Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Developmental Therapeutics
Precision gas therapy by ultrasound-triggered for anticancer therapeutics
- First Published: 20 March 2023
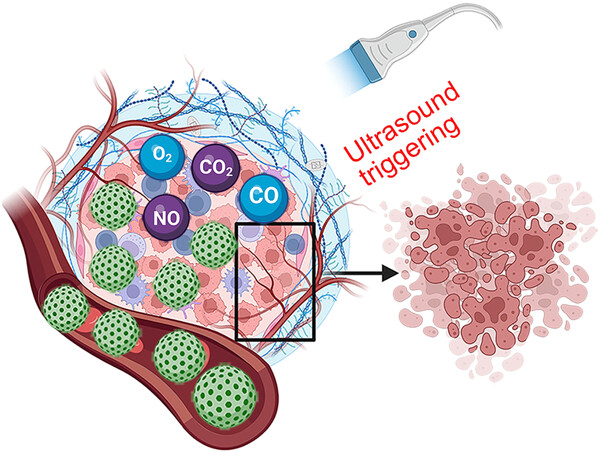
The gas-generating platforms for tumor therapy precisely have been as a green treatment method. We summarized a nice overview on the mechanism, the common gas release pathways of NO, O2, CO, CO2 under ultrasound, and their applications for tumor therapy. We believe this review could represent a new field on antitumor.
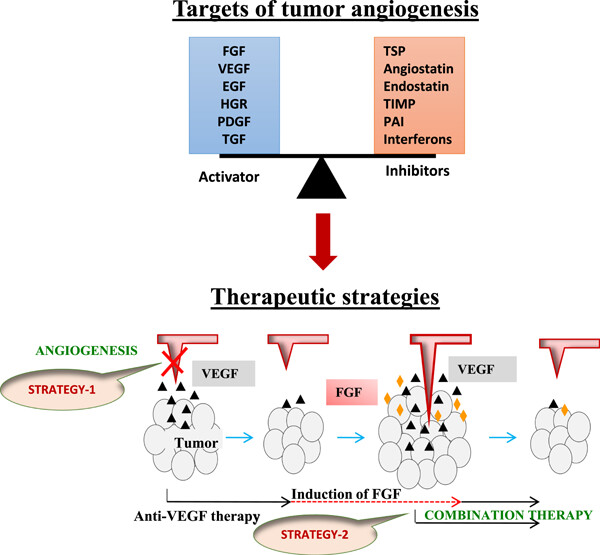
Insight on the cellular and molecular basis of blood vessel formation: A specific focus on tumor targets and therapy
- First Published: 08 February 2023
New technologies and machines for stereotactic radiation therapy
- First Published: 07 December 2022
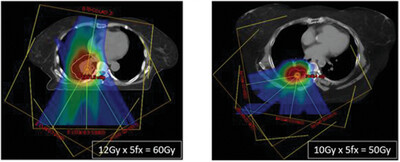
Stereotactic Radiosurgery (SRS) and Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy (SBRT) have been increasingly utilized in Radiation Oncology to treat early stage tumors, metastatic targets, and retreatment of relapsed diseases due to its efficiency, treatment effect and cost effectiveness in the past two decades. SRS and SBRT both demand high specifications for their delivery machines as they deliver radiation doses with fewer treatment fractions and higher doses per fraction. Manufacturers have either invented specialized technologies solely or customized their existing machines for this purpose. In this paper, we review the major technologies and treatment machines for SRS and SBRT, describe their main features, and discuss the advantages and disadvantages.
Update on therapeutic strategy for esophageal anastomotic leak: A systematic literature review
- First Published: 16 December 2022
Crosstalk between ferroptosis and stress—Implications in cancer therapeutic responses
- First Published: 11 June 2022
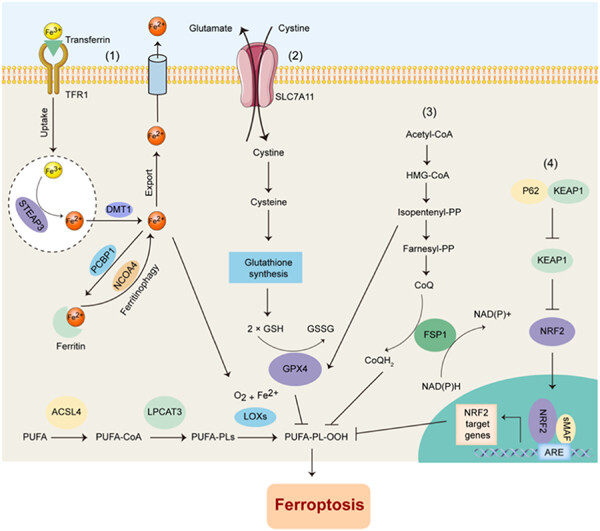
This review summarizes the hallmarks of ferroptosis, discusses how ferroptosis can be modulated by multiple extrinsic or intrinsic stresses, and highlights the interconnection between ferroptosis and cancer therapy response. A better understanding of the complex regulatory networks of ferroptosis and its interplay with current therapies could ultimately help to develop novel therapeutic approaches against cancer
Neoantigen vaccine and neoantigen-specific cell adoptive transfer therapy in solid tumors: Challenges and future directions
- First Published: 30 August 2022
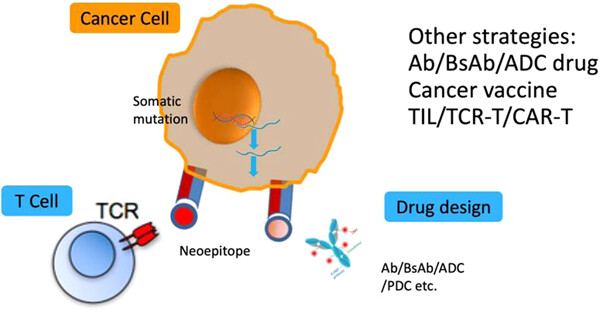
Recent technological advances of next-generation sequencing and bioinformatics have made it possible to discover more abundant and specific neoantigens encoded by tumor-specific somatic mutations. Precise cancer medicine of therapeutic vaccines designed from personalized neoantigens have been proven effective and safe in patients with melanoma, non-small cell lung cancer, and head and neck squamous carcinoma, and so forth. Discoveries of the phenotypes, functionality, and long-lasting memory potential of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes trigger deeper evaluation of cancer vaccine study and vaccine-induced neoantigen-specific CD4+ and CD8+ T-cell adoptive transfer therapy, which is warranted to improve immunotherapeutic activity and optimize vaccination strategies.
Gastrointestinal Cancer
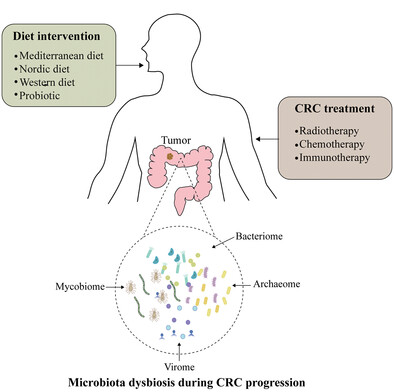
Development and treatment of colorectal cancer: Insights from multi-kingdom microbiota
- First Published: 12 April 2023
Studying host genetic background effects on multimorbidity of intestinal cancer development, type 2 diabetes and obesity in response to oral bacterial infection and high-fat diet using the collaborative cross (CC) lines
- First Published: 14 February 2021
A rare case of giant panda cancer: Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
- First Published: 11 November 2022
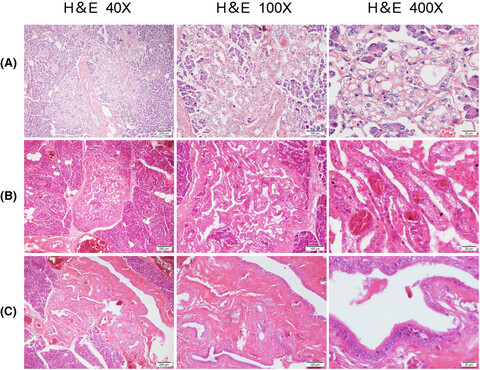
Pancreatic tissues' tumors exhibited three different situations. (A) Several glandular tubular adenocarcinoma structures could be seen in pancreatic tissue. (B) Tubular area could be seen in the pancreas, exhibiting papillary growth in the area. (C) The ductal epithelium in the pancreas was replaced by high columnar mucous cells, which showed pseudostratified columnar epithelial cells.
The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on colorectal cancer diagnosis and management: a Binational Colorectal Cancer Audit study
- First Published: 07 July 2021
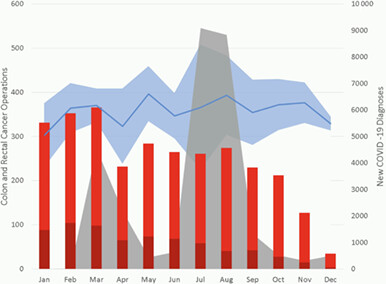
This paper examines the impact of COVID-19 on colorectal cancer diagnosis and management in Australia and New Zealand by comparing patients receiving colorectal cancer surgery during the pandemic against averages from the same period over the preceding three years. The key findings are a significant reduction in total colorectal cancer operations, particularly in rectal cancers, cancers presented at a more advanced stage and operations were more likely to be emergencies. The response to COVID-19 has had measurably negative effects on the diagnosis and management of colorectal cancer in two countries that have had significantly fewer COVID-19 cases than many other countries.
Sarcopenia is a strong predictive factor of clinical and oncological outcomes following curative colorectal cancer resection
- First Published: 07 March 2021
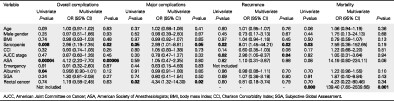
Sarcopenia as assessed on computed tomography was investigated as a predictor of outcomes following colorectal cancer resection. Associations were found with length of stay, complications and recurrence at 1 year. Sarcopenia was found to be a better predictive factor for recurrence and morbidity than other traditional measures of nutrition.
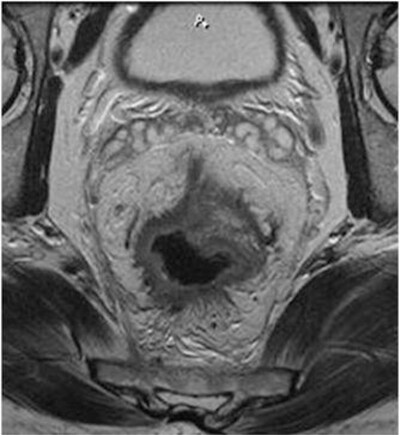
Pictorial essay on MRI local staging of rectal carcinoma: An easy approach
- First Published: 18 April 2022
The therapeutic effects of berberine for gastrointestinal cancers
- First Published: 13 March 2023

Multiple effects of berberine (BBR) as a gastrointestinal (GI) cancer therapeutic agent. BBR acts as a potential anti-GI cancer agent by inducing apoptosis, autophagy, and cell-cycle arrest, as well as metastasis and angiogenesis inhibition. It plays an important role in suppressing GI cancer cells.
A global assessment of recent trends in gastrointestinal cancer and lifestyle-associated risk factors
- First Published: 25 September 2021
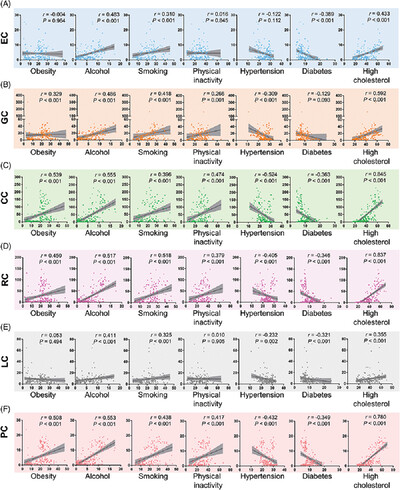
Prevalence of gastrointestinal cancers was positively correlated with national human development index levels, but negatively with hypertension and diabetes rates. Age-specific trends were observed in stomach cancer and esophagus cancer for incidence and in liver cancer and pancreatic cancer for mortality, as well as sex-specific trends for stomach cancer and pancreatic cancer in the elder.These findings suggest that future research has to focus on the specific etiology of gastrointestinal cancers behind these epidemiologic transitions and improve therapeutic strategies for patients with comorbid metabolic diseases.
Survival trends of patients with non-metastatic gastric adenocarcinoma in the US and European countries: the impact of decreasing resection rates
- First Published: 06 June 2022
Frequent loss of metastatic ability in subclones of Apc, Kras, Tgfbr2, and Trp53 mutant intestinal tumor organoids
- First Published: 28 December 2022
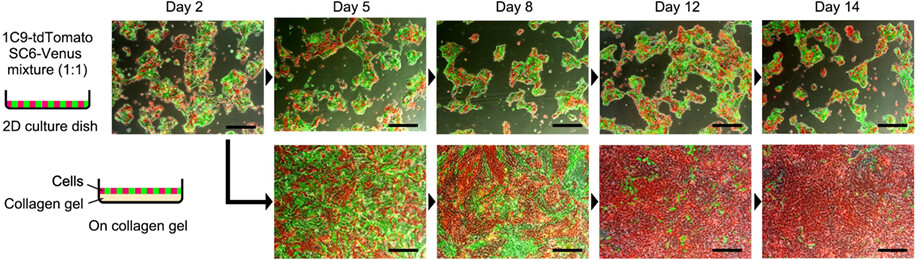
We have performed subcloning of metastatic intestinal tumor-derived organoids from single cells. Notably, approximately 30% of subclones showed loss of metastatic ability associated with growth suppression, although driver mutations were not affected. The results suggest that cancer evolution is regulated not only by positive selection but also by negative selection.
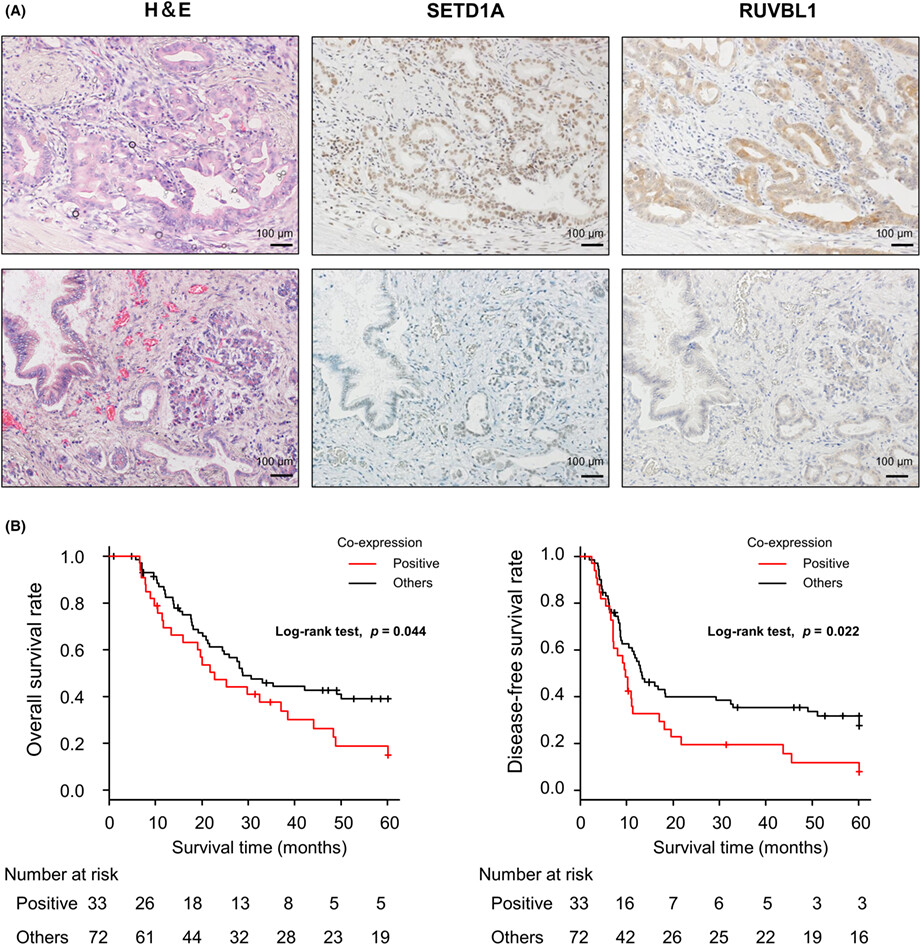
Identification of a novel target of SETD1A histone methyltransferase and the clinical significance in pancreatic cancer
- First Published: 22 October 2022
Determinants of survival outcomes among esophageal cancer patients at a national referral hospital in Kenya
- First Published: 20 November 2022
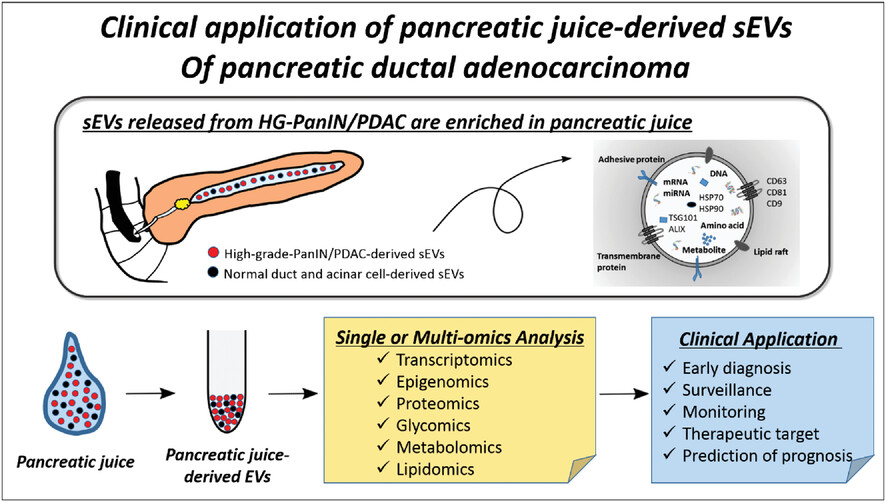
Clinical application of pancreatic juice-derived small extracellular vesicles of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
- First Published: 28 March 2023