A Label-Free Deoxyribozyme Sensor for m6A Demethylase Activity Detection†
Xiuyuan Wang
College of Chemistry and Molecular Sciences, Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, 430072 China
Search for more papers by this authorShusheng Yu
College of Chemistry and Molecular Sciences, Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, 430072 China
Search for more papers by this authorYuqiu He
College of Chemistry and Molecular Sciences, Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, 430072 China
Search for more papers by this authorFuan Wang
College of Chemistry and Molecular Sciences, Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, 430072 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Xiaoqing Liu
College of Chemistry and Molecular Sciences, Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, 430072 China
E-mail: [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorXiuyuan Wang
College of Chemistry and Molecular Sciences, Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, 430072 China
Search for more papers by this authorShusheng Yu
College of Chemistry and Molecular Sciences, Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, 430072 China
Search for more papers by this authorYuqiu He
College of Chemistry and Molecular Sciences, Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, 430072 China
Search for more papers by this authorFuan Wang
College of Chemistry and Molecular Sciences, Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, 430072 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Xiaoqing Liu
College of Chemistry and Molecular Sciences, Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, 430072 China
E-mail: [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorDedicated to the 130th Anniversary of Wuhan University.
Comprehensive Summary
A label-free deoxyribozyme (DNAzyme) biosensor for m6A demethylase activity detection is developed. When demethylase FTO (Fat mass and obesity-associated protein), an important m6A demethylase of ALKBH demethylase family is present, the m6A group is specifically demethylated, and the cleavage activity of DNAzyme is restored. This allows the cleavage product that contains G-quadruplex sequence to bind to thioflavin T (ThT) and generate fluorescence signals. The biosensor shows high specificity and sensitivity, and fast reaction speed. Our study demonstrates a new design of allosteric DNAzyme for sensing. This method represents the first label-free nucleic acid biosensor for FTO assay, providing a feasible route towards inhibitors screening.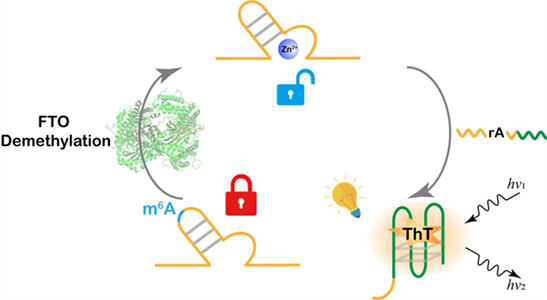
Supporting Information
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| cjoc202300633-sup-0001-supinfo.pdfPDF document, 1.2 MB |
Appendix S1: Supporting Information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1 Roundtree, I. A.; Evans, M. E.; Pan, T.; He, C. Dynamic RNA Modifications in Gene Expression Regulation. Cell 2017, 169, 1187–1200.
- 2 Zaccara, S.; Ries, R. J.; Jaffrey, S. R. Reading, Writing and Erasing mRNA Methylation. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2019, 20, 608–624.
- 3 Su, R.; Dong, L.; Li, C.; Nachtergaele, S.; Wunderlich, M.; Qing, Y.; Deng, X.; Wang, Y.; Weng, X.; Hu, C.; Yu, M.; Skibbe, J.; Dai, Q.; Zou, D.; Wu, T.; Yu, K.; Weng, H.; Huang, H.; Ferchen, K.; Qin, X.; Zhang, B.; Qi, J.; Sasaki, A. T.; Plas, D. R.; Bradner, J. E.; Wei, M.; Marcucci, G.; Jiang, X.; Mulloy, J. C.; Jin, J.; He, C.; Chen, J. R-2HG Exhibits Anti-Tumor Activity by Targeting FTO/m6A/MYC/CEBPA Signaling. Cell 2018, 172, 90–105.
- 4 Xie, B.; Liu, T.; Chen, S.; Zhang, Y.; He, D.; Shao, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, C. Combination of DNA Demethylation and Chemotherapy to Trigger Cell Pyroptosis for Inhalation Treatment of Lung Cancer. Nanoscale 2021, 13, 18608–18615.
- 5 Fawcett, K. A.; Barroso, I. The Genetics of Obesity: FTO Leads the Way. Trends Genet. 2010, 26, 266–274.
- 6 Li, Z.; Weng, H.; Su, R.; Weng, X.; Zuo, Z.; Li, C.; Huang, H.; Nachtergaele, S.; Dong, L.; Hu, C.; Qin, X.; Tang, L.; Wang, Y.; Hong, G.-M.; Huang, H.; Wang, X.; Chen, P.; Gurbuxani, S.; Arnovitz, S.; Li, Y.; Li, S.; Strong, J.; Neilly, M. B.; Larson, R. A.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, P.; Jin, J.; He, C.; Chen, J. FTO Plays an Oncogenic Role in Acute Myeloid Leukemia as a N6-Methyladenosine RNA Demethylase. Cancer Cell 2017, 31, 127–141.
- 7 Wei, J.; Liu, F.; Lu, Z.; Fei, Q.; Ai, Y.; He, P. C.; Shi, H.; Cui, X.; Su, R.; Klungland, A.; Jia, G.; Chen, J.; He, C. Differential m6A, m6Am, and m1A Demethylation Mediated by FTO in the Cell Nucleus and Cytoplasm. Mol. Cell 2018, 71, 973–985.
- 8 Yang, S.; Wei, J.; Cui, Y.-H.; Park, G.; Shah, P.; Deng, Y.; Aplin, A. E.; Lu, Z.; Hwang, S.; He, C.; He, Y.-Y. m6A mRNA Demethylase FTO Regulates Melanoma Tumorigenicity and Response to Anti-PD-1 Blockade. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2782.
- 9 Beck, S.; Rakyan, V. K. The Methylome: Approaches for Global DNA Methylation Profiling. Trends Genet. 2008, 24, 231–237.
- 10 Bock, C.; Tomazou, E. M.; Brinkman, A. B.; Müller, F.; Simmer, F.; Gu, H.; Jäger, N.; Gnirke, A.; Stunnenberg, H. G.; Meissner, A. Quantitative Comparison of Genome-Wide DNA Methylation Mapping Technologies. Nat. Biotechnol. 2010, 28, 1106–1114.
- 11 Laird, P. W. Principles and Challenges of Genome-Wide DNA Methylation Analysis. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2010, 11, 191–203.
- 12 Zhao, L.; Fan, T.; Han, Y.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, F. Demethylase FTO Activity Analysis Based on Methyl Sensitive Enzyme MazF and Hybridization Chain Reaction. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 341, 129983.
- 13
Li, F.; Kennedy, S.; Hajian, T.; Gibson, E.; Seitova, A.; Xu, C.; Arrowsmith, C. H.; Vedadi, M. A Radioactivity-Based Assay for Screening Human m6A-RNA Methyltransferase, METTL3-METTL14 Complex, and Demethylase ALKBH5. SLAS Discov. 2016, 21, 290–297.
10.1177/1087057115623264 Google Scholar
- 14 Wang, Y.; Zhang, C.-H.; Tang, L.-J.; Jiang, J.-H. Enzymatic Control of Plasmonic Coupling and Surface Enhanced Raman Scattering Transduction for Sensitive Detection of DNA Demethylation. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 8602–8606.
- 15 Zhao, Y.; Chen, F.; Wu, Y.; Dong, Y.; Fan, C. Highly Sensitive Fluorescence Assay of DNA Methyltransferase Activity via Methylation-Sensitive Cleavage Coupled with Nicking Enzyme-Assisted Signal amplification. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 42, 56–61.
- 16 Zhou, Y.; Li, B.; Wang, M.; Yang, Z.; Yin, H.; Ai, S. Enzyme-Based Electrochemical Biosensor for Sensitive Detection of DNA Demethylation and the Activity of DNA Demethylase. Anal. Chim. Acta 2014, 840, 28–32.
- 17 Shen, Q.; Fan, M.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, H. Electrochemical DNA Sensor-Based Strategy for Sensitive Detection of DNA Demethylation and DNA Demethylase Activity. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 934, 66–71.
- 18 Zhang, L.; Pan, M.; Zou, Z.; Fan, L.; Liu, X. Hybridization Chain Reaction-Mediated Luminescent Silver Nanocluster System for Amplified Detection of miRNA-21. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 2020, 48, 1193–1201.
- 19 Gong, L.; Zhao, Z.; Lv, Y.-F.; Huan, S.-Y.; Fu, T.; Zhang, X.-B.; Shen, G.-L.; Yu, R.-Q. DNAzyme-Based Biosensors and Nanodevices. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 979–995.
- 20 Wang, Q.; Tan, K.; Wang, H.; Shang, J.; Wan, Y.; Liu, X.; Weng, X.; Wang, F. Orthogonal Demethylase-Activated Deoxyribozyme for Intracellular Imaging and Gene Regulation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 6895–6904.
- 21 Shao, C.; Lu, N.; Sun, D. A G-Quadruplex/Hemin Complex with Switchable Peroxidase Activity by DNA Hybridization. Chin. J. Chem. 2012, 30, 1575–1581.
- 22 Wang, F.; Wang, C.; Liu, Y.; Lan, W.; Wang, R.; Huang, S.; Cao, C. NMR Studies on the Interaction between Oncogene RET G-QUADRUPLEX and Berberine. Chin. J. Chem. 2020, 38, 1656–1662.
- 23 Liu, L.; Shao, Y.; Peng, J.; Huang, C.; Liu, H.; Zhang, L. Molecular Rotor-Based Fluorescent Probe for Selective Recognition of Hybrid G-Quadruplex and as a K+ Sensor. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 1622–1631.
- 24 Fan, L.; Jiang, Q.; Pan, M.; Wang, W.; Zhang, L.; Liu, X. Dual-Mode Sensing of Biomarkers by Mimic Enzyme-Natural Enzyme Cascade Signal Amplification. Acta Chim. Sinica 2020, 78, 419.
- 25 Liang, M.; Song, G.; Wan, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, F.; Liu, X. Surface Engineering of Carbon Dots for Highly Sensitive α-Glucosidase Assay and Inhibition Evaluation. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2024, 35, 108573.
- 26 Liu, W.; Fu, Y.; Zheng, B.; Cheng, S.; Li, W.; Lau, T.-C.; Liang, H. Kinetics and Mechanism of Conformational Changes in a G-Quadruplex of Thrombin-Binding Aptamer Induced by Pb2+. J. Phys. Chem. B 2011, 115, 13051–13056.
- 27 Nakatsuka, N.; Yang, K.-A.; Abendroth, J. M.; Cheung, K. M.; Xu, X.; Yang, H.; Zhao, C.; Zhu, B.; Rim, Y. S.; Yang, Y.; Weiss, P. S.; Stojanović, M. N.; Andrews, A. M. Aptamer-Field-Effect Transistors Overcome Debye Length Limitations for Small-Molecule Sensing. Science 2018, 362, 319–324.
- 28 Cheung, K. M.; Yang, K.-A.; Nakatsuka, N.; Zhao, C.; Ye, M.; Jung, M. E.; Yang, H.; Weiss, P. S.; Stojanović, M. N.; Andrews, A. M. Phenylalanine Monitoring via Aptamer-Field-Effect Transistor Sensors. ACS Sens. 2019, 4, 3308–3317.
- 29 Jia, G.; Fu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Dai, Q.; Zheng, G.; Yang, Y.; Yi, C.; Lindahl, T.; Pan, T.; Yang, Y.-G.; He, C. N6-Methyladenosine in Nuclear RNA Is a Major Substrate of the Obesity-Associated FTO. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2011, 7, 885–887.
- 30 Zhao, L.; Fan, T.; Han, Y.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, F. Demethylase FTO Activity Analysis Based on Methyl Sensitive Enzyme MazF and Hybridization Chain Reaction. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 341, 129983.
- 31 Qiao, Y.; Zhou, B.; Zhang, M.; Liu, W.; Han, Z.; Song, C.; Yu, W.; Yang, Q.; Wang, R.; Wang, S.; Shi, S.; Zhao, R.; Chai, J.; Chang, J. A Novel Inhibitor of the Obesity-Related Protein FTO. Biochemistry 2016, 55, 1516–1522.
- 32 Huang, Y.; Su, R.; Sheng, Y.; Dong, L.; Dong, Z.; Xu, H.; Ni, T.; Zhang, Z. S.; Zhang, T.; Li, C.; Han, L.; Zhu, Z.; Lian, F.; Wei, J.; Deng, Q.; Wang, Y.; Wunderlich, M.; Gao, Z.; Pan, G.; Zhong, D.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, N.; Gan, J.; Jiang, H.; Mulloy, J. C.; Qian, Z.; Chen, J.; Yang, C.-G. Small-Molecule Targeting of Oncogenic FTO Demethylase in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Cancer Cell 2019, 35, 677–691.




