Achieving Seconds-to-Hours Duration-Tunable Organic Long Persistent Luminescence from Carbon Dots-Based Exciplex Systems by Energy Gaps Regulation†
Yixuan Xu
International Joint Research Center for Photo-responsive Molecules and Materials, School of Chemical and Material Engineering, Jiangnan University, Wuxi, Jiangsu, 214122 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Kai Jiang
International Joint Research Center for Photo-responsive Molecules and Materials, School of Chemical and Material Engineering, Jiangnan University, Wuxi, Jiangsu, 214122 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorLinger Feng
International Joint Research Center for Photo-responsive Molecules and Materials, School of Chemical and Material Engineering, Jiangnan University, Wuxi, Jiangsu, 214122 China
Search for more papers by this authorXinyuan Tong
International Joint Research Center for Photo-responsive Molecules and Materials, School of Chemical and Material Engineering, Jiangnan University, Wuxi, Jiangsu, 214122 China
Search for more papers by this authorZuxu Zhou
International Joint Research Center for Photo-responsive Molecules and Materials, School of Chemical and Material Engineering, Jiangnan University, Wuxi, Jiangsu, 214122 China
Search for more papers by this authorFengshi Li
International Joint Research Center for Photo-responsive Molecules and Materials, School of Chemical and Material Engineering, Jiangnan University, Wuxi, Jiangsu, 214122 China
Search for more papers by this authorYi Zhang
State Key Laboratory of Food Science and Resources, Jiangnan University, Wuxi, Jiangsu, 214122 China
Search for more papers by this authorJiaren Du
International Joint Research Center for Photo-responsive Molecules and Materials, School of Chemical and Material Engineering, Jiangnan University, Wuxi, Jiangsu, 214122 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Hengwei Lin
International Joint Research Center for Photo-responsive Molecules and Materials, School of Chemical and Material Engineering, Jiangnan University, Wuxi, Jiangsu, 214122 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorYixuan Xu
International Joint Research Center for Photo-responsive Molecules and Materials, School of Chemical and Material Engineering, Jiangnan University, Wuxi, Jiangsu, 214122 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Kai Jiang
International Joint Research Center for Photo-responsive Molecules and Materials, School of Chemical and Material Engineering, Jiangnan University, Wuxi, Jiangsu, 214122 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorLinger Feng
International Joint Research Center for Photo-responsive Molecules and Materials, School of Chemical and Material Engineering, Jiangnan University, Wuxi, Jiangsu, 214122 China
Search for more papers by this authorXinyuan Tong
International Joint Research Center for Photo-responsive Molecules and Materials, School of Chemical and Material Engineering, Jiangnan University, Wuxi, Jiangsu, 214122 China
Search for more papers by this authorZuxu Zhou
International Joint Research Center for Photo-responsive Molecules and Materials, School of Chemical and Material Engineering, Jiangnan University, Wuxi, Jiangsu, 214122 China
Search for more papers by this authorFengshi Li
International Joint Research Center for Photo-responsive Molecules and Materials, School of Chemical and Material Engineering, Jiangnan University, Wuxi, Jiangsu, 214122 China
Search for more papers by this authorYi Zhang
State Key Laboratory of Food Science and Resources, Jiangnan University, Wuxi, Jiangsu, 214122 China
Search for more papers by this authorJiaren Du
International Joint Research Center for Photo-responsive Molecules and Materials, School of Chemical and Material Engineering, Jiangnan University, Wuxi, Jiangsu, 214122 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Hengwei Lin
International Joint Research Center for Photo-responsive Molecules and Materials, School of Chemical and Material Engineering, Jiangnan University, Wuxi, Jiangsu, 214122 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorComprehensive Summary
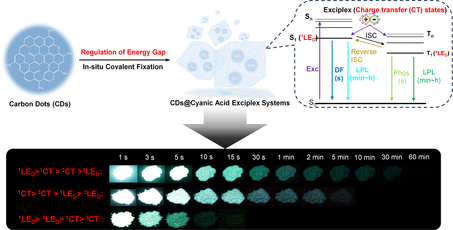
Duration-tunable afterglow materials have garnered considerable attention in various applications. Herein, carbon dots (CDs)-based long persistent luminescence (LPL) composites with a tunable duration in an ultrawide range of seconds-to-hours levels were designed and prepared for the first time. In contrast to the established CD-based afterglow materials, we reported that CD-based composites exhibit LPL in the form of exciplexes and long-lived charge-separated states, enabling the LPL to be prolonged from several seconds to over one hour, exceeding the typical regulation range (limited to 1 min). Further studies revealed that the relationship between the excited and charge-transfer states of CDs plays a pivotal role in activating the LPL and regulating its duration. Furthermore, these composites exhibited high photoluminescence (PL) quantum yields of up to 60.63%, and their LPL was robust under ambient conditions, even in aqueous media. Their robust and superior LPL performance endows these composites with a strong competitive advantage in dynamic display systems, such as tags for time-resolved data encryption and displays of the remaining time of takeaways. This study offers an approach to preparing CDs-based LPL composites with tunable durations and may provide new insights for the development of rare-earth-free LPL materials.
Supporting Information
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| cjoc_202300795_sm_suppl.pdfPDF document, 2.8 MB |
Appendix S1: Supporting Information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1 Liang, L.; Chen, J.; Shao, K.; Qin, X.; Pan, Z.; Liu, X. Controlling Persistent Luminescence in Nanocrystalline Phosphors. Nat. Mater. 2023, 22, 289–304.
- 2 Huang, K.; Le, N.; Wang, J. S.; Huang, L.; Zeng, L.; Xu, W.-C.; Li, Z.; Li, Y.; Han, G. Designing Next Generation of Persistent Luminescence: Recent Advances in Uniform Persistent Luminescence Nanoparticles. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2107962.
- 3 Li, Y.; Gecevicius, M.; Qiu, J. Long Persistent Phosphors from Fundamentals to Applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 2090–2136.
- 4 Yuan, L.; Jin, Y.; Su, Y.; Wu, H.; Hu, Y.; Yang, S. Optically Stimulated Luminescence Phosphors: Principles, Applications, and Prospects. Laser Photonics Rev. 2020, 14, 2000123.
- 5 Xu, J.; Tanabe, S. Persistent Luminescence Instead of Phosphorescence: History, Mechanism, and Perspective. J. Lumin. 2019, 205, 581–620.
- 6 Wu, S.; Li, Y.; Ding, W.; Xu, L.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, L. Recent Advances of Persistent Luminescence Nanoparticles in Bioapplications. Nano-Micro Lett. 2020, 12, 70.
- 7 Sun, S. K.; Wang, H. F.; Yan, X. P. Engineering Persistent Luminescence Nanoparticles for Biological Applications: From Biosensing/Bioimaging to Theranostics. Acc. Chem. Res. 2018, 51, 1131–1143.
- 8 Jiang, Y.; Huang, J.; Zhen, X.; Zeng, Z.; Li, J.; Xie, C.; Miao, Q.; Chen, J.; Chen, P.; Pu, K. A Generic Approach Towards Afterglow Luminescent Nanoparticles for Ultrasensitive in vivo Imaging. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2064.
- 9 Fan, Y.; Wang, P.; Lu, Y.; Wang, R.; Zhou, L.; Zheng, X.; Li, X.; Piper, J. A.; Zhang, F. Lifetime-Engineered NIR-II Nanoparticles Unlock Multiplexed in vivo Imaging. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2018, 13, 941–946.
- 10 Shen, H.; Liao, S.; Li, Z.; Wang, Y.; Huan, S.; Zhang, X. B.; Song, G. Organic Afterglow Nanoparticles in Bioapplications. Chemistry 2023, 29, e202301209.
- 11 Liu, Y.; Teng, L.; Lyu, Y.; Song, G.; Zhang, X. B.; Tan, W. Ratiometric Afterglow Luminescent Nanoplatform Enables Reliable Quantification and Molecular Imaging. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 2216.
- 12 Yang, L.; Gai, S.; Ding, H.; Yang, D.; Feng, L.; Yang, P. Recent Progress in Inorganic Afterglow Materials: Mechanisms, Persistent Luminescent Properties, Modulating Methods, and Bioimaging Applications. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2023, 11, 2202382.
- 13 Wang, Y.; Guo, H. Research Advances on Human-Eye-Sensitive Long Persistent Luminescence Materials. Front. Chem. 2021, 9, 654347.
- 14 Wang, Z.; Zhang, X. Y.; Mo, J. T.; Su, C. Y.; Pan, M. Ultralong Room-Temperature Phosphorescence from Organic–Inorganic Hybrid Perovskitoid Based on Metal-Organic Complex Component. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2023, 11, 2203114.
- 15 Forni, A.; Lucenti, E.; Botta, C.; Cariati, E. Metal Free Room Temperature Phosphorescence from Molecular Self-Interactions in the Solid State. J. Mater. Chem. C 2018, 6, 4603–4626.
- 16 Gan, N.; Shi, H.; An, Z.; Huang, W. Recent Advances in Polymer-Based Metal-Free Room-Temperature Phosphorescent Materials. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1802657.
- 17 Mukherjee, S.; Thilagar, P. Recent Advances in Purely Organic Phosphorescent Materials. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 10988–11003.
- 18 Guo, S.; Dai, W.; Chen, X.; Lei, Y.; Shi, J.; Tong, B.; Cai, Z.; Dong, Y. Recent Progress in Pure Organic Room Temperature Phosphorescence of Small Molecular Host–Guest Systems. ACS Mater. Lett. 2021, 3, 379–397.
- 19 Zhao, W.; He, Z.; Tang, B. Z. Room-Temperature Phosphorescence from Organic Aggregates. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2020, 5, 869–885.
- 20 Xu, S.; Chen, R.; Zheng, C.; Huang, W. Excited State Modulation for Organic Afterglow: Materials and Applications. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 9920–9940.
- 21 Zhao, W.; He, Z.; Lam, Jacky, W. Y.; Peng, Q.; Ma, H.; Shuai, Z.; Bai, G.; Hao, J.; Tang, B. Z. Rational Molecular Design for Achieving Persistent and Efficient Pure Organic Room-Temperature Phosphorescence. Chemistry 2016, 1, 592–602.
- 22 Hirata, S. Recent Advances in Materials with Room-Temperature Phosphorescence: Photophysics for Triplet Exciton Stabilization. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2017, 5, 1700116.
- 23 Gu, L.; Shi, H.; Bian, L.; Gu, M.; Ling, K.; Wang, X.; Ma, H.; Cai, S.; Ning, W.; Fu, L.; Wang, H.; Wang, S.; Gao, Y.; Yao, W.; Huo, F.; Tao, Y.; An, Z.; Liu, X.; Huang, W. Colour-Tunable Ultra-Long Organic Phosphorescence of a Single-Component Molecular Crystal. Nat. Photonics 2019, 13, 406–411.
- 24 Gu, L.; Shi, H.; Gu, M.; Ling, K.; Ma, H.; Cai, S.; Song, L.; Ma, C.; Li, H.; Xing, G.; Hang, X.; Li, J.; Gao, Y.; Yao, W.; Shuai, Z.; An, Z.; Liu, X.; Huang, W. Dynamic Ultralong Organic Phosphorescence by Photoactivation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 8425–8431.
- 25 Cai, S.; Ma, H.; Shi, H.; Wang, H.; Wang, X.; Xiao, L.; Ye, W.; Huang, K.; Cao, X.; Gan, N.; Ma, C.; Gu, M.; Song, L.; Xu, H.; Tao, Y.; Zhang, C.; Yao, W.; An, Z.; Huang, W. Enabling Long-Lived Organic Room Temperature Phosphorescence in Polymers by Subunit Interlocking. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4247.
- 26 Jia, W.; Wang, Q.; Shi, H.; An, Z.; Huang, W. Manipulating the Ultralong Organic Phosphorescence of Small Molecular Crystals. Chemistry 2020, 26, 4437–4448.
- 27 An, Z.; Zheng, C.; Tao, Y.; Chen, R.; Shi, H.; Chen, T.; Wang, Z.; Li, H.; Deng, R.; Liu, X.; Huang, W. Stabilizing Triplet Excited States for Ultralong Organic Phosphorescence. Nat. Mater. 2015, 14, 685–90.
- 28 Kabe, R.; Adachi, C. Organic Long Persistent Luminescence. Nature 2017, 550, 384–387.
- 29 Alam, P.; Cheung, T. S.; Leung, N. L. C.; Zhang, J.; Guo, J.; Du, L.; Kwok, R. T. K.; Lam, J. W. Y.; Zeng, Z.; Phillips, D. L.; Sung, H. H. Y.; Williams, I. D.; Tang, B. Z. Organic Long-Persistent Luminescence from a Single-Component Aggregate. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 3050–3062.
- 30 Li, W.; Li, Z.; Si, C.; Wong, M. Y.; Jinnai, K.; Gupta, A. K.; Kabe, R.; Adachi, C.; Huang, W.; Zysman-Colman, E.; Samuel, I. D. W. Organic Long-Persistent Luminescence from a Thermally Activated Delayed Fluorescence Compound. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 2003911.
- 31 Jinnai, K.; Kabe, R.; Lin, Z.; Adachi, C. Organic Long-Persistent Luminescence Stimulated by Visible Light in P-Type Systems Based on Organic Photoredox Catalyst Dopants. Nat. Mater. 2022, 21, 338–344.
- 32 Miao, Q.; Xie, C.; Zhen, X.; Lyu, Y.; Duan, H.; Liu, X.; Jokerst, J. V.; Pu, K. Molecular Afterglow Imaging with Bright, Biodegradable Polymer Nanoparticles. Nat. Biotechnol. 2017, 35, 1102–1110.
- 33 Palner, M.; Pu, K.; Shao, S.; Rao, J. Semiconducting Polymer Nanoparticles with Persistent Near-Infrared Luminescence for In Vivo Optical Imaging. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 11477–11480.
- 34 Liu, J.; Li, R.; Yang, B. Carbon Dots: A New Type of Carbon-Based Nanomaterial with Wide Applications. ACS Cent. Sci. 2020, 6, 2179–2195.
- 35 Kang, Z.; Lee, S. T. Carbon Dots: Advances in Nanocarbon Applications. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 19214–19224.
- 36 Xu, A.; Wang, G.; Li, Y.; Dong, H.; Yang, S.; He, P.; Ding, G. Carbon- Based Quantum Dots with Solid-State Photoluminescent: Mechanism, Implementation, and Application. Small 2020, 16, e2004621.
- 37 Wang, B.; Lu, S. The Light of Carbon Dots: From Mechanism to Applications. Matter 2022, 5, 110–149.
- 38 Jiang, K.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z.; Lin, H. Afterglow of Carbon Dots: Mechanism, Strategy and Applications. Mater. Chem. Front. 2020, 4, 386–399.
- 39 Wei, X.; Yang, J.; Hu, L.; Cao, Y.; Lai, J.; Cao, F.; Gu, J.; Cao, X. Recent Advances in Room Temperature Phosphorescent Carbon Dots: Preparation, Mechanism, and Applications. J. Mater. Chem. C 2021, 9, 4425–4443.
- 40 Sun, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhuang, J.; Zhang, H.; Hu, C.; Zheng, M.; Lei, B.; Liu, Y. The Room Temperature Afterglow Mechanism in Carbon Dots: Current State and Further Guidance Perspective. Carbon 2020, 165, 306–316.
- 41 Zhou, S.; Wang, F.; Feng, N.; Xu, A.; Sun, X.; Zhou, J.; Li, H. Room Temperature Phosphorescence Carbon Dots: Preparations, Regulations, and Applications. Small 2023, 19, 2301240.
- 42 Kai, J.; Yuhui, W.; Xiaolu, G.; Congzhong, C.; Hengwei, L. Facile, Quick, and Gram-Scale Synthesis of Ultralong-Lifetime Room-Temperature- Phosphorescent Carbon Dots by Microwave Irradiation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 6216–6220.
- 43 Han, B.; Lei, X.; Li, D.; Liu, Q.; Chen, Y.; Wang, J.; He, G. Shallow Traps in Carbon Nitride Quantum Dots to Achieve 6.47 s Ultralong Lifetime and Wavelength-Tunable Room Temperature Phosphorescence. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2023, 11, 2202293.
- 44 Sun, Y.; Liu, S.; Sun, L.; Wu, S.; Hu, G.; Pang, X.; Smith, A. T.; Hu, C.; Zeng, S.; Wang, W.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, M. Ultralong Lifetime and Efficient Room Temperature Phosphorescent Carbon Dots Through Multi-Confinement Structure Design. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5591.
- 45 Zhang, T.; Wu, X.; Liu, L.; Yang, Y.; Zhuang, J.; Li, Z.; Bi, H. Supramolecular Surface Engineering of Carbon Dots Enables Matrix-Free Room Temperature Phosphorescence. Chin. J. Chem. 2023, 41, 2330–2336.
- 46 Vandewal, K.; Albrecht, S.; Hoke, E. T.; Graham, K. R.; Widmer, J.; Douglas, J. D.; Schubert, M.; Mateker, W. R.; Bloking, J. T.; Burkhard, G. F.; Sellinger, A.; Frechet, J. M.; Amassian, A.; Riede, M. K.; McGehee, M. D.; Neher, D.; Salleo, A. Efficient Charge Generation by Relaxed Charge-Transfer States at Organic Interfaces. Nat. Mater. 2014, 13, 63–68.
- 47 Jailaubekov, A. E.; Willard, A. P.; Tritsch, J. R.; Chan, W. L.; Sai, N.; Gearba, R.; Kaake, L. G.; Williams, K. J.; Leung, K.; Rossky, P. J.; Zhu, X. Y. Hot Charge-Transfer Excitons Set the Time Limit for Charge Separation at Donor/Acceptor Interfaces in Organic Photovoltaics. Nat. Mater. 2013, 12, 66–73.
- 48 Deotare, P. B.; Chang, W.; Hontz, E.; Congreve, D. N.; Shi, L.; Reusswig, P. D.; Modtland, B.; Bahlke, M. E.; Lee, C. K.; Willard, A. P.; Bulovic, V.; Van Voorhis, T.; Baldo, M. A. Nanoscale Transport of Charge-Transfer States in Organic Donor-Acceptor Blends. Nat. Mater. 2015, 14, 1130–1134.
- 49 Jiang, K.; Wang, Y.; Lin, C.; Zheng, L.; Du, J.; Zhuang, Y.; Xie, R.; Li, Z.; Lin, H. Enabling Robust and Hour-Level Organic Long Persistent Luminescence from Carbon Dots by Covalent Fixation. Light Sci. Appl. 2022, 11, 80.
- 50 Hu, H.; Li, J.; Gong, X. Hour-Level Persistent Multicolor Phosphorescence Enabled by Carbon Dot-Based Nanocomposites through a Multi-Confinement-Based Approach. Small 2023, e2308457.
- 51 Di, Y.; Liu, W.; Shi, S.; Wu, T.; Wang, M.; Liu, X. One-Step Synthesis of Color-Tunable Carbon Dots-Based Organic Long Persistent Luminescence Materials. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 479, 147589.
- 52 Lin, Z.; Kabe, R.; Wang, K.; Adachi, C. Influence of Energy Gap Between Charge-Transfer and Locally Excited States on Organic Long Persistence Luminescence. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 191.
- 53 Nishimura, N.; Lin, Z.; Jinnai, K.; Kabe, R.; Adachi, C. Many Exciplex Systems Exhibit Organic Long-Persistent Luminescence. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2000795.
- 54 Bolton, O.; Lee, K.; Kim, H. J.; Lin, K. Y.; Kim, J. Activating Efficient Phosphorescence from Purely Organic Materials by Crystal Design. Nat. Chem. 2011, 3, 205–210.
- 55 Deng, Y.; Zhao, D.; Chen, X.; Wang, F.; Song, H.; Shen, D. Long Lifetime Pure Organic Phosphorescence Based on Water Soluble Carbon Dots. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 5751.
- 56 Jiang, K.; Gao, X.; Feng, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z.; Lin, H. Carbon Dots with Dual-Emissive, Robust, and Aggregation-Induced Room-Temperature Phosphorescence Characteristics. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 1263–1269.
- 57 Ding, H.; Yu, S. B.; Wei, J. S.; Xiong, H. M. Full-Color Light-Emitting Carbon Dots with a Surface-State-Controlled Luminescence Mechanism. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 484–491.
- 58 Siddique, A. B.; Hossain, S. M.; Pramanick, A. K.; Ray, M. Excitation Dependence and Independence of Photoluminescence in Carbon Dots and Graphene Quantum Dots: Insights into the Mechanism of Emission. Nanoscale 2021, 13, 16662–16671.
- 59 Pan, L.; Sun, S.; Zhang, A.; Jiang, K.; Zhang, L.; Dong, C.; Huang, Q.; Wu, A.; Lin, H. Truly Fluorescent Excitation-Dependent Carbon Dots and Their Applications in Multicolor Cellular Imaging and Multidimensional Sensing. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 7782–7787.
- 60 Jiang, K.; Sun, S.; Zhang, L.; Lu, Y.; Wu, A.; Cai, C.; Lin, H. Red, Green, and Blue Luminescence by Carbon Dots: Full-Color Emission Tuning and Multicolor Cellular Imaging. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 5360–5363.
- 61 Zheng, Y.; Arkin, K.; Hao, J.; Zhang, S.; Guan, W.; Wang, L.; Guo, Y.; Shang, Q. Multicolor Carbon Dots Prepared by Single-Factor Control of Graphitization and Surface Oxidation for High-Quality White Light-Emitting Diodes. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2021, 9, 2100688.
- 62 Jiang, K.; Wang, Y.; Cai, C.; Lin, H. Activating Room Temperature Long Afterglow of Carbon Dots via Covalent Fixation. Chem. Mater. 2017, 29, 4866–4873.
- 63
Jiang, K.; Sun, S.; Zhang, L.; Lu, Y.; Wu, A.; Cai, C.; Lin, H. Red, Green, and Blue Luminescence by Carbon Dots: Full-Color Emission Tuning and Multicolor Cellular Imaging. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 127, 5450–5453.
10.1002/ange.201501193 Google Scholar
- 64 Zheng, Y.; Wei, H.; Liang, P.; Xu, X.; Zhang, X.; Li, H.; Zhang, C.; Hu, C.; Zhang, X.; Lei, B.; Wong, W. Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhuang, J. Near-Infrared-Excited Multicolor Afterglow in Carbon Dots-Based Room-Temperature Afterglow Materials. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 22253–22259.
- 65 Yeh, T. F.; Teng, C. Y.; Chen, S. J.; Teng, H. Nitrogen-Doped Graphene Oxide Quantum Dots as Photocatalysts for Overall Water-Splitting Under Visible Light Illumination. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 3297–303.
- 66 Li, W.; Zhou, W.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhuang, J.; Liu, Y.; Lei, B.; Hu, C. A Universal Strategy for Activating the Multicolor Room-Temperature Afterglow of Carbon Dots in a Boric Acid Matrix. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 7278–7283.
- 67 Debye, P.; Edwards, J. O. Long-Lifetime Phosphorescence and the Diffusion Process. J. Chem. Phys. 1952, 20, 236–239.
- 68 Ohkita, H.; Sakai, W.; Tsuchida, A.; Yamamoto, M. Charge Recombination Luminescence via the Photoionization of a Dopant Chromophore in Polymer Solids. Macromolecules 1997, 30, 5376–5383.
- 69 Ohkita, H.; Sakai, W.; Tsuchida, A.; Yamamoto, M. Charge Recombination of Electron−Cation Pairs Formed in Polymer Solids at 20 K through Two-Photon Ionization. J. Phys. Chem. B 1997, 101, 10241–10247.
- 70 Jankus, V.; Chiang, C. J.; Dias, F.; Monkman, A. P. Deep Blue Exciplex Organic Light-Emitting Diodes with Enhanced Efficiency; P-type or E-type Triplet Conversion to Singlet Excitons? Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 1455–1459.
- 71 Park, Y. S.; Lee, S.; Kim, K. H.; Kim, S. Y.; Lee, J. H.; Kim, J. J. Exciplex-Forming Co-host for Organic Light-Emitting Diodes with Ultimate Efficiency. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2013, 23, 4914–4920.
- 72 Sarma, M.; Wong, K.-T. Exciplex: An Intermolecular Charge-Transfer Approach for TADF. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 19279–19304.
- 73 Noda, H.; Nakanotani, H.; Adachi, C. Excited State Engineering for Efficient Reverse Intersystem Crossing. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaao6910.
- 74 Mamada, M.; Tian, G.; Nakanotani, H.; Su, J.; Adachi, C. The Importance of Excited-State Energy Alignment for Efficient Exciplex Systems Based on a Study of Phenylpyridinato Boron Derivatives. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 12380–12384.
- 75 Cai, X.; Qiu, W.; Li, M.; Li, B.; Wang, Z.; Wu, X.; Chen, D.; Jiang, X.; Cao, Y.; Su, S.-J. Nonaromatic Amine Containing Exciplex for Thermally Activated Delayed Fluorescent Electroluminescence. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2019, 7, 1801554.




