Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Cover Picture
- Page: 933
- First Published: 01 April 2024

The disulfide-based poly(ether-b-amide) copolymer with polyamide hard segment and polyether soft segment is a new developed material that can be easily repaired under moderate conditions. The amorphous aggregated structure facilitates the diffusion of segments as well as the recombination of disulfide bonds and H-bonds. Due to the excellent low-temperature flexibility, rapid self-healing capability and convenient recyclability, the material shows great potential application in the fields of low-temperature packaging, sealing and solid propellants. More details are discussed in the article by Dong et al. on page 943—950.
Inside Cover Picture
Inside Cover Picture
- Page: 934
- First Published: 01 April 2024

Perovskite nanocrystals have shown tremendous potential in the field of optoelectronics, finding numerous applications. Rare-earth elements serve as excellent alternatives to lead in perovskite nanocrystals owing to their abundant 4f energy level and distinct electronic arrangement. By partially or completely replacing lead, these elements not only reduce the environmental impact, but also introduce a range of unique effects and applications. More details are discussed in the review article by Zhang et al. on page 1032—1056.
Contents
Concise Reports
A Disulfide-Based Poly(ether-b-amide) Copolymer with Rapid Self-healing Ability under Moderate Conditions
- Pages: 943-950
- First Published: 19 December 2023
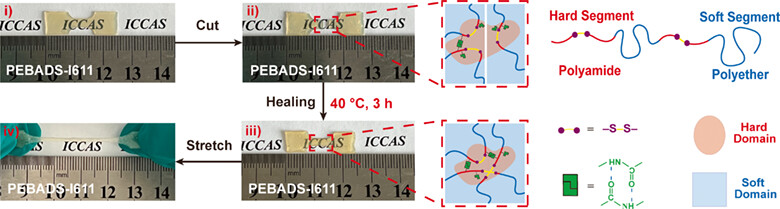
A disulfide-based poly(ether-b-amide) copolymer with rapid self-healing capability under moderate conditions was successfully prepared by employing polyamide synthesized from 4,4’-dithiodibutyric acid and isophorondiamine as hard segment and PTMO as soft segment, which showed great potential in the fields of low-temperature packaging, sealing and propellants.
A Label-Free Deoxyribozyme Sensor for m6A Demethylase Activity Detection
- Pages: 951-956
- First Published: 27 December 2023
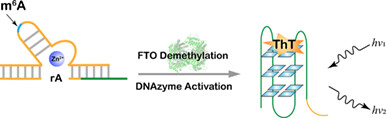
We report a label-free deoxyribozyme (DNAzyme) biosensor for m6A demethylase activity detection. The nucleic acid probes consist of a methylation-blocked DNAzyme strand and a designed substrate strand. When demethylase is present, the m6A group is specifically demethylated, and the cleavage activity of DNAzyme is restored. This allows the cleavage product encoded with G-quadruplex binding to thioflavin T (ThT) to generate fluorescence output signals.
Synergistic Brønsted Base/Photoredox-Catalyzed Three-Component Coupling with Malonates to Synthesize δ-Hydroxy Esters and δ-Keto Esters
- Pages: 957-962
- First Published: 18 January 2024
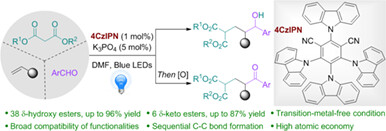
Herein, we describe a redox-neutral three-component 1,2-dialkylation from malonates, styrenes, and aldehydes through the synergistic Brønsted base/photoredox catalyzed radical-polar crossover process, providing an efficient and clean approach to a broad variety of δ-hydroxy esters. This developed protocol features exceptionally mild and transition-metal-free conditions, broad compatibility of substrate scope and functional groups, and high atomic economy. Importantly, photocatalytic three-component 1,2-alkylacylation towards valuable intermediate δ-keto esters was also achieved through the combination of the RPC process and following two-electron oxidation from the same starting materials.
Tailoring the Properties of Polyhydroxyalkanoates from Plastics to Elastomers via Stereoselective Copolymerizations of rac-β-Butyrolactone and β-Propiolactone
- Pages: 963-972
- First Published: 18 January 2024
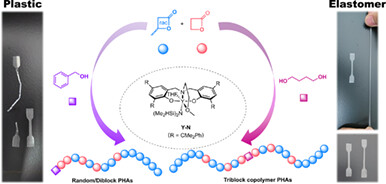
The ring-opening copolymerizations of racemic-β-butyrolactone (rac-β-BL) and β-propiolactone (β-PL) were performed using the syndio-selective amino-alkoxy-bis(phenolate)-yttrium catalyst, resulting in polyhydroxyalkanoates with tunable properties comparable to traditional fossil-based plastics. Moreover, through one-pot synthesis, we transformed the copolymers into soft and ductile thermoplastic elastomers by utilizing monomers' different copolymerization rates and a bifunctional initiator.
Electrochemical Oxygen Evolution Performance of Nitrogen-Doped Ultra-Thin Carbon Nanosheets Composite Ru1Co Single Atom Alloy Catalysts
- Pages: 973-979
- First Published: 29 December 2023
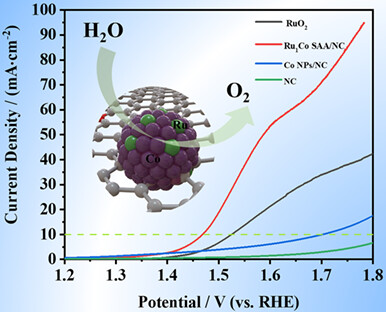
A one-step pyrolysis method was employed to load Ru1Co single atom alloy onto a nitrogen-doped ultra-thin carbon sheet, resulting in an electrocatalytic oxygen evolution catalyst suitable for use in an acidic environment. The catalyst exhibited excellent activity and stability in oxygen evolution, with an overpotential of only 238 mV at a current density of 10 mA·cm–2. The structure of the single atom alloy was characterized using synchrotron radiation, which confirmed the involvement of Ru in the oxygen evolution process. Moreover, this approach maximized the utilization efficiency of Ru atomic sites and effectively reduced catalytic costs.
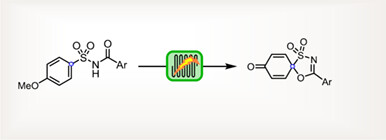
Electrochemical Dearomative Spirocyclization of N-Acyl Sulfonamides in a Continuous-Flow Cell
- Pages: 980-984
- First Published: 26 December 2023
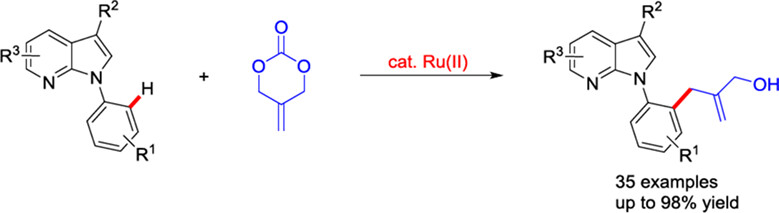
Ru(II)-Catalyzed ortho C—H Allylation of N-Aryl-7-azaindoles with 2-Methylidene Cyclic Carbonate
- Pages: 985-989
- First Published: 26 December 2023
Visible-Light-Driven Four-Component Radical Relay Aminocarbonylation of Unactivated Alkenes
- Pages: 990-996
- First Published: 18 January 2024
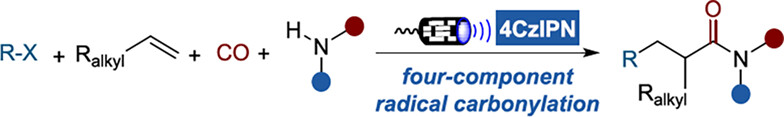
A visible-light-driven four-component radical relay aminocarbonylation reaction of unactivated alkenes using 4CzIPN as an organic photocatalyst is developed, providing robust access to β-fluoroalkyl amides with good yields and selectivity under metal-free conditions. Importantly, this strategy also shows good compatibility with tertiary carbon radicals.
Thermoelectric Properties of an Indandione-Terminated Quinoidal Compound: Effect of the n-Type Dopants
- Pages: 997-1003
- First Published: 18 January 2024
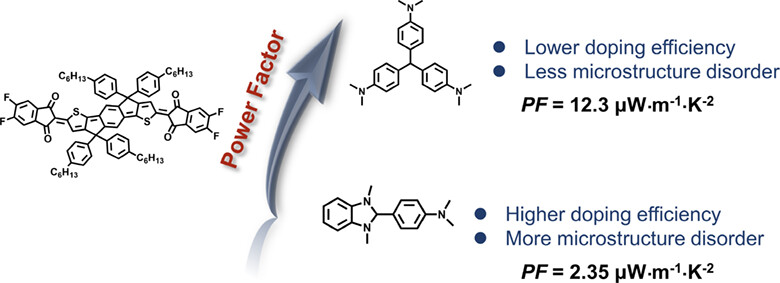
Indandione-terminated quinoidal compound Q-4F was doped using two n-dopants N-DMBI and LCV through solution process. N-DMBI exhibited a higher doping ability for Q-4F than LCV. However, unperturbed molecular packing and favorable morphology can be realized after LCV doping, thereby leading to a high thermoelectrics performance.
Emerging Topic
Exploration of Strong Metal-Support Interaction in Heterogeneous Catalysts by in situ Transmission Electron Microscopy
- Pages: 1004-1008
- First Published: 12 December 2023
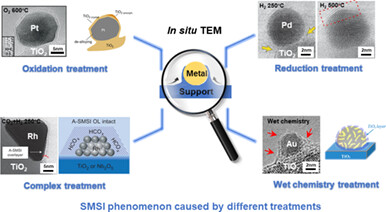
Strong metal-support interactions (SMSI) are a key concept in heterogeneous catalysis, which govern the catalytic performance in various processes. We here provide a brief summary of the recent progress utilizing in situ TEM to study the SMSI phenomenon and the relationship between structure and performance of the supported catalyst under reaction conditions. Meanwhile, a brief perspective about the use of in situ TEM for further study of SMSI is also presented, showing prospects in this field that will stimulate upsurging research in promoting the catalytic efficiency of supported catalysts.
Recent Advances
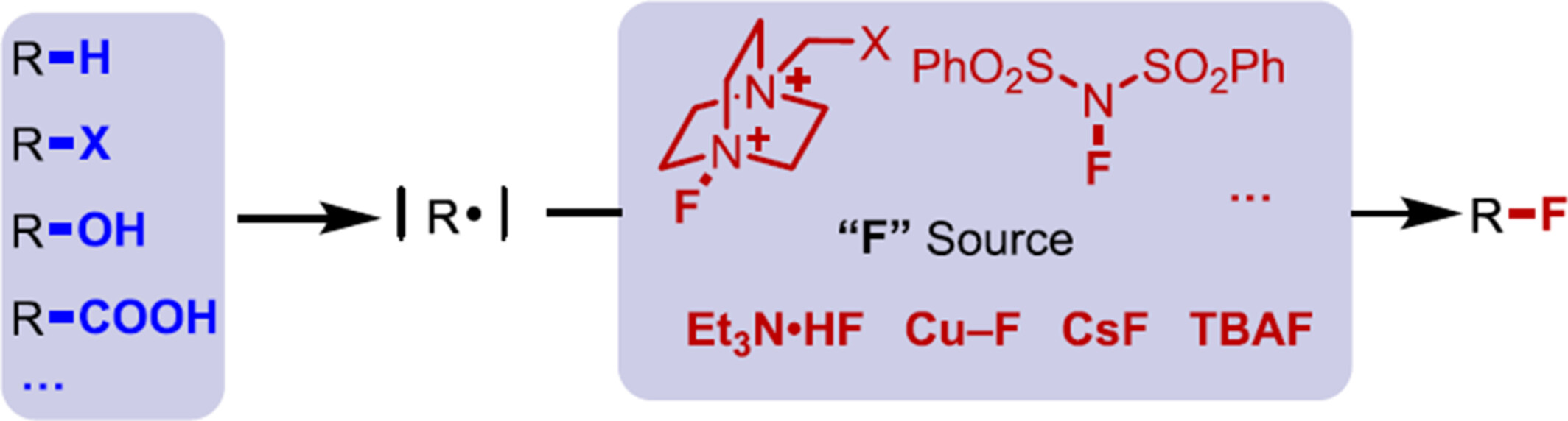
Recent Advances in C—F Bond Formation from Carbon-Centered Radicals
- Pages: 1009-1031
- First Published: 07 December 2023
Critical Review
A Comprehensive Review on Mechanisms and Applications of Rare-Earth Based Perovskite Nanocrystals†
- Pages: 1032-1056
- First Published: 05 February 2024
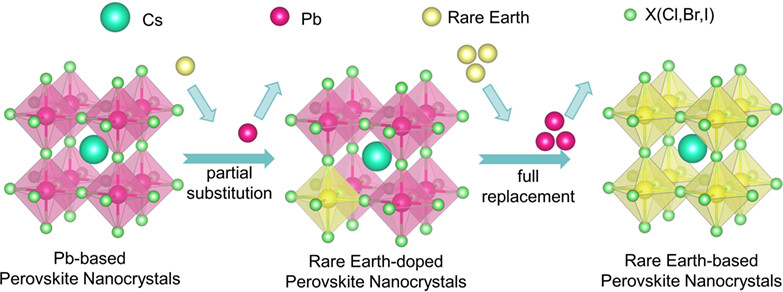
In lead-based perovskite nanocrystals, a fraction of lead is substituted with rare earth elements for the purpose of doping. Given the adverse effects of lead on human health and the environment, the complete substitution of lead with rare earth ions to achieve lead-free characteristics has emerged as a prominent trend.
Inside Back Cover
Inside Back Cover
- Page: 1059
- First Published: 01 April 2024

Polyhydroxyalkanoates with tunable properties can be readily prepared through stereoselective ring-opening copolymerization of rac-β-butyrolactone and β-propiolactone. By simply adjusting the polymerization conditions, such as the type of initiators and polymerization time, a variety of biodegradable copolyesters spanning from plastics to elastomers can be effectively produced in a one-pot process. Further insights and details can be found in the article by Tang et al. on page 963—972.
Back Cover
Back Cover
- Page: 1060
- First Published: 01 April 2024

Radical/polar crossover (RPC) is a rapidly growing subset of photoredox reactions in which the newly formed radical intermediates preferentially undergo the single-electron reduction or oxidation to re-enter the ionic reaction space. It should be noted that there is only one report on photoredox-catalyzed RPC-type difunctionalizations of alkenes with malonates as radical precursors, namely alkene hydroalkylation. Based on the above well-established RPC-type strategy, aldehydes are employed as new electrophiles for exploring a new three-component dicarbofunctionalizations of alkenes. More details are discussed in the article by Yi et al. on page 957—962.