Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Gastrointestinal Cancer
PD-L1 expression by different scoring methods and different cutoff values and correlation with clinicopathological characteristics in gastric cancer: A retrospective study
- First Published: 21 January 2023
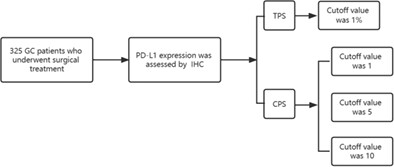
We aimed to investigate the associations of PD-L1 expression with clinicopathological characteristics by different scoring methods and different cutoff values. PD-L1 CPS ≥5 was associated with high expression of Ki67 and pTNM staging. PD-L1 CPS ≥10 was more often observed in GC patients with larger tumor size or lymph node metastasis. PD-L1 TPS ≥1% and PD-L1 CPS ≥1 were independent of clinicopathological features.
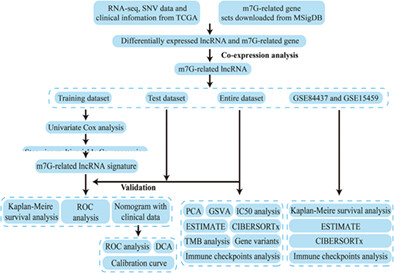
A novel N7-methylguanosine-related long noncoding RNAs signature for predicting prognosis and immune microenvironment in gastric cancer patients
- First Published: 08 November 2022
Radiotherapy guidelines for rectal cancer in China (2020 Edition)
- First Published: 01 March 2022
Investigation of the systemic inflammatory index as a predictor of downstaging in locally advanced rectal cancer patients with preoperative chemoradiation
- First Published: 03 March 2022
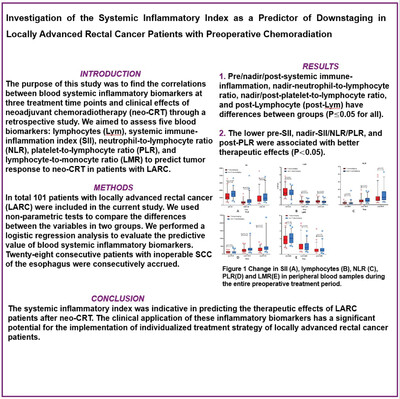
Purpose: To find the correlations between blood systemic inflammatory biomarkers at three treatment time points and clinical effects of neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy (neo-CRT) through a retrospective study.
Methods: In total 101 patients with locally advanced rectal cancer (LARC) were included in the current study. Patients were divided into two groups based on the T-downstaging, among which 54 patients had T-downstaging. We used non-parametric tests to compare the differences between the variables in two groups. We performed a logistic regression analysis to evaluate the predictive value of blood systemic inflammatory biomarkers.
Results: Pre/nadir/post-systemic immune-inflammation (SII), nadir-neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), nadir/post-platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (PLR), and post-Lymphocyte (post-Lym) have differences between groups (P 0.05 for all). We included P 0.05 indicators and clinical related factors into the multivariate analysis, respectively, and we found that lower pre-SII, nadir-SII/NLR/PLR, and post-PLR were associated with better therapeutic effects (P 0.05).
Conclusions: The systemic inflammatory index was indicative in predicting the therapeutic effects of LARC patients after neo-CRT.
Research progress in the establishment of pancreatic cancer models and preclinical applications
- First Published: 05 October 2022
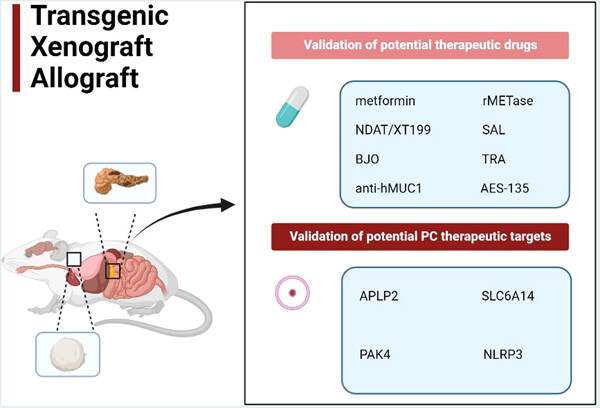
In recent years, some novel mouse pancreatic cancer models (including orthotopic and heterotopic models) which can show more realistic features of human pancreatic cancer and contribute to the validation of drugs and targets with therapeutic potential in pancreatic cancer have been established by using different technical means. This is of great significance for clinically improving the prognosis of pancreatic cancer patients.
Advances in medical treatment of advanced hepatobiliary and pancreatic cancer in 2022
- First Published: 01 March 2023
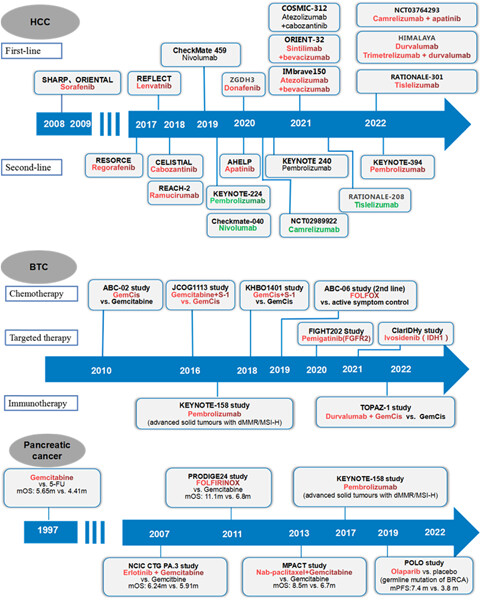
Key studies in the development of systemic therapy for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), biliary tract cancer (BTC), and pancreatic cancer. The development of immunotherapy and targeted therapy has raised the survival rate of advanced HCC to a new high. Research on targeted therapy for specific gene mutations has made great progress in precise therapy of BTC, and immunotherapy has also achieved positive results, adding new treatment options. Chemotherapy is still the main treatment for pancreatic cancer, while targeted therapy and immunotherapy have also seen some dawn in exploratory research.
Genitourinary Cancer
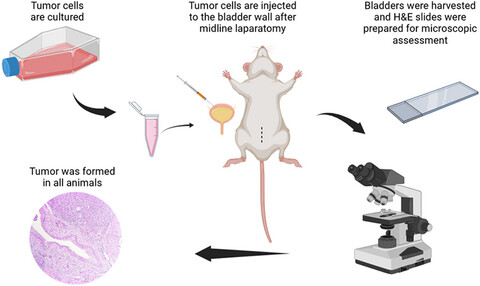
Evaluation of direct intramural injection to the bladder wall as a method for developing orthotopic tumor models
- First Published: 30 November 2022
Macrophage inhibitory cytokine-1 induced by a high-fat diet promotes prostate cancer progression by stimulating tumor-promoting cytokine production from tumor stromal cells
- First Published: 27 March 2021
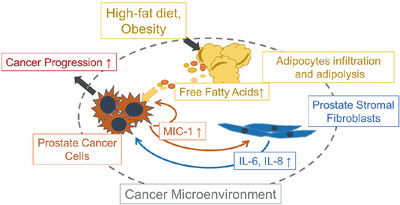
MIC-1 production was increased in PCa cells, which was affected by adipocyte infiltration and adipolysis. MIC-1 directly stimulated the surrounding PrSC cells to secrete protumorigenic cytokines such as IL-8 and IL-6 in the PCa stromal microenvironment, especially under a HFD condition. These upregulated functional cytokines directly and/or indirectly stimulated PCa cell proliferation, invasion, and metastasis.
Junction plakoglobin regulates and destabilizes HIF2α to inhibit tumorigenesis of renal cell carcinoma
- First Published: 16 February 2021
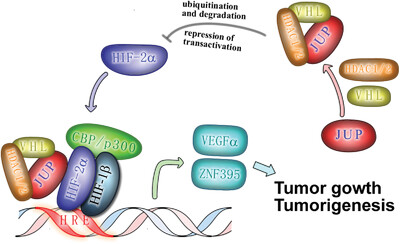
We provide a mechanism by which the tumor suppressor JUP interact with the HIF2α transcription factor in ccRCC cells. JUP downregulation is likely to trigger the aberrant upregulation of HIF2α stability and transactivity, which further exerts effects on tumorigenesis in ccRCC. These results have important implications in both the diagnosis and treatment of RCC.
Incidence rate, basic characteristics, and survival outcomes of bladder squamous cell carcinoma
- First Published: 02 August 2022
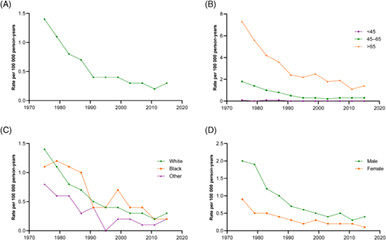
Objective: To explore the incidence rate (IR), clinicopathological characteristics, and prognostic factors of bladder squamous cell carcinoma (BSCC) based on surveillance, epidemiology, and end results (SEER) database. Methods: We extracted the IRs of BSCC from 1975 to 2016 in the SEER database, and plotted the trending curves. Then, the clinicopathological characteristics of BSCC patients diagnosed from 2010 to 2015 were selected and compared with those of patients with urothelial carcinoma (UC) in the same period. Furthermore, differences in overall survival (OS) and cancer-specific survival (CSS) of BSCC and UC patients were compared. Finally, COX regression models were constructed to explore the risk factors affecting OS and CSS in BSCC patients. Results: The IR of BSCC showed a downward trend from 1975 to 2000 and stabilized at about 0.3/100 000 after 2000. BSCC patients had a later stage at diagnosis and worse prognosis when compared with those with UC. Older age, higher TNM stage, no surgical treatment, and unmarried status were significantly related to worse prognosis of BSCC patients. Conclusion: This study explored the IR trends, clinicopathological characteristics, and prognostic factors of BSCC. In the future, prospective, large sample, and well-designed clinical studies are needed to verify our results.
An exceptional prostate cancer case: Importance of cancer screening
- First Published: 03 June 2022
Bladder cancer prospective cohort study on high-risk non-muscle invasive bladder cancer after photodynamic diagnosis-assisted transurethral resection of the bladder tumor (BRIGHT study)
- First Published: 15 March 2022
The Mini-Cog: A simple screening tool for cognitive impairment useful in predicting the risk of delirium after major urological cancer surgery
- First Published: 06 March 2022
Acute toxicity and patient-reported symptom score after conventional versus moderately hypofractionated proton therapy for prostate cancer
- First Published: 19 October 2021

The acute adverse event rates and International Prostate Symptom Score (IPSS) up to 6 months in 289 patients treated with hypofractionated (2.5 Gy or 3.0 relative biological effectiveness (RBE)/fraction) versus conventionally fractionated (2.0 Gy(RBE)/fraction) proton beam therapy (PBT). Although significant increases in the IPSS were observed at the end of PBT in all groups, the score had returned to the pre-PBT value, and no significant differences were found in the acute adverse event rates or IPSS among the fractionation schedules early after PBT, suggesting that a shorter treatment course might have greater benefit for patients with localised prostate cancer.
Visualising the urethra for prostate radiotherapy planning
- First Published: 24 May 2021
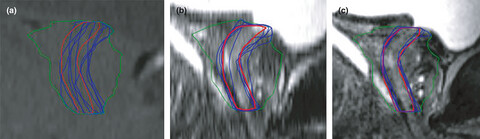
Whilst traditional diagnostic MRI sequences provide excellent delineation of the prostate, uncertainty often remains as to the true path of the urethra within the gland. This study aims to assess if a high resolution isotropic 3D T2 MRI series can reduce inter-observer variability in urethral delineation for radiotherapy planning.
Dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry assessment of bone health in Australian men with prostate cancer commencing androgen deprivation therapy
- First Published: 27 January 2023
Patterns of care for men with prostate cancer: the 45 and Up Study
- First Published: 04 March 2021
Urine-based liquid biopsy in bladder cancer: Opportunities and challenges
- First Published: 21 February 2023
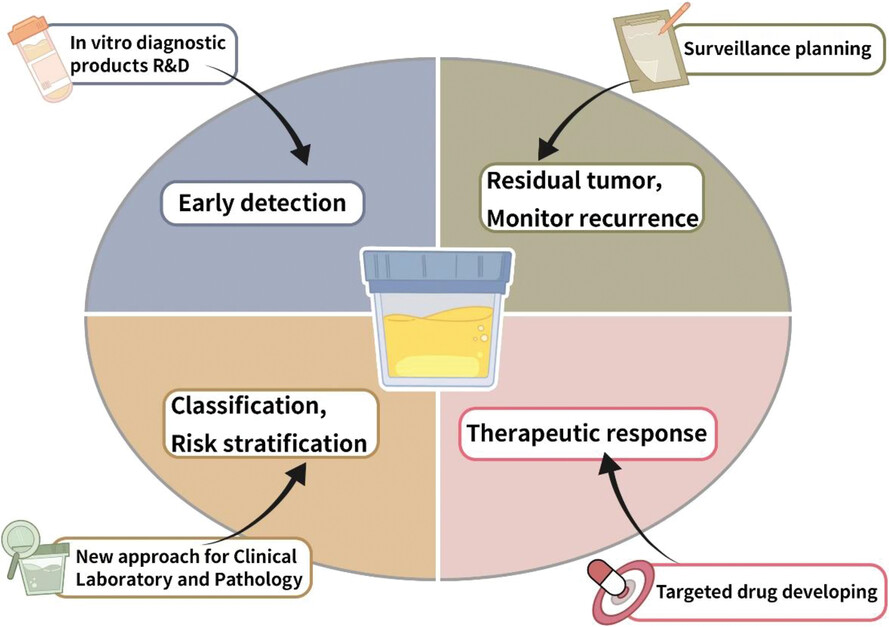
- (1) Development of liquid biopsy has great potential of clinical application in non-invasive detection of tumours.
- (2) Urine-based biomarkers or tests for clinical management in bladder cancer can be widely used for early detection, minimal residual, recurrence monitoring and therapeutic response.
- (3) Many challenges need to be overcomed in the discovery and validation studies of urine biomarkers for bladder cancer.
Prostate cancer management with lifestyle intervention: From knowledge graph to Chatbot
- First Published: 20 February 2022
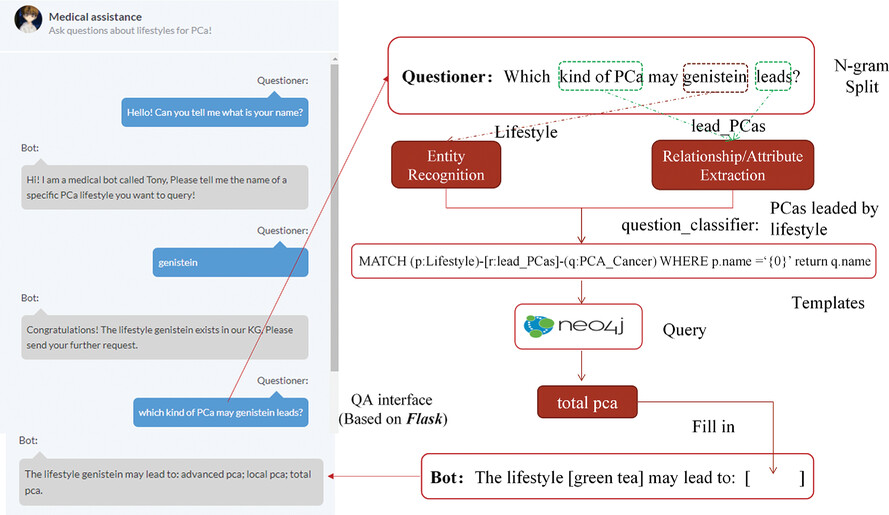
Personal lifestyle is an important cause of prostate cancer (PCa) and positive lifestyles will be important to the prevention of the disease. A knowledge graph is a convenient way to present the relationship between PCa and lifestyle. A healthcare chatbot was developed to answer basic questions about the association between PCa and lifestyle.