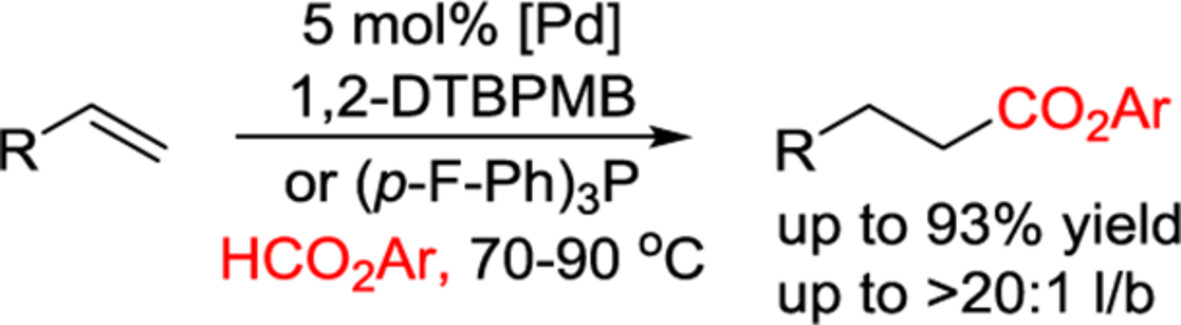Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Cover Picture
- Page: 1325
- First Published: 15 May 2024

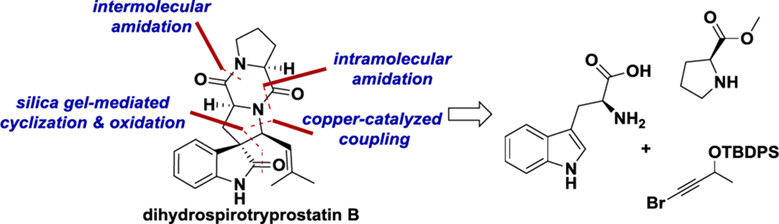
The cover image portrays the asymmetric synthesis of dihydrospirotryprostatin B, achieved through a chiral pool strategy utilizing readily available tryptamine-ynamide. This tryptamine-ynamide was constructed from three synthetic building blocks: L-tryptophan, methyl-L-proline ester, and bromoalkyne. For a comprehensive understanding of this process, refer to the article authored by Liu et al., pages 1355—1359.
Inside Cover Picture
Inside Cover Picture
- Page: 1326
- First Published: 15 May 2024

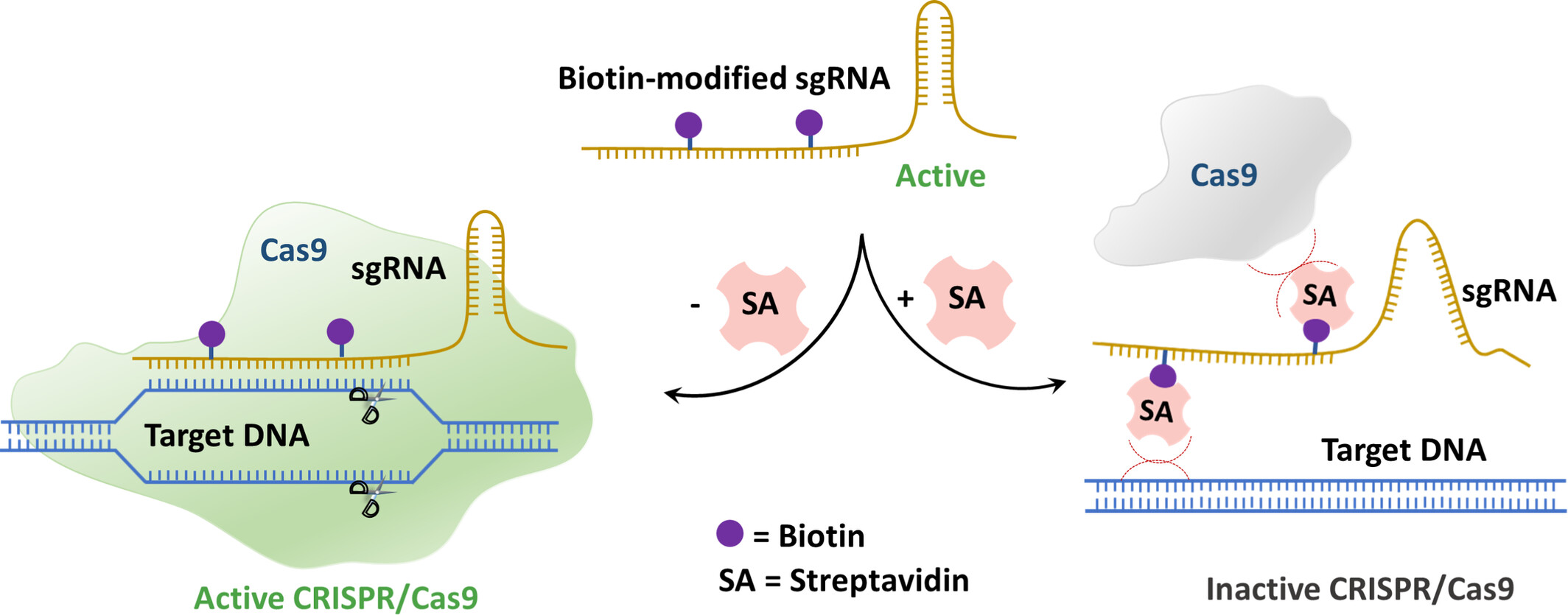
Considering the small molecular weight of biotin and the large spatial steric hindrance of streptavidin, they can be regarded as an ideal OFF switch due to their interaction properties. Using the streptavidin-biotin interaction as a "brake system" for CRISPR/Cas9, effectively allows for the shut-down of the enzymatic activity of CRISPR/Cas9. More details are discussed in the article by Tian et al. on page 1387—1393.
Contents
Concise Reports
Artificial Water Channel Promoting Depolymerization of Actin Filaments to Trigger Cancer Cell Apoptosis
- Pages: 1335-1340
- First Published: 19 February 2024
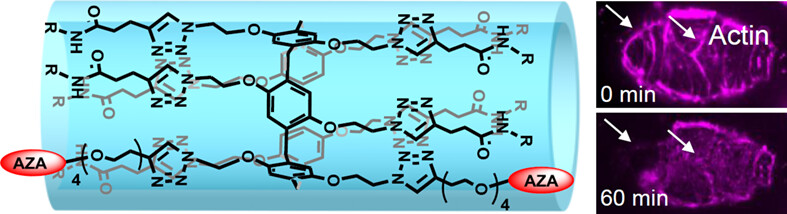
A new strategy to design antitumor reagents has been developed based on artificial water channel (AWC)-promoted depolymerization of actin filaments. Its effectivity has been demonstrated in vitro and in vivo by using colorectal cancer as a disease model. The AWC conjugated with acetazolamide (AZA) moiety exhibited targeting behavior and water permeability to induce the depolymerization of the actin and apoptosis of the cancer cells.
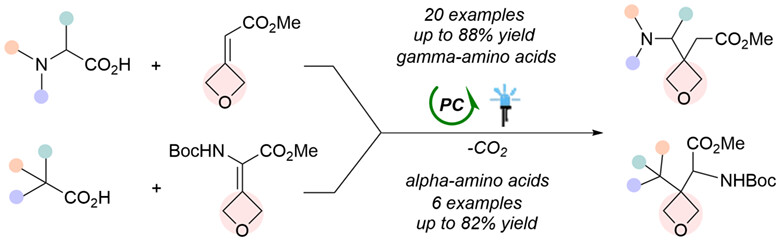
Synthesis of Diverse Oxetane Amino Acids via Visible-Light-Induced Photocatalytic Decarboxylative Giese-Type Reaction
- Pages: 1341-1346
- First Published: 12 February 2024
Understanding the Interfacial Energy Structure and Electron Extraction Process in Inverted Organic Solar Cells with Phosphine-Doped Cathode Interlayers
- Pages: 1347-1354
- First Published: 13 February 2024
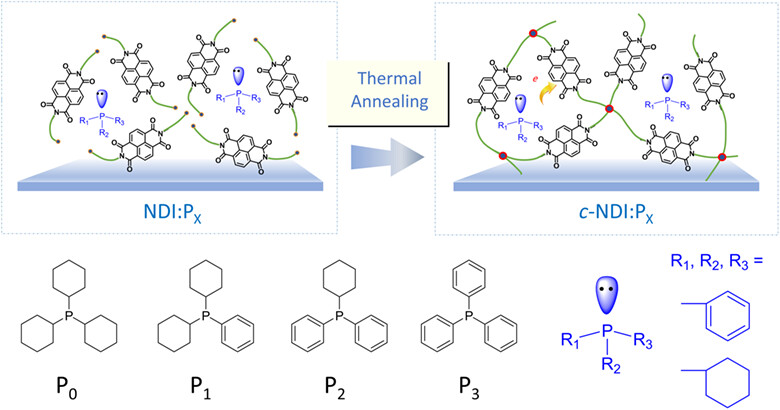
A series of cross-linked and phosphine-doped cathode interlayers (CILs), namely c-NDI:P0, c-NDI:P1, c-NDI:P2, and c-NDI:P3, are developed for inverted organic solar cells. We elucidate the relationship between the depletion region width at the heterojunction interface and the electron extraction ability of CILs. By incorporating c-NDI:P0, a low depletion width of 0.8 nm along with a high power conversion efficiency (PCE) of 17.7% can be obtained in the inverted OSC based on PBDB-TF:BTP-eC9.
Asymmetric Synthesis of Dihydrospirotryprostatin B via a Silica Gel-Mediated Cyclization of Tryptamine-Ynamide
- Pages: 1355-1359
- First Published: 13 February 2024
Transition-Metal-Free Allylic Defluorination Cross-Electrophile Coupling Employing Rongalite
- Pages: 1360-1366
- First Published: 23 February 2024
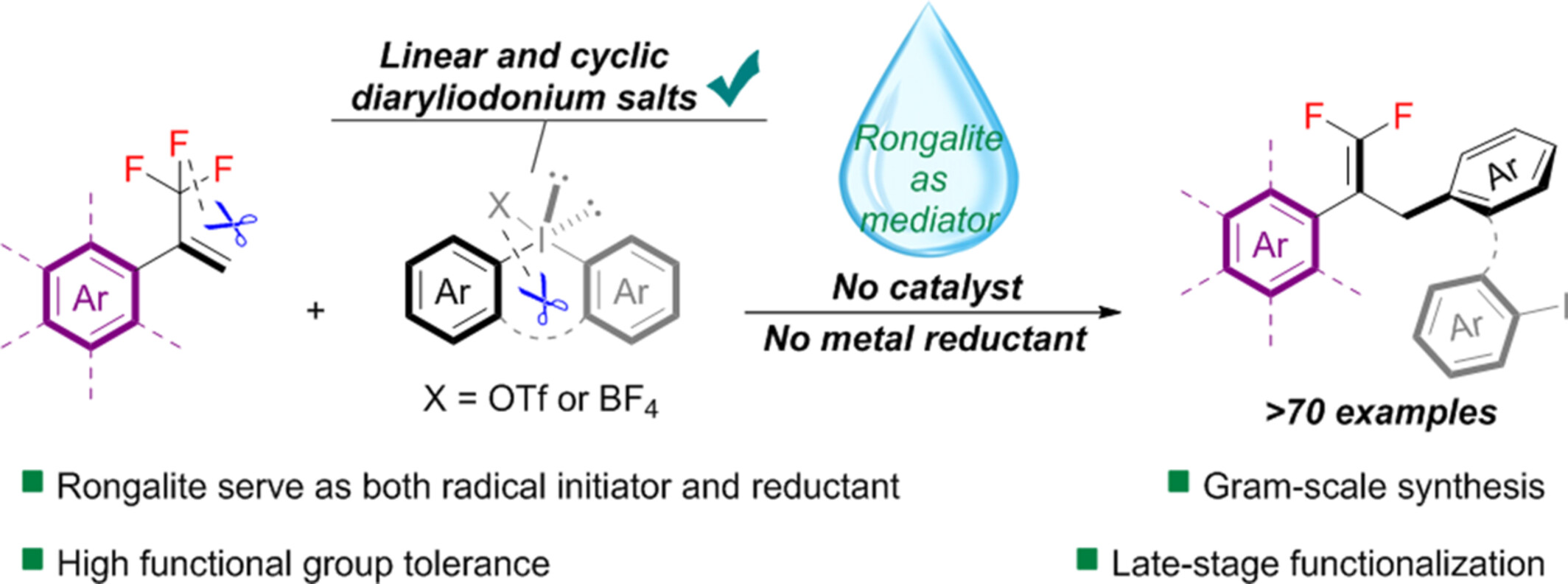
A transition-metal-free allylic defluorination reductive cross-coupling between CF3-alkenes and diaryliodonium salts mediated by rongalite has been described for the first time. This procedure was compatible with both linear and cyclic diaryliodonium salts, enabling a wide variety of substrates. The utility of this approach was demonstrated through gram-scale synthesis and efficient late-stage functionalizations of anti-inflammatory drugs.
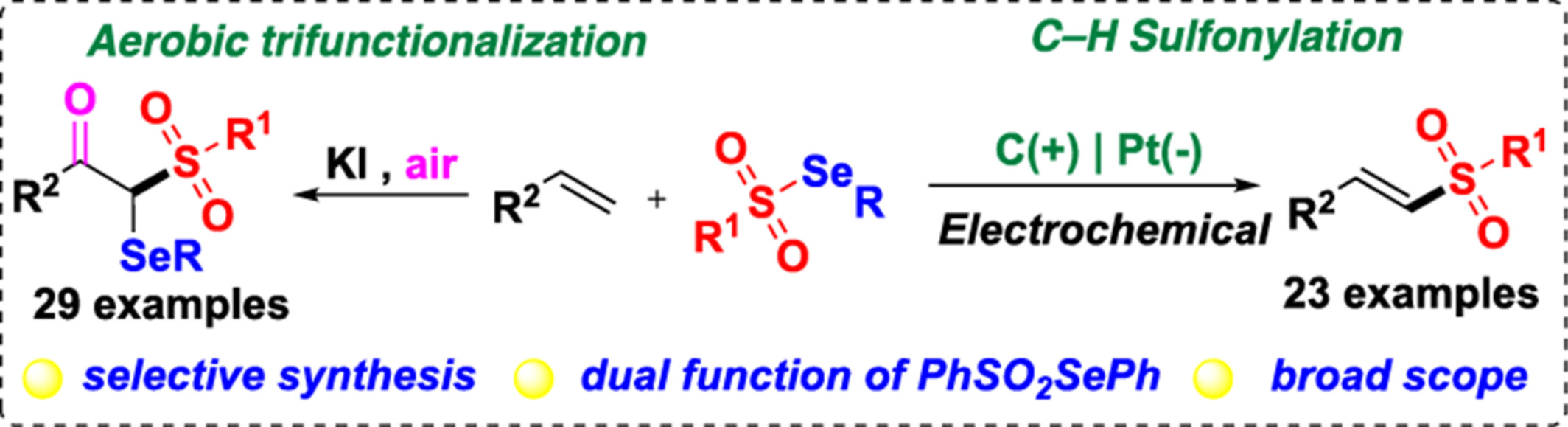
Controllable Construction of Vinyl Sulfones and β-Keto Selenosulfones via Selective Oxidative Sulfonylation of Alkenes
- Pages: 1367-1372
- First Published: 23 February 2024
An Efficient Probe for Bacterial Nitroreductase Imaging and Detection Based on NanoLuc-Furimazine Bioluminescent Pair
- Pages: 1373-1380
- First Published: 23 February 2024
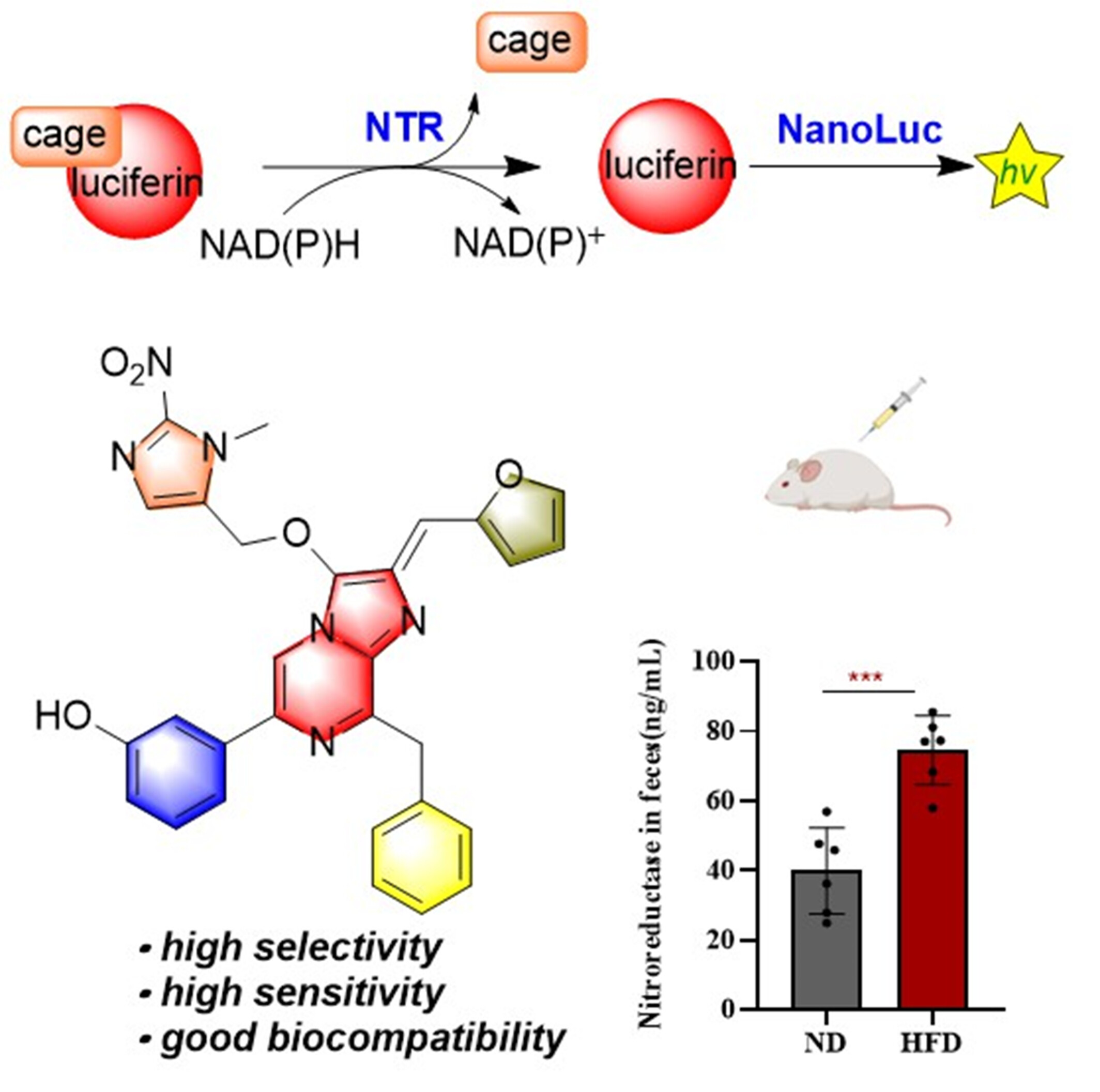
A panel of furimazine-based bioluminescent probes has been developed for the detection of pathogenic bacterial nitroreductase. The probe containing 2-nitro-N-methyl-imidazolyl possessed up to a 560-fold increment in bioluminescent intensity, with detection limit as low as 16 ng/mL, making it suitable for bioluminescent visualization in vivo.
Pd-Catalyzed Highly Regioselective Hydroesterification of Terminal Alkyl Olefins with Formates
- Pages: 1381-1386
- First Published: 13 March 2024
Regulating CRISPR/Cas9 Using Streptavidin-Biotin Interactions†
- Pages: 1387-1393
- First Published: 29 February 2024
Switchable Multicomponent Cyclization Reactions to Access Fluoroalkylated Dihydropyrimidines and Pyrimidines under Solvent-Free Conditions
- Pages: 1394-1398
- First Published: 23 February 2024
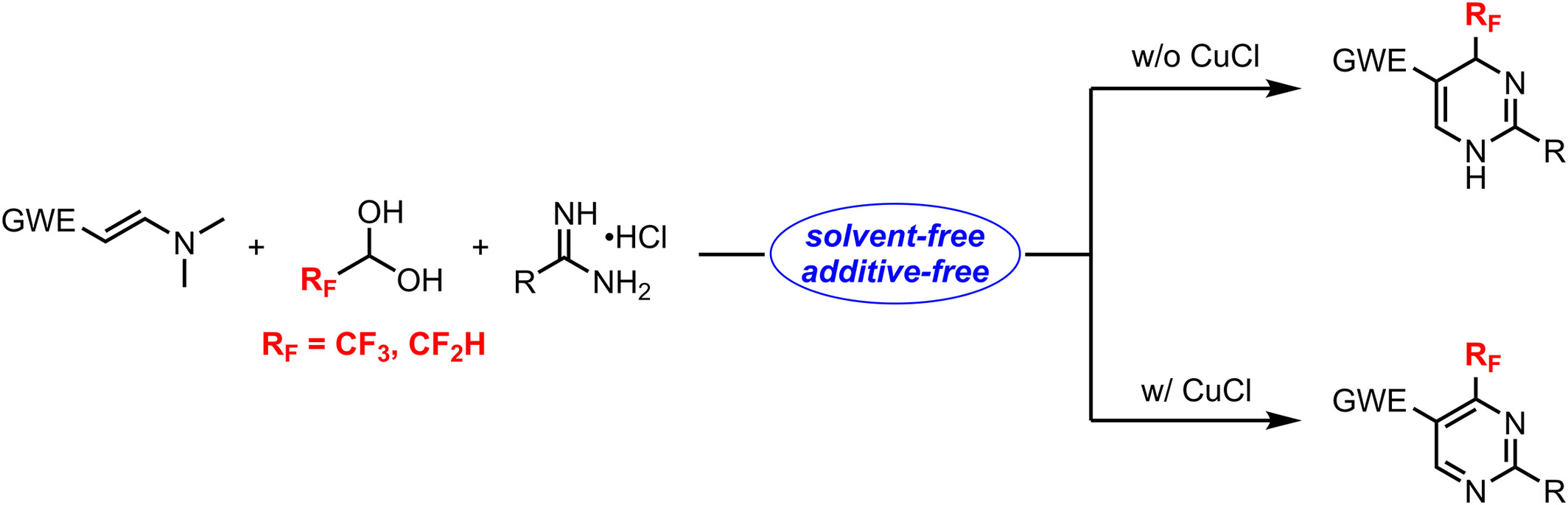
A switchable strategy for the construction of diverse 4-fluoroalkyl-1,4-dihydropyrimidines and 4-fluoroalkyl-pyrimidines via a solvent/additive-free [3 + 2 + 1] annulation, starting from readily available enamines, trifluoroacetaldehyde hydrate or 1-ethoxy-2,2-difluoroethanol and amidines hydrochloride has been developed.
Stereospecific Assembly of Trisubstituted Alkenes via Photoinduced Nitrogen-Centered Radical-Triggered C—C Bond Cleavage/Functionalization of Oxime Esters
- Pages: 1399-1406
- First Published: 29 February 2024
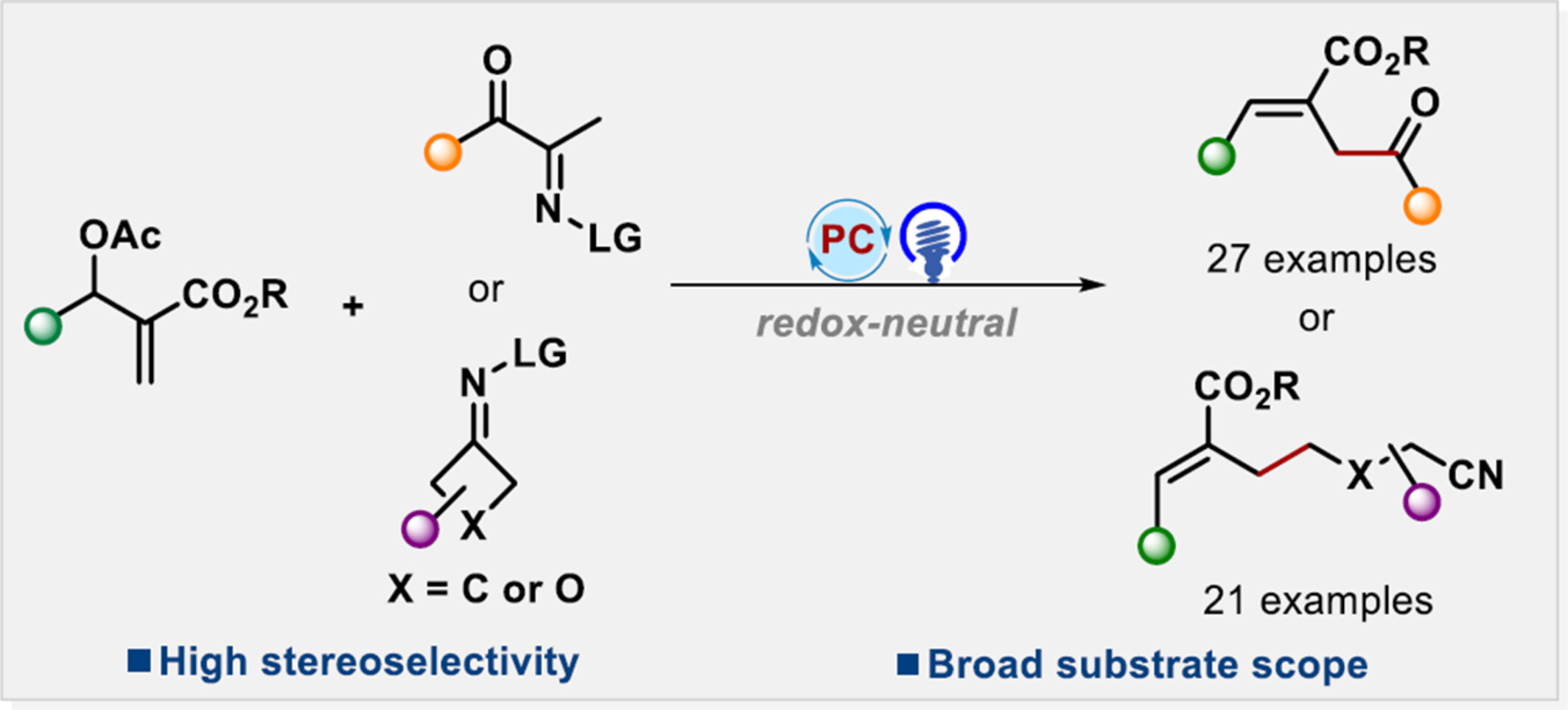
A general and convenient photoredox-catalyzed acylation and alkylcyanation of MBH acetates has been established, enabling the assembly of the C(sp2)–C(sp3) bond by a nitrogen-centered radical strategy for the synthesis of trisubstituted alkenes in moderate to excellent chemical yields (48 examples in total).
Achieving Seconds-to-Hours Duration-Tunable Organic Long Persistent Luminescence from Carbon Dots-Based Exciplex Systems by Energy Gaps Regulation
- Pages: 1407-1417
- First Published: 13 March 2024
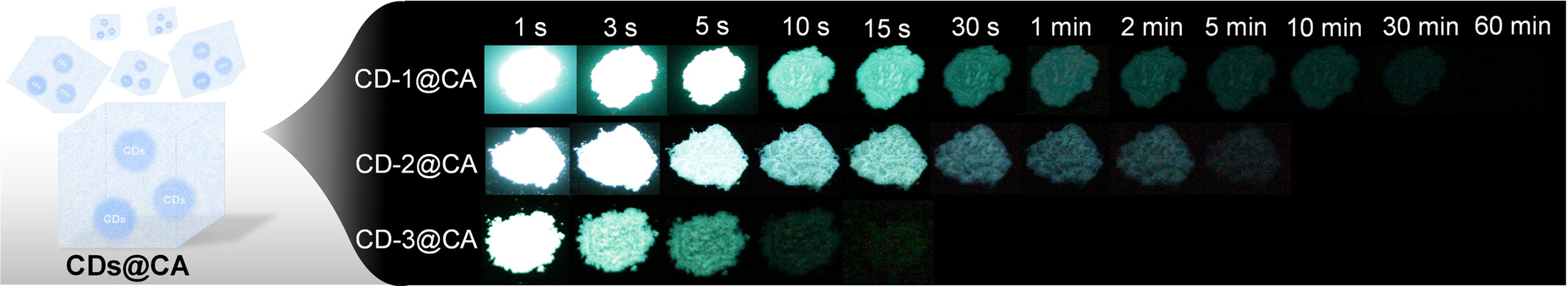
Carbon dots (CDs)-based long persistent luminescence (LPL) composites with a tunable duration in an ultrawide range from second- to hour-level are designed and prepared for the first time. The relationship of energy levels between excited states of CDs and charged-transfer (CT) states of the corresponding composites plays a pivotal role in activating LPL and regulating the LPL durations. These LPL composites have been preliminarily employed in dynamic displaying systems.
Critical Review
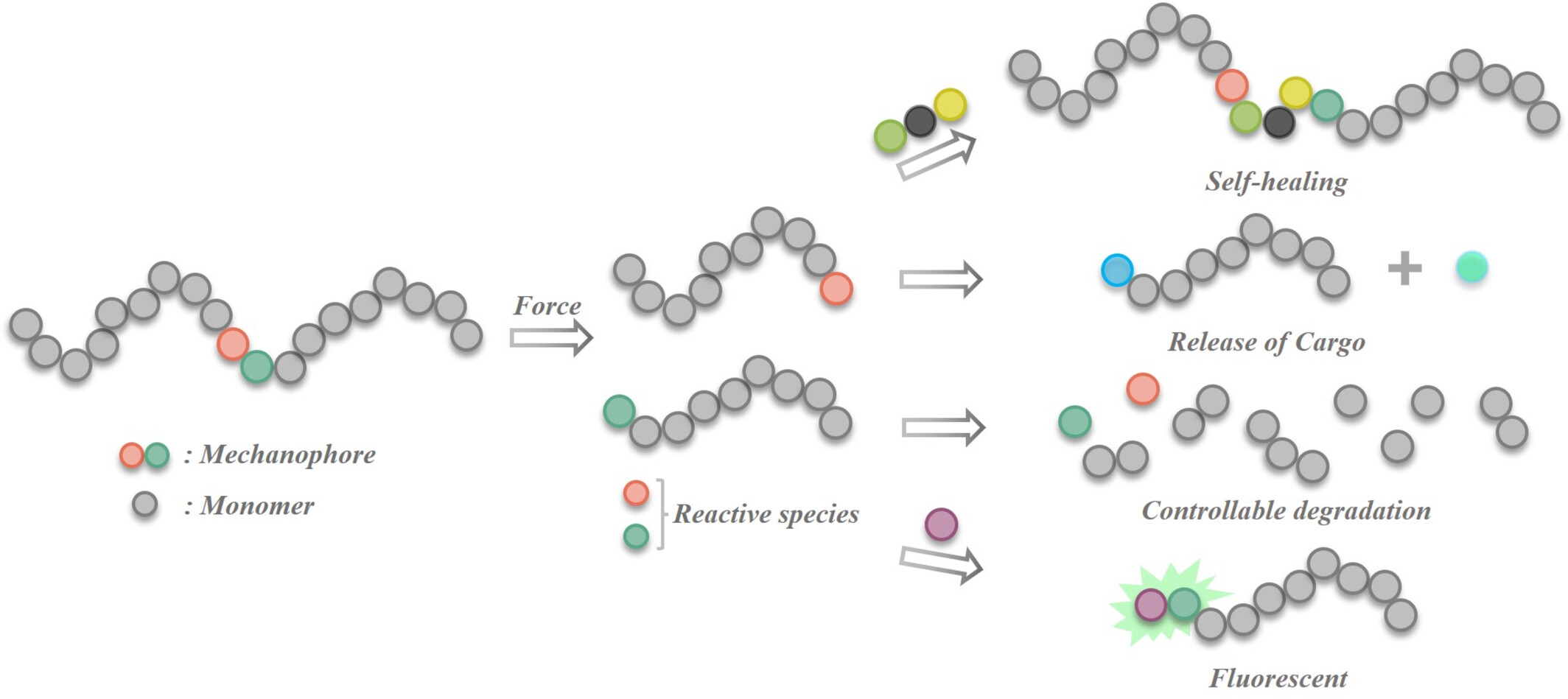
Polymer Mechanochemistry on Reactive Species Generated from Mechanochemical Reactions†
- Pages: 1418-1432
- First Published: 27 March 2024
Inside Back Cover
Inside Back Cover
- Page: 1435
- First Published: 15 May 2024

The cover displays a selective oxidative sulfonylation of alkenes with selenium sulfonate depended on the reaction conditions. The electrochemical C—H sulfonylation proceeded smoothly to afford (E)-vinyl sulfones with good selectivity in an undivided cell without external oxidant. While aerobic trifunctionalization of alkenes occurred in the presence of KI in the air, which provides β-keto selenosulfones via the formation of C—O, C—S, and C—Se bonds in one-pot. This selective synthesis is like interstellar racing, reaching distant planets from the same starting point through different paths. Following control experiments, a plausible mechanism is proposed to rationalize the experimental results. More details are discussed in the article by Cao et al. on page 1367—1372.
Back Cover
Back Cover
- Page: 1436
- First Published: 15 May 2024

Synthetically useful phenyl esters can be efficiently produced from terminal olefins via Pd-catalyzed regioselective hydroesterification with aryl formates and can be readily converted to other carboxylic acid derivatives. The hydroesterification reaction process is operationally simple and requires no handling of toxic CO or strong acid. More details are discussed in the article by Shi et al. on page 1381—1386.