Thermoelectric Properties of an Indandione-Terminated Quinoidal Compound: Effect of the n-Type Dopants†
Yingying Liu
School of Materials Science and Engineering and Tianjin Key Laboratory of Molecular Optoelectronic Science, Tianjin University, and Collaborative Innovation Center of Chemical Science and Engineering (Tianjin), Tianjin, 300072 China
Search for more papers by this authorCheng Wang
School of Materials Science and Engineering and Tianjin Key Laboratory of Molecular Optoelectronic Science, Tianjin University, and Collaborative Innovation Center of Chemical Science and Engineering (Tianjin), Tianjin, 300072 China
Search for more papers by this authorTianzuo Wang
School of Materials Science and Engineering and Tianjin Key Laboratory of Molecular Optoelectronic Science, Tianjin University, and Collaborative Innovation Center of Chemical Science and Engineering (Tianjin), Tianjin, 300072 China
Search for more papers by this authorFei Jiao
Tianjin Key Laboratory of Molecular Optoelectronic Science, Department of Chemistry, School of Science, Tianjin University, Tianjin, 300072 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Shaoqiang Dong
Institute of Molecular Aggregation Science, Tianjin University, Tianjin, 300072 China
*E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Yunfeng Deng
School of Materials Science and Engineering and Tianjin Key Laboratory of Molecular Optoelectronic Science, Tianjin University, and Collaborative Innovation Center of Chemical Science and Engineering (Tianjin), Tianjin, 300072 China
Joint School of National University of Singapore and Tianjin University, International Campus of Tianjin University, Binhai New City, Fuzhou, Fujian, 350207 China
*E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorYanhou Geng
School of Materials Science and Engineering and Tianjin Key Laboratory of Molecular Optoelectronic Science, Tianjin University, and Collaborative Innovation Center of Chemical Science and Engineering (Tianjin), Tianjin, 300072 China
Joint School of National University of Singapore and Tianjin University, International Campus of Tianjin University, Binhai New City, Fuzhou, Fujian, 350207 China
Search for more papers by this authorYingying Liu
School of Materials Science and Engineering and Tianjin Key Laboratory of Molecular Optoelectronic Science, Tianjin University, and Collaborative Innovation Center of Chemical Science and Engineering (Tianjin), Tianjin, 300072 China
Search for more papers by this authorCheng Wang
School of Materials Science and Engineering and Tianjin Key Laboratory of Molecular Optoelectronic Science, Tianjin University, and Collaborative Innovation Center of Chemical Science and Engineering (Tianjin), Tianjin, 300072 China
Search for more papers by this authorTianzuo Wang
School of Materials Science and Engineering and Tianjin Key Laboratory of Molecular Optoelectronic Science, Tianjin University, and Collaborative Innovation Center of Chemical Science and Engineering (Tianjin), Tianjin, 300072 China
Search for more papers by this authorFei Jiao
Tianjin Key Laboratory of Molecular Optoelectronic Science, Department of Chemistry, School of Science, Tianjin University, Tianjin, 300072 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Shaoqiang Dong
Institute of Molecular Aggregation Science, Tianjin University, Tianjin, 300072 China
*E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Yunfeng Deng
School of Materials Science and Engineering and Tianjin Key Laboratory of Molecular Optoelectronic Science, Tianjin University, and Collaborative Innovation Center of Chemical Science and Engineering (Tianjin), Tianjin, 300072 China
Joint School of National University of Singapore and Tianjin University, International Campus of Tianjin University, Binhai New City, Fuzhou, Fujian, 350207 China
*E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorYanhou Geng
School of Materials Science and Engineering and Tianjin Key Laboratory of Molecular Optoelectronic Science, Tianjin University, and Collaborative Innovation Center of Chemical Science and Engineering (Tianjin), Tianjin, 300072 China
Joint School of National University of Singapore and Tianjin University, International Campus of Tianjin University, Binhai New City, Fuzhou, Fujian, 350207 China
Search for more papers by this authorDedicated to the Special Issue of Emerging Investigators in 2023.
Comprehensive Summary
The investigation of n-type doping holds a significant interest for the application of thermoelectrics. Herein, the doping of an indandione-terminated compound Q-4F with a singlet open-shell ground state was studied using two n-dopants N-DMBI and LCV. Both of these two dopants can effectively dope Q-4F due to the large offset between the singly occupied molecular orbital (SOMO) of dopants and the lowest unoccupied molecular orbital (LUMO) of Q-4F. N-DMBI has a higher doping ability than LCV as demonstrated by the UV-vis-NIR and EPR measurements. However, in comparison to N-DMBI doped Q-4F, LCV doped system exhibits much higher electrical conductivity and power factor due to its unperturbed molecular packing and favorable morphology after doping. The optimal conductivity of LCV doped Q-4F is 7.16 × 10–2 ± 0.16 S·cm–1 and the highest power factor reaches 12.3 ± 0.85 μW·m–1·K–2. These results demonstrate that the modulation of n-dopants is a powerful strategy to balance the doping efficiency and microstructure toward a maximum thermoelectric performance.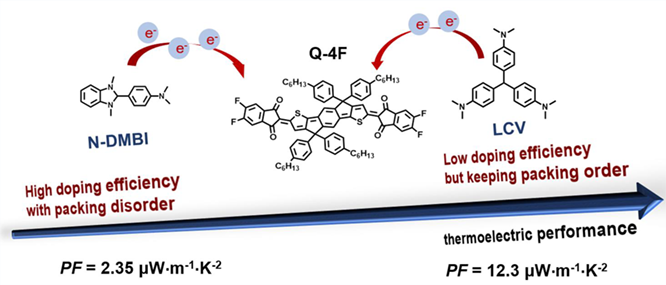
Supporting Information
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| cjoc202300650-sup-0001-supinfo.pdfPDF document, 845.7 KB |
Appendix S1: Supporting Information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1(a)Massetti, M.; Jiao, F.; Ferguson, A. J.; Zhao, D.; Wijeratne, K.; Würger, A.; Blackburn, J. L.; Crispin, X.; Fabiano, S. Unconventional Thermoelectric Materials for Energy Harvesting and Sensing Applications. Chem. Rev. 2021, 121, 12465–12547; (b) Wang, D.; Liu, L.; Gao, X.; Di, C. A.; Zhu, D. Recent Advances in Molecular Design of Organic Thermoelectric Materials. CCS Chem. 2021, 3, 2212–2225; (c) Zhang, F.; Di, C. A. Exploring Thermoelectric Materials from High Mobility Organic Semiconductors. Chem. Mater. 2020, 32, 2688–2702; (d) Bell, L. E. Cooling, Heating, Generating Power, and Recovering Waste Heat with Thermoelectric Systems. Science 2008, 321, 1457–1461; (e) Russ, B.; Glaudell, A.; Urban, J. J.; Chabinyc, M. L.; Segalman, R. A. Organic thermoelectric materials for energy harvesting and temperature control. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2016, 1, 16050; (f) Ding, L.; Yu, Z.-D.; Wang, X. Y.; Yao, Z. F.; Lu, Y.; Yang, C. Y.; Wang, J. Y.; Pei, J. Polymer Semiconductors: Synthesis, Processing, and Applications. Chem. Rev. 2023, 123, 7421–7497; (g) Huang, W.; Xie, L. Organic Electronics, a Promising King of Freedom to Change Future Life Style of Human Being. Chin. J. Chem. 2015, 33, 803–805; (h) Shi, D.; Yu, X.; Chen, L.; Chen, D.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, D. Selenophene-Flanked Diketopyrrolopyrrole Based Conjugated Polymers for Ambipolar Field-Effect Transistors. Chin. J. Chem. 2020, 38, 1075–1080.
- 2(a) Snyder, G. J.; Toberer, E. S. Complex thermoelectric materials. Nat. Mater. 2008, 7, 105–114; (b) Champier, D. Thermoelectric generators: A review of applications. Energy Convers. Manage. 2017, 140, 167–181; (c) Yang, C. Y.; Jin, W. L.; Wang, J.; Ding, Y. F.; Nong, S.; Shi, K.; Lu, Y.; Dai, Y. Z.; Zhuang, F. D.; Lei, T.; Di, C. A.; Zhu, D.; Wang, J. Y.; Pei, J. Enhancing the n-Type Conductivity and Thermoelectric Performance of Donor–Acceptor Copolymers through Donor Engineering. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1802850.
- 3(a) Zhang, Q.; Sun, Y.; Xu, W.; Zhu, D. Organic Thermoelectric Materials: Emerging Green Energy Materials Converting Heat to Electricity Directly and Efficiently. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 6829–6851; (b) Bubnova, O.; Crispin, X. Towards polymer-based organic thermoelectric generators. Energy Environ. Sci. 2012, 5, 9345–9362.
- 4(a) Shi, K.; Zhang, F.; Di, C. A.; Yan, T. W.; Zou, Y.; Zhou, X.; Zhu, D.; Wang, J. Y.; Pei, J. Toward High Performance n-Type Thermoelectric Materials by Rational Modification of BDPPV Backbones. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 6979–6982; (b) Alsufyani, M.; Stoeckel, M. A.; Chen, X.; Thorley, K.; Hallani, R. K.; Puttisong, Y.; Ji, X.; Meli, D.; Paulsen, B. D.; Strzalka, J.; Regeta, K.; Combe, C.; Chen, H.; Tian, J.; Rivnay, J.; Fabiano, S.; McCulloch, I. Lactone Backbone Density in Rigid Electron-Deficient Semiconducting Polymers Enabling High n-type Organic Thermoelectric Performance. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202113078; (c) Griggs, S.; Marks, A.; Bristow, H.; McCulloch, I. n-Type organic semiconducting polymers: stability limitations, design considerations and applications. J. Mater. Chem. C 2021, 9, 8099–8128; (d) Feng, K.; Guo, H.; Wang, J.; Shi, Y.; Wu, Z.; Su, M.; Zhang, X.; Son, J. H.; Woo, H. Y.; Guo, X. Cyano-Functionalized Bithiophene Imide-Based n-Type Polymer Semiconductors: Synthesis, Structure− Property Correlations, and Thermoelectric Performance. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 1539–1552; (e) Tang, H.; Liang, Y.; Liu, C.; Hu, Z.; Deng, Y.; Guo, H.; Yu, Z.; Song, A.; Zhao, H.; Zhao, D.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, X.; Pei, J.; Ma, Y.; Cao, Y.; Huang, F. A solution-processed n-type conducting polymer with ultrahigh conductivity. Nature 2022, 611, 271–277; (f) Guo, H.; Yang, C. Y.; Zhang, X.; Motta, A.; Feng, K.; Xia, Y.; Shi, Y.; Wu, Z.; Yang, K.; Chen, J.; Liao, Q.; Tang, Y.; Sun, H.; Woo, H. Y.; Fabiano, S.; Facchetti, A.; Guo, X. Transition metal-catalysed molecular n-doping of organic semiconductors. Nature 2021, 599, 67–73; (g) Shi, Y.; Zhang, X.; Du, T.; Han, Y.; Deng, Y.; Geng, Y. A High-Performance n-Type Thermoelectric Polymer from C−H/C−H Oxidative Direct Arylation Polycondensation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202219262; (h) Du, T.; Liu, Y.; Deng, Y.; Geng, Y. Enhanced n-Type Thermoelectric Performance of Conjugated Polymers Based on an Indandione-Terminated Quinoidal Unit through Comonomer Optimization. Chin. J. Chem. 2023, 41, 776–782.
- 5(a) Deng, S.; Dong, C.; Liu, J.; Meng, B.; Hu, J.; Min, Y.; Tian, H.; Liu, J.; Wang, L., An n-Type Polythiophene Derivative with Excellent Thermoelectric Performance. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202216049; (b) Lu, Y.; Wang, J. Y.; Pei, J. Achieving Efficient n-Doping of Conjugated Polymers by Molecular Dopants. Acc. Chem. Res. 2021, 54, 2871–2883; (c) Yan, X.; Xiong, M.; Li, J. T.; Zhang, S.; Ahmad, Z.; Lu, Y.; Wang, Z.-Y.; Yao, Z. F.; Wang, J. Y.; Gu, X.; Lei, T., Pyrazine-Flanked Diketopyrrolopyrrole (DPP): A New Polymer Building Block for High-Performance n-Type Organic Thermoelectrics. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 20215–20221; (d) Li, J. T.; Lei, T. Recent Progress on Addressing the Key Challenges in Organic Thermoelectrics. Chem. - Asian J. 2021, 16, 1508–1518.
- 6(a) Huang, D.; Yao, H.; Cui, Y.; Zou, Y.; Zhang, F.; Wang, C.; Shen, H.; Jin, W.; Zhu, J.; Diao, Y.; Xu, W.; Di, C. A.; Zhu, D., Conjugated- Backbone Effect of Organic Small Molecules for n-Type Thermoelectric Materials with ZT over 0.2. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 13013–13023; (b) Geng, X.; Du, T.; Xu, C.; Liu, Y.; Deng, Y.; Geng, Y. Realizing p-Type and n-Type Doping of a Single Conjugated Polymer via Incorporation of a Thienoisatin-Terminated Quinoidal Unit. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2300809; (c) Du, T.; Liu, Y.; Wang, C.; Deng, Y.; Geng, Y. n-Type Conjugated Polymers Based on an Indandione- Terminated Quinoidal Building Block. Macromolecules 2022, 55, 5975–5984.
- 7 Takimiya, K.; Kawabata, K. Thienoquinoidal System: Promising Molecular Architecture for Optoelectronic Applications. J. Synth. Org. Chem., Jpn. 2018, 76, 1176–1184.
- 8 Huang, D.; Wang, C.; Zou, Y.; Shen, X.; Zang, Y.; Shen, H.; Gao, X.; Yi, Y.; Xu, W.; Di, C. A.; Zhu, D. Bismuth Interfacial Doping of Organic Small Molecules for High Performance n-type Thermoelectric Materials. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 10672–10675.
- 9 Yuan, D.; Huang, D.; Rivero, S. M.; Carreras, A.; Zhang, C.; Zou, Y.; Jiao, X.; McNeill, C. R.; Zhu, X.; Di, C. A.; Zhu, D.; Casanova, D.; Casado, J. Cholesteric Aggregation at the Quinoidal-to-Diradical Border Enabled Stable n-Doped Conductor. Chem 2019, 5, 964–976.
- 10(a) Scaccabarozzi, A. D.; Basu, A.; Aniés, F.; Liu, J.; Zapata-Arteaga, O.; Warren, R.; Firdaus, Y.; Nugraha, M. I.; Lin, Y.; Campoy-Quiles, M.; Koch, N.; Müller, C.; Tsetseris, L.; Heeney, M.; Anthopoulos, T. D., Doping Approaches for Organic Semiconductors. Chem. Rev. 2022, 122, 4420–4492; (b) Lu, Y.; Yu, Z. D.; Liu, Y.; Ding, Y. F.; Yang, C. Y.; Yao, Z. F.; Wang, Z. Y.; You, H. Y.; Cheng, X. F.; Tang, B.; Wang, J. Y.; Pei, J. The Critical Role of Dopant Cations in Electrical Conductivity and Thermoelectric Performance of n-Doped Polymers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 15340–15348.
- 11(a) Yuan, D.; Huang, D.; Zhang, C.; Zou, Y.; Di, C. A.; Zhu, X.; Zhu, D. Efficient Solution-Processed n-Type Small-Molecule Thermoelectric Materials Achieved by Precisely Regulating Energy Level of Organic Dopants. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 28795–28801; (b) Han, J.; Chiu, A.; Ganley, C.; McGuiggan, P.; Thon, S. M.; Clancy, P.; Katz, H. E. 3,4,5-Trimethoxy Substitution on an N-DMBI Dopant with New N-Type Polymers: Polymer-Dopant Matching for Improved Conductivity-Seebeck Coefficient Relationship. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 27212–27219.
- 12(a) Qiu, L.; Liu, J.; Alessandri, R.; Qiu, X.; Koopmans, M.; Havenith, R. W. A.; Marrink, S. J.; Chiechi, R. C.; Anton Koster, L. J.; Hummelen, J. C. Enhancing doping efficiency by improving host-dopant miscibility for fullerene-based n-type thermoelectrics. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 21234–21241; (b) Liu, J.; Qiu, L.; Alessandri, R.; Qiu, X.; Portale, G.; Dong, J.; Talsma, W.; Ye, G.; Sengrian, A. A.; Souza, P. C. T.; Loi, M. A.; Chiechi, R. C.; Marrink, S. J.; Hummelen, J. C.; Koster, L. J. A. Enhancing Molecular n-Type Doping of Donor–Acceptor Copolymers by Tailoring Side Chains. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1704630.
- 13 Yan, X.; Xiong, M.; Deng, X. Y.; Liu, K. K.; Li, J. T.; Wang, X. Q.; Zhang, S.; Prine, N.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, W.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J. Y.; Gu, X.; So, S. K.; Zhu, J.; Lei, T. Approaching disorder-tolerant semiconducting polymers. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 5723.
- 14 Wei, P.; Oh, J. H.; Dong, G.; Bao, Z. Use of a 1H-Benzoimidazole Derivative as an n-Type Dopant and To Enable Air-Stable Solution-Processed n-Channel Organic Thin-Film Transistors. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 8852–8853.
- 15 Saglio, B.; Mura, M.; Massetti, M.; Scuratti, F.; Beretta, D.; Jiao, X.; McNeill, C. R.; Sommer, M.; Famulari, A.; Lanzani, G.; Caironi, M.; Bertarelli, C. N-Alkyl substituted 1H-benzimidazoles as improved n-type dopants for a naphthalene-diimide based copolymer. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 15294–15302.
- 16 Yang, C. Y.; Ding, Y. F.; Huang, D.; Wang, J.; Yao, Z. F.; Huang, C. X.; Lu, Y.; Un, H. I.; Zhuang, F. D.; Dou, J.-H.; Di, C. A.; Zhu, D.; Wang, J.-Y.; Lei, T.; Pei, J. A thermally activated and highly miscible dopant for n-type organic thermoelectrics. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3292.
- 17 Wei, H.; Chen, P. A.; Guo, J.; Liu, Y.; Qiu, X.; Chen, H.; Zeng, Z.; Nguyen, T. Q.; Hu, Y. Low-Cost Nucleophilic Organic Bases as n-Dopants for Organic Field-Effect Transistors and Thermoelectric Devices. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2102768.
- 18 Han, J.; Ganley, C.; Hu, Q.; Zhao, X.; Clancy, P.; Russell, T. P.; Katz, H. E. Using Preformed Meisenheimer Complexes as Dopants for n-Type Organic Thermoelectrics with High Seebeck Coefficients and Power Factors. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2010567.
- 19 Li, F.; Werner, A.; Pfeiffer, M.; Leo, K.; Liu, X. Leuco Crystal Violet as a Dopant for n-Doping of Organic Thin Films of Fullerene C60. J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 17076–17082.
- 20(a) Du, T.; Gao, R.; Deng, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhou, Q.; Geng, Y. Indandione- Terminated Quinoids: Facile Synthesis by Alkoxide-Mediated Rearrangement Reaction and Semiconducting Properties. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 221–225; (b) Sun, L.; Du, T.; Wang, C.; Geng, D.; Li, L.; Han, Y.; Deng, Y. Indandione-Terminated Quinoidal Compounds for Low-Bandgap Small Molecules with Strong Near-Infrared Absorption: Effect of Conjugation Length on the Properties. Chem. Eur. J. 2021, 27, 17437–17443.
- 21 Zeng, Y.; Zheng, W.; Guo, Y.; Han, G.; Yi, Y. Doping mechanisms of N-DMBI-H for organic thermoelectrics: hydrogen removal vs. hydride transfer. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 8323–8328.
- 22 Liang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Souri, M.; Luo, X.; Boehm, A. M.; Li, R.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, T.; Kim, D. Y.; Mei, J.; Marder, S. R.; Graham, K. R. Influence of dopant size and electron affinity on the electrical conductivity and thermoelectric properties of a series of conjugated polymers. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 16495–16505.
- 23(a) Jacobs, I. E.; D'Avino, G.; Lemaur, V.; Lin, Y.; Huang, Y.; Chen, C.; Harrelson, T. F.; Wood, W.; Spalek, L. J.; Mustafa, T.; O'Keefe, C. A.; Ren, X.; Simatos, D.; Tjhe, D.; Statz, M.; Strzalka, J. W.; Lee, J. K.; McCulloch, I.; Fratini, S.; Beljonne, D.; Sirringhaus, H. Structural and Dynamic Disorder, Not Ionic Trapping, Controls Charge Transport in Highly Doped Conducting Polymers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 3005–3019; (b) Chen, C.; Jacobs, I. E.; Kang, K.; Lin, Y.; Jellett, C.; Kang, B.; Lee, S. B.; Huang, Y.; BaloochQarai, M.; Ghosh, R.; Statz, M.; Wood, W.; Ren, X.; Tjhe, D.; Sun, Y.; She, X.; Hu, Y.; Jiang, L.; Spano, F. C.; McCulloch, I.; Sirringhaus, H. Observation of Weak Counterion Size Dependence of Thermoelectric Transport in Ion Exchange Doped Conducting Polymers Across a Wide Range of Conductivities. Adv. Energy Mater. 2023, 13, 2202797.
- 24(a) Zhao, X.; Cai, H.; Deng, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Shi, Y.; Han, Y.; Geng, Y. Low-Band gap Conjugated Polymers with Strong Absorption in the Second Near-Infrared Region Based on Diketopyrrolopyrrole-Containing Quinoidal Units. Macromolecules 2021, 54, 3498–3506; (b) Huang, J.; Lu, S.; Chen, P.-A.; Wang, K.; Hu, Y.; Liang, Y.; Wang, M.; Reichmanis, E. Rational Design of a Narrow-Bandgap Conjugated Polymer Using the Quinoidal Thieno[3,2-b]thiophene-Based Building Block for Organic Field-Effect Transistor Applications. Macromolecules 2019, 52, 4749–4756.
- 25 Li, Z.; Hou, X.; Han, Y.; Fan, W.; Ni, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Zhu, J.; Wu, S.; Huang, K.-W.; Wu, J. [8]Cyclo-para-phenylmethine as a Super-Cyclooctatetraene: Dynamic Behavior, Global Aromaticity, and Open-Shell Diradical Character in the Neutral and Dicationic States. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202210697.
- 26 Hestand, N. J.; Spano, F. C. Expanded Theory of H- and J-Molecular Aggregates: The Effects of Vibronic Coupling and Intermolecular Charge Transfer. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 7069–7163.
- 27(a) Liu, J.; Ye, G.; Zee, B. v. d.; Dong, J.; Qiu, X.; Liu, Y.; Portale, G.; Chiechi, R. C.; Koster, L. J. A. N-Type Organic Thermoelectrics of Donor–Acceptor Copolymers: Improved Power Factor by Molecular Tailoring of the Density of States. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1804290; (b) Bardagot, O.; Kubik, P.; Marszalek, T.; Veyre, P.; Medjahed, A. A.; Sandroni, M.; Grévin, B.; Pouget, S.; Nunes Domschke, T.; Carella, A.; Gambarelli, S.; Pisula, W.; Demadrille, R. Impact of Morphology on Charge Carrier Transport and Thermoelectric Properties of N-Type FBDOPV-Based Polymers. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2000449.
- 28(a) Naab, B. D.; Zhang, S.; Vandewal, K.; Salleo, A.; Barlow, S.; Marder, S. R.; Bao, Z. Effective Solution- and Vacuum-Processed n-Doping by Dimers of Benzimidazoline Radicals. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 4268–4272; (b) Naab, B. D.; Guo, S.; Olthof, S.; Evans, E. G. B.; Wei, P.; Millhauser, G. L.; Kahn, A.; Barlow, S.; Marder, S. R.; Bao, Z. Mechanistic Study on the Solution-Phase n-Doping of 1,3-Dimethyl-2-aryl- 2,3-dihydro-1H-benzoimidazole Derivatives. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 15018–15025.
- 29 Alsufyani, M.; Stoeckel, M. A.; Chen, X.; Thorley, K.; Hallani, R. K.; Puttisong, Y.; Ji, X.; Meli, D.; Paulsen, B. D.; Strzalka, J.; Regeta, K.; Combe, C.; Chen, H.; Tian, J.; Rivnay, J.; Fabiano, S.; McCulloch, I. Lactone Backbone Density in Rigid Electron-Deficient Semiconducting Polymers Enabling High n-type Organic Thermoelectric Performance. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202113078.
- 30(a) Dong, C.; Deng, S.; Meng, B.; Liu, J.; Wang, L. A Distannylated Monomer of a Strong Electron-Accepting Organoboron Building Block: Enabling Acceptor–Acceptor-Type Conjugated Polymers for n-Type Thermoelectric Applications. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 16184–16190; (b) Wang, Y.; Takimiya, K. Naphthodithiophenediimide–Bithiopheneimide Copolymers for High-Performance n-Type Organic Thermoelectrics: Significant Impact of Backbone Orientation on Conductivity and Thermoelectric Performance. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 2002060.




