Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Cover Picture: Controlled Nanoscale Mechanical Phenomena Discovered with Ultrafast Electron Microscopy (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 48/2007)
- Page: 9119
- First Published: 05 December 2007

Ultrafast electron microscopy …︁…︁ has been used to view the reversible expansion and contraction of a single crystal of [Cu(TCNQ)] (see film strip; TCNQ=7,7,8,8-tetracyanoquinodimethane), induced with near-infrared laser pulses, as well as the photoinduced reduction of copper ions to form discrete metal clusters (see picture, top right), as described by A. H. Zewail et al. in their Communication on Page 9206 ff. The crystal expands along the π-stacking axis of the TCNQ molecules upon exposure to light, but rapidly returns to its original state in the absence of laser light.
Inside Cover
Inside Cover: Total Synthesis and Configurational Assignment of Pasteurestin A and B (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 48/2007)
- Page: 9120
- First Published: 05 December 2007

Application in veterinary medicine was proposed for the sesquiterpenoids pasteurestins A and B because of their strong and selective activity against Pasteurella haemolytica. A Vollhardt [2+2+2] cycloaddition was the key step in their total synthesis, which is described by J. Mulzer et al. on page 9320 ff., and subsequently their absolute and relative configurations could be established and their biological activities more precisely specified. Another feature of the synthesis of pasteurestin B is a tin(II) enolate mediated Reformatsky-type condensation.
Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract: Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 48/2007
- Pages: 9123-9136
- First Published: 05 December 2007
Corrigenda
[12]Annulene Gemini Surfactants: Structure and Self-Assembly
- Page: 9135
- First Published: 05 December 2007
News
Spotlights on our sister journals: Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 48/2007
- Pages: 9138-9139
- First Published: 05 December 2007
Bioorganic Chemistry: Awards to C. Bertozzi, M. Movassaghi, and K. A. Scheidt
- Page: 9142
- First Published: 05 December 2007
Book Reviews
Renewable Resources and Renewable Energy. A Global Challenge. Edited by Mauro Graziani and Paolo Fornasiero.
- Page: 9143
- First Published: 05 December 2007
On Chirality and the Universal Asymmetry. Reflections on Image and Mirror Image. By Georges H. Wagnière.
- Pages: 9143-9144
- First Published: 05 December 2007
Highlight
Enantioselective Insertion of Metal Carbenes into NH Bonds: A Potentially Versatile Route to Chiral Amine Derivatives
- Pages: 9148-9150
- First Published: 05 December 2007
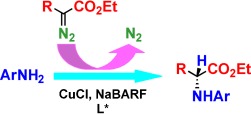
Back to copper: The Rh-catalyzed reactions of diazocarbonyl compounds with amines, leading to NH insertion products, have found wide application. However, an enantioselective variant has remained elusive. A return to copper catalysis, first reported for carbene NH insertions over 50 years ago, in the presence of chiral ligands and a large noncoordinating counterion, has resulted in enantioselective NH insertion into anilines.
Correspondence
1,7-Diaza[12]annulene Derivatives? 100-Year-Old Pyridinium Salts!
- Pages: 9152-9153
- First Published: 05 December 2007
![1,7-Diaza[12]annulene Derivatives? 100-Year-Old Pyridinium Salts!](/cms/asset/d8fa710c-3871-44dd-8360-bac4c616bc73/mcontent.jpg)
The 103-year-old reaction of N-(2,4-dinitrophenyl)pyridinium chloride with primary amines was rediscovered by two research groups recently. Since neither authors nor referees knew the pertinent literature, the products were assigned the structure of the diaza[12]annulenes 1, although they are nothing but N-substituted pyridinium salts.
Essay
Interconnections and Independence: Heinrich Wieland (1877–1957) and His Era
- Pages: 9154-9179
- First Published: 05 December 2007

The dramatic societal upheavals and radical value shifts that occurred during the first half of the 20th century influenced every aspect of life, including the scientific and research systems. A biography of Heinrich Wieland, awarded the Nobel Prize for Chemistry in 1927, one embedded in a chronicle of the times, shows clearly how this one individual adapted to multiple drastic changes in his environment.
Review
Trifluoromethylboranes and -Borates: New Synthetic Strategies and Applications
- Pages: 9180-9196
- First Published: 05 December 2007
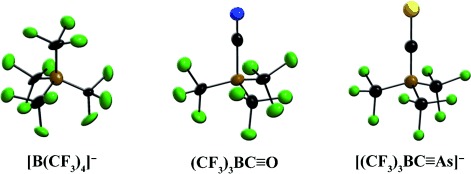
Sought for weak coordination: The first synthesis of the [B(CF3)4]− ion by fluorination of the [B(CN)4]− ion marks the beginning of a new development in the field of B-CF3 chemistry. In concentrated sulfuric acid one of the CF3 groups is transformed into a CO ligand. The borane carbonyl (CF3)3BCO is a reactive species and excellent starting material for the synthesis of various (CF3)3B compounds, for example, the pnicogeneethynyl complexes [(CF3)3BCPnic]− (Pnic=N, P, As).
Communications
Reactivity of an Aromatic σ,σ,σ-Triradical: The 2,4,6-Tridehydropyridinium Cation†
- Pages: 9198-9201
- First Published: 05 December 2007
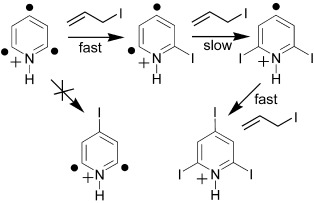
Tri-, bi-, and monoradicals: The reactivity of a σ,σ,σ-triradical, 2,4,6-tridehydropyridinium cation, was compared with that of related mono- and biradicals in a Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometer. The triradical has a doublet ground state and contains three interacting radical sites. The reactivity of the triradical more closely resembles that of related monoradicals than related biradicals.
How to Make Five Contiguous Stereocenters in One Reaction: Asymmetric Organocatalytic Synthesis of Pentasubstituted Cyclohexanes†
- Pages: 9202-9205
- First Published: 05 December 2007
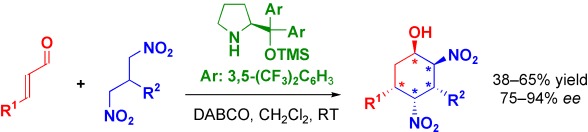
Give me five! An organocatalyzed two-component domino reaction has been developed in which two new CC bonds and five stereocenters are created in a one-pot fashion (see scheme; DABCO=1,4-diazabicyclo[2.2.2]octane, TMS=trimethylsilyl). The striking features of this transformation are the high preference for one diastereomer (out of 32 possible isomers) and enantioselectivities of up to 94 %.
Controlled Nanoscale Mechanical Phenomena Discovered with Ultrafast Electron Microscopy†
- Pages: 9206-9210
- First Published: 05 December 2007
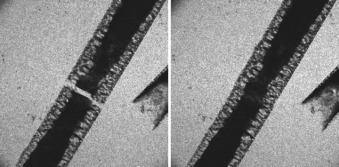
On again, off again: The reversible expansion and contraction of single crystals of [Cu(TCNQ)] induced by near-infrared laser pulses was studied with ultrafast electron microscopy (TCNQ=7,7,8,8-tetracyanoquinodimethane). The crystal expands along the π-stacking axis of the TCNQ molecules, but not perpendicular to this axis, when exposed to light. The crystal returned to its original structure when the laser light was blocked.
Total Synthesis and Stereochemical Reassignment of (+)-Neopeltolide†
- Pages: 9211-9214
- First Published: 05 December 2007
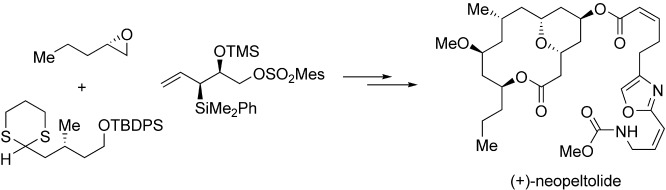
Take a closer look! The first enantioselective total synthesis, stereochemical reassignment, and absolute configuration of the metabolite neopeltolide is described (see picture). Synthetic highlights of this route include a modified Evans–Tishchenko reduction to introduce the C11 stereocenter, [4+2] annulation to construct the pyran system, and a Still–Gennari olefination to install the oxazole side chain.
Rhodanine-Based Tau Aggregation Inhibitors in Cell Models of Tauopathy†
- Pages: 9215-9219
- First Published: 05 December 2007
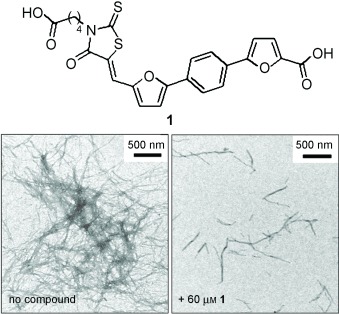
Breaking up the crowd: The pathological aggregation of tau protein correlates closely with the progression of Alzheimer's disease. Rhodanine-based inhibitors of tau aggregation (e.g. 1) have been identified, and it has been shown that tau aggregation in a cell model is reversible and can be inhibited by small molecules at nanomolar concentrations (see SEM images).
i-Motif Formation with Locked Nucleic Acid (LNA)†
- Pages: 9220-9222
- First Published: 05 December 2007
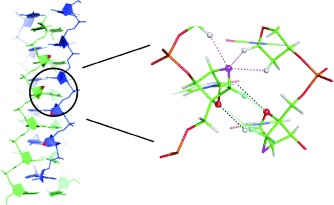
Dotting the i: The i-motif is a four-stranded DNA structure that consists of intercalated hemiprotonated C:C+ base pairs. Although they contain 2′-ribo oxygen atoms, LNA-modified TC5 oligonucleotides are also able to form stable tetrameric i-motif structures at low pH values (see view into one of the two narrow grooves of such a structure), as shown by a combination of CD, UV, and NMR spectroscopy.
Thiamine Biosynthesis in Escherichia coli: Identification of the Intermediate and By-Product Derived from Tyrosine†
- Pages: 9223-9226
- First Published: 05 December 2007
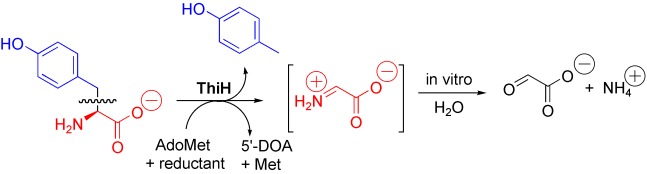
In anaerobic organisms such as E. coli the tyrosine lyase ThiH is essential for the biosynthesis of the thiazole moiety of the vitamin thiamine. ThiH is a member of the “radical AdoMet” family. The products formed by cleavage of tyrosine in vitro have been identified and suggest a radical-mediated cleavage resulting in p-cresol and dehydroglycine which is hydrolyzed to glyoxylate.
Covalent Interlinking of an Aldehyde and an Amine on a Au(111) Surface in Ultrahigh Vacuum†
- Pages: 9227-9230
- First Published: 05 December 2007
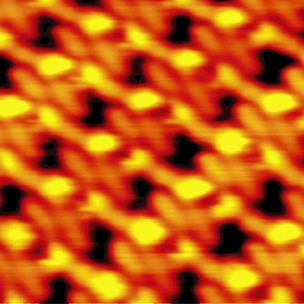
Getting a reaction: A condensation reaction occurs between a dialdehyde and an amine coadsorbed on a Au(111) surface in an ultrahigh vacuum. The self-assembled structures formed by the diimine reaction product on the surface have been investigated by scanning tunneling microscopy (see image). A solvent-free reaction path is proposed from DFT calculations.
Enantioselective Radical Reactions: Stereoselective Aldol Synthesis from Cyclic Ketones†
- Pages: 9231-9234
- First Published: 05 December 2007
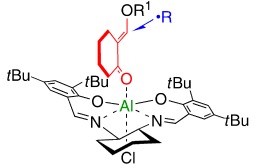
Radicalized aldols: Enones with a fixed s-cis geometry can undergo enantioselective radical reactions. The synthesis of aldol products derived from cyclic ketones in excellent yields and enantioselectivity demonstrates that s-cis-enones are excellent substrates for radical reactions. A tentative model to explain the stereochemical outcome of the reaction consists of nucleophilic radical addition to the si face (see picture).
Interfacial Assembly of Nanoparticles in Discrete Block-Copolymer Aggregates†
- Pages: 9235-9238
- First Published: 05 December 2007
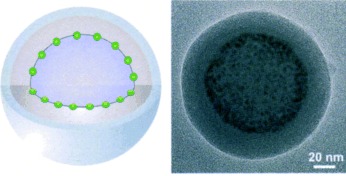
In the nanosphere: The cooperative self-assembly of CdSe/ZnS nanoparticles and an amphiphilic block copolymer leads to unique spherical assemblies. In these assemblies, the nanoparticles (green circles) are located at the interface between an outer polymer shell and an inner polymer core (see picture).
A Genetically Encoded Bidentate, Metal-Binding Amino Acid†
- Pages: 9239-9242
- First Published: 05 December 2007
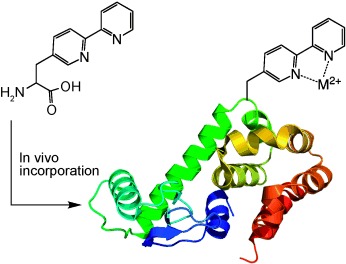
A two-ring binder: To facilitate the design of metalloproteins, the bidentate, metal-binding amino acid bipyridylalanine (BpyAla) was genetically encoded in E. coli in response to the amber nonsense codon with high fidelity and yield. The incorporation of BpyAla requires a BpyAla-specific aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase, which was evolved in a stepwise fashion. The structural basis of selective recognition of BpyAla by this synthetase was also determined.
Direct Synthesis of Anisotropic Polymer Nanoparticles†
- Pages: 9243-9247
- First Published: 05 December 2007
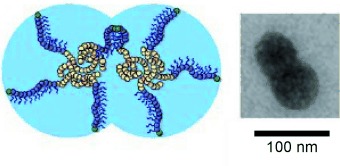
No (self-)assembly required: Both spherical and anisotropic “dumbbell” polymer nanoparticles with targeted shapes in the <100-nm size range were prepared by direct synthesis not relying on self-assembly. Atom-transfer polymerization techniques at high concentrations produce both spherical and dumbbell-like nanoparticles directly from simple vinyl monomers on a multigram scale.
Free-Radical-Based, Specific Desulfurization of Cysteine: A Powerful Advance in the Synthesis of Polypeptides and Glycopolypeptides†
- Pages: 9248-9252
- First Published: 05 December 2007
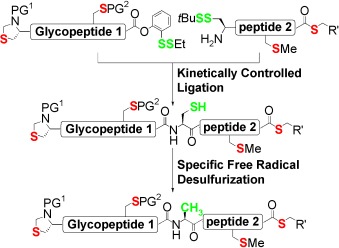
Being specific: The specific conversion of Cys (seleno-Cys) into Ala by a free-radical-mediated reduction can be achieved in an aqueous medium under mild conditions (see scheme, PG=protecting group). The conversion can be achieved in the presence of all 20 natural amino acids as well as a range of functional groups. This native chemical ligation followed by the Cys into Ala conversion will enable the synthesis of complex peptides and glycopeptides.
Origin and Dynamics of Oxygen Storage/Release in a Pt/Ordered CeO2–ZrO2 Catalyst Studied by Time-Resolved XAFS Analysis†
- Pages: 9253-9256
- First Published: 05 December 2007
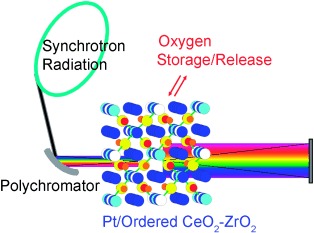
Electronic and structural dynamics of an industrially relevant Pt/CeO2–ZrO2 catalyst with an ordered arrangement of Ce and Zr ions during oxygen storage/release processes at 573–773 K were studied in real time by time-resolved energy-dispersive XAFS at the Zr K edge and Ce L3 edge (see experimental setup). On the basis of these results, the roles of Ce and Zr ions in the function of the mixed-oxide catalyst were elucidated.
Alkylation of Aryl N-(2-Pyridylsulfonyl)aldimines with Organozinc Halides: Conciliation of Reactivity and Chemoselectivity†
- Pages: 9257-9260
- First Published: 05 December 2007
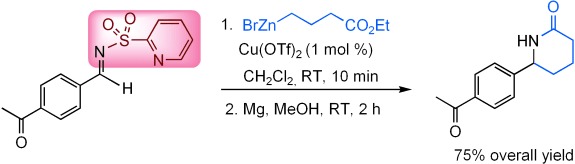
The best of both worlds: With a coordinating 2-pyridylsulfonyl group as the N-activating group, aromatic aldimines show unprecedented high reactivity towards the direct addition of alkyl zinc bromide reagents in the presence of catalytic amounts of Cu(OTf)2. The reaction combines high reactivity with wide functional-group compatibility to provide ready access to functionalized benzylamines and derivatives (see example). Tf=trifluoromethanesulfonyl.
Oligopyrrole Synthesis by 1,3-Dipolar Cycloaddition of Azomethine Ylides with Bissulfonyl Ethylenes†
- Pages: 9261-9264
- First Published: 05 December 2007
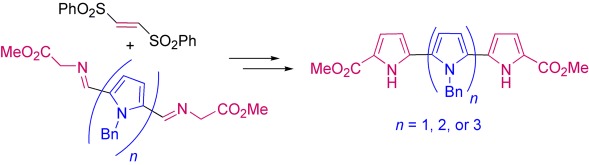
One by one or two by two: In a general approach to the iterative construction of oligopyrroles, the cycloaddition of azomethine ylides derived from pyrrolyl α-iminoesters with 1,2-bis(phenylsulfonyl)ethylene is followed by the elimination of the sulfonyl groups in situ under basic conditions. This strategy is amenable to the introduction of one or two pyrrole units in each iterative cycle.
Total Syntheses of Amphidinolide H and G†
- Pages: 9265-9270
- First Published: 05 December 2007
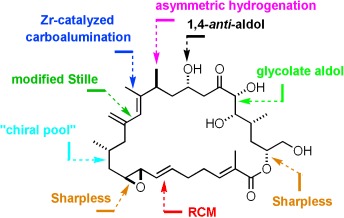
Eureka! The first conquest of the exceptionally potent cytotoxic agent amphidinolide H, which exhibits activity in the picomolar range against human epidermoid cancer cells, was long overdue. The successful route critically hinges upon the scrupulous optimization of the fragment-coupling events (see picture; RCM=ring-closing metathesis) and on the careful adjustment of the peripheral protecting-group pattern.
Combining Resonant Piezoelectric Micromembranes with Molecularly Imprinted Polymers†
- Pages: 9271-9274
- First Published: 05 December 2007
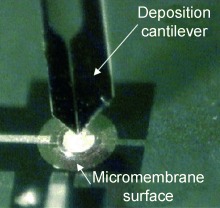
Layered chips: The experimental proof of concept of the combination of resonant microelectromechanical systems with molecularly imprinted polymers (MIPs) has been shown for the first time. The use of micromembrane gravimetric sensors carrying piezoelectric thin films, the surfaces of which are coated with MIPs by using a cantilever-based deposition tool (see image), is reported. The multiplexed format of the chips shows the potential of the system for the specific, label-free, reliable detection of target molecules.
Concise Total Synthesis of Cruentaren A†
- Pages: 9275-9278
- First Published: 05 December 2007
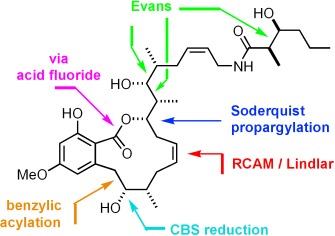
Converging on the target: The highly cytotoxic F-ATPase inhibitor cruentaren A constitutes an interesting lead in the quest for innovative chemotherapeutic agents for the treatment of various diseases, including cancer. Its synthesis was achieved in an overall yield of 3 % by an expeditious convergent route involving a ring-closing alkyne metathesis reaction (RCAM) for the formation of the macrocyclic ring (see picture).
A Water-Based Synthesis of Octahedral, Decahedral, and Icosahedral Pd Nanocrystals†
- Pages: 9279-9282
- First Published: 05 December 2007
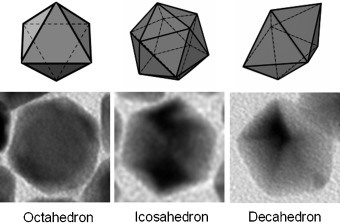
Shapes from water: Pd nanocrystals with controllable shapes are synthesized by reducing a Pd salt with citric acid in aqueous solution. Citric acid favors the formation of octahedra, icosahedra, or decahedra (see picture) owing to its strong binding to the {111} facets of Pd. Shape control of these nanocrystals is readily accomplished by adjusting the amounts of Na2PdCl4 precursor and citric acid added to the reaction mixture.
Longer Guests Drive the Reversible Assembly of Hyperextended Capsules†
- Pages: 9283-9286
- First Published: 05 December 2007
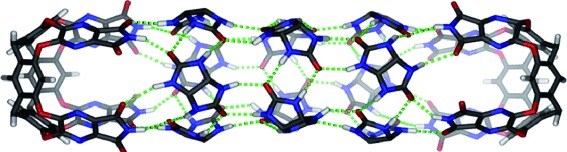
Hyperextension: A hydrogen-bonded, dimeric capsule can be expanded with four, eight, or twelve glycoluril spacers (see picture) that increase the cavity's volume by up to 530 Å3 and its length by up to 21 Å. The extended assemblies are chiral and encapsulate a variety of normal alkanes. The expanded capsules suggest that increasingly complex capsules may emerge from other spacers with hydrogen-bonding capabilities and curved surfaces.
A Stable Room-Temperature Molecular Assembly of Zwitterionic Organic Dipoles Guided by a Si(111)-7×7 Template Effect†
- Pages: 9287-9290
- First Published: 05 December 2007
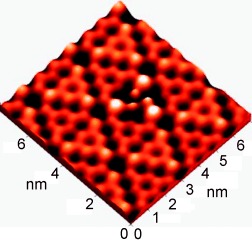
Chiral assemblies of achiral molecules: High-resolution STM images of zwitterionic organic dipoles deposited on Si(111)-7×7 show a chiral molecular assembly on this surface (see picture). Density functional calculations demonstrate that a sulfonato group can act as an electrostatic shield that protects the π skeleton of organic molecules from the dangling bonds of semiconductor surfaces, which is a major advance in the deposition of π-conjugated molecules.
Diastereodivergent Synthesis of Enantiomerically Pure Homoallylic Amine Derivatives Containing Quaternary Carbon Stereocenters†
- Pages: 9291-9294
- First Published: 05 December 2007
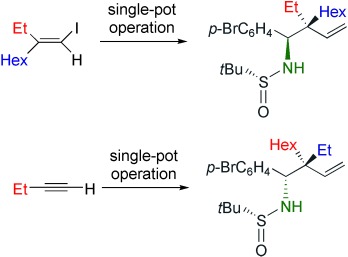
Freedom of choice: Both enantiomers of free homoallylic amines with two stereogenic centers (including a quaternary center) can be prepared at will from vinyl copper intermediates derived from either a vinyl iodide or an alkyne (see examples; the sulfinyl group is cleaved readily under mild acidic conditions). In this one-pot strategy, zinc homologation of the vinyl copper species is followed by treatment with a sulfinylimine derivative.
All-Carbon Intramolecular Conjugate Displacement Reactions: An Effective Route to Carbocycles†
- Pages: 9295-9297
- First Published: 05 December 2007
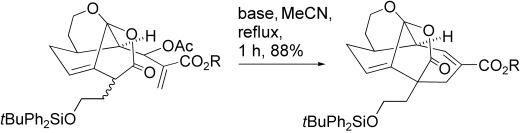
Working together: Synergy between Michael addition and SN2′ displacement allows stabilized carbanions or the nucleophilic carbon atoms of enamines to undergo intramolecular addition to an α,β-unsaturated ester unit bearing an allylic leaving group to generate unsaturated carbocycles (see scheme). The starting esters are available by a selenium-based alternative to the classical Baylis–Hillman reaction, and complex structures can be assembled.
Enzymatic Release and Macrolactonization of Cryptophycins from a Safety-Catch Solid Support†
- Pages: 9298-9300
- First Published: 05 December 2007
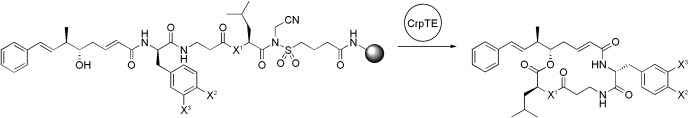
Thioesters need not apply: Cryptophycin thioesterase (Crp TE) cleaves and macrolactonizes linear cryptophycin substrates bound to activated safety-catch PEGA resin. This novel enzymatic solid-phase approach was used to further investigate the tolerance of Crp TE for structural variations of substrates.
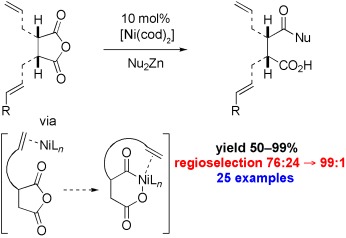
Alkene-Directed Regioselective Nickel-Catalyzed Cross-Coupling of Cyclic Anhydrides with Diorganozinc Reagents†
- Pages: 9301-9304
- First Published: 05 December 2007
Interaction of Malachite Green with Guanine-Rich Single-Stranded DNA: Preferential Binding to a G-Quadruplex†
- Pages: 9305-9307
- First Published: 05 December 2007
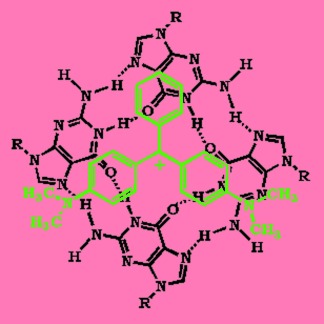
Bound to be better: The formation of a strong complex between the chromophoric dye malachite green (MG, in green) and the G-quadruplex structure (represented in black) of the guanine-rich single-strand oligomer sequence d(G2T)13G results in a 100-fold enhancement of the fluorescence yield of MG. The existence of an intra- or interstrand G-quadruplex structure depends on the oligomer concentration and the ionic strength of the solution.
DNA-Based Catalytic Enantioselective Michael Reactions in Water†
- Pages: 9308-9311
- First Published: 05 December 2007
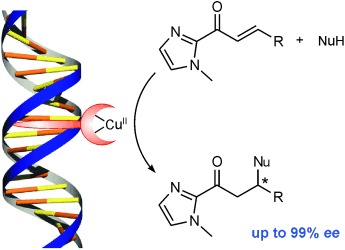
High, but not dry: A highly enantioselective Michael reaction in water has been developed by using a simple DNA-based catalyst. Enantioselectivities of up to 99 % ee could be obtained by using nitromethane and dimethyl malonate as the nucleophiles and α,β-unsaturated 2-acylimidazoles as the Michael acceptors. The reactions can be performed on a preparative scale and the catalyst can be recycled.
The 1,2,3-Triazole Ring as a Peptido- and Olefinomimetic Element: Discovery of Click Vanilloids and Cannabinoids†
- Pages: 9312-9315
- First Published: 05 December 2007
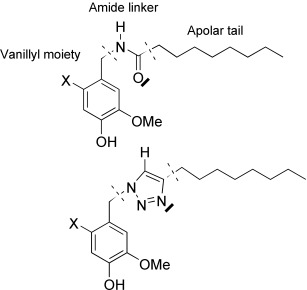
Fooling nature: The replacement of amide and alkene groups in a biological setting with the 1,2,3-triazole group led to the discovery of compounds with a unique vanilloid/cannabinoid mixed profile. For example, the natural amides (see picture, above) and their triazole mimics (below) exhibit similar agonistic (X=H) or antagonistic (X=I) activity towards the TRPV1 receptor; however, only the triazole derivatives also show cannabinomimetic activity.
Bond Formation with Maintenance of Twofold Charge: Generation of C2O32+ in the Reaction of CO22+ with CO2†
- Pages: 9316-9319
- First Published: 05 December 2007
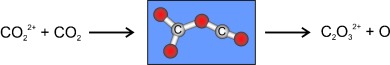
100 years after the prediction of the existence of C2O3 by Berthelot, doubly charged C2O32+ has been identified as a product in the reaction of CO22+ with CO2 (see scheme). The occurrence of this reaction for such a small dication indicates that bond-forming processes might play a much larger role in reactions of dications than has been anticipated to date.
Total Synthesis and Configurational Assignment of Pasteurestin A and B†
- Pages: 9320-9322
- First Published: 05 December 2007
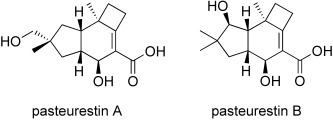
Fresh pasture for the [2+2+2] cycloaddition: The two sesquiterpenoids pasteurestin A and B, which exhibit strong and selective antibacterial activity against Pasteurella haemolytica, have been prepared in a synthesis relying on a [2+2+2] Vollhardt enediyne cycloaddition. The previously unknown absolute and relative configurations were established, and the biological profile was specified more precisely.
Unusual Coordination Behavior of Pn-Ligand Complexes with Tl+†
- Pages: 9323-9326
- First Published: 05 December 2007
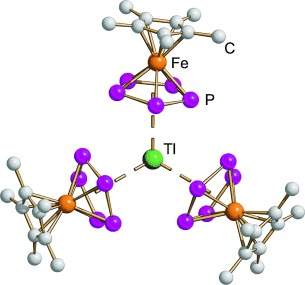
Pentaphosphaferrocene coordinates as a π ligand to the large monocation Tl+. In addition, one of the phosphorus atoms of each cyclo-P5 moiety coordinates to a neighboring Tl+ ion to give a one-dimensional polymer. Even at low temperatures, fast rotation of the P5 rings is observed in solution and in the solid state.
Strong Evidence for a Transient Phosphinidenoid Complex†
- Pages: 9327-9330
- First Published: 05 December 2007
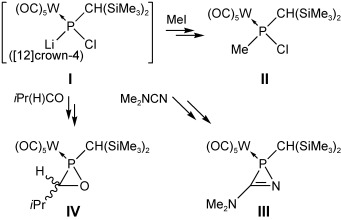
Caught in the trap: Two different routes to the thermally unstable phosphinidenoid complex I are described, and chemical evidence for this novel intermediate is provided through selective reactions. For example, methyl iodide, dimethylcyanamide, or butyraldehyde furnished complexes II, III, and IV (see scheme) under very mild conditions.
Enantioselective Preparation of 1,1-Diarylethanes: Aldehydes as Removable Steering Groups for Asymmetric Synthesis†
- Pages: 9331-9334
- First Published: 05 December 2007
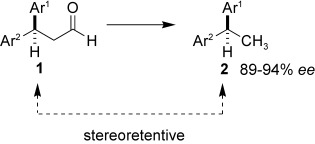
Cut it out! Convenient procedures have been delineated for the synthesis of optically active, functionalized 1,1-diarylethanes by decarbonylation of β,β-diarylpropionaldehydes. The process can be conducted as a one-pot 1,4-addition/decarbonylation sequence. Aldehydes are used as removable steering groups in this new strategy for the preparation of optically active building blocks.
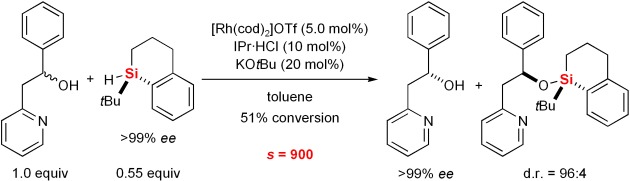
Chiral Recognition with Silicon-Stereogenic Silanes: Remarkable Selectivity Factors in the Kinetic Resolution of Donor-Functionalized Alcohols†
- Pages: 9335-9338
- First Published: 05 December 2007
Enantioselective Strecker Reaction Catalyzed by an Organocatalyst Lacking a Hydrogen-Bond-Donor Function†
- Pages: 9339-9341
- First Published: 05 December 2007
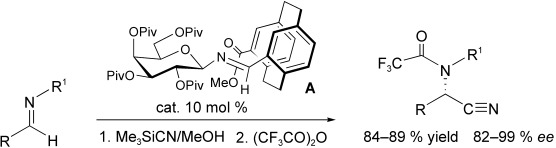
Self-activation: N-Glycosyl imines A of planar chiral [2.2]paracyclophane carbaldehydes act as efficient enantioselective organocatalysts for the Strecker synthesis of α-amino nitriles, although they do not contain a hydrogen-bond donor or a Brønsted acid function. They activate themselves by deprotononation of hydrogen cyanide and catalyze the formation of both aliphatic and aromatic amino nitriles with high enantioselctivity.