Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Cover Picture
- Page: 1437
- First Published: 01 June 2024

A DNA-based force circuit has been designed to delve into the directional anisotropy inherent in protein-protein interactions. This innovative approach particularly focuses on the forced dissociation between the SET domain of the MLL1 protein and the histone H3 tail. It artistically represents this interaction through the metaphor of a loong and a phoenix entwined in a butterfly knot, encapsulating the concept of a multidirectional force field. Further elaboration on this concept can be found in the article by Yu et al. on pages 1456—1464.
Inside Cover Picture
Contents
Comprehensive Report
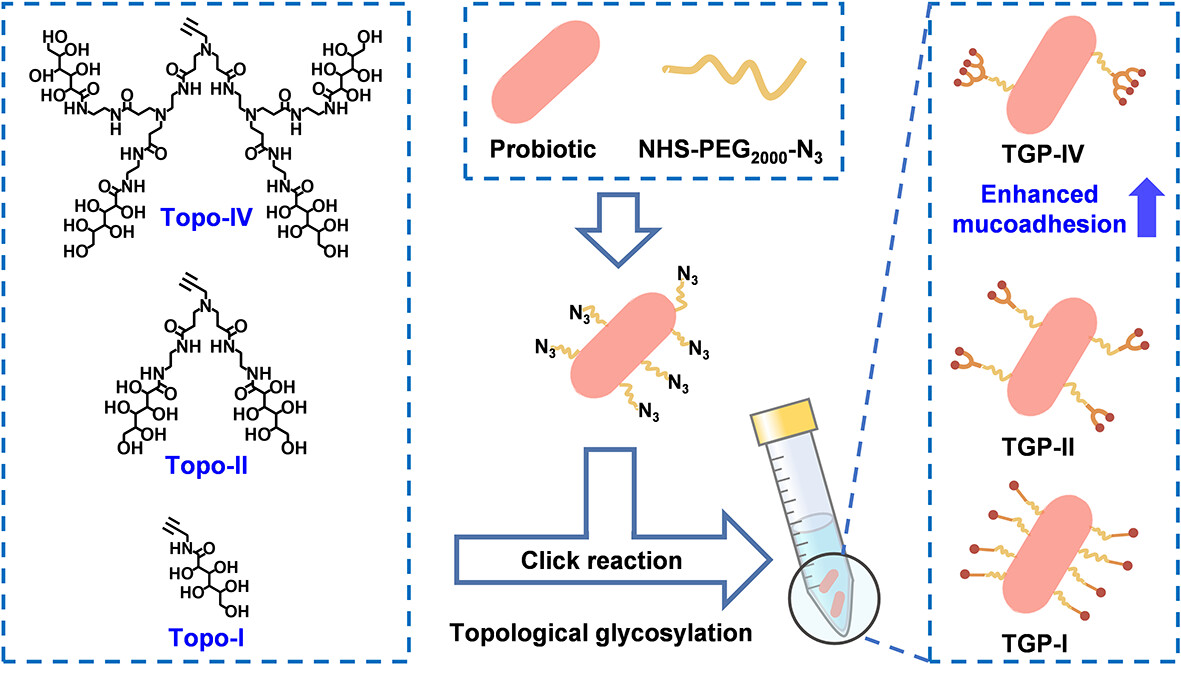
Surface Topological Glycosylation-Mediated Mucoadhesion of Bacteria
- Pages: 1447-1455
- First Published: 13 March 2024
Concise Reports
A DNA Force Circuit for Exploring Protein-Protein Interactions at the Single-Molecule Level†
- Pages: 1456-1464
- First Published: 23 February 2024
Free-Standing Multiscale Porous High Entropy NiFeCoZn Alloy as the Highly Active Bifunctional Electrocatalyst for Alkaline Water Splitting
- Pages: 1465-1473
- First Published: 13 March 2024
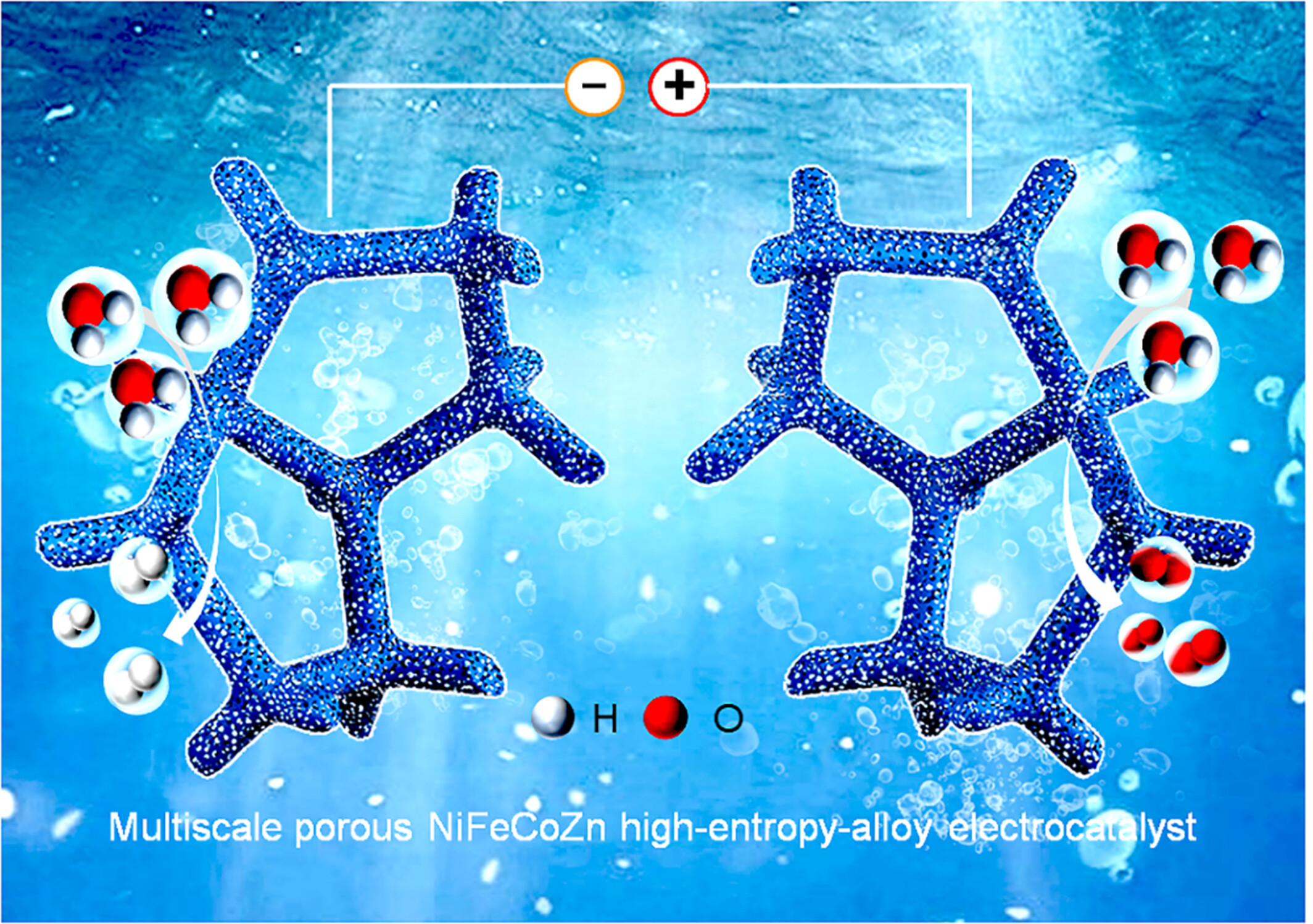
The free-standing multiscale porous NiFeCoZn high-entropy-alloy is in-situ constructed on the surface of NiZn intermetallic and Ni heterojunction over nickel foam (NiFeCoZn/NiZn-Ni/NF) by one scalable electroplating-annealing-etching protocal. The as-made NiFeCoZn/NiZn-Ni/NF fulfills the outstanding electrocatalytic performances with the small overpotentials (η500 = 184/348 mV), low Tafel slopes, as well as exceptional long-term catalytic durability for 400 h in alkaline solution toward both hydrogen evolution reaction and oxygen evolution reaction.
Chiral Phenol-2NO Ligand Cooperation with Achiral Organic Base in the Zn(II)-Catalyzed Asymmetric Alkylation Reaction of Indoles
- Pages: 1474-1480
- First Published: 01 March 2024
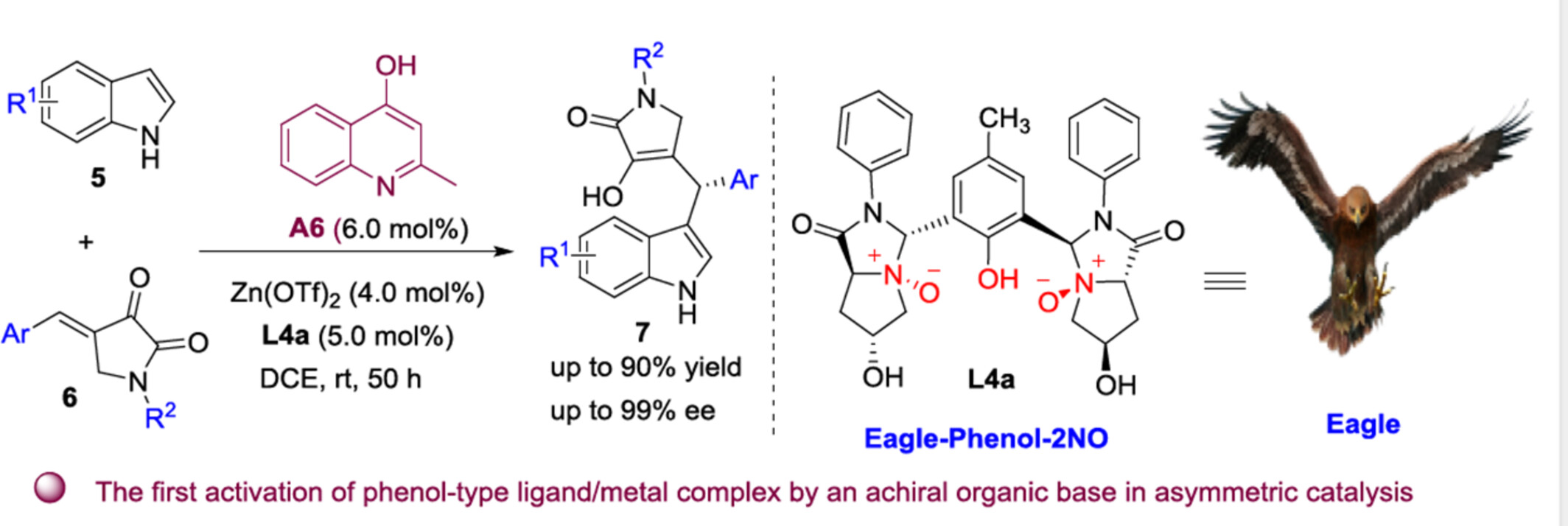
A new class of rigid-featured chiral tridentate Phenol-2NO ligands, that incorporate the advantages of both the phenol skeleton and pyrroloimidazolone-based N-oxide moiety, was rationally designed and developed. This represented the first activation of phenol-type ligand/metal complex by an achiral organic base as the additive in asymmetric catalysis.
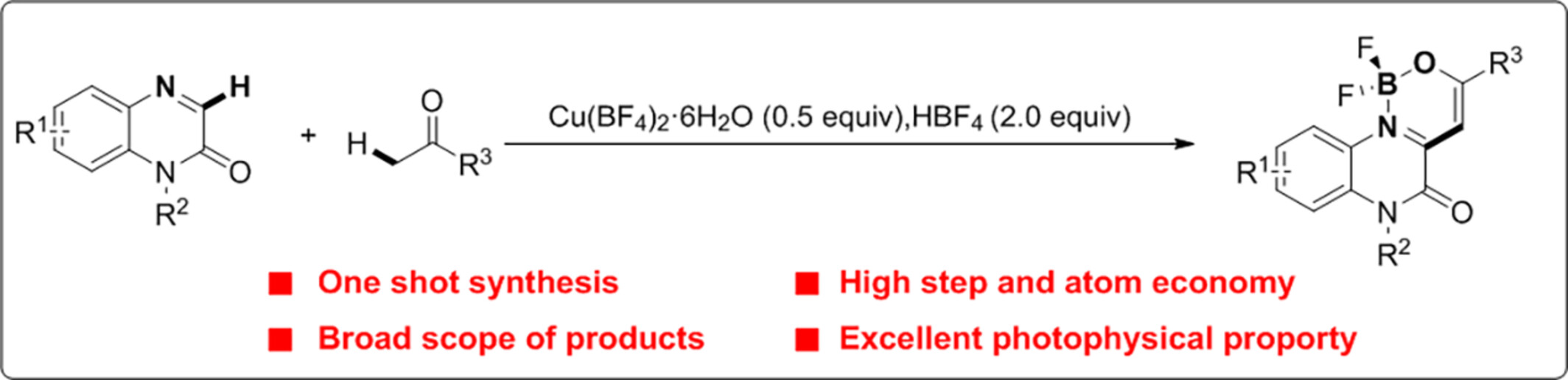
Feasible Synthesis of N,O-Bidentate Difluoroboron Chromophores through Direct Functionalization of Quinoxalin-2(1H)-ones with Ketones in One Shot
- Pages: 1481-1486
- First Published: 07 March 2024
An Assembly of Pyrano[3,2-b]indol-2-ones via NHC-Catalyzed [3 + 3] Annulation of Indolin-3-ones with Ynals
- Pages: 1487-1492
- First Published: 10 March 2024
![An Assembly of Pyrano[3,2-b]indol-2-ones via NHC-Catalyzed [3 + 3] Annulation of Indolin-3-ones with Ynals†](/cms/asset/30e30ddc-253e-429e-b90b-e407133cbd13/cjoc202300728-toc-0001-m.jpg)
N-Heterocyclic carbenes (NHCs) serve as organocatalysts for the [3 + 3] annulation of readily available N-Ts indolin-3-ones with ynals in the presence of oxidant condition via an intermediate alkynyl acylazolium. The method provides pyrano[3,2-b]indol-2-ones with moderate to high yields. Further transformations lead to diverse densely-functionalized carbazoles with potential electroluminescent materials and other bioactivities.
Artemordins A—S, Cadinane-Type Sesquiterpenoid Dimers from Artemisia ordosica and Their Antihepatoma Activities
- Pages: 1493-1508
- First Published: 07 March 2024
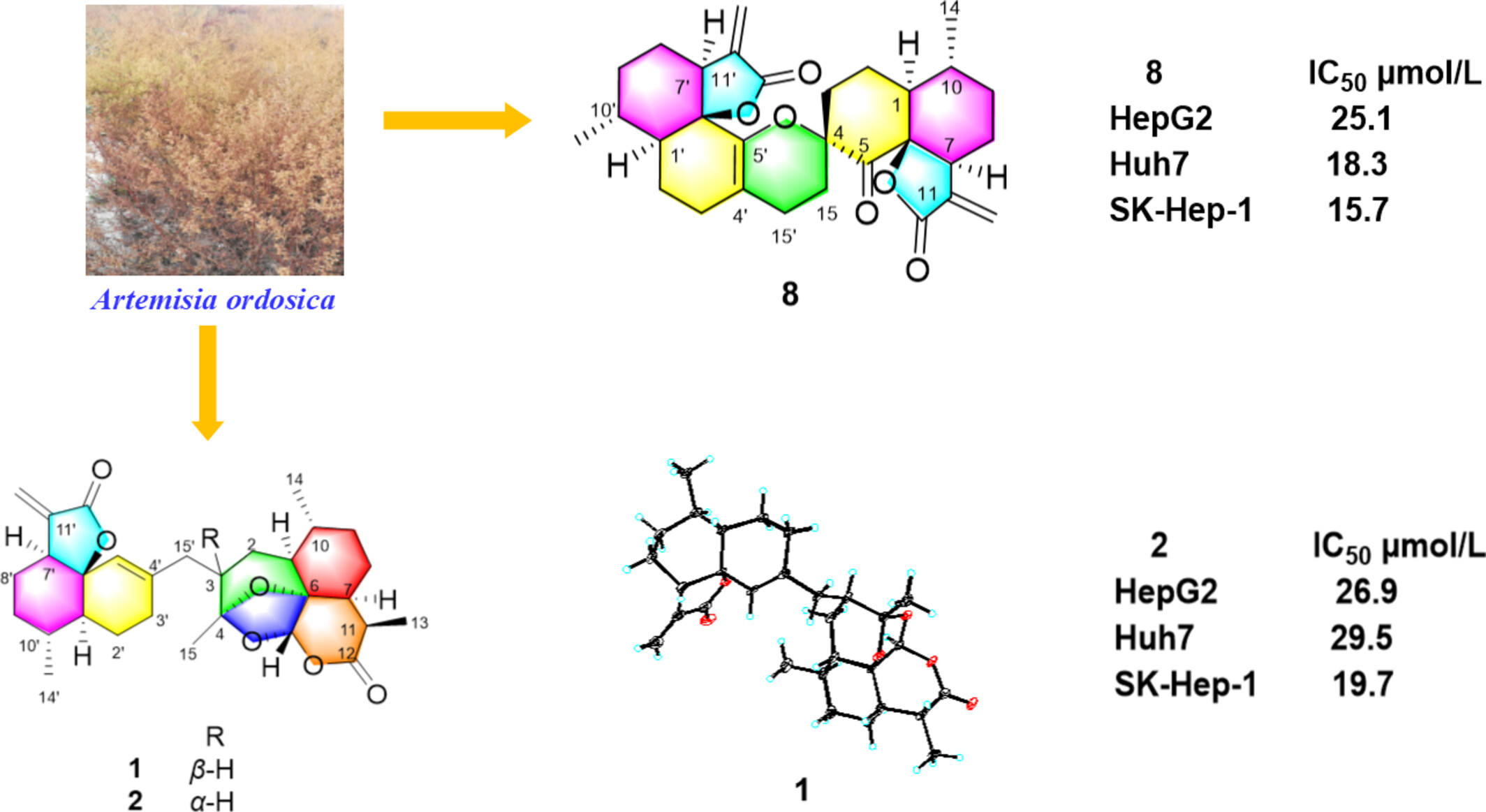
Nineteen new cadinane-involving sesquiterpenoid dimer, artemordins A—S (1—19) were isolated from Artemisia ordosica. Notably, artemordins A—F (1—6) were the first examples of two cadinane units connected by unprecedented C—C single bond with an oxido-rearranged 6/5/6/6 fused ring system; artemordins G—J (7—10) were biogenetically formed by [4 + 2] cycloaddition and possessed a novel 5/6/6/6/6/6/5—heptacyclic fused ring system. Artemordins B and H (2 and 8) exhibited inhibitory activities on three hepatoma cell lines with IC50 values of 26.9 and 25.1 μmol/L (HepG2), 29.5 and 18.3 μmol/L (Huh7), 19.7 and 15.7 μmol/L (SK-Hep-1).
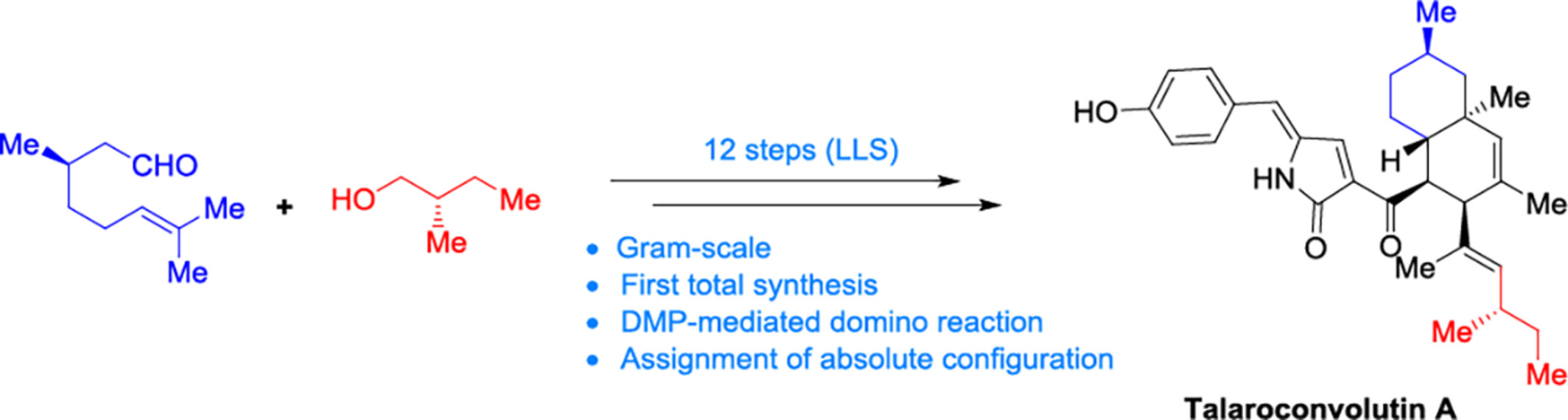
Total Synthesis and Stereochemical Assignment of Talaroconvolutin A and Talarofuranone: Gram-scale Synthesis of Ferroptosis Inducer Talaroconvolutin A
- Pages: 1509-1514
- First Published: 07 March 2024
Recent Advances
Critical Review
Flexible and Stretchable Electrodes for In Vivo Electrophysiological and Electrochemical Monitoring
- Pages: 1523-1545
- First Published: 25 March 2024

The emergence of flexible and stretchable electrodes offers seamless and conformable biological-electronic interfaces and has demonstrated significant advantages for in vivo electrochemical and electrophysiological monitoring. In this review, we summarize the recent advances in the fabrication and functionalization of flexible and stretchable electrodes, and highlight their application in monitoring bioelectrical and biochemical signals in vivo.
Inside Back Cover
Inside Back Cover
- Page: 1551
- First Published: 01 June 2024

Sugar moieties play a regulatory role in bacterial activity by mediating interactions with mucus. Bacterial surface is decorated with topological sugars that are functionalized with an alkyne group and varying branching patterns. As the sugar branching numbers increase, topologically glycosylated bacteria demonstrate enhanced adhesion to mucin and tissue mucus, which offers valuable insights into bacterial behavior manipulation through surface modifications. More details are discussed in the article by Liu et al. on page 1447—1455.
Back Cover
Back Cover
- Page: 1552
- First Published: 01 June 2024
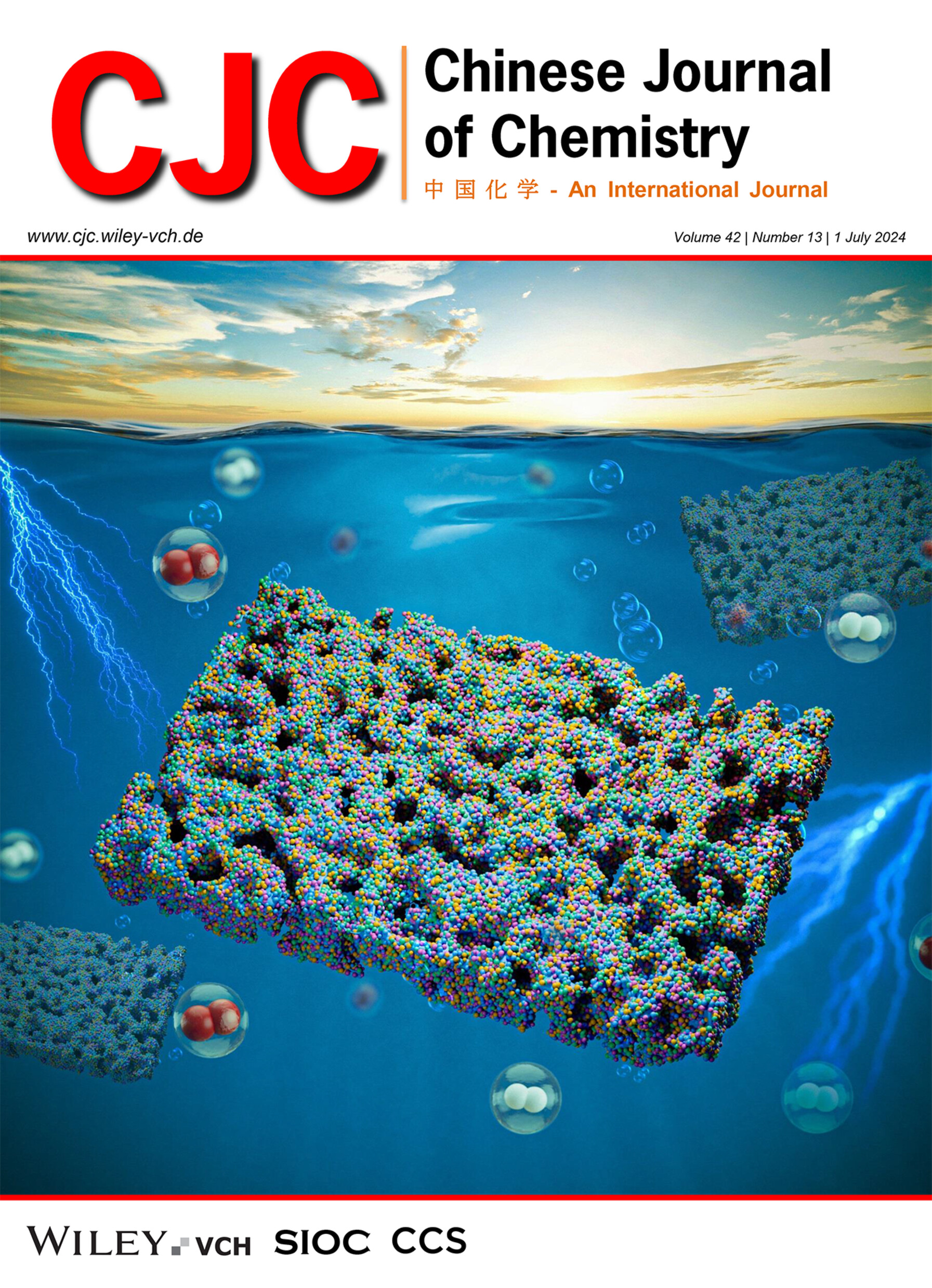
High entropy alloys as one class of multi-component catalysts have intrinsic advantages for water splitting electrolysis owning to the rich active sites and modulated electron structure. This work describes the simple and scalable fabrication of free-standing multiscale porous NiFeCoZn/NiZn-Ni/NF electrocatalysts with the outstanding bifunctional electrocatalytic performances toward overall water splitting in alkaline media. The coupling cooperation between the high-entropy effects and specific hierarchical porous architecture for NiFeCoZn/NiZn-Ni/NF, the overpotentials for HER and OER are greatly decreased along with the dramatic enhancement of the catalytic durability. Expressively, the electrolyzer constructed with NiFeCoZn/NiZn-Ni/NF as both cathode and anode exhibits a low cell voltage of 1.72 V to deliver the current density of 500 mA·cm–2 for overall water splitting, which is much lower than that of commercial Pt/C/NF(–)IIRuO2/NF(+). More details are discussed in the article by Xu et al. on page 1465—1473.