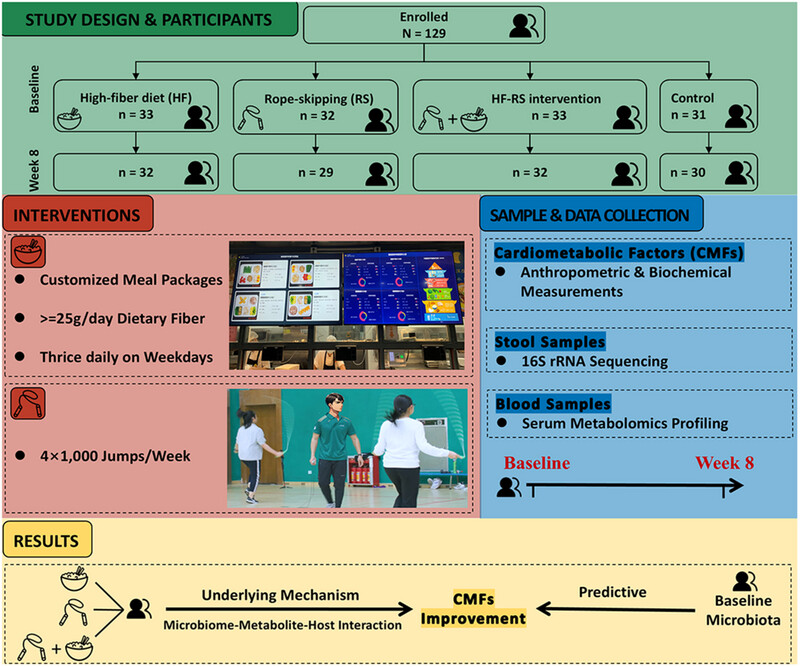
An 8-week randomized controlled trial were conducted to compare the effects of fiber-rich diet (FR) and/or rope-skipping (RS) on cardiometabolic factors (CMFs) in youth with overweight/obesity. The results showed that FR and/or RS were all effective in improving CMFs. These benefits may drive by gut microbiome–metabolite–host interactions. Moreover, the predictability of gut microbiota composition supports making targeted decisions in selecting interventions.
REVIEW
Tissue-resident memory T cells in diseases and therapeutic strategies
- First Published: 12 January 2025
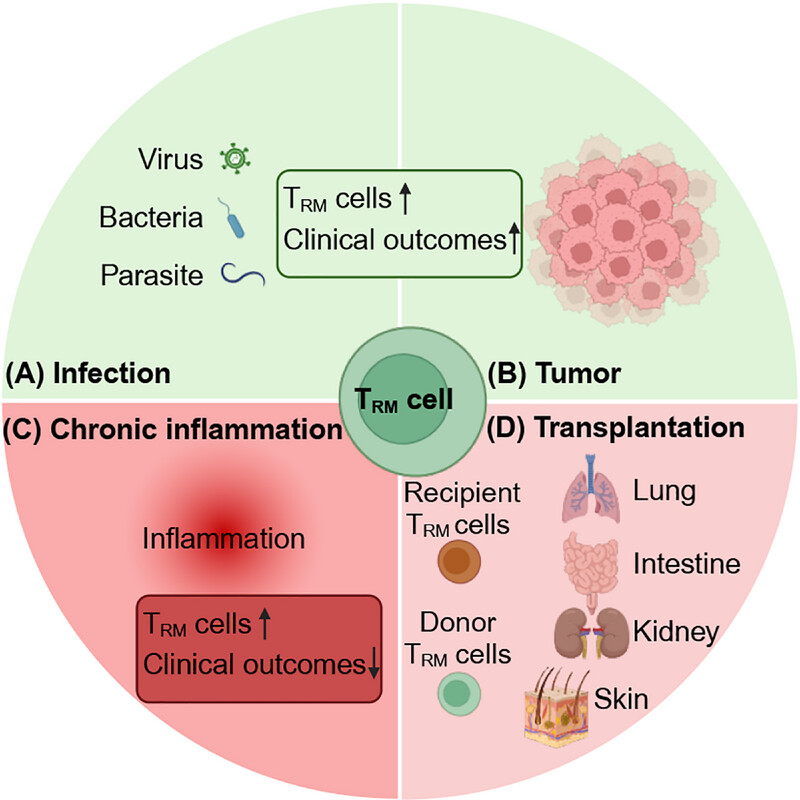
Tissue-resident memory T (TRM) cells are crucial components of the immune system and play vital roles in antiviral, antibacterial, and antitumor immunity, as well as chronic inflammation conditions and graft-versus-host diseases. Understanding the intricate regulation of TRM cells is crucial for developing targeted therapeutic strategies, such as vaccines and immunotherapies, that enhance their protective functions while minimizing potential adverse effects.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Eupalinolide B inhibits periodontitis development by targeting ubiquitin conjugating enzyme UBE2D3
- First Published: 14 January 2025
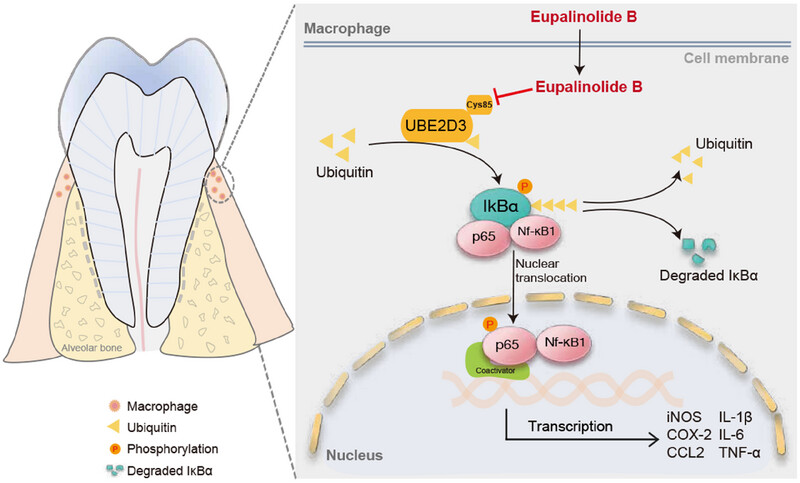
This study shows application of a small molecule compound Eupalinolide B in periodontitis, which effectively alleviates periodontal inflammation and alveolar bone loss. By using an array of chemical biology approaches, direct binding protein target, UBE2D3, and mechanisms of actions of Eupalinolide B in the treatment of periodontitis were revealed.
Ginsenoside Rk2 alleviates hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury by enhancing AKT membrane translocation and activation
- First Published: 14 January 2025
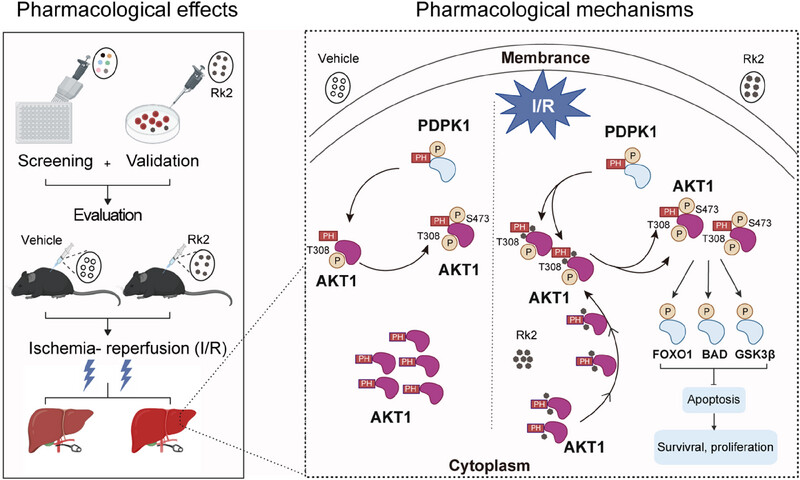
•Rk2, a rare dehydroprotopanaxadiol saponin, effectively alleviates hepatic IRI in vivo and in vitro.
•Rk2 represents a novel AKT1 agonist by facilitating its membrane translocation and phosphorylation.
•Rk2 enhances the interaction with PDPK1, leading to the activation of AKT1 and its downstream signaling.
REVIEW
The crosstalk between senescence, tumor, and immunity: molecular mechanism and therapeutic opportunities
- First Published: 14 January 2025
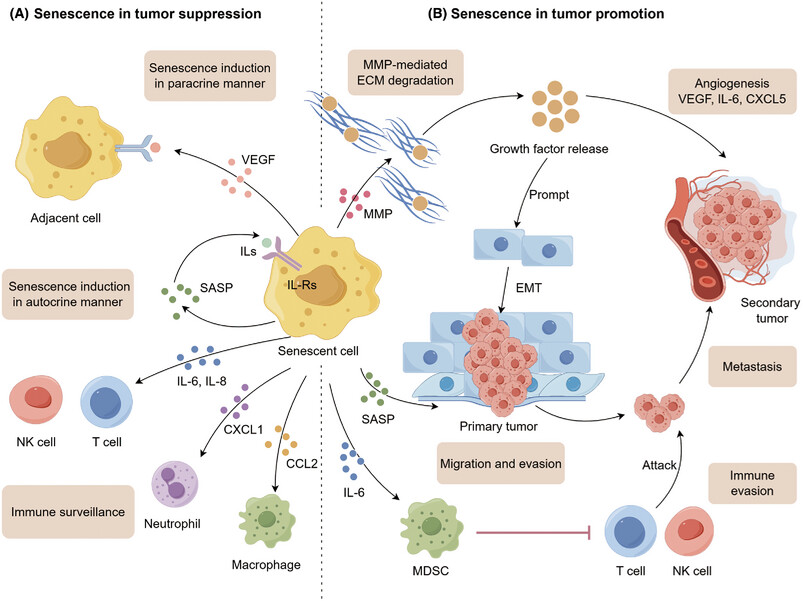
Cellular senescence plays both tumor-suppressive and tumor-progressive effects. It is critical to weigh the balance of the “bright” and “dark” sides of senescence. Immune cell senescence is an important strategy for tumors to occur immune escape. By contrary, senescent tumor cells can reshape the immune microenvironment to boost immune clearance.
Connection between oral health and chronic diseases
- First Published: 14 January 2025
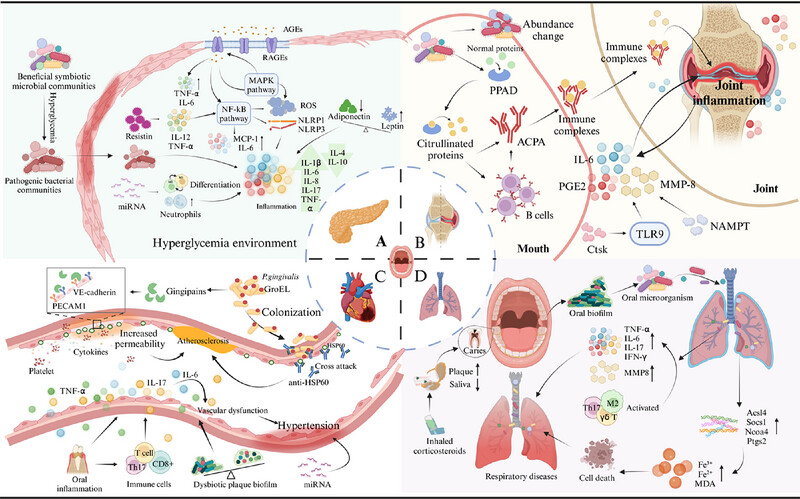
Mechanisms linking oral health to chronic diseases. The figure highlights oral health connections to diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, rheumatoid arthritis, and respiratory diseases. Key mechanisms include inflammation, microbial dysbiosis, oxidative stress, and immune dysregulation, emphasizing the systemic impacts of oral diseases like periodontitis.
HIGHLIGHT
Harnessing dendritic cells for pancreatic cancer immunotherapy: a novel promising approach
- First Published: 14 January 2025