Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Genitourinary Cancer
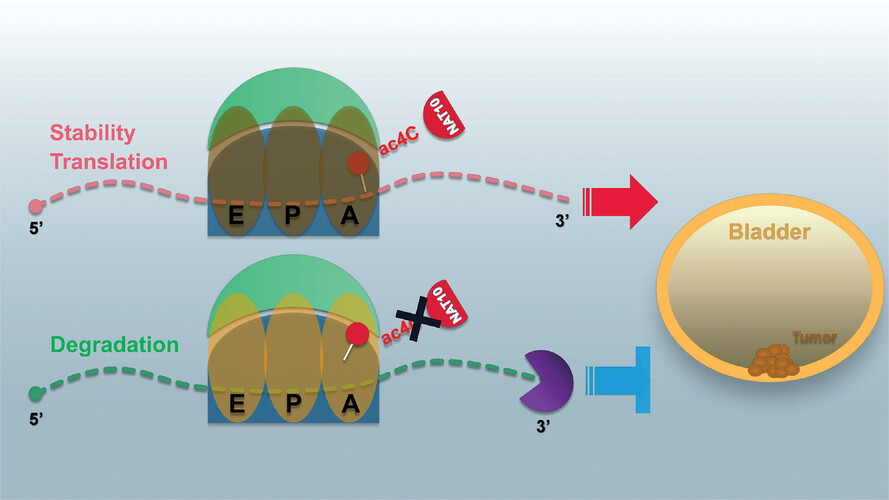
NAT10-mediated mRNA N4-acetylcytidine modification promotes bladder cancer progression
- First Published: 06 May 2022
-
NAT10 is highly expressed in BLCA patients and its abnormal level predicts bladder cancer progression and low overall survival rate. NAT10 is necessary and sufficient for BLCA tumorigenic properties.
-
NAT10 is responsible for ac4C modification of target transcripts, including BCL9L, SOX4 and AKT1.
-
NAT10 may serve as an effective and novel therapeutic target for BLCA.
Comprehensive methylome sequencing reveals prognostic epigenetic biomarkers for prostate cancer mortality
- First Published: 30 September 2022
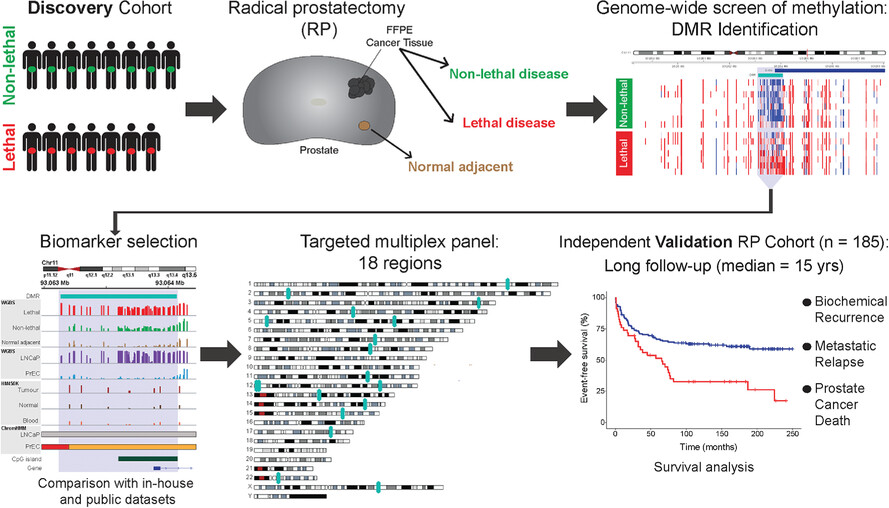
Comprehensive whole-genome bisulphite sequencing of prostate cancer tissue identified 1420 differentially methylated regions (DMRs) between patients with lethal disease versus non-lethal disease. DMRs were used to develop a targeted sequencing biomarker panel which validated cancer-specific methylation patterns in an independent cohort (n = 185). The epigenetic biomarker panel improves accuracy of identifying patients at risk of death compared to existing clinicopathological markers.
Altering phosphoinositides in high-fat diet-associated prostate tumor xenograft growth
- First Published: 28 October 2021
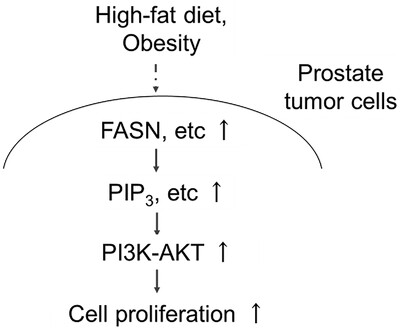
HFD-induced alteration of PIPs, especially PIP3, may activate proliferative signaling transduction, such as the PI3K/AKT pathway through the upregulation of FASN, and influence PCa progression. Therefore, PI3K/AKT signaling and FASN could be the important targets for dietary intervention and/or chemoprevention in PCa incidence and progression.
Cancer-specific survival after diagnosis in men versus women: A pan-cancer analysis
- First Published: 30 June 2022
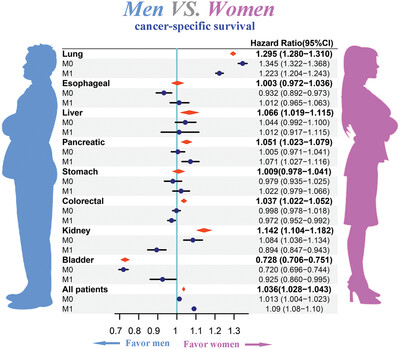
Comprehensive understanding of survival differences in gender after cancer diagnosis is critical for cancer prevention and treatment. We compared the gender differences of cancer-specific survival in lung, esophageal, liver, pancreatic, stomach, colorectal, kidney, and bladder cancer. Totally, gender seemed to be a significant factor influencing cancer-specific survival, and the prognosis of female patients was better than male patients.
Ferredoxin 1, the key regulator of cuproptosis, was associated with prognosis and immune cell infiltration in clear cell renal cell carcinoma
- First Published: 07 March 2023
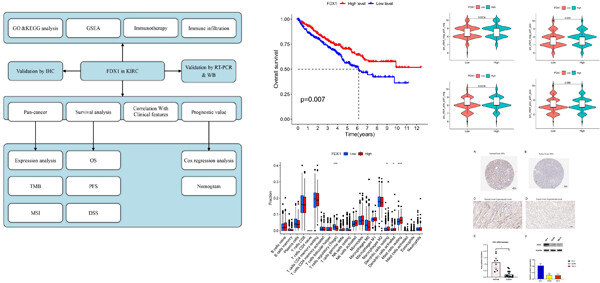
Ferredoxin 1 (FDX1) is a key gene in the process of Cuproptosis, and its expression level reflects the role of copper death in cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) to a certain extent. For the first time, we used a combination of bioinformatics and experimental validation to explore the role of FDX1 in ccRCC prognosis, immunotherapy, and immune cell infiltration.
The landscape of TIGIT target and clinical application in diseases
- First Published: 08 December 2022
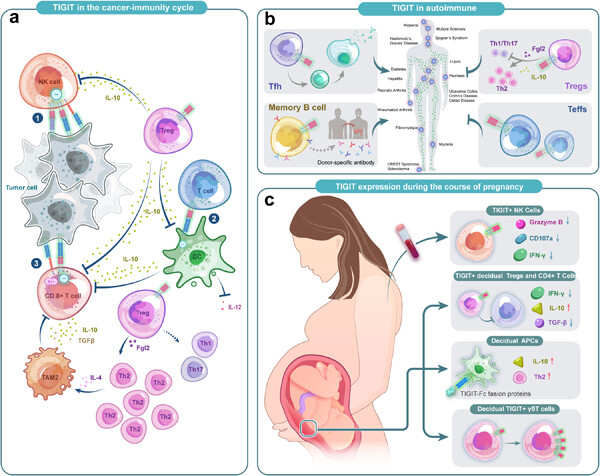
T-cell immunoglobulin and ITIM structural domain (TIGIT), a novel immune checkpoint, is widely expressed in a variety of immune cells. Recently studies have shown that TIGIT is extensively involved in various cancerous and noncancerous diseases such as chronic inflammation, autoimmune diseases, and abnormal pregnancy status. Thus, targeting TIGIT could be an effective immunotherapy option in the future.
Evaluation of emergency department treat-and-release encounters after major gastrointestinal surgery
- First Published: 01 May 2023
Identification of novel somatic fusions of ERG-VEGFA, TMPRSS2-ERG, and VEGFA-TMPRSS2 in prostate cancer treated with anlotinib and androgen deprivation therapy: A case report
- First Published: 09 June 2022
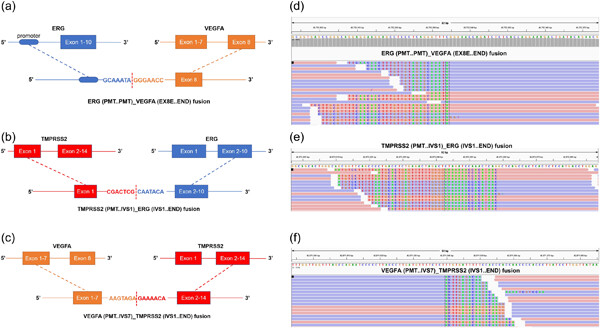
Three gene fusions ERG (PMT. . PMT)_VEGFA (vascular endothelial growth factor A, EX8E. . END), TMPRSS2 (PMT. . IVS1)_ERG (IVS1. . END), and VEGFA (PMT. . IVS7)_TMPRSS2 (IVS1. . END) were identified in a patient's prostate cancer tissue. The administration of anlotinib, a tyrosine kinase inhibitor, in the combination of GnRHa (gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonist, Goserelin) and abiraterone not only reduced bone pain dramatically but also stabilized the disease for more than 2 years in the patient with these fusions.
Machine learning-based prognostic and metastasis models of kidney cancer
- First Published: 08 August 2022
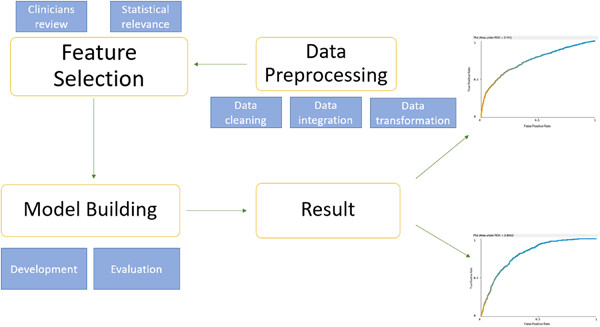
We used the data of 12,394 kidney cancer patients in the SEER (surveillance, epidemiology, and final results) database to construct a research cohort, combine with statistical relevance and clinical experience to screen for factors related to kidney cancer survival and prognosis. Eight machine learning models (Support Vector Machines, Logistic Regression, Decision Trees, Random Forests, XGBoost, AdaBoost, K-Nearest Neighbors, and Multilayer Perceptrons) were developed to predict kidney cancer survival and tumor metastasis, using six indicators (Accuracy, Precision, Sensitivity, Specificity, F1 Score and AUROC) to validate, evaluate and optimize models. This study can provide decision support for early intervention in renal cancer patients.
Geriatric Oncology
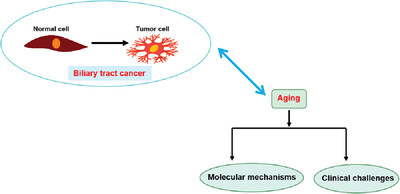
Aging and biliary tract cancers: Epidemiology, molecular biology, and clinical practice
- First Published: 13 June 2022
Noninferior oncological outcomes in adults aged 80 years or older compared with younger patients who underwent radical nephroureterectomy for upper tract urothelial carcinoma
- First Published: 31 July 2022
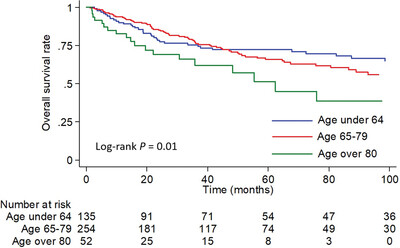
RFS and CSS did not significantly differ between the three groups, but OS was significantly poorer in patients ≥80 years old. Radical nephroureterectomy exerts the same anticancer effects in older patients as in younger patients and may be an option for patients aged ≥80 years who can tolerate surgery.
Flexible bronchoscopy for lung cancer diagnosis in patients aged ≥85 years
- First Published: 16 November 2021
Ostomy prevalence and survival in elderly patients with stage III and IV rectal cancer
- First Published: 29 June 2021
Clinical benefit of platinum doublet combination therapy in older adults with advanced non-small cell lung cancer: A prospective multicenter study by the National Hospital Organization in Japan
- First Published: 18 April 2023
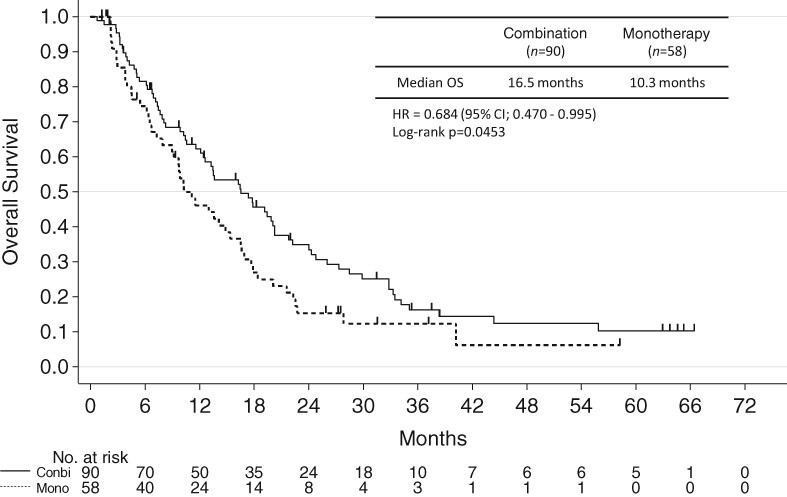
Here, we report that platinum doublet combination therapy may be beneficial in older patients with NSCLC. The OS was significantly longer in patients treated with platinum doublet combination therapy than in those who received monotherapy. Moreover, we identified several laboratory values that reflect prolonged exhaustion owing to inflammation and might be predictors of outcomes in older patients with NSCLC.
Efficacy and safety of carboplatin and etoposide in older extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer patients with a poor performance status
- First Published: 25 January 2023
A rare presentation of lung squamous cell carcinoma metastasis to the distal phalanx of the little finger: a case report
- First Published: 01 August 2022

Acrometastases of the hand are extremely rare and may be the first manifestation of lung cancer, but they consider a poor prognosis marker. It is important for physicians who encounter patients with a persistent lesion at the site of a wound located in the hand to earlier diagnosis. This recognition will improve patient care and may lead to earlier diagnosis of malignancy.
Prediction of death rates for cardiovascular diseases and cancers
- First Published: 09 February 2023
Global Health
COVID-19 pandemic impact on cytopathology practice in the post-lockdown period: An international, multicenter study
- First Published: 10 January 2022
A persistent reduction in the cytological specimen volume during the post-lockdown period has been observed. The relative increase in the cytological workload in the late part of the post-lockdown period is a promising finding of a slow return to normality.