Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
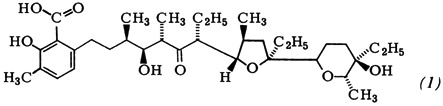
Graphical Abstract (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2/1979)
- First Published: February 1979
Reviews
Structure and Bonding in Cyclic Sulfur-Nitrogen Compounds
- Pages: 91-97
- First Published: February 1979
The scope and variety of sulfur-nitrolgen rings become more comprehensible on adopting the coordination number of sulfur as a classification principle. In compounds of two-coordinate sulfur (and nitrogen) the π-electrons are largely delocalized; the coordination number and bond length can be correlated in some compounds of sulfur with higher coordination number.
Empirical Parameters of Solvent Polarity as Linear Free-Energy Relationships
- Pages: 98-110
- First Published: February 1979
Effects of solvents on the rates of chemical reactions and on equilibria have long been known, but there are still no reliable methods for their description and prediction. Empirical parameters derived, e.g. from series of reactions, are of great value in this connection.
New Applications of Computers in Chemistry
- Pages: 111-123
- First Published: February 1979
The design of entirely new syntheses, and the classification and documentation of structures, substructures, and reactons are examples of new applications of computers to chemistry. The starting point is a mathematical model of constitutional chemistry based on the extension of the concept of isomerism to ensembles of molecules.
Activation Analysis—Its Present State of Development and Its Importance as an Analytical Tool
- Pages: 123-147
- First Published: February 1979
Communications
Synthesis of the Mast Cell Degranulating (MCD) Peptide from Bee Venom†
- Pages: 147-148
- First Published: February 1979
Potential value in the therapy of rheumatism and other inflammation processes could attach to the MCD peptide from bee venom if it were available in larger quantities. The peptide consists of 22 amino acids and contains two disulfide bridges. Its first total synthesis has now been accomplished.
Selective Electrochemical Removal of Protecting Groups in Nucleotide Synthesis
- Pages: 148-149
- First Published: February 1979
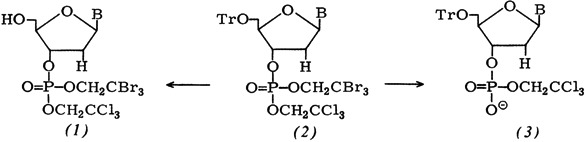
Selective removal of an ester group from the completely protected nucleoside 3′-phosphate (2) by electrochemical reduction solves a serious problem of nucleotide synthesis. Reaction (2) → (3) requires a potential of −0.5 V; (2) → (1) can be accomplished by acid hydrolysis. At −1.2 V the remaining ester groups are removed from (1).
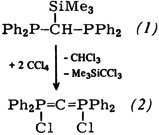
Di-tert-Butyl Acetylenedicarboxylate and Its Cyclotrimerization
- Pages: 149-150
- First Published: February 1979
Synthesis and Properties of Tetrabutylammonium Octaiododirhenate(III),[(n-C4H9)4N]2[Re2I8]
- Pages: 150-151
- First Published: February 1979
Long-Chain Alkylammonium Ions as Phase Transfer Reagents for the Synthesis of Mixed-Ligand Complexes of the Platinum Metals
- Pages: 151-152
- First Published: February 1979
Phase transfer reactions have great preparative potential in inorganic chemistry. Thus the first halo complexes of Os, Ir, Pt, and Re have now been synthesized in the presence of [(C12H25)3NH]HSO4; they contain not only fluorine but also bromine and iodine as ligands. The following anions are examples (XCL or Br):
Detection of Large-Ring Sulfur Molecules in Liquid Sulfur: Simple Preparation of S12, α-S18, and S20 from S8†
- Pages: 152-153
- First Published: February 1979
The molecular composition of liquid sulfur has been a topic of discussion for generations. It was known to contain the homocyclic species S6 and S7, as well as S8. The isolation of S12, α-S18, and S20, and the detection of Sx with x = 23—34 are new accomplishments.
23Na-NMR Study of the Competition of Biogenic Amines with Sodium Ion for Binding to Lasalocid (X-537A)†
- Pages: 153-154
- First Published: February 1979
Reversal of the Selectivity Principle in Free-Radical Addition to Alkenes†
- Pages: 154-155
- First Published: February 1979
The selectivity of alkenes in radical reactions increases with increasing reactivity, i.e. the most selective alkenes are the most reactive ones. This result could be of interest, say in radical polymerization.
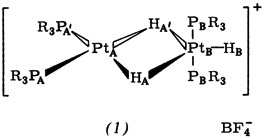
A New Cationic Binuclear Trihydrido Complex Containing One Four-and One Five-Coordinate Platinum Atom†
- Pages: 155-156
- First Published: February 1979
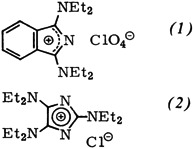
Stable Aza- and Diazacyclopentadienylium Salts†
- Pages: 156-157
- First Published: February 1979
An Example of the Equilibrium Ethylenehydridometal ⇌ Ethylmetal Complex†
- Pages: 157-158
- First Published: February 1979
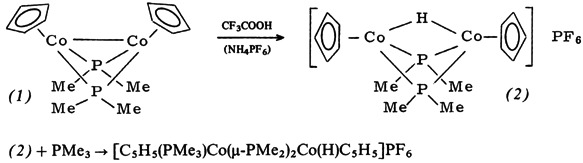
Stepwise Addition of a Lewis Acid and a Lewis Base to a Metal-Metal Bond†
- Pages: 158-159
- First Published: February 1979
Surprising Transformation of Azulene by Cycloaddition with 1-(Diethylamino)propyne†
- Pages: 161-162
- First Published: February 1979
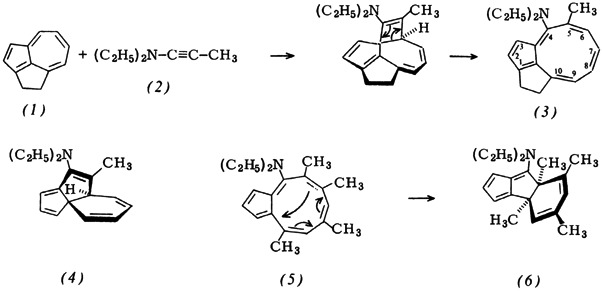
The cyclopentacyclononene derivative (3). the first compound to contain this ring system and also the first stable cyclononatetraene not to have an annelated benzene ring, has been synthesized from the “ethanoazulene” (1). This synthesis is possible because azulene reacts readily with the ynamine (2), to give the tricyclic species (4). Although 4,6,8-methylazulene initially gives the desired ring system (5), immediate transannular bonding occurs. The bracket in (1) prevents this reaction.
Facile Ring Enlargement of Azulene to Give the Cyclopentacyclononene System by Dipolar Cycloaddition†
- Pages: 162-163
- First Published: February 1979
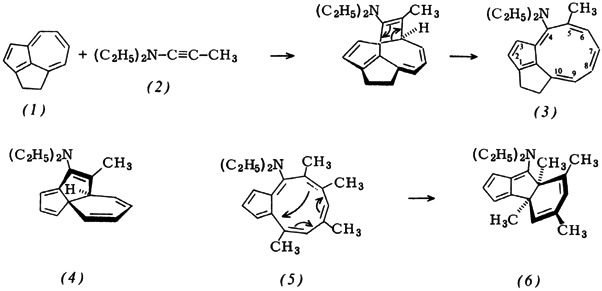
The cyclopentacyclononene derivative (3). the first compound to contain this ring system and also the first stable cyclononatetraene not to have an annelated benzene ring, has been synthesized from the “ethanoazulene” (1). This synthesis is possible because azulene reacts readily with the ynamine (2), to give the tricyclic species (4). Although 4,6,8-methylazulene initially gives the desired ring system (5), immediate transannular bonding occurs. The bracket in (1) prevents this reaction.
3-Bromo-3-methyl-2-trimethylsiloxy-1-butene—A New Cycloaddition Reagent†
- Pages: 163-164
- First Published: February 1979
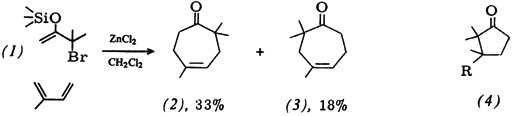
Faclie Regeneration of Carbonyl Compounds from 1,3-Dithiane 1-Oxides via 1-Ethoxy-1,3-dithianium Salts†
- Pages: 165-166
- First Published: February 1979
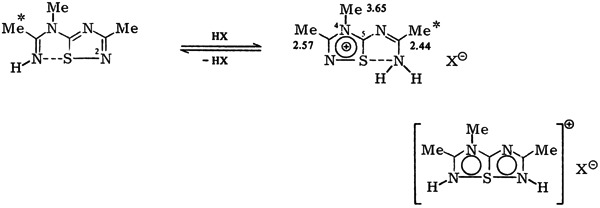
Bond Switch with Participation of π-Bonded SIV in Thiathiophthene-Analogous Systems†
- Pages: 166-167
- First Published: February 1979
Synchronous Mechanism of the 1,1-Cycloaddition of Nitrile Ylides to CC Double Bonds†
- Pages: 167-168
- First Published: February 1979
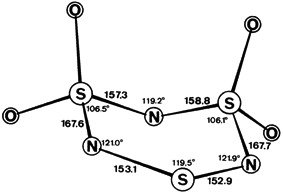
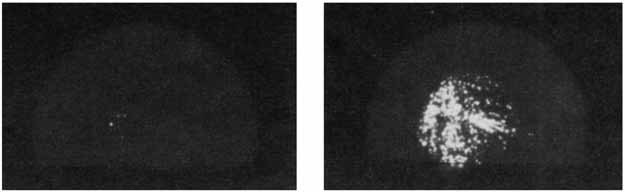
S as Simultaneous End-on and Side-on Bonded Ligand in the Novel Transition-Metal Complex [Mo4(NO)4S13]4−
as Simultaneous End-on and Side-on Bonded Ligand in the Novel Transition-Metal Complex [Mo4(NO)4S13]4−
- Pages: 168-169
- First Published: February 1979
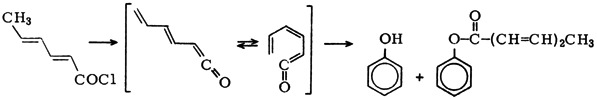
Flash Vacuum Thermolysis of Doubly Unsaturated Acyl Halides to Give Phenols†
- Page: 170
- First Published: February 1979
Book Reviews
Book Review: Koordinationschemische Katalyse Organischer Reaktionen (Coordination-Chemical Catalysis of Organic Reactions). By H. Pracejus
- Page: 171
- First Published: February 1979
Book Review: Fundamentals of Chemical Relaxation (Monographs in Modern Chemistry 10). By H. Strehlow and W. Knoche
- Page: 171
- First Published: February 1979
Book Review: Collision Spectroscopy. Ed. by R. G. Cooks
- Pages: 171-172
- First Published: February 1979





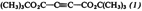
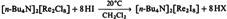
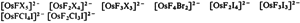
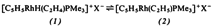
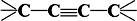
![S as Simultaneous End-on and Side-on Bonded Ligand in the Novel Transition-Metal Complex [Mo4(NO)4S13]4−](/cms/asset/bb2b3e7d-d0ff-4e8e-9c5f-b7dd7170e058/must001.jpg)
 ligands in the stabilization of unusual coordination compounds of transition metals.
ligands in the stabilization of unusual coordination compounds of transition metals.