Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Head and Neck Cancer
‘Having the mask on didn't worry me until … they clamped my head down so I wouldn't move’: A qualitative study exploring anxiety in patients with head and neck cancer during radiation therapy
- First Published: 01 February 2023

Patients undergoing radiation therapy for head and neck cancer experience anxiety specifically related to the immobilisation mask, a tight-fighting mask patients are required to wear for the duration of each treatment session. The findings from this research provides valuable insight into how and when healthcare providers may be able assist patients to manage mask anxiety. Recommendations include increased communication from health care providers; delivery of visual information to improve patient preparedness; exposure/opportunities to interact with the masks prior to treatment commencing and increased control of music/soundtrack selection.
Metastatic cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma to the parotid: Adjuvant radiotherapy and treatment outcomes
- First Published: 15 February 2023
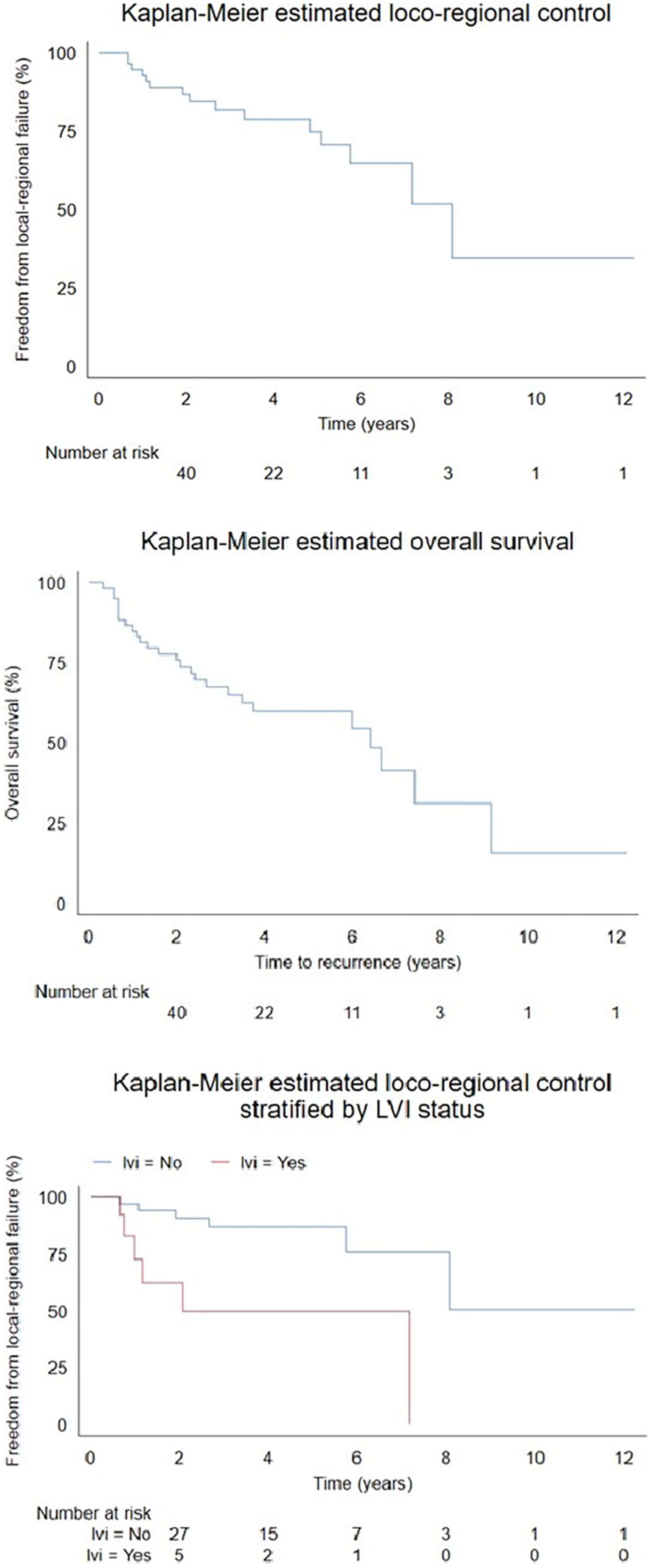
In this study, we have reviewed treatment outcomes for patients with metastatic cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma of the parotid gland treated at Townsville Hospital over a 10-year period. We have demonstrated high loco-regional control rates in our cohort that is comparable to other published series. Lymphovascular invasion was identified as a predictor for loco-regional recurrence.
Identification of pyroptosis-related clusters for prediction of overall survival and characterization of tumor microenvironment infiltration in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma
- First Published: 22 March 2023
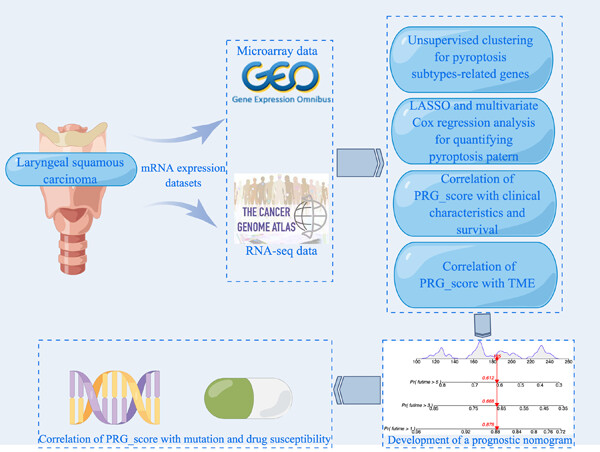
We present a systematic overview of the immune microenvironment of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma (LSCC) based on genetics and transcriptional profiles of pyroptosis-related genes (PRGs) and construct a prognostic model based on the Risk score. These findings can assist in predicting patient prognosis, guiding optimal treatment choices, and developing new immunotherapies for LSCC.
Establishment and verification of a radiomics nomogram to predict distant metastasis in patients with descending type of nasopharyngeal carcinoma
- First Published: 13 December 2022
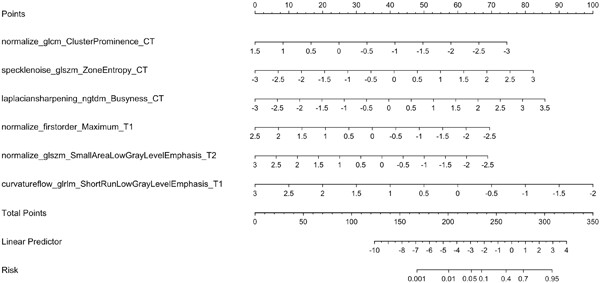
We established a nomogram based on lymph nodes radiomic risk factors to predict distant metastasis in type D nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients. The area under curve values, sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy of the three models of CT, MRI, and multimodal radiomics were compared and analyzed. The multimodal radiomics model was significantly better than the CT or MRI single model in these aspects.
m7G-related genes—NCBP2 and EIF4E3 determine immune contexture in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma by regulating CCL4/CCL5 expression
- First Published: 17 April 2023
CDK4/6 and autophagy inhibitors synergize to suppress the growth of human head and neck squamous cell carcinomas
- First Published: 03 May 2023
Effect of ear exercises on hearing loss in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma after radiotherapy
- First Published: 08 August 2022
Association between mutation profiles and clinicopathological features in Chinese patients with thyroid cancer
- First Published: 17 June 2021
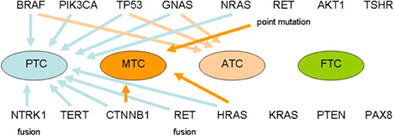
Molecular profiles of the four TC subtypes were different. PTC samples were dominated by BRAF mutations and MTC samples were dominated by RET point mutations. Multiple mutations in TC patients were significantly more frequent in cases of patients aged 55 and over (p <.001) and advanced AJCC cancer stage (p <.001).
Proton beam radiation therapy treatment for head and neck cancer
- First Published: 01 December 2021
Patterns of care in the radiotherapeutic management of head and neck cancer of unknown primary origin: in search of a standard
- First Published: 09 February 2022
Complications associated with energy-based devices during thyroidectomy from 2010–2020
- First Published: 28 April 2022
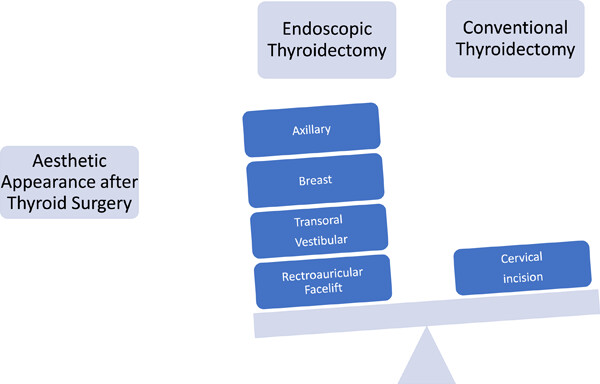
Comparison of cosmetic outcomes between remote-access and conventional thyroidectomy: A review of the current literature
- First Published: 18 April 2022
Emerging roles of circular RNAs in the invasion and metastasis of head and neck cancer: Possible functions and mechanisms
- First Published: 19 February 2023
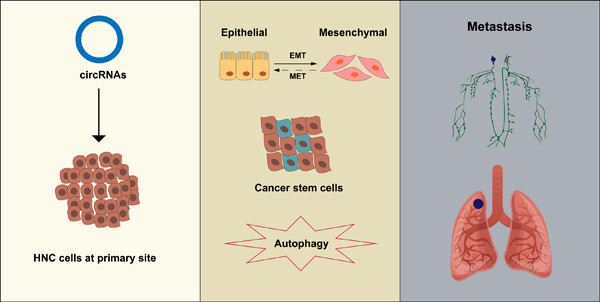
This review outlines the critical roles of circular RNAs (circRNAs) in the invasion and metastasis of head and neck cancer (HNC). circRNAs mainly act on the epithelial-mesenchymal transition, cancer stem cells, and autophagy, thereby affecting HNC metastasis. Furthermore, lung and lymph nodes are the most common sites of HNC metastasis.
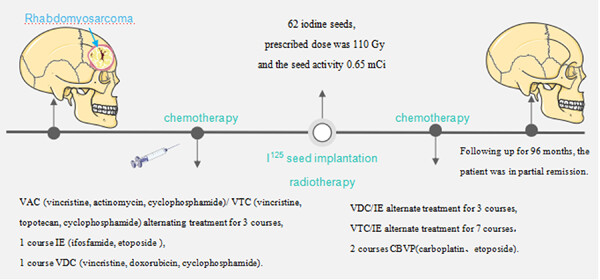
Particle implantation combined with chemotherapy for rhabdomyosarcoma of the head and neck: A 8-year long-term follow-up case report
- First Published: 20 April 2023
Preferences of patients, clinicians, and healthy controls for the management of a Bethesda III thyroid nodule
- First Published: 09 May 2023
Health Services Research and Quality Improvement
Rates of adherence to cancer treatment guidelines in Australia and the factors associated with adherence: A systematic review
- First Published: 07 March 2023
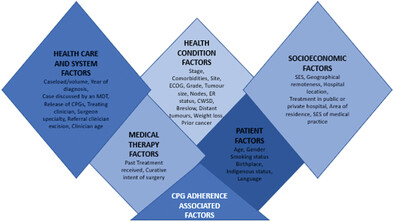
In Australia, adherence to cancer guideline recommendations, ranged from 29% to 100%. Receipt of guideline recommended treatments was highest for patients who were younger, never smokers, non-Indigenous Australians, with less advanced stage disease, without comorbidities, with good-excellent ECOG performance status, and who lived in moderately accessible places and were treated in metropolitan facilities.
Two Singapore public healthcare AI applications for national screening programs and other examples
- First Published: 19 August 2022
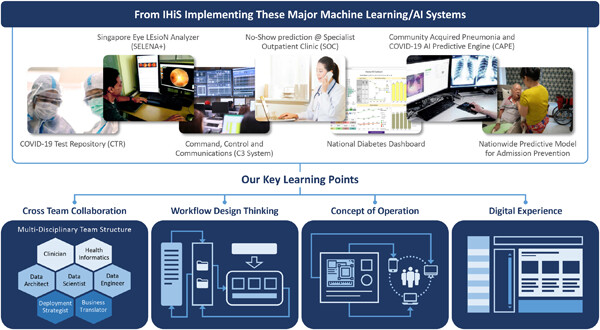
This article explains how two AI systems have been incorporated into the everyday operations of two Singapore public healthcare nation-wide screening programs. Ways in which healthcare needs and the clinical operations context influenced the approach to designing or deploying the AI systems are highlighted, illustrating the multiplicity of factors that shape the requirements for successful large-scale deployments of AI systems that are deeply embedded within clinical workflows.
Implementation science: A critical but undervalued part of the healthcare innovation ecosystem
- First Published: 12 October 2022
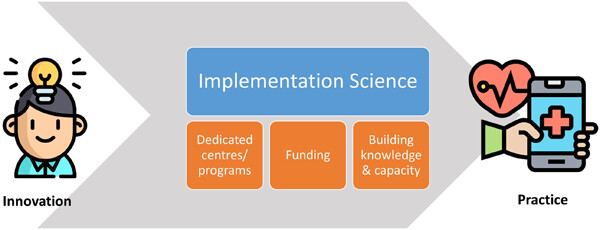
This review highlights the role of implementation science in the healthcare innovation ecosystem, summarize how settings have leveraged it to promote translation of innovation into practice, and describe our own experience of embedding implementation science into an academic medical center in Singapore. Three key thrusts were common in promoting implementation science: (1) establishing dedicated centers, (2) offering funding and (3) building knowledge and capacity among staff.
Construction of a predictive model for cognitive impairment risk in patients with advanced cancer
- First Published: 09 February 2023