Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
EDITORIAL
A path forward to improving the specificity of immunotherapies
- First Published: 13 September 2022
COMMENTARY
The dawn has come for new therapeutics to treat atherosclerosis: Targeting neuroimmune cardiovascular interfaces in artery brain circuits
- First Published: 02 September 2022
Combination anti-HIV antibodies to achieve antiretroviral therapy-free virological suppression in infected individuals
- First Published: 13 September 2022
Pharmacologic inhibition of MIF nuclease: A new treatment paradigm to treat cell death
- First Published: 20 September 2022
Can electronic cigarettes help pregnant smokers quit, and are they as safe to use in pregnancy as nicotine replacement treatments?
- First Published: 20 September 2022
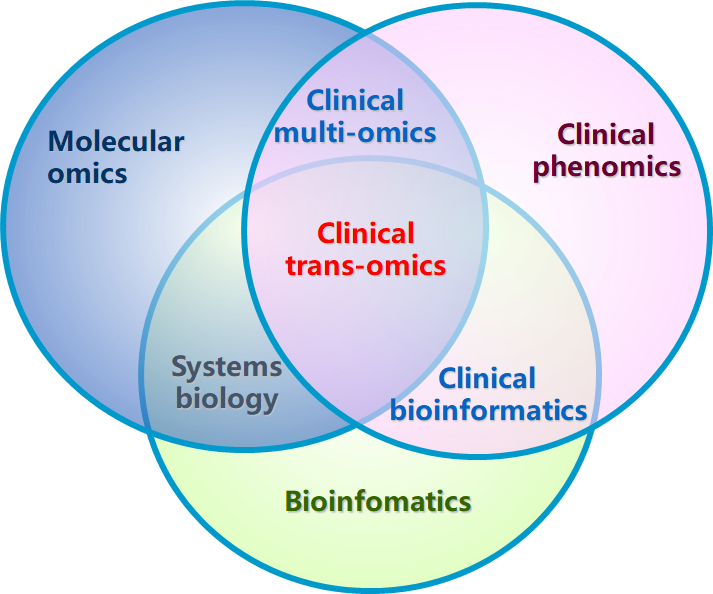
From spirometry to spatial omics in pursuit of asthma endotypes
- First Published: 23 September 2022
Short prokaryotic Argonaute system repurposed as a nucleic acid detection tool
- First Published: 26 September 2022
RESEARCH ARTICLES
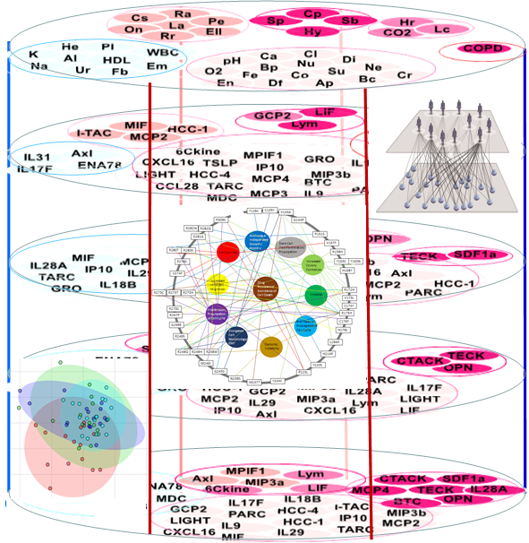
Microbial and human transcriptome in vaginal fluid at midgestation: Association with spontaneous preterm delivery
- First Published: 14 September 2022
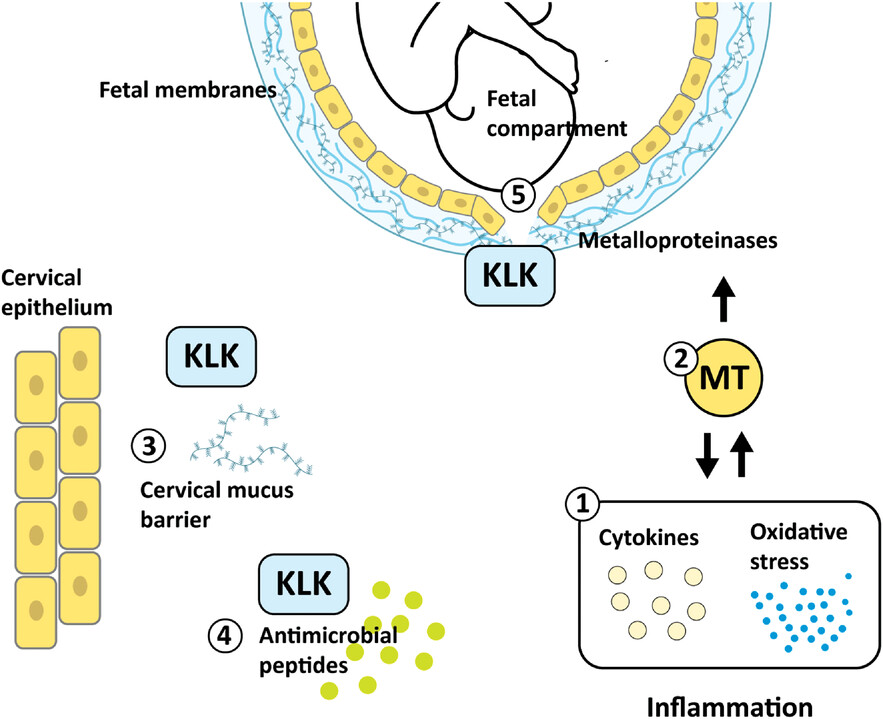
Kallikreins (KLKs) and metallothioneins (MTs) mRNA are increased in vaginal fluid in gestational week 18-20 in women who subsequently deliver preterm. MTs are activated in response to cytokine-mediated inflammation and oxidative stress (1). MTs regulate metalloproteinases which degrades the extracellular matrix and have been associated with preterm prelabour rupture of foetal membranes (PPROM) (2). KLKs can be mechanistically involved in preterm delivery via degradation of the cervical mucus barrier (3), modulation of anti-microbial peptides (4) and preterm prelabour rupture of foetal membranes (PPROM) (5).
Inhibition of proteasomal deubiquitinases USP14 and UCHL5 overcomes tyrosine kinase inhibitor resistance in chronic myeloid leukaemia
- First Published: 09 September 2022
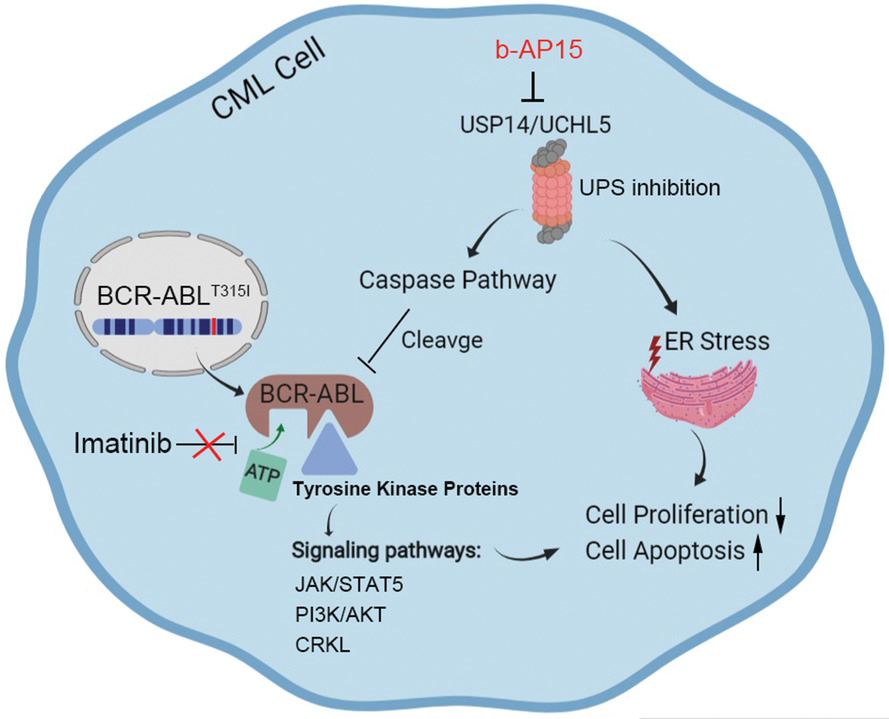
- b-AP15, an inhibitor of proteasomal deubiquitinases USP14 and UCHL5, induces cell apoptosis and downregulates BCR-ABL signaling in BCR-ABLWT and BCR-ABLT315I CML cell lines and primary CML cells.
- Silencing of USP14 and UCHL5 suppresses cell proliferation and decreases BCR-ABL expression in CML cells.
- USP14 and UCHL5 are potential targets for combating T315I mutant-triggered TKI resistance in CML.
LETTER TO THE EDITOR
Chrysin targets myeloid-derived suppressor cells and enhances tumour response to anti-PD-1 immunotherapy
- First Published: 19 September 2022
RESEARCH ARTICLES
Mitochondrial regulation of acute extrafollicular B-cell responses to COVID-19 severity
- First Published: 14 September 2022
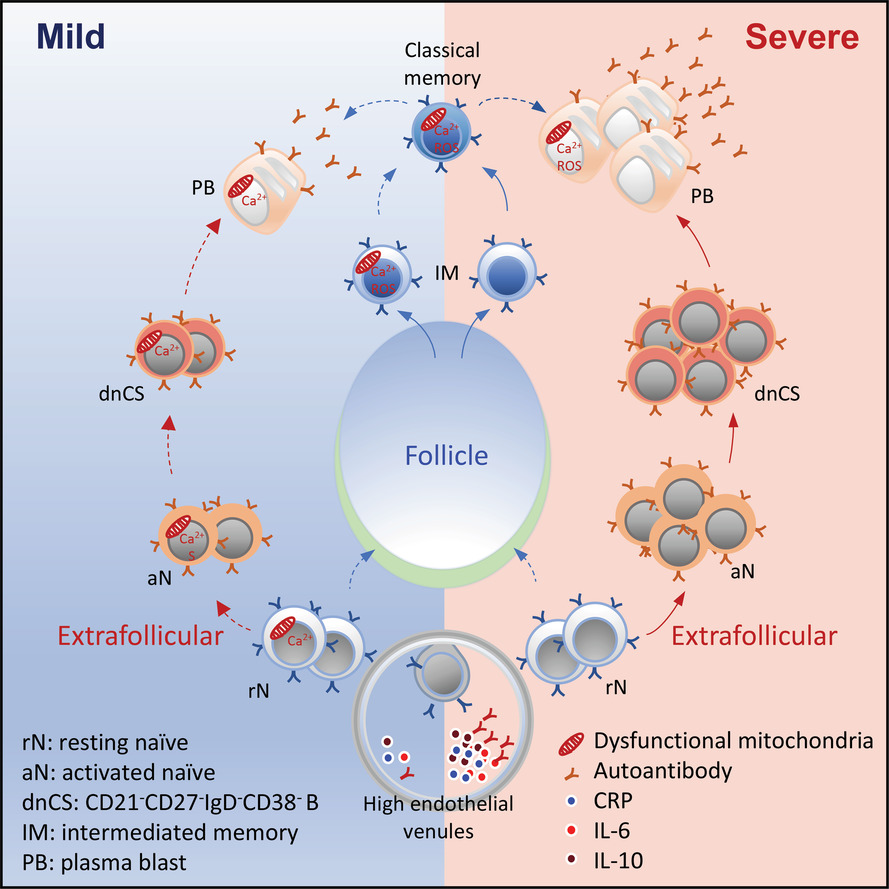
- Severe COVID-19 patients displayed rapid extrafollicular (aN and dnCS) B cell activation.
- Mild patients engaged mitochondrial dysfunction (MD) to suppress excessive extrafollicular responses.
- Intracellular calcium drives MD, leading to the suppression of B cell response.
- Low MD in B cells correlates with higher amounts of antibodies, inflammation and severe COVID-19.
Monoclonal antibody-mediated immunosuppression enables long-term survival of transplanted human neural stem cells in mouse brain
- First Published: 13 September 2022
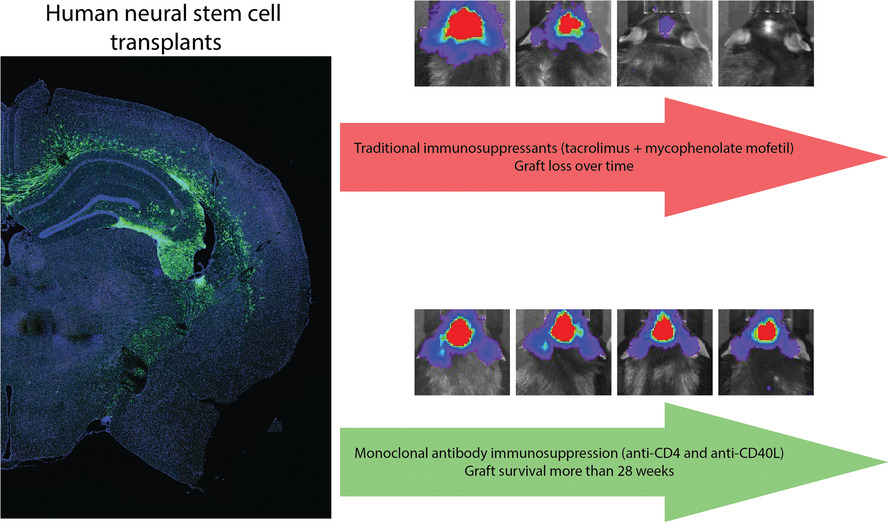
- – Traditional immunosuppression with tacrolimus and mycophenolate mofetil did not sustain human neural stem cell xenograft survival in mouse brain for more than 2 weeks.
- – Immunosuppression with monoclonal antibodies targeting CD4 and CD40L enabled long-term persistence of human stem cell transplants.
- – Transplants survive past 28 weeks in C57BL/6 mice and the 5XFAD animal model of Alzheimer's disease.
The combination of DNA methylome and transcriptome revealed the intergenerational inheritance on the influence of advanced maternal age
- First Published: 14 September 2022
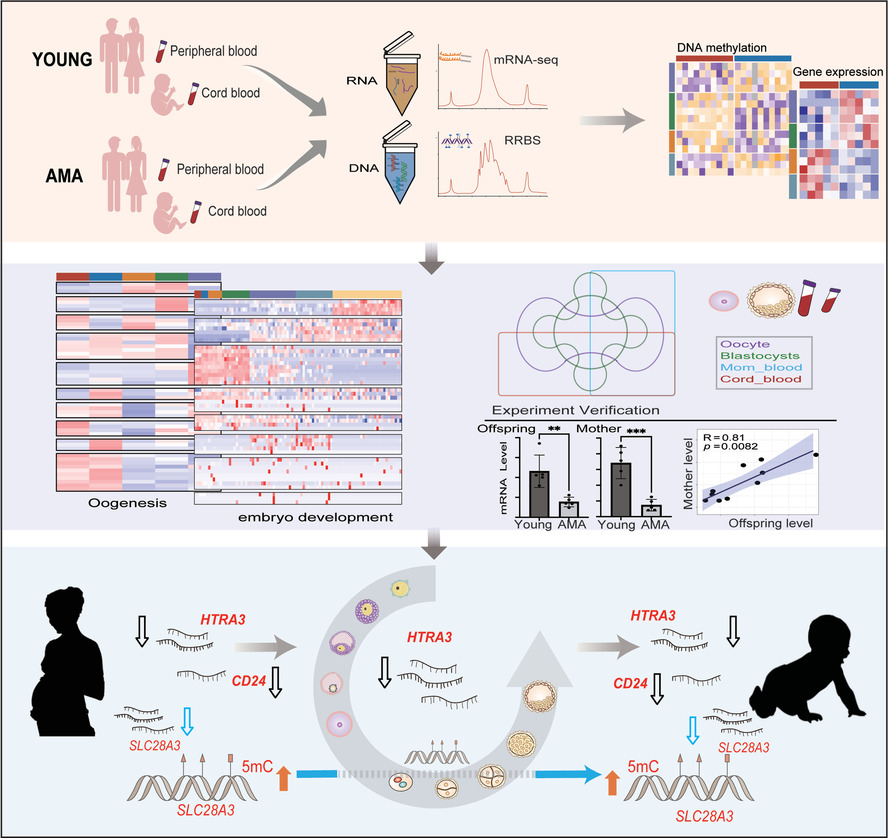
- A series of advanced maternal age (AMA)-related changes are identified in the parental and offspring's DNA methylome, as well as the maternal and offspring's transcriptome.
- Specific DNA methylome and transcriptional changes present intergenerationally correlation.
- Part of the AMA-related differentially expressed genes shared by mother and offspring groups, such as HTRA3, were already significantly changed in MII oocyte or blastocyst.
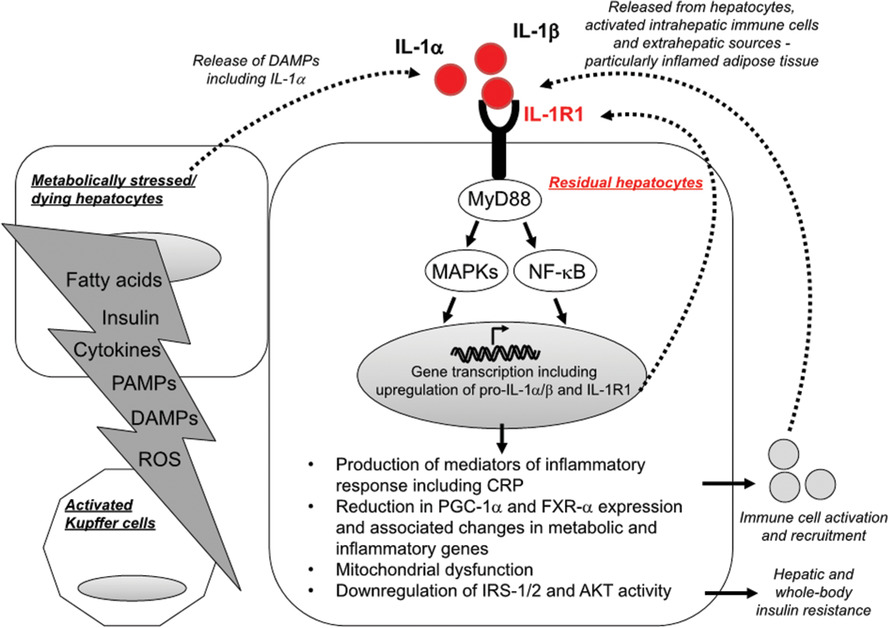
Hepatic interleukin-1 receptor type 1 signalling regulates insulin sensitivity in the early phases of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
- First Published: 13 September 2022
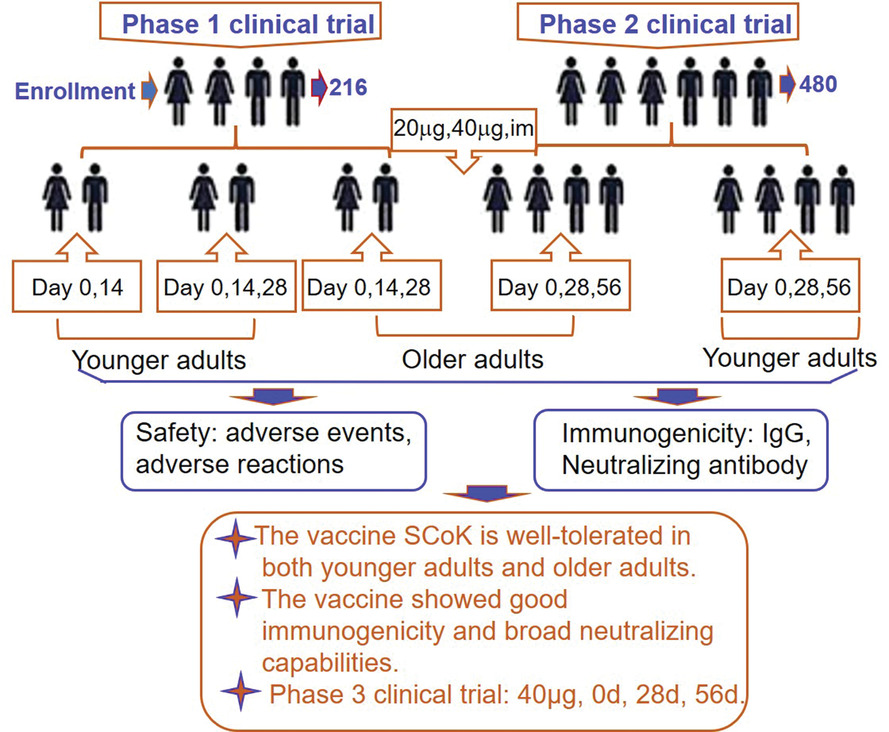
A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 1 and phase 2 clinical trial to evaluate efficacy and safety of a SARS-CoV-2 vaccine SCoK in adults
- First Published: 14 September 2022
The positive regulatory loop of TCF4N/p65 promotes glioblastoma tumourigenesis and chemosensitivity
- First Published: 18 September 2022
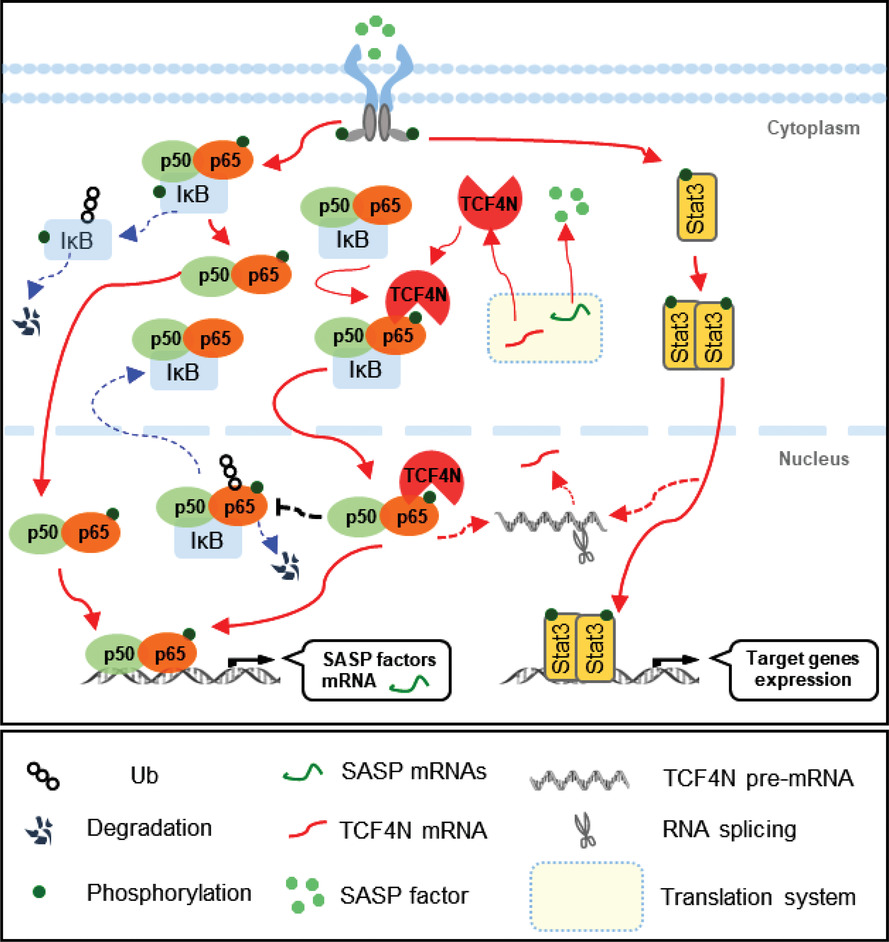
The positive regulatory loop of TCF4N/p65 promotes glioblastoma (GBM) tumourigenesis and chemosensitivity: TCF4N upregulates NF-κB activity by binding and promoting p65 S536 phosphorylation, nuclear-translocation and stability; p65 promotes alternative splicing of TCF7L2 pre-mRNA, resulting in an increase of TCF4N.
Extracellular vesicle expansion of PMIS-miR-210 expression inhibits colorectal tumour growth via apoptosis and an XIST/NME1 regulatory mechanism
- First Published: 18 September 2022
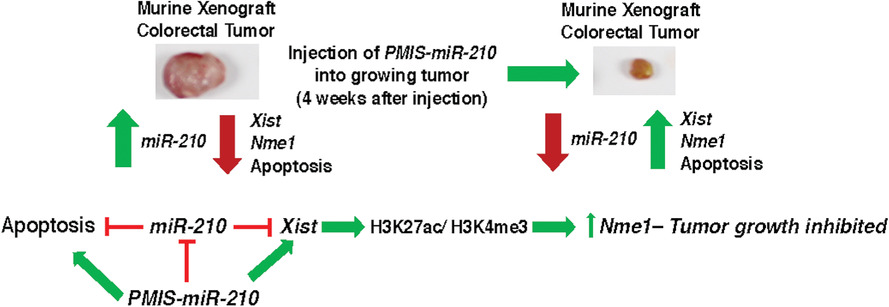
- A new 120 nt microRNA inhibitor therapeutic is specific, stable, efficient and non-toxic to cells
- Injection of the inhibitor into growing colorectal tumors inhibits and reduces tumor growth.
- miR-210 inhibition activates apoptosis, XIST and NME1 to reduce tumor growth
- This approach highlights the therapeutic application of the plasmid-based microRNA inhibition system (PMIS) for treating tumors.
NAT10: An RNA cytidine transferase regulates fatty acid metabolism in cancer cells
- First Published: 23 September 2022
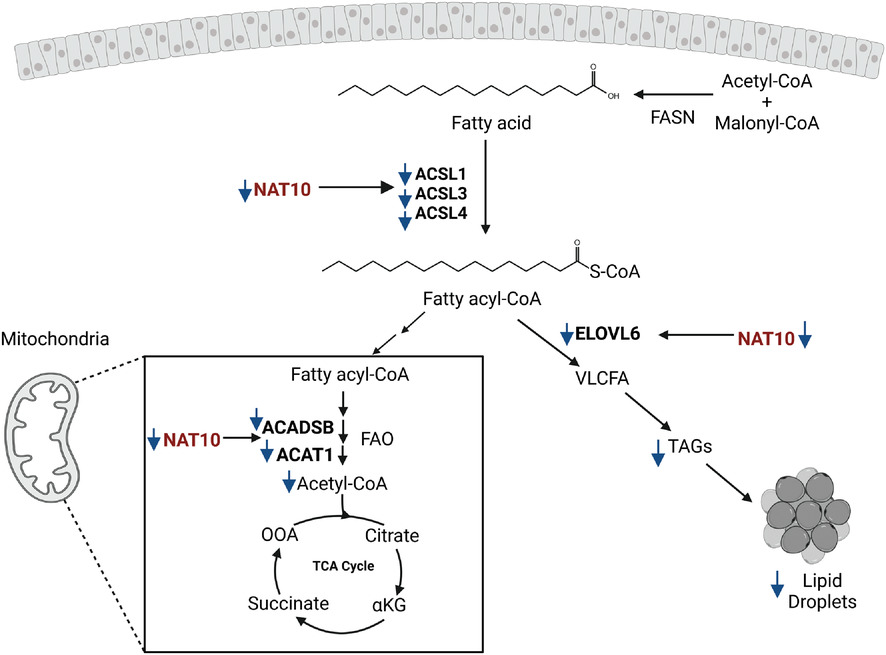
- NAT10 is highly expressed in approximately 92% of cancer and it is related to cancer cell survival.
- NAT10 regulates fatty acid metabolism through ac4C-mediated mRNA stability of ELOVL6, ACSL1, ACSL3, ACSL4, ACADSB and ACAT1.
- Targeting NAT10 could be beneficial for treating severe cancer cases driven by fatty acid metabolism.
Positive epigenetic regulation loop between AR and NSUN2 promotes prostate cancer progression
- First Published: 28 September 2022
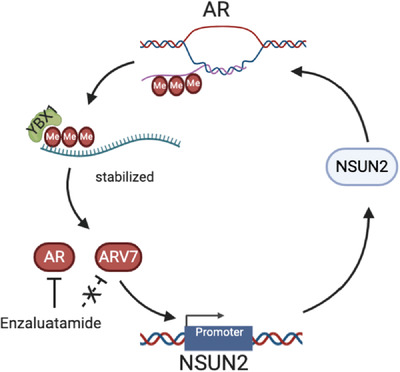
- NSUN2 expression is upregulated in PCa and associated with a worse prognosis.
- AR mRNA is modified by NSUN2 and is stabilized in an m5C-YBX1-dependent manner.
- The m5C modification located in the 5′ region of AR mRNA, influenced several AR variants including AR-V7.
- NSUN2 expression is also transcriptionally regulated by AR and can respond to ADT and ARSI treatment.
Sphingosine 1-phosphate lyase facilitates cancer progression through converting sphingolipids to glycerophospholipids
- First Published: 20 September 2022
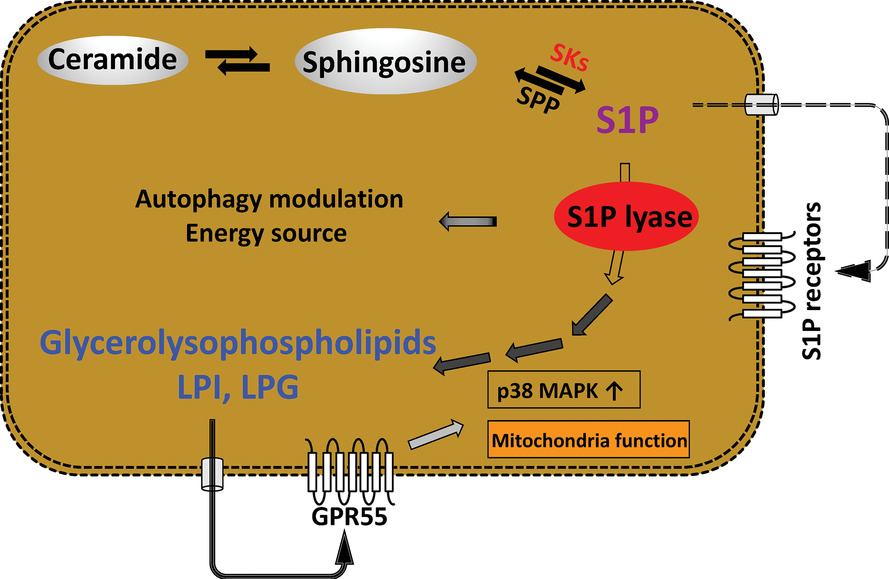
- In human HCC, S1P lyase (SPL) levels were specifically and positively linked with levels of glycerophospholipids, including lysophosphatidylinositol (LPI).
- SPL facilitates cancer progression in both a GPR55 (LPI receptor)-dependent and GPR55-independent manner.
- The novel metabolic pathway, in which SPL converts sphingolipids to glycerophospholipids, might be a novel pharmacologic target for the cancer treatment.
In-depth proteomic analysis reveals unique subtype-specific signatures in human small-cell lung cancer
- First Published: 23 September 2022
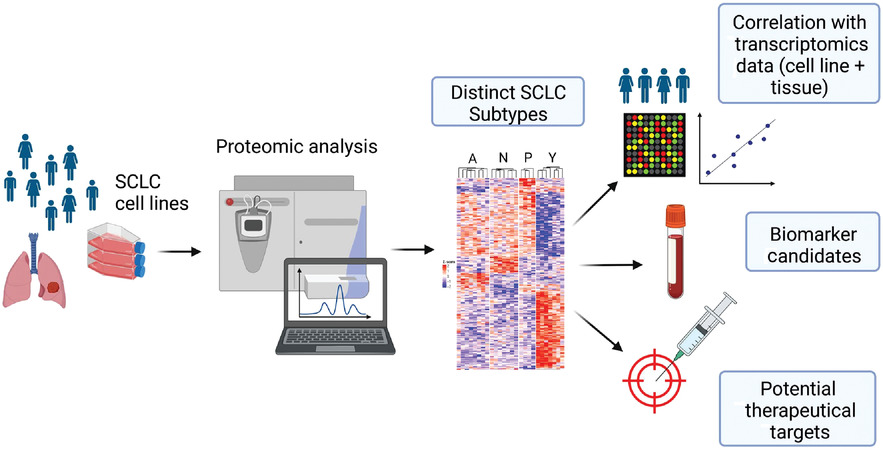
- The first mass spectrometry–based proteomic analysis on small-cell lung cancer (SCLC) cell lines, reporting unique proteomic profiles of its proposed molecular subtypes.
- SCLC subgroups detected by proteomics are consistent with mRNA-based subtypes.
- Unique proteomic profiles of SCLC subtypes highlight potential subtype-specific therapeutic vulnerabilities and diagnostic biomarkers.
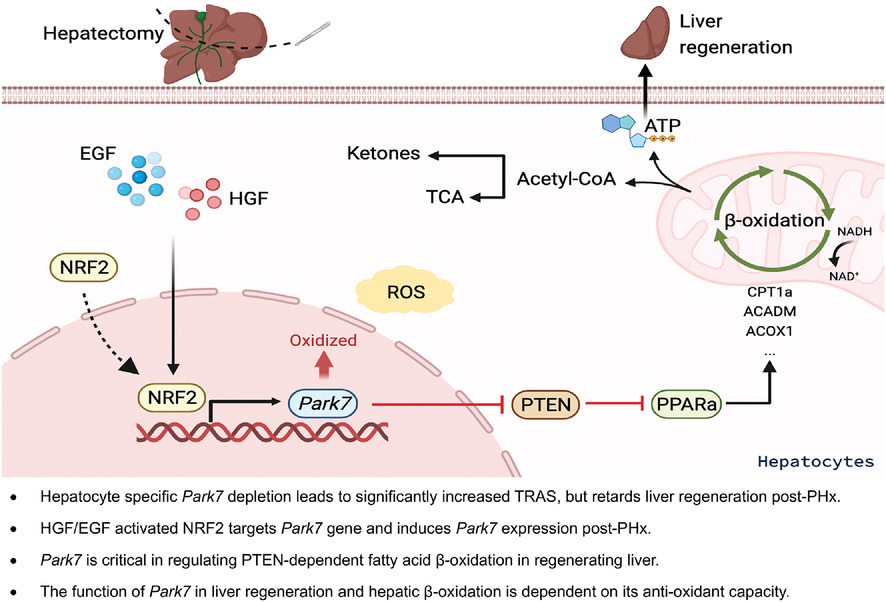
PARK7 deficiency inhibits fatty acid β-oxidation via PTEN to delay liver regeneration after hepatectomy
- First Published: 23 September 2022
LETTER TO THE EDITOR
Single-cell RNA landscape of cell fate decision of renal proximal tubular epithelial cells and immune-microenvironment in kidney fibrosis
- First Published: 09 September 2022
3′UTR shortening of profibrotic genes and reversibility of fibrosis in patients with end-stage right ventricular failure
- First Published: 09 September 2022
Loss of Sirtuin 1 (SIRT1) potentiates endothelial dysfunction via impaired glycolysis during infectious challenge
- First Published: 14 September 2022
Ultrasensitive tumour-agnostic non-invasive detection of colorectal cancer recurrence using ctDNA methylation
- First Published: 14 September 2022
Integrative analysis identifies three molecular subsets in ovarian cancer
- First Published: 18 September 2022
Immunomodulation by intravenous omega-3 fatty acid treatment in older subjects hospitalized for COVID-19: A single-blind randomized controlled trial
- First Published: 19 September 2022
TCR repertoire and transcriptional signatures of circulating tumour-associated T cells facilitate effective non-invasive cancer detection
- First Published: 22 September 2022
Dietary alpha-ketoglutarate inhibits SARS CoV-2 infection and rescues inflamed lungs to restore O2 saturation by inhibiting pAkt
- First Published: 19 September 2022
Ketogenic diets in healthy dogs induce gut and serum metabolome changes suggestive of anti-tumourigenic effects: A model for human ketotherapy trials
- First Published: 23 September 2022
Orally-administrated mitochondria attenuate pulmonary hypertension with the aid of erythrocytes as carriers
- First Published: 23 September 2022
CRBN is downregulated in lung cancer and negatively regulates TLR2, 4 and 7 stimulation in lung cancer cells
- First Published: 27 September 2022
MTHFR inhibits TRC8-mediated HMOX1 ubiquitination and regulates ferroptosis in ovarian cancer
- First Published: 23 September 2022
RESEARCH ARTICLES
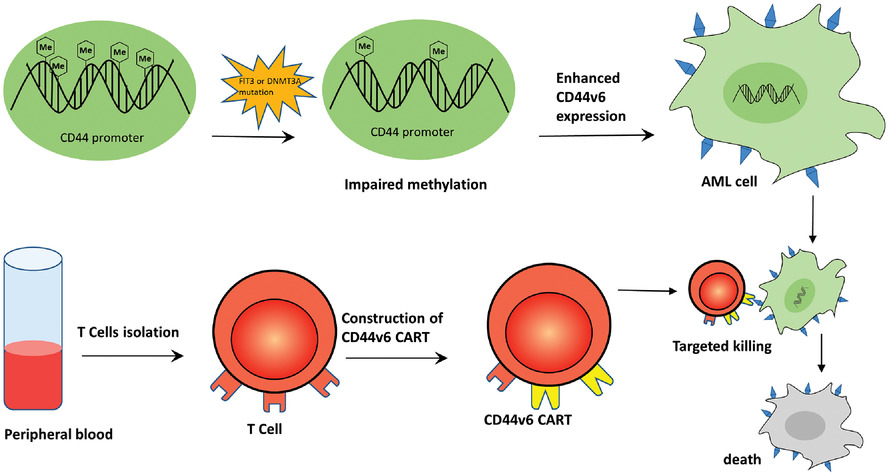
CD44v6 chimeric antigen receptor T cell specificity towards AML with FLT3 or DNMT3A mutations
- First Published: 26 September 2022