Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Pictures
Cover Picture: Efficient Electrocatalysis for the Preparation of (Hetero)aryl Chlorides and Vinyl Chloride with 1,2-Dichloroethane (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 14/2019)
- Page: 4413
- First Published: 27 February 2019

“It′s a kind of magic” can be said of the bifunctional electrocatalysis strategy in which 1,2-dichloroethane (DCE) serves as both a chlorinating agent and a source of the useful byproduct vinyl chloride. In their Communication on page 4566 ff., N. Jiao et al. describe how HCl generated by catalytic dehydrogenation of DCE serves as the chloride source for the synthesis of value-added (hetero)aryl chlorides.
Inside Cover: Fcc versus Non-fcc Structural Isomerism of Gold Nanoparticles with Kernel Atom Packing Dependent Photoluminescence (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 14/2019)
- Page: 4414
- First Published: 03 March 2019

Just like magic cubes or transformers , metal nanoclusters (ultrasmall nanoparticles) can have the same compositions but different structures. This structural isomerism brings an excellent opportunity for structure–property investigations. In their Communication on page 4510 ff., Z. Wu et al. introduce an ion-induction synthesis method and obtain the second pair of genuine structural isomers of metal nanoclusters in the solid/liquid phase with distinctly different kernel atom packing (fcc vs. non-fcc), and reveal photoluminescence that is dependent on the kernel atom packing.
Inside Back Cover: Chemical and Topographical Single-Cell Imaging by Near-Field Desorption Mass Spectrometry (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 14/2019)
- Page: 4743
- First Published: 12 March 2019

A multimodal single-cell imaging platform greatly expands the abilities of mass spectrometry imaging (MSI) at nanoscale resolutions. In their Communication on page 4541 ff., W. Hang, X. Yan, J. Li, and co-workers report the development of a near-field desorption mass spectrometer and correlated chemical and topographical single-cell imaging. This high lateral resolution MSI technique allows the acquisition of more in-depth cellular information compared with current microscale laser-based MSI methods.
Back Cover: Photoelectrochemical C−H Alkylation of Heteroarenes with Organotrifluoroborates (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 14/2019)
- Page: 4744
- First Published: 27 February 2019

Light and electric current power the C−H alkylation of heteroaromatics under oxidant-free conditions. Organotrifluoroborates are converted into radicals that participate in intermolecular oxidative transformations without overoxidation to carbocations. As H.-C. Xu and co-workers describe in their Communication on page 4592 ff., this photoelectrochemical approach may provide a platform for further sustainable synthetic methodologies.
Frontispiece
Frontispiece: Second-Sphere Biomimetic Multipoint Hydrogen-Bonding Patterns to Boost CO2 Reduction of Iron Porphyrins
- First Published: 19 March 2019

CO2 Reduction Urea groups in an iron porphyrin catalyst give multipoint hydrogen-bonding stabilization of CO2. In their Communication on page 4504 ff., Z. Halime, A. Aukauloo et al. show that this catalyst enabled improved CO2 reduction.
Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract: Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 14/2019
- Pages: 4417-4431
- First Published: 19 March 2019
Corrigenda
Corrigendum: An Enantioconvergent and Concise Synthesis of Lasonolide A
- Page: 4431
- First Published: 19 March 2019
News
Spotlights on our sister journals: Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 14/2019
- Pages: 4434-4438
- First Published: 19 March 2019
Author Profile
News
Horst Pracejus Prize: A. Berkessel / Carl Duisberg Memorial Prize: S. Luber / GDCh Honorary Membership: F. Diederich
- Page: 4441
- First Published: 03 March 2019
Minireviews
Organic Solar Cells
Polymer Donors for High-Performance Non-Fullerene Organic Solar Cells
- Pages: 4442-4453
- First Published: 28 August 2018
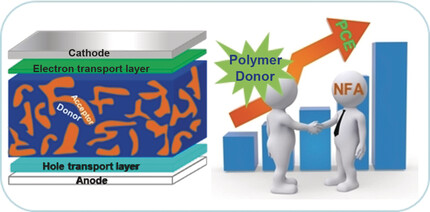
Polymer power: Polymer donors have shown remarkable photovoltaic performance in non-fullerene organic solar cells (OSCs). The molecular design strategies are analyzed in terms of developing suitable polymer donors for non-fullerene acceptors to further improve the power conversion efficiency (PCE) of non-fullerene organic solar cells.
Biocatalysis
Towards the Evolution of Artificial Metalloenzymes—A Protein Engineer's Perspective
- Pages: 4454-4464
- First Published: 15 November 2018
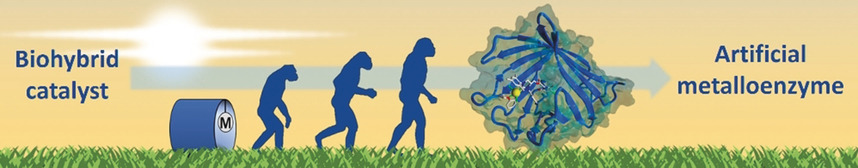
Evolution revolution: In the past, incorporating artificial cofactors into proteins hampered high-throughput approaches for the directed evolution of biohybrid catalysts. This Minireview provides an overview of the challenges, approaches, and success stories in the directed evolution of biohybrid catalysts and their transformation into highly specialized and enantioselective artificial metalloenzymes.
Reviews
Flexible Electronics
Recent Advances in Flexible Perovskite Solar Cells: Fabrication and Applications
- Pages: 4466-4483
- First Published: 17 October 2018
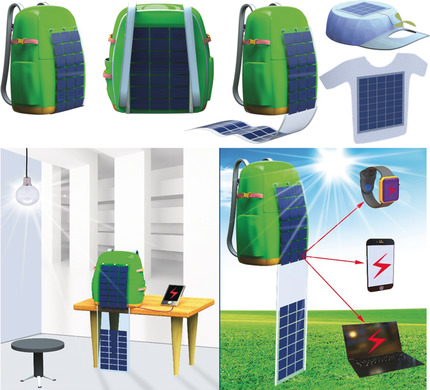
Flexible perovskite solar cells have attracted significant attention owing to their promising potential in practical applications. This Review discusses the prerequisite conditions for flexible perovskite solar cells, provides an outlook of flexible perovskite devices in portable electronic products, and estimates their production cost by roll-to-roll vacuum deposition for commercialization.
Water Splitting
Modulating Electronic Structures of Inorganic Nanomaterials for Efficient Electrocatalytic Water Splitting
- Pages: 4484-4502
- First Published: 01 October 2018
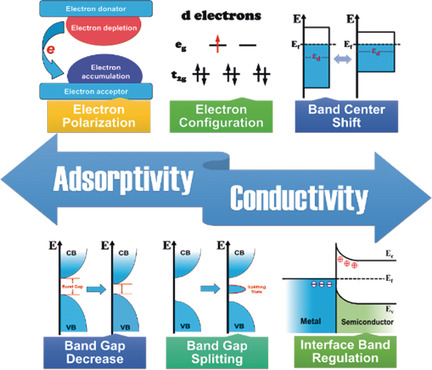
Making split happen: Strategies to regulate electronic structures of materials to optimize their electrocatalytic activities in water splitting are summarized in this Review. The structure–electronic-behavior–activity relationships are highlighted as well as current challenges on understanding the electronic behaviors.
Communications
CO2 Reduction
Second-Sphere Biomimetic Multipoint Hydrogen-Bonding Patterns to Boost CO2 Reduction of Iron Porphyrins
- Pages: 4504-4509
- First Published: 20 February 2019
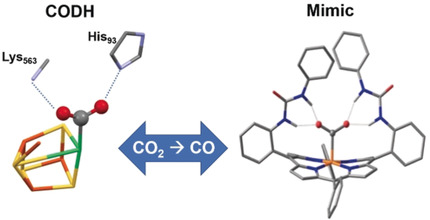
Like CODH: Urea groups at an iron porphyrin catalyst give multipoint hydrogen-bonding stabilization resembling that found in the CO2 adduct of carbon monoxide dehydrogenase (CODH). The catalyst gave improved CO2 reduction to CO. Entrapped water molecules within the molecular clefts were found to be the source of protons for the CO2 reduction.
Gold Nanoclusters | Very Important Paper
Fcc versus Non-fcc Structural Isomerism of Gold Nanoparticles with Kernel Atom Packing Dependent Photoluminescence
- Pages: 4510-4514
- First Published: 05 February 2019
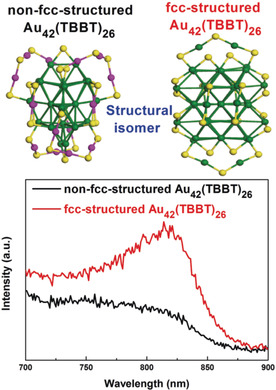
Cores and effect: A so-called “ion-induction” method gives a unique gold nanocluster with a twist mirror symmetry structure. The as-synthesized nanocluster has the same composition but a different packing of the core kernel atoms (fcc vs. non-fcc) with an existing gold nanocluster Au42(TBBT)26 (TBBT=4-tert-butylbenzenethiolate), and shows photoluminescence that is dependent on the kernel-atom packing.
Artificial Intelligence
Prediction of Major Regio-, Site-, and Diastereoisomers in Diels–Alder Reactions by Using Machine-Learning: The Importance of Physically Meaningful Descriptors
- Pages: 4515-4519
- First Published: 06 November 2018
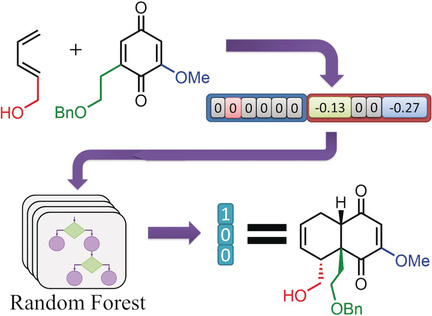
Machine learning can predict the major regio-, site-, and diastereoselective outcomes of Diels–Alder reactions better than standard quantum-mechanical methods (accuracies exceeding 90 %) provided that 1) the diene/dienophile substrates are represented by “physical-organic” descriptors reflecting the electronic and steric characteristics of their substituents and 2) the positions of such substituents relative to the reaction core are encoded (“vectorized”) in an informative way.
Chemical Systems
Propagation of Oscillating Chemical Signals through Reaction Networks
- Pages: 4520-4525
- First Published: 06 November 2018
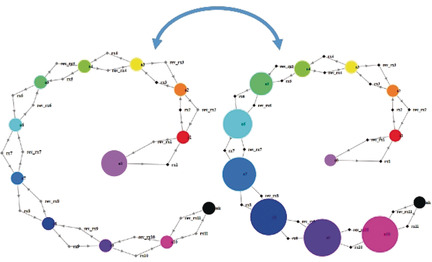
Reaction networks do not like high frequencies: Similar to electronic systems that can tune to and process signals of select frequencies, systems/networks of chemical reactions “propagate” oscillatory concentration inputs in a frequency-dependent manner. In particular, simulations in the Kinetix software reveal that for diverse system architectures oscillations are transmitted only up to a certain threshold value and are dampened for higher frequencies.
Immunochemistry
Development of α-Gal–Antibody Conjugates to Increase Immune Response by Recruiting Natural Antibodies
- Pages: 4526-4530
- First Published: 12 February 2019
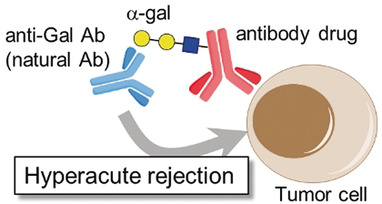
α-Gal–antibody (Ab) conjugates have been developed that can dramatically increase cellular cytotoxicity by recruiting natural Abs through the interaction between α-gal and anti-gal Abs. The potency of the α-gal–Ab conjugates increased with the amount of α-gal conjugated to the Ab. The method developed here will enable the re-development of Abs to improve their potency.
Photopharmacology
A Photoswitchable Agonist for the Histamine H3 Receptor, a Prototypic Family A G-Protein-Coupled Receptor
- Pages: 4531-4535
- First Published: 08 February 2019
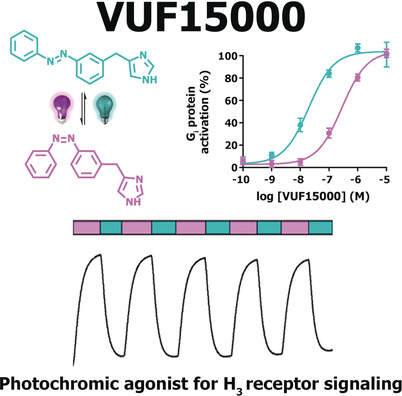
Shedding light on G-protein-coupled receptor activation: VUF15000 is a photoswitchable histamine H3 receptor agonist showing full Gi protein activation in both its trans and cis isomer. Moreover, it shows dynamic optical H3 receptor modulation in electrophysiology experiments. VUF15000 can serve as a valuable photochromic tool compound for unraveling the H3 receptor signaling cascade with spatiotemporal precision.
Solid-State Motion | Hot Paper
Spontaneous and Fast Molecular Motion at Room Temperature in the Solid State
- Pages: 4536-4540
- First Published: 28 January 2019
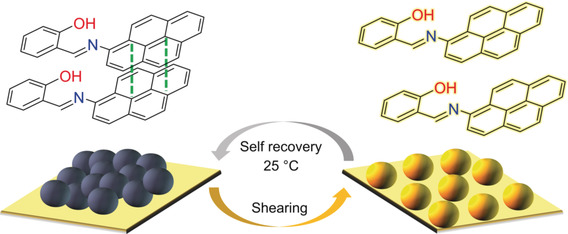
Beacons lit by molecular motion: Intermolecular forces drive the formation of π-π interactions even in the solid state. Shear forces/scratching disrupt the interactions, turning on emission. The quenched π-π-interactions quickly reform even in a film, allowing the visualization of the molecular motions. Theoretical calculations show that the formation of π-interactions is highly favorable and driving this motion.
Mass Spectrometry | Hot Paper
Chemical and Topographical Single-Cell Imaging by Near-Field Desorption Mass Spectrometry
- Pages: 4541-4546
- First Published: 02 January 2019
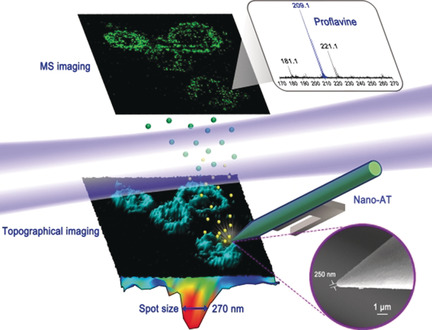
Multimodal single-cell imaging platform: A near-field desorption mass spectrometer has been developed for simultaneously acquiring nanoscale chemical and topographical information of single cells. The improved lateral resolution and detection sensitivity allow for more in-depth cellular information to be obtained than is possible with current microscale laser-based mass spectrometry imaging methods.
Drug Delivery
Release of Amino- or Carboxy-Containing Compounds Triggered by HOCl: Application for Imaging and Drug Design
- Pages: 4547-4551
- First Published: 20 February 2019
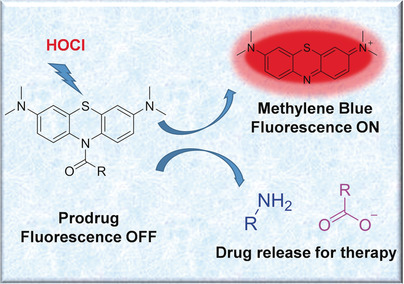
Triple action: An HOCl-responsive platform has been developed that integrates detection, imaging, and therapeutic functions. The probes derived from this platform can detect HOCl by using NIR emission in vitro and in vivo with high sensitivity and selectivity. Additionally, they rapidly release amino- or carboxy-containing compounds from prodrugs, during HOCl detection and imaging, to realize a therapeutic effect.
SuFEx Chemistry | Hot Paper
Bifluoride Ion Mediated SuFEx Trifluoromethylation of Sulfonyl Fluorides and Iminosulfur Oxydifluorides
- Pages: 4552-4556
- First Published: 10 February 2019
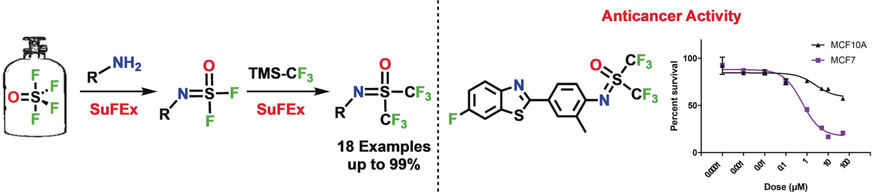
An expedient SuFEx trifluoromethylation of sulfonyl fluorides and iminosulfur oxyfluorides is described. The efficient S−F exchange with TMSCF3 is initiated by sub-stoichiometric quantities of bifluoride ion [FHF]− in anhydrous DMSO. The selective anticancer properties of previously inaccessible bis(trifluoromethyl)sulfur oxyimines are also demonstrated.
Biosensors
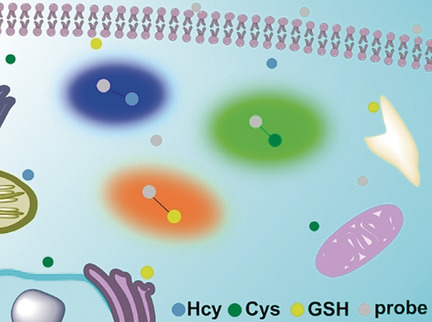
Simultaneous Visualization of Endogenous Homocysteine, Cysteine, Glutathione, and their Transformation through Different Fluorescence Channels
- Pages: 4557-4561
- First Published: 11 February 2019
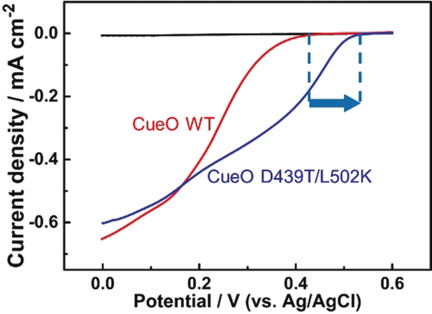
Protein Engineering
Directed Evolution of a Bacterial Laccase (CueO) for Enzymatic Biofuel Cells
- Pages: 4562-4565
- First Published: 28 January 2019
Organic Electrochemistry | Hot Paper
Efficient Electrocatalysis for the Preparation of (Hetero)aryl Chlorides and Vinyl Chloride with 1,2-Dichloroethane
- Pages: 4566-4570
- First Published: 21 January 2019
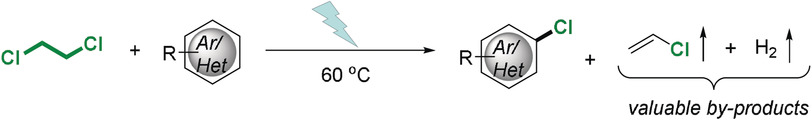
One stone, two birds: In a novel bifunctional electrocatalytic reaction, the catalytic dehydrochlorination of 1,2-dichloroethane occurs at the cathode simultaneously with the oxidative chlorination of a (hetero)arene at the anode. The HCl released at the cathode serves as the chloride source at the anode.
Electrocatalysis
A Dissolution/Precipitation Equilibrium on the Surface of Iridium-Based Perovskites Controls Their Activity as Oxygen Evolution Reaction Catalysts in Acidic Media
- Pages: 4571-4575
- First Published: 23 January 2019
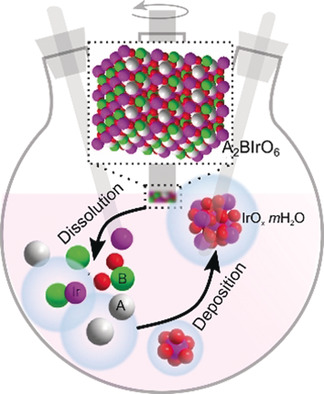
Dissolution/precipitation equilibrium: By coupling electrochemical measurements with iridium dissolution studies, it is shown that the deposition of an IrOx layer on the surface of IrV-based perovskites is responsible for their OER activity. The iridium Pourbaix diagram is reconstructed to help guide future research in controlling the dissolution/precipitation equilibrium of iridium species for the design of better Ir-based OER catalysts.
Metal Ceramics
A Series of MAX Phases with MA-Triangular-Prism Bilayers and Elastic Properties
- Pages: 4576-4580
- First Published: 06 February 2019
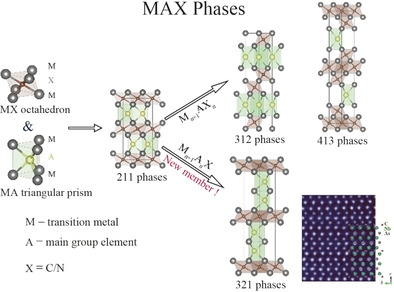
Get the MAX: A series of MAX phases (M=transition metals, A=main group elements, and X=C/N) with outstanding elastic properties, named 321 phases, is added to the family of MAX phases. 321 phases share common symmetry and constituent units with the conventional Mn+1AXn phases. 321 phases are the first series of MAX phases that can be expressed as Mn+1AnX with n>1.
Polymers
Metabolically Active, Fully Hydrolysable Polymersomes
- Pages: 4581-4586
- First Published: 05 February 2019
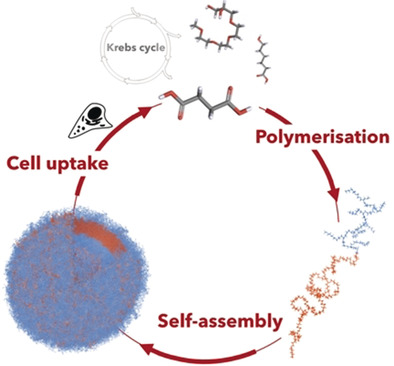
Class act: The synthesis and aqueous self-assembly of a new class of amphiphilic aliphatic polyesters are presented. They self-assemble into biodegradable polymersomes capable of entering cells. Their degradation products are bioactive, giving rise to differentiated cellular responses inducing stromal cell proliferation and macrophage apoptosis. Both effects emerge only when the copolymers enter cells as polymersomes.
Photocatalysis
Stacking-Layer-Number Dependence of Water Adsorption in 3D Ordered Close-Packed g-C3N4 Nanosphere Arrays for Photocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution
- Pages: 4587-4591
- First Published: 07 February 2019
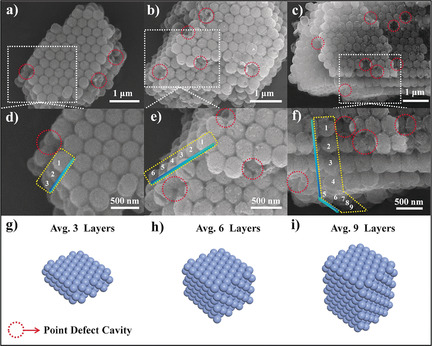
Finding the right number: 3D ordered close-packed g-C3N4 nanosphere arrays are constructed by a two-step nanocasting method. Through a precise control of the average nanosphere stacking layer number in the arrays, a stacking-layer-number dependence of water adsorption is revealed, which subsequently leads to a remarkably improved photocatalytic hydrogen evolution on the optimized sample.
Photoelectrochemistry | Hot Paper
Photoelectrochemical C−H Alkylation of Heteroarenes with Organotrifluoroborates
- Pages: 4592-4595
- First Published: 16 January 2019

A radical approach: A photoelectrochemical method has been developed for the C−H alkylation of heteroarenes with organotrifluoroborates under oxidant-free conditions. A variety of heteroarenes can be functionalized with primary, secondary, and tertiary alkyl groups with excellent regio- and chemoselectivity.
Counterion-Directed Catalysis
Practical and Scalable Kinetic Resolution of BINOLs Mediated by a Chiral Counterion
- Pages: 4596-4600
- First Published: 19 February 2019
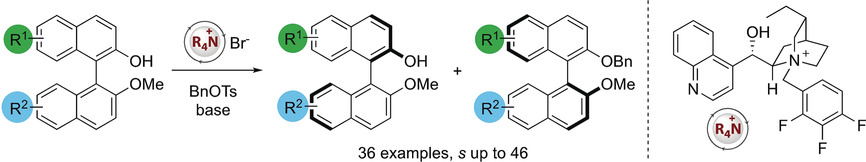
BINOLs are valuable building blocks, chiral ligands, and catalysts that are effective across a remarkable range of different chemical transformations. Here an ammonium salt catalyzed kinetic resolution of racemic BINOLs with benzyl tosylate is demonstrated. This is a scalable and practical process that can be applied across >30 different C2- and non-C2-symmetric BINOLs.
Biocatalysis | Hot Paper
Interfacing Formate Dehydrogenase with Metal Oxides for the Reversible Electrocatalysis and Solar-Driven Reduction of Carbon Dioxide
- Pages: 4601-4605
- First Published: 06 February 2019
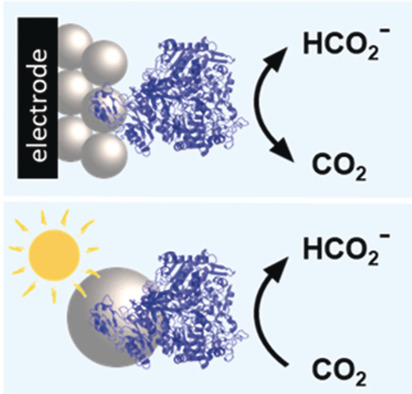
Electro- and solar-driven CO2 utilization: Reversible electrocatalysis with formate dehydrogenase on porous metal oxides is established. A self-assembled colloidal system containing formate dehydrogenase immobilized on dye-sensitized TiO2 provides a benchmark for the selective reduction of CO2 to formate in aqueous solution.
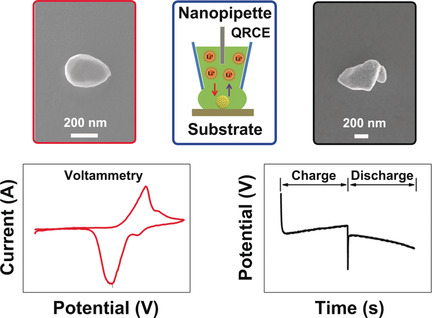
Electrochemistry
Correlative Electrochemical Microscopy of Li-Ion (De)intercalation at a Series of Individual LiMn2O4 Particles
- Pages: 4606-4611
- First Published: 05 February 2019
Borylation
Migratory Arylboration of Unactivated Alkenes Enabled by Nickel Catalysis
- Pages: 4612-4616
- First Published: 10 February 2019
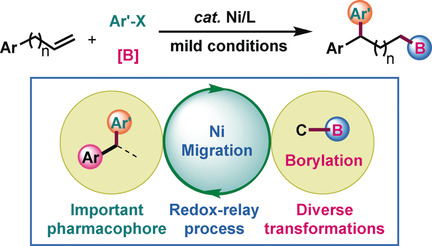
An unprecedented arylboration of unactivated terminal alkenes, featuring 1,n-regioselectivity (n>2), has been achieved by nickel catalysis. An array of valuable alkylboronic esters are prepared with this method. Mechanism studies indicate that a nickel migration and a selective bond-formation step are involved in this reaction.
Solid Oxide Electrolysis Cells
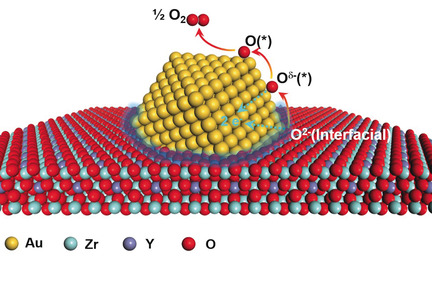
Oxygen Evolution Reaction over the Au/YSZ Interface at High Temperature
- Pages: 4617-4621
- First Published: 08 February 2019
Hydrogen Production
Organic Proton-Buffer Electrode to Separate Hydrogen and Oxygen Evolution in Acid Water Electrolysis
- Pages: 4622-4626
- First Published: 31 January 2019
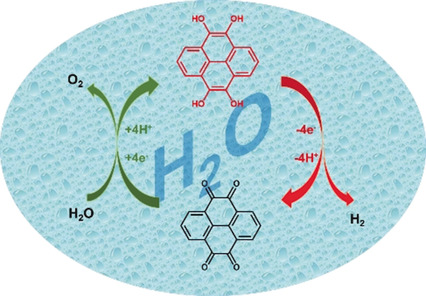
A battery electrode of pyrene-4,5,9,10-tetraone is used as a solid-state proton buffer to separate the hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) and oxygen evolution reaction (OER) during acidic water electrolysis in space and time, providing a flexible and membrane-free architecture for electrochemical water splitting.
Syngas Conversion
Direct Production of Higher Oxygenates by Syngas Conversion over a Multifunctional Catalyst
- Pages: 4627-4631
- First Published: 01 February 2019
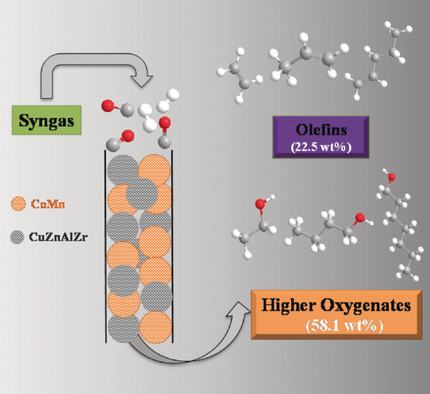
A stable multifunctional catalyst composed of CoMn oxides and CuZnAlZr oxides was developed for direct conversion of syngas to higher oxygenates and olefins with a total selectivity of 80.6 wt % at a CO conversion of 29.0 %. The interaction manner of the two components plays a crucial role in suppressing C1 products formation and enhancing the selectivity to higher oxygenates.
Cancer Therapy
Microenvironment-Induced In Situ Self-Assembly of Polymer–Peptide Conjugates That Attack Solid Tumors Deeply
- Pages: 4632-4637
- First Published: 29 January 2019
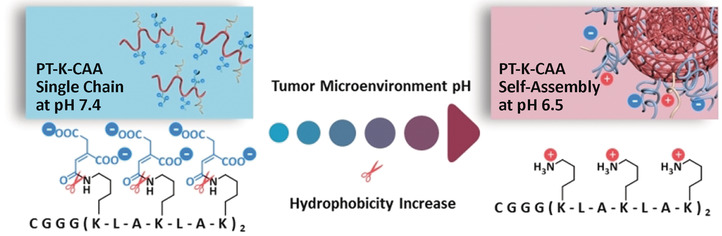
Reaching new depths: Polymer–peptide conjugates (PPCs) designed to undergo an acid-induced increase in hydrophobicity with a narrow pH-response range (from pH 7.4 to 6.5) underwent in vivo self-assembly in the tumor microenvironment (see picture). The PPCs in single-chain form can penetrate deeply into the tumor and self-assemble into nanoaggregates at molecular concentrations around the IC50 values of the PPCs for enhanced cancer therapy.
Antitumor Agents
Restraining Cancer Cells by Dual Metabolic Inhibition with a Mitochondrion-Targeted Platinum(II) Complex
- Pages: 4638-4643
- First Published: 28 January 2019
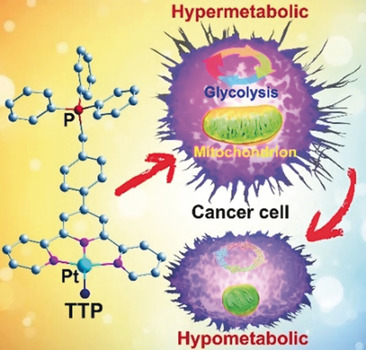
Blocking both avenues: A triphenylphosphonium-modified terpyridine platinum(II) complex (see structure) exhibited enhanced cytotoxicity against human ovarian cancer cells and showed strong inhibitory effects on both mitochondrial and glycolytic metabolisms. The morphology and function of mitochondria were severely damaged and the levels of mitochondrial and cellular reactive oxygen species decreased, thus inducing the cells to enter a hypometabolic state.
Self-Assembly
Modular Design of Noble-Metal-Free Mixed Metal Oxide Electrocatalysts for Complete Water Splitting
- Pages: 4644-4648
- First Published: 07 February 2019
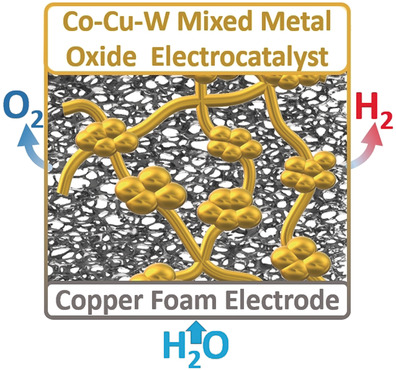
Efficient electrochemical water splitting is achieved by hydrothermal deposition of a bifunctional mixed metal oxide electrocatalyst on copper foam electrodes. Individual metal oxide components are chosen for catalytic activity, electrical conductivity, and structural/chemical stability. The modular synthesis based on molecular precursors could lead to a new class of multifunctional catalysts for challenging energy conversion and storage reactions.
Metal–Organic Polyhedra | Hot Paper
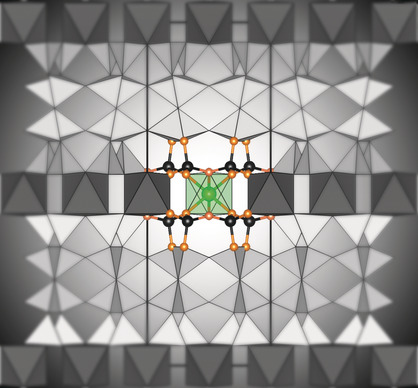
From Octahedral to Icosahedral Metal–Organic Polyhedra Assembled from Two Types of Polyoxovanadate Clusters
- Pages: 4649-4653
- First Published: 07 February 2019
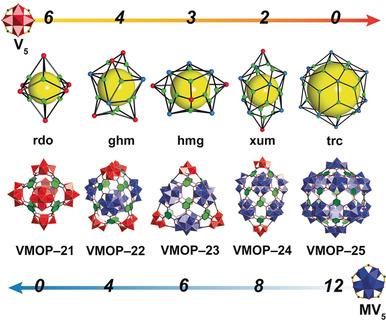
Get the MOP: The concept of reticular chemistry is used for the design of metal–organic polyhedra (MOPs) leading to a sequence of theoretically expected and experimentally characterized 3-coordinated, 4-coordinated and 5-coordinated MOPs based on polyoxovanadate building blocks that all obey the minimal transitivity (simplest possible) principle.
Gene Therapy
Towards DNA Nanomachines for Cancer Treatment: Achieving Selective and Efficient Cleavage of Folded RNA
- Pages: 4654-4658
- First Published: 28 January 2019
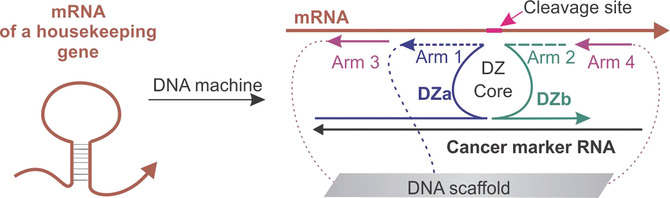
A mean machine: A deoxyribozyme-based DNA nanomachine (DNA machine) was developed to bind a fragment of a housekeeping gene mRNA using arms 1–4 and cleave it only in the presence of the cancer marker N-Myc (see picture). The DNA machine was equipped with RNA-binding functions for efficient unwinding of folded RNA and can be seen as an initial step towards the development of anticancer gene-therapy agents based on multifunctional DNA associations.
Controlled Release
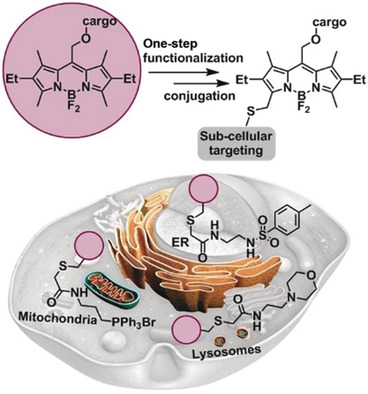
Organelle-Targeted BODIPY Photocages: Visible-Light-Mediated Subcellular Photorelease
- Pages: 4659-4663
- First Published: 07 February 2019
Hydrogenation
Spiro-Bicyclic Bisborane Catalysts for Metal-Free Chemoselective and Enantioselective Hydrogenation of Quinolines
- Pages: 4664-4668
- First Published: 14 February 2019
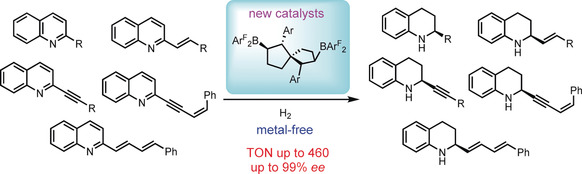
B,B bicycles: A series of C2-symmetric spiro-bicyclic bisboranes has been prepared. These bisboranes demonstrate highly effective and selective asymmetric hydrogenation of quinolines. The exceedingly broad functional-group tolerance allows access to various enantioenriched and functionalized tetrahydroquinilines, which are inaccessible by previous methods using either borane or transition-metal catalysts.
Electrocatalysis | Hot Paper
Aqueous CO2 Reduction with High Efficiency Using α-Co(OH)2-Supported Atomic Ir Electrocatalysts
- Pages: 4669-4673
- First Published: 06 February 2019
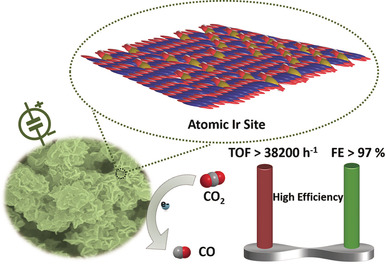
High-density atomic Ir supported on α-Co(OH)2 had outstanding performance for CO2 reduction to CO. The faradaic efficiency can reach 97.6 % with a TOF of 38 290 h−1. The high catalytic activity is attributed to more active sites for CO2 adsorption and activation and the higher efficiency in stabilizing the CO2.− intermediate.
Fluorogenic Probes
Illuminating the Function of the Hydroxyl Radical in the Brains of Mice with Depression Phenotypes by Two-Photon Fluorescence Imaging
- Pages: 4674-4678
- First Published: 09 February 2019
Hydrogen Evolution Reaction | Hot Paper
CoP-Doped MOF-Based Electrocatalyst for pH-Universal Hydrogen Evolution Reaction
- Pages: 4679-4684
- First Published: 04 February 2019
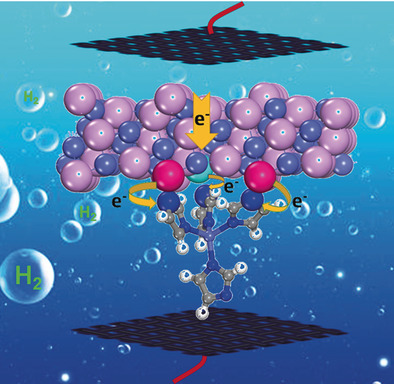
Co-based MOF nanorods have been doped with CoP species through controlled partial phosphorization to promote electron transfer from CoP to Co-MOF and achieve the optimal free energy of hydrogen adsorption. The resulting CoP/Co-MOF hybrid exhibits extraordinary performance toward HER including pH-universal Pt-like activity and high stability.
High-Pressure Chemistry
Open-Shell 3d Transition Metal Nitridophosphates MIIP8N14 (MII=Fe, Co, Ni) by High-Pressure Metathesis
- Pages: 4685-4689
- First Published: 15 October 2018
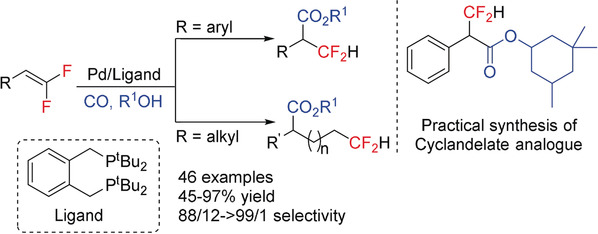
Fluoroalkenes
Pd-Catalyzed Selective Carbonylation of gem-Difluoroalkenes: A Practical Synthesis of Difluoromethylated Esters
- Pages: 4690-4694
- First Published: 19 February 2019
Silacycles
Rhodium-Catalyzed Reaction of Silacyclobutanes with Unactivated Alkynes to Afford Silacyclohexenes
- Pages: 4695-4699
- First Published: 11 February 2019
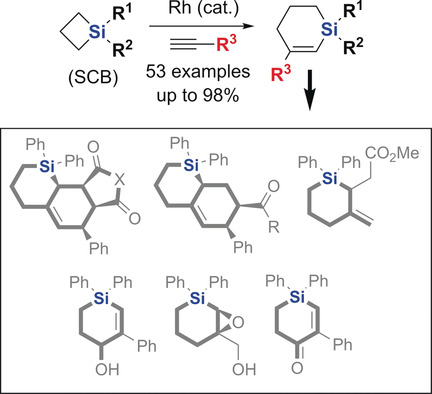
Centered on Si: A Rh-catalyzed reaction of silacyclobutanes (SCBs) with unactivated alkynes has been developed to form silacyclohexenes with high chemoselectivities. The approach tolerates a range of functionalities on the alkynes and silicon. Good enantioselectivities (e.r. up to 91.9) at the stereogenic silicon center were achieved using a newly synthesized chiral phosphoramidite ligand.
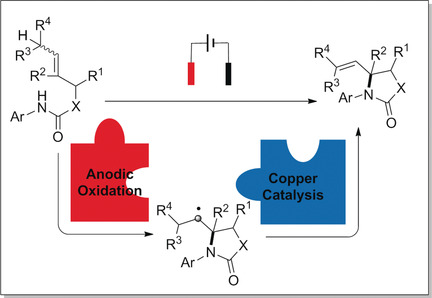
Electrochemical Organic Synthesis
Formal Aza-Wacker Cyclization by Tandem Electrochemical Oxidation and Copper Catalysis
- Pages: 4700-4704
- First Published: 30 January 2019
Dual Catalysis | Very Important Paper
Dynamic Kinetic Resolution of Aldehydes by Hydroacylation
- Pages: 4705-4709
- First Published: 10 February 2019

Dynamic duo: Racemic α-allyl aldehydes undergo stereoconvergent hydroacylation to generate α,γ-disubstituted cyclopentanones with high diastereo- and enantioselectivities. In this dynamic kinetic resolution, a primary amine catalyst racemizes the aldehyde substrate via enamine formation and hydrolysis while a rhodium catalyst promotes cyclization.
Synthetic Methods
Regioselectivity Switch in Palladium-Catalyzed Allenylic Cycloadditions of Allenic Esters: [4+1] or [4+3] Cycloaddition/Cross-Coupling
- Pages: 4710-4713
- First Published: 11 February 2019
![Regioselectivity Switch in Palladium-Catalyzed Allenylic Cycloadditions of Allenic Esters: [4+1] or [4+3] Cycloaddition/Cross-Coupling](/cms/asset/5d81e66a-f94e-4e86-a039-000833798020/anie201901511-toc-0001-m.jpg)
Switch it: The use of metal-butadienyl species in a cycloaddition is exemplified by the first Pd-catalyzed asymmetric allenylic [4+1] cycloaddition. Notably, tuning the Pd catalysts switched the reactivity toward an unprecedented [4+3] cycloaddition/cross-coupling. These reactions lead to diverse and valuable carbocycles and heterocycles, and also provide a straightforward synthesis to [3]dendralenes.
Atropselective Synthesis
Atropselective Dibrominations of a 1,1′-Disubstituted 2,2′-Biindolyl with Diverging Point-to-Axial Asymmetric Inductions. Deriving 2,2′-Biindolyl-3,3′-diphosphane Ligands for Asymmetric Catalysis
- Pages: 4714-4719
- First Published: 16 January 2019
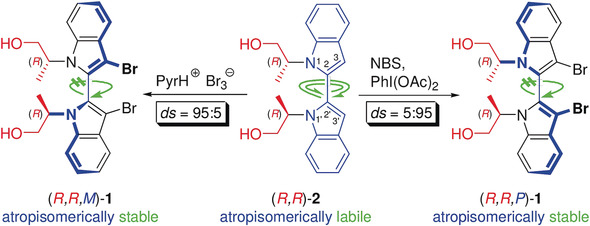
Locking a labile atropisomer: The biindolyl (R,R)-2 consists of diastereomeric atropisomers, which interconvert on the NMR timescale at +30 °C but not at −10 °C. (R,R)-2 was dibrominated providing the biindolyls 1 (M)- or (P)-selectively, depending on the achiral reagent. The two dibromides were elaborated into atropisomerically pure biindolyldiphosphanes, which induced higher ee values than BINAP in some Ru-catalyzed β-ketoester hydrogenations.
Solvation Dynamics
Mechanism-Dependent Modulation of Ultrafast Interfacial Water Dynamics in Intrinsically Disordered Protein Complexes
- Pages: 4720-4724
- First Published: 31 January 2019
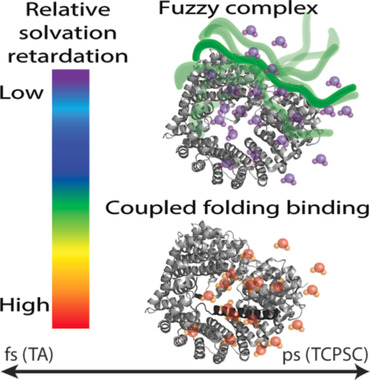
The dance of water: Water dynamics at the interface of intrinsically disordered proteins was studied on the femto- to nanosecond timescale by using a combination of advanced site-specific spectroscopic tools. The results offer new insight into the relationship between solvation dynamics and the binding mechanism of proteins of central relevance to nuclear transport.
Radical Nanoparticles | Hot Paper
Ultra-Fast Synthesis of Multivalent Radical Nanoparticles by Ring-Opening Metathesis Polymerization-Induced Self-Assembly
- Pages: 4725-4731
- First Published: 09 January 2019

Particularly radical: Radical core–shell nanoparticles can be synthesized by ring-opening metathesis polymerization-induced self-assembly (ROMPISA). The radical nanoparticles exhibited high chemoselectivity, catalytic, and recycling capacity in oxidation reactions, and biocompatibility and antioxidant activity in vitro.
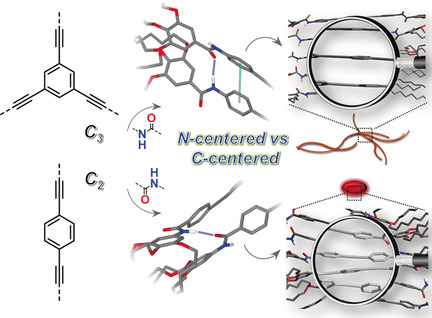
Self-Assembly
Interplay between H-Bonding and Preorganization in the Evolution of Self-Assembled Systems
- Pages: 4732-4736
- First Published: 08 January 2019
Membrane Channels
Small-Molecule Permeation across Membrane Channels: Chemical Modification to Quantify Transport across OmpF
- Pages: 4737-4741
- First Published: 31 January 2019
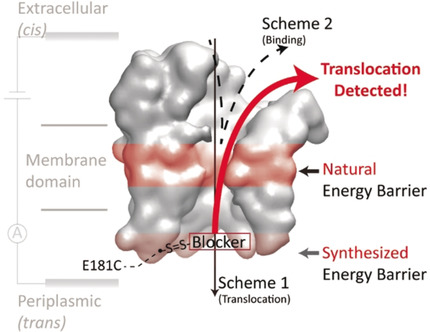
A molecule counter, added at the channel exit of a bacterial cell membrane pore creates an additional energy barrier to quantify molecules that permeate. The efficiency with charged peptides was tested. In a second series the antibiotic norfloxacin was tested. Introducing the partial channel blocker allows to distinguish binding from translocation for a broad range of molecules.