Electrochemical Dearomative Spirocyclization of N-Acyl Sulfonamides in a Continuous-Flow Cell†
Ting Liu
Key Laboratory of Molecule Synthesis and Function Discovery (Fujian Province University), College of Chemistry, Fuzhou University, Fuzhou, Fujian, 350108 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorZhaojiang Shi
Key Laboratory of Molecule Synthesis and Function Discovery (Fujian Province University), College of Chemistry, Fuzhou University, Fuzhou, Fujian, 350108 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorYaofeng Yuan
Key Laboratory of Molecule Synthesis and Function Discovery (Fujian Province University), College of Chemistry, Fuzhou University, Fuzhou, Fujian, 350108 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Yuqi Lin
Key Laboratory of Molecule Synthesis and Function Discovery (Fujian Province University), College of Chemistry, Fuzhou University, Fuzhou, Fujian, 350108 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Ke-Yin Ye
Key Laboratory of Molecule Synthesis and Function Discovery (Fujian Province University), College of Chemistry, Fuzhou University, Fuzhou, Fujian, 350108 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorTing Liu
Key Laboratory of Molecule Synthesis and Function Discovery (Fujian Province University), College of Chemistry, Fuzhou University, Fuzhou, Fujian, 350108 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorZhaojiang Shi
Key Laboratory of Molecule Synthesis and Function Discovery (Fujian Province University), College of Chemistry, Fuzhou University, Fuzhou, Fujian, 350108 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorYaofeng Yuan
Key Laboratory of Molecule Synthesis and Function Discovery (Fujian Province University), College of Chemistry, Fuzhou University, Fuzhou, Fujian, 350108 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Yuqi Lin
Key Laboratory of Molecule Synthesis and Function Discovery (Fujian Province University), College of Chemistry, Fuzhou University, Fuzhou, Fujian, 350108 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Ke-Yin Ye
Key Laboratory of Molecule Synthesis and Function Discovery (Fujian Province University), College of Chemistry, Fuzhou University, Fuzhou, Fujian, 350108 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorDedicated to the Special Issue of Emerging Investigators in 2024.
Comprehensive Summary
The development of efficient and sustainable methods to obtain spirocyclic compounds is of significance as these structures are widely found in pharmaceuticals and agrochemicals. Herein, we disclose an electrochemical dearomative spirocyclization of N-acyl sulfonamides in a continuous-flow cell. The reaction is simple and efficient without external catalysts or supporting electrolytes and could be applied in a decagram-scale synthesis.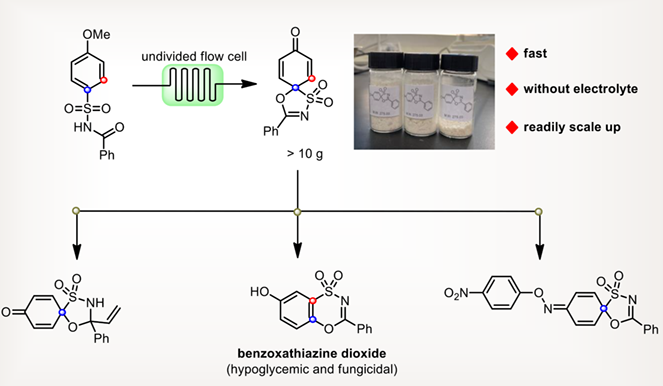
Supporting Information
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| cjoc202300673-sup-0001-supinfo.pdfPDF document, 5.6 MB |
Appendix S1: Supporting Information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1 Chupakhin, E.; Babich, O.; Prosekov, A.; Asyakina, L.; Krasavin, M. Spirocyclic Motifs in Natural Products. Molecules 2019, 24, 4165–4201.
- 2 Smith, L. K.; Baxendale, I. R. Total syntheses of natural products containing spirocarbocycles. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2015, 13, 9907–9933.
- 3 Brodney, M. A.; Barreiro, G.; Ogilvie, K.; Hajos-Korcsok, E.; Murray, J.; Vajdos, F.; Ambroise, C.; Christoffersen, C.; Fisher, K.; Lanyon, L.; Liu, J.; Nolan, C. E.; Withka, J. M.; Borzilleri, K. A.; Efremov, I.; Oborski, C. E.; Varghese, A.; O’Neill, B. T. Spirocyclic Sulfamides as β-Secretase 1 (BACE-1) Inhibitors for the Treatment of Alzheimer's Disease: Utilization of Structure Based Drug Design, WaterMap, and CNS Penetration Studies To Identify Centrally Efficacious Inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 9224–9239.
- 4 Hiesinger, K.; Dar’in, D.; Proschak, E.; Krasavin, M. Spirocyclic Scaffolds in Medicinal Chemistry. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 64, 150–183.
- 5 Hostetler, G.; Dunn, D.; McKenna, B. A.; Kopec, K.; Chatterjee, S. 1-Thia-4,7-diaza-spiro[4.4]nonane-3,6-dione: A Structural Motif for 5-hydroxytryptamine 6 Receptor Antagonism. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2014, 83, 149–153.
- 6 Zheng, Y.; Tice, C. M.; Singh, S. B. The use of spirocyclic scaffolds in drug discovery. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 24, 3673–3682.
- 7 Ding, A.; Meazza, M.; Guo, H.; Yang, J. W.; Rios, R. New development in the enantioselective synthesis of spiro compounds. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 5946–5996.
- 8 Lovering, F.; Bikker, J.; Humblet, C. Escape from Flatland: Increasing Saturation as an Approach to Improving Clinical Success. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 6752–6756.
- 9 Rios, R. Enantioselective methodologies for the synthesis of spiro compounds. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 1060–1074.
- 10 Kotha, S.; Panguluri, N. R.; Ali, R. Design and Synthesis of Spirocycles. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2017, 2017, 5316–5342.
- 11 Yang, W. C.; Zhang, M. M.; Feng, J. G. Recent Advances in the Construction of Spiro Compounds via Radical Dearomatization. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2020, 362, 4446–4461.
- 12 Luo, W.; Jiang, K.; Yin, B. Copper-Initiated Radical Dearomative 2,5-Alkylarylation of Furans via Trihalomethylation/Spirocyclization Cascade. Chin. J. Chem. 2022, 40, 2893–2899.
- 13 Lu, L.; Zheng, Z.; Yang, Y.; Liu, B.; Yin, B. Access to Polycyclic Indol(en)ines via Base-Catalyzed Intramolecular Dearomatizing 3-Alkenylation of Alkynyl Indoles. Chin. J. Chem. 2021, 39, 2207–2212.
- 14 Wu, W.-T.; Zhang, L.; You, S.-L. Catalytic asymmetric dearomatization (CADA) reactions of phenol and aniline derivatives. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 1570–1580.
- 15 Ciufolini, M.; Braun, N.; Canesi, S.; Ousmer, M.; Chang, J.; Chai, D. Oxidative Amidation of Phenols through the Use of Hypervalent Iodine Reagents: Development and Applications. Synthesis 2007, 3759–3772.
- 16 Elsherbini, M.; Winterson, B.; Alharbi, H.; Folgueiras-Amador, A. A.; Génot, C.; Wirth, T. Continuous-Flow Electrochemical Generator of Hypervalent Iodine Reagents: Synthetic Applications. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 9811–9815.
- 17 Liang, H.; Ciufolini, M. A. Oxidative Spirocyclization of Phenolic Sulfonamides: Scope and Applications. Chemistry 2010, 16, 13262–13270.
- 18 Pouységu, L.; Deffieux, D.; Quideau, S. Hypervalent iodine-mediated phenol dearomatization in natural product synthesis. Tetrahedron 2010, 66, 2235–2261.
- 19 Habert, L.; Cariou, K. Photoinduced Aerobic Iodoarene-Catalyzed Spirocyclization of N-Oxy-amides to N-Fused Spirolactams. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 60, 171–175.
- 20 Frontana-Uribe, B. A.; Little, R. D.; Ibanez, J. G.; Palma, A.; Vasquez-Medrano, R. Organic electrosynthesis: a promising green methodology in organic chemistry. Green Chem. 2010, 12, 2099–2119.
- 21 Jiao, K.-J.; Xing, Y.-K.; Yang, Q.-L.; Qiu, H.; Mei, T.-S. Site-Selective C—H Functionalization via Synergistic Use of Electrochemistry and Transition Metal Catalysis. Acc. Chem. Res. 2020, 53, 300–310.
- 22 Kingston, C.; Palkowitz, M. D.; Takahira, Y.; Vantourout, J. C.; Peters, B. K.; Kawamata, Y.; Baran, P. S. A Survival Guide for the “Electro-curious”. Acc. Chem. Res. 2019, 53, 72–83.
- 23 Cheng, X.; Lei, A.; Mei, T.-S.; Xu, H.-C.; Xu, K.; Zeng, C. Recent Applications of Homogeneous Catalysis in Electrochemical Organic Synthesis. CCS Chem. 2022, 4, 1120–1152.
- 24 Ma, C.; Fang, P.; Liu, Z.-R.; Xu, S.-S.; Xu, K.; Cheng, X.; Lei, A.; Xu, H.-C.; Zeng, C.; Mei, T.-S. Recent advances in organic electrosynthesis employing transition metal complexes as electrocatalysts. Sci. Bull. 2021, 66, 2412–2429.
- 25 Moeller, K. D. Using Physical Organic Chemistry To Shape the Course of Electrochemical Reactions. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 4817–4833.
- 26 Novaes, L. F. T.; Liu, J.; Shen, Y.; Lu, L.; Meinhardt, J. M.; Lin, S. Electrocatalysis as an enabling technology for organic synthesis. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 7941–8002.
- 27 Wang, X.; Xu, X.; Wang, Z.; Fang, P.; Mei, T. Advances in Asymmetric Organotransition Metal-Catalyzed Electrochemistry. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2020, 40, 3738–3747.
- 28 Yan, M.; Kawamata, Y.; Baran, P. S. Synthetic Organic Electrochemical Methods Since 2000: On the Verge of a Renaissance. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 13230–13319.
- 29 Amano, Y.; Nishiyama, S. Oxidative synthesis of azacyclic derivatives through the nitrenium ion: application of a hypervalent iodine species electrochemically generated from iodobenzene. Tetrahedron Lett. 2006, 47, 6505–6507.
- 30 Estruch-Blasco, M.; Bosque, I.; Guijarro, D.; Gonzalez-Gomez, J. C. Electrochemically site-selective alkoxylation of twisted 2-arylbenzoic acids via spirolactonization. Org. Chem. Front. 2021, 8, 5130–5138.
- 31 Hua, J.; Fang, Z.; Bian, M.; Ma, T.; Yang, M.; Xu, J.; Liu, C.; He, W.; Zhu, N.; Yang, Z.; Guo, K. Electrochemical Synthesis of Spiro[4.5]trienones through Radical-Initiated Dearomative Spirocyclization. ChemSusChem 2020, 13, 2053–2059.
- 32 Li, L.; Hou, Z.-W.; Li, P.; Wang, L. Electrochemical Dearomatizing Spirocyclization of Alkynes with Dimethyl 2-Benzylmalonates to Spiro[4.5]deca-trienones. J. Org. Chem. 2022, 87, 8697–8708.
- 33 Li, N.; Shi, Z.; Wang, W. Z.; Yuan, Y.; Ye, K. Y. Electrochemical Dearomative Spirocyclization. Chem. Asian J. 2023, 18, e202300122.
- 34 Nishiyama, S.; Amano, Y. Effects of Aromatic Substituents of Electrochemically Generated Hypervalent Iodine Oxidant on Oxidation Reactions. Heterocycles 2008, 75, 1997–2003.
- 35 Raji Reddy, C.; Kolgave, D. H. Electrochemical Selenylative Carbannulation of Biaryl Ynones to Seleno-Dibenzocycloheptenones/Spiro[5.5]Trienones. J. Org. Chem. 2021, 86, 17071–17081.
- 36 Wei, W.; Scheremetjew, A.; Ackermann, L. Electrooxidative palladium- and enantioselective rhodium-catalyzed [3+2] spiroannulations. Chem. Sci. 2022, 13, 2783–2788.
- 37 Yang, W.-C.; Zhang, M.-M.; Sun, Y.; Chen, C.-Y.; Wang, L. Electrochemical Trifluoromethylthiolation and Spirocyclization of Alkynes with AgSCF3: Access to SCF3-Containing Spiro[5,5]trienones. Org. Lett. 2021, 23, 6691–6696.
- 38 Yu, K.; Kong, X.; Yang, J.; Li, G.; Xu, B.; Chen, Q. Electrochemical Oxidative Halogenation of N-Aryl Alkynamides for the Synthesis of Spiro[4.5]trienones. J. Org. Chem. 2020, 86, 917–928.
- 39 Li, N.; Shi, Z.; Yuan, Y.; Li, Z.; Ye, K.-Y. Rapid synthesis of spirodienones via electrochemical dearomative spirocyclization in flow. Org. Chem. Front. 2022, 9, 6586–6591.
- 40 Liu, D.; Xu, H. C. Electrochemical Rearrangement of Indoles to Spirooxindoles in Continuous Flow. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2022, 26, e202200987.
- 41 Lv, S.; Zhang, G.; Chen, J.; Gao, W. Electrochemical Dearomatization: Evolution from Chemicals to Traceless Electrons. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2019, 362, 462–477.
- 42 Zhang, C.; Bu, F.; Zeng, C.; Wang, D.; Lu, L.; Zhang, H.; Lei, A. Electrochemical Oxidation Dearomatization of Anisol Derivatives toward Spiropyrrolidines and Spirolactones. CCS Chem. 2022, 4, 1199–1207.
- 43 Atobe, M.; Tateno, H.; Matsumura, Y. Applications of Flow Microreactors in Electrosynthetic Processes. Chem. Rev. 2017, 118, 4541–4572.
- 44 Elsherbini, M.; Wirth, T. Electroorganic Synthesis under Flow Conditions. Acc. Chem. Res. 2019, 52, 3287–3296.
- 45 Horcajada, R.; Okajima, M.; Suga, S.; Yoshida, J.-i. Microflow electroorganic synthesis without supporting electrolyte. Chem. Commun. 2005, 1303–1305.
- 46 Noël, T.; Cao, Y.; Laudadio, G. The Fundamentals Behind the Use of Flow Reactors in Electrochemistry. Acc. Chem. Res. 2019, 52, 2858–2869.
- 47 Shi, Z.; Li, Y.; Li, N.; Wang, W. Z.; Lu, H. K.; Yan, H.; Yuan, Y.; Zhu, J.; Ye, K. Y. Electrochemical Migratory Cyclization of N-Acylsulfonamides. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202206058.
- 48 Iwakawa, T.; Tamura, H.; Murabayashi, A.; Hayase, Y. Cycloaddition in Synthesis of Sulfonamide Derivatives. IV. One-Pot Synthesis of 3-Dimethylamino-4,1,2-benzoxathiazine 1,1-Dioxides, 3-Methoxy-4-methyl-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine 1,1-Dioxide and 3-Dimethylamino-1,4,2-benzodithiazine 1,1-Dioxides. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1991, 39, 1939–1943.
- 49 Kornahrens, A. F.; Cognetta, A. B., 3rd; Brody, D. M.; Matthews, M. L.; Cravatt, B. F.; Boger, D. L. Design of Benzoxathiazin-3-one 1,1-Dioxides as a New Class of Irreversible Serine Hydrolase Inhibitors: Discovery of a Uniquely Selective PNPLA4 Inhibitor. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 7052–7061.
- 50 Suzue, S.; Irikura, T. Studies on hypoglycemic agents. IV. Synthesis of 1,4,3-benzoxathiazine-4,4-dioxides. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1968, 16, 806–813.
- 51 Wertheim, E. Preparation of N-Benzoyl-o-aminobenzenesulfonamide. Condensation to Heterocyclic Compounds. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1934, 56, 971–973.
- 52Deposition Numbers 2264187 (for 24), 2306398 (for 28) contain the supplementary crystallographic data for this paper. These data are provided free of charge by the joint Cambridge Crystallographic Data Centre and Fachinformationszentrum Karlsruhe Access Structures service www.ccdc.cam.ac.uk/structures.
- 53 Xu, F.; Qian, X.-Y.; Li, Y.-J.; Xu, H.-C. Synthesis of 4H-1,3-Benzoxazines via Metal- and Oxidizing Reagent-Free Aromatic C—H Oxygenation. Org. Lett. 2017, 19, 6332–6335.




