Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Hematologic Malignancies
Matching-adjusted indirect comparison of isatuximab plus carfilzomib and dexamethasone with daratumumab plus lenalidomide and dexamethasone in relapsed multiple myeloma
- First Published: 01 February 2023
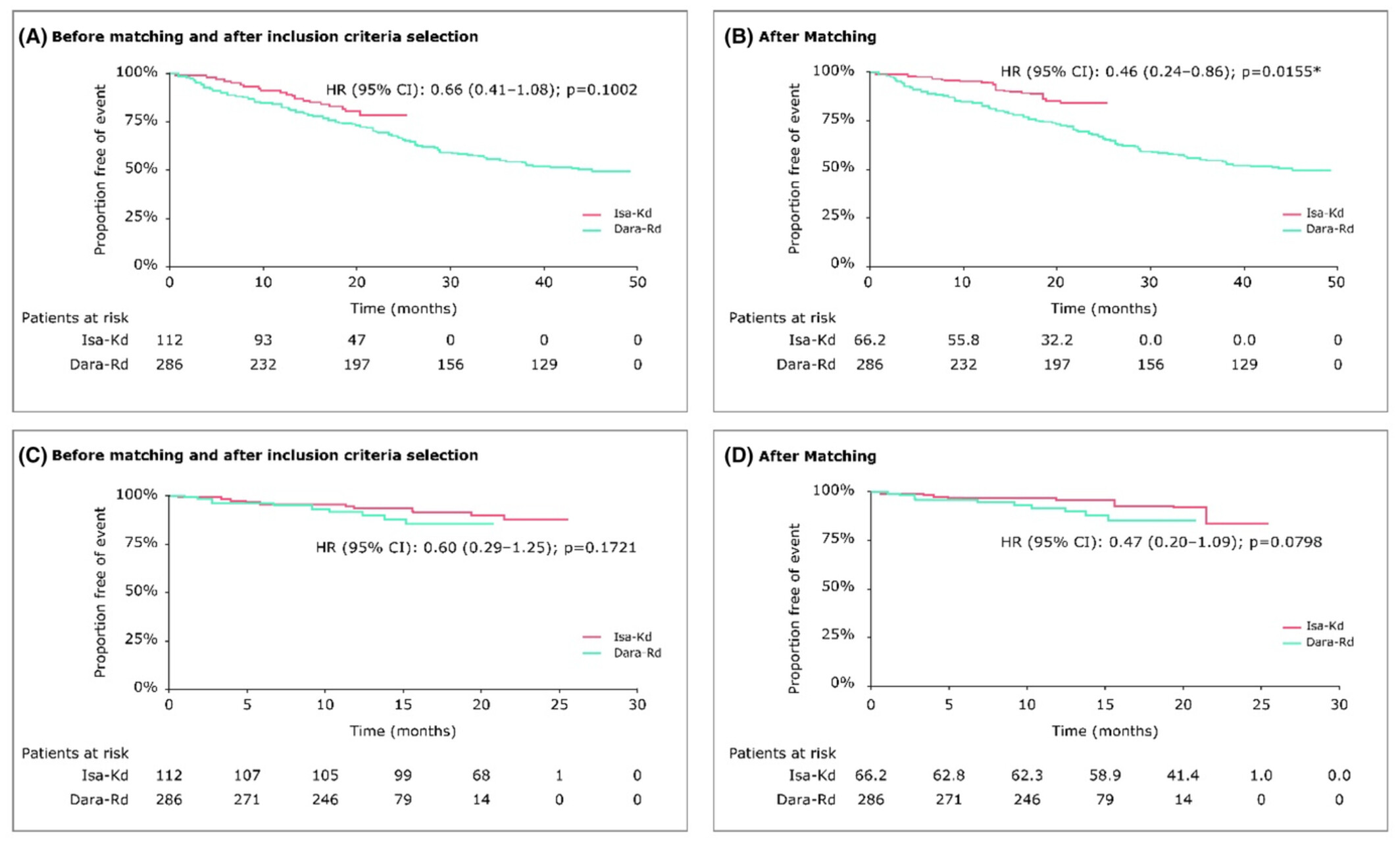
Matching-adjusted indirect comparison results for Isa-Kd vs. Dara-Rd: Kaplan-Meier curves of progression-free survival before matching and after inclusion criteria selection (A) and after matching (B); Kaplan-Meier curves of overall survival before matching and after inclusion criteria selection (C) and after matching (D). CI, confidence interval; Dara-Rd, daratumumab + lenalidomide + dexamethasone; HR, hazard ratio; Isa-Kd, isatuximab + carfilzomib + dexamethasone. *Statistically significant at 0.05 level.
Examining the utility of lower dose radiotherapy for localised primary ocular adnexal MALT lymphoma
- First Published: 06 March 2021
We aimed to examine our institution’s experience with the use of orbital RT for treating early-stage primary ocular adnexal MALT lymphoma (POAML).The use of lower dose orbital RT such as 20 Gy in 10 fractions (or radio biologically equivalent) yields excellent local disease control in the management of ocular adnexal MALT lymphoma.
Changes in five-year survival for people with acute leukaemia in South Australia, 1980–2016
- First Published: 16 February 2022
Severe graft-versus-host disease post allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation due to loss of HLA heterozygosity in recipient lymphocytes after full graft rejection
- First Published: 18 April 2023
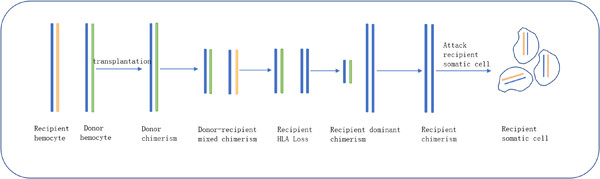
This paper presents a unique case of a 13-year-old female patient diagnosed with concomitant germ cell tumors and acute lymphoblastic leukemia, who underwent allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation and subsequently developed severe graft-versus-host disease (GVHD)-like manifestations (hereon, we call GVH-like-disease, GVHLD) despite the absence of donor chimerism and recurrent hematological malignancy. The underlying etiology was found to be HLA loss of heterozygosity (HLA-LOH) in the patient's newly reconstituted hematopoietic lineage. This is the first report of fatal GVHLD caused by HLA-LOH in the recipient's own immune system without donor chimerism. The paper highlights the importance of understanding the role of HLA-LOH in GVHLD pathogenesis.
Causal relationship between 14 site-specific cancers and venous thromboembolism
- First Published: 07 December 2022
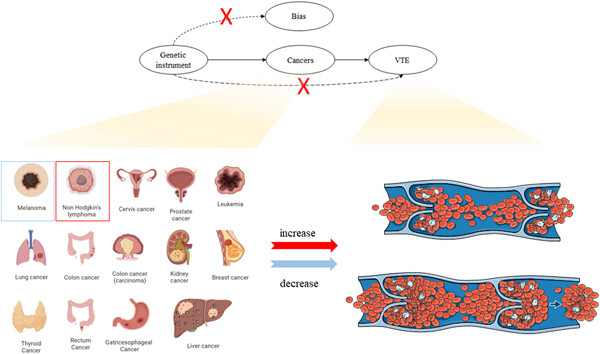
Using Mendelian randomization study, we elucidated the causal effect between 14 site-specific cancers and venous thromboembolism. Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma increases risk of venous thromboembolism while melanoma decreases its risk. footnotes: VTE: venous thromboembolism; some icons were referenced from the Biorender (https://biorender.com/).
Lung Cancer
Effectiveness and safety of Endostar combined with chemotherapy in treating advanced NSCLC patients with different ages
- First Published: 08 April 2023
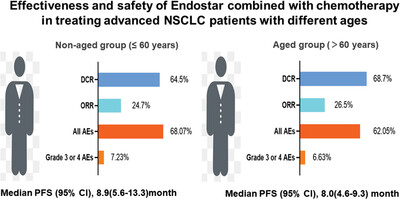
Lung cancer ranks as the leading cause of cancer death in 2020 worldwide. Approximately 85% of newly diagnosed lung cancers are non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). However, the benefit of Endostar used in treating patients with advanced NSCLC of different ages is still unclear in real-world clinical settings. This study aimed to assess the effectiveness and safety of Endostar combined with chemotherapy in the treatment of patients with NSCLC in different age groups (≤60 years vs.>60 years) in a real-world study and indicated the potential of the combination of Endostar and chemotherapy in treating older patients with NSCLC in real clinical settings.
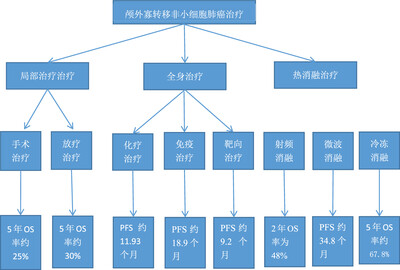
Local thermal ablative therapies for extracranial oligometastatic disease of non-small-cell lung cancer
- First Published: 22 May 2022
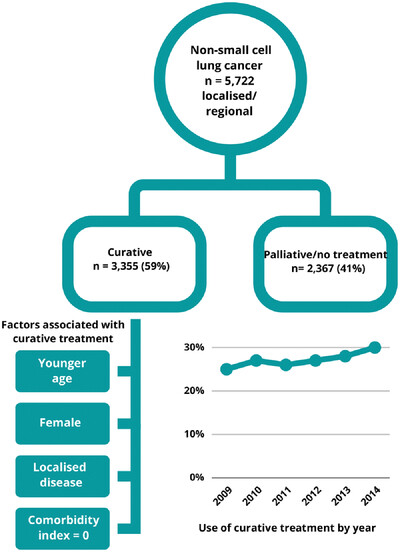
Patterns of curative treatment for non-small cell lung cancer in New South Wales, Australia
- First Published: 17 July 2022
Acquiring tissue for advanced lung cancer diagnosis and comprehensive biomarker testing: A National Lung Cancer Roundtable best-practice guide
- First Published: 01 March 2023
Activity and bioavailability of tepotinib for leptomeningeal metastasis of NSCLC with MET exon 14 skipping mutation
- First Published: 02 January 2021
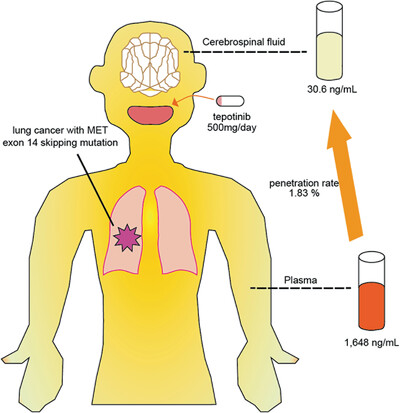
Tepotinib have high retention in the tumor and sustained inhibition of MET and its downstream pathways. Tepotinib is a key drug for cancer patients with MET exon 14 skipping mutation. However, its bioavailability in the CSF in humans has not been elucidated. The blood brain barrier protects the CNS from toxicity, but also prevents therapeutic drugs from accessing the brain. We report a case of leptomeningeal metastasis successfully treated with tepotinib in a patient with poor PS and on the bioavailability of tepotinib in the CSF in humans.
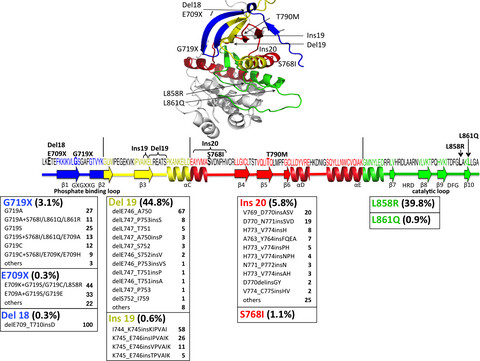
Not all epidermal growth factor receptor mutations in lung cancer are created equal: Perspectives for individualized treatment strategy
- First Published: 20 June 2016
Charcoal cigarette filters and lung cancer risk in Aichi Prefecture, Japan
- First Published: 19 May 2005
The earlier, the better? A review of neoadjuvant immunotherapy in resectable non-small-cell lung cancer
- First Published: 25 May 2022
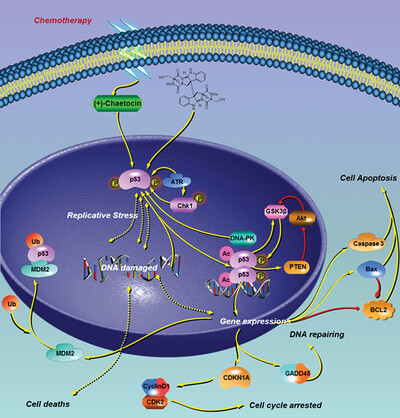
Marine toxin (+)-chaetocin-induced apoptosis of lung large cell carcinoma cell lines through cell cycle arrest via CDKN1A expression and replicative stress
- First Published: 06 May 2022
Chromium (VI) promotes lung cancer initiation by activating EGF/ALDH1A1 signalling
- First Published: 14 December 2022
Lysophosphatidylcholine inhibits lung cancer cell proliferation by regulating fatty acid metabolism enzyme long-chain acyl-coenzyme A synthase 5
- First Published: 13 January 2023
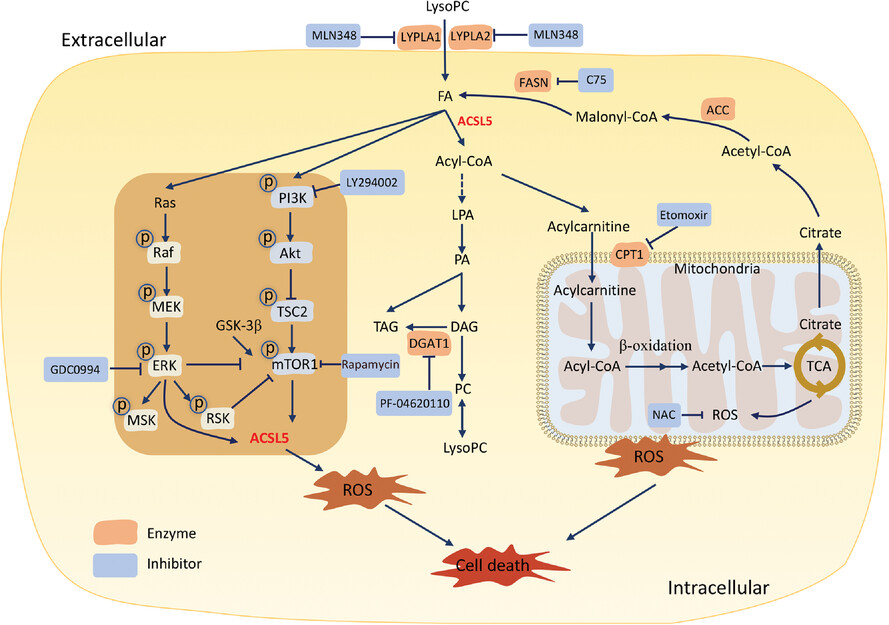
- LysoPC reprograms lipid metabolisms by increasing the accumulation of fatty acids and activating acyl-CoA-dominated metabolic mode under the control and regulation of ACSL5.
- LysoPC up-regulates the expression of ACSL5 and activates the ACSL5-oriented lipid metabolism by promoting the phosphorylation of PI3K/mTOR and Ras/ERK signal pathways.
- LysoPC inhibited lung cancer cell proliferation by promoting ACSL5, leading to the disorder of FA degradation.
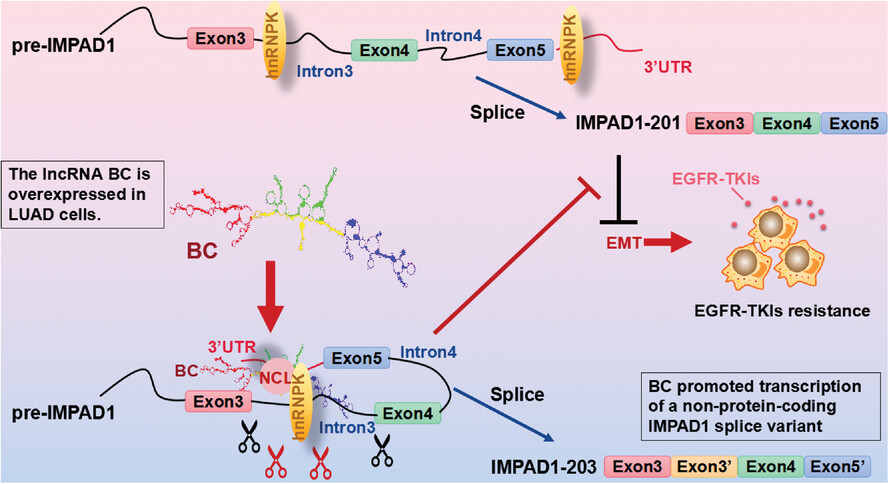
LncRNA BC promotes lung adenocarcinoma progression by modulating IMPAD1 alternative splicing
- First Published: 17 January 2023
Clinical validation of a semi-automated segmentation algorithm for target volume definition on planning CT and CBCT in stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) for peripheral lung lesions
- First Published: 24 November 2022
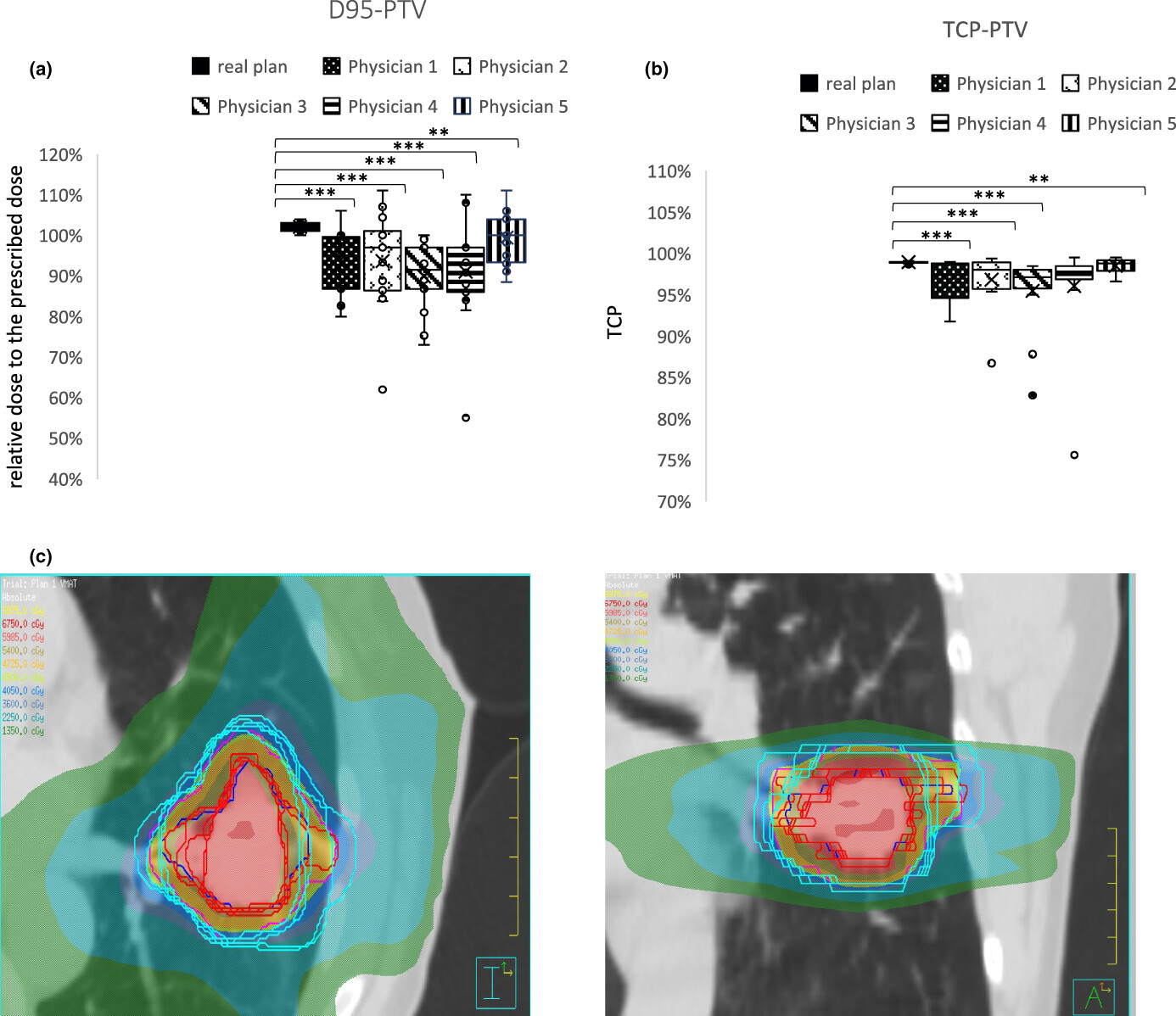
The Interobserver variability for target volume delineation in the SBRT of pulmonary lesions - could have major negative dosimetric consequences, which could threaten the tumour control probability. In this study, we introduce an easy-use semi-automated delineation tool for peripheral lung lesions in free breathing (FB) and four-dimensional (4D) planning CT and cone beam CT (CBCT). The Dice similarity coefficient (DSC) showed the reliability of the tool alone or better in a supervised application. The semi-automated delineation tool can accurately track the interfraction and intrafraction changes or deformations of tumours through the therapy in CBCT, opening the door for its use in adaptive planning.
Volumetric modulated arc therapy (VMAT) comparison to 3D-conformal technique in lung stereotactic ablative radiotherapy (SABR)
- First Published: 24 November 2022
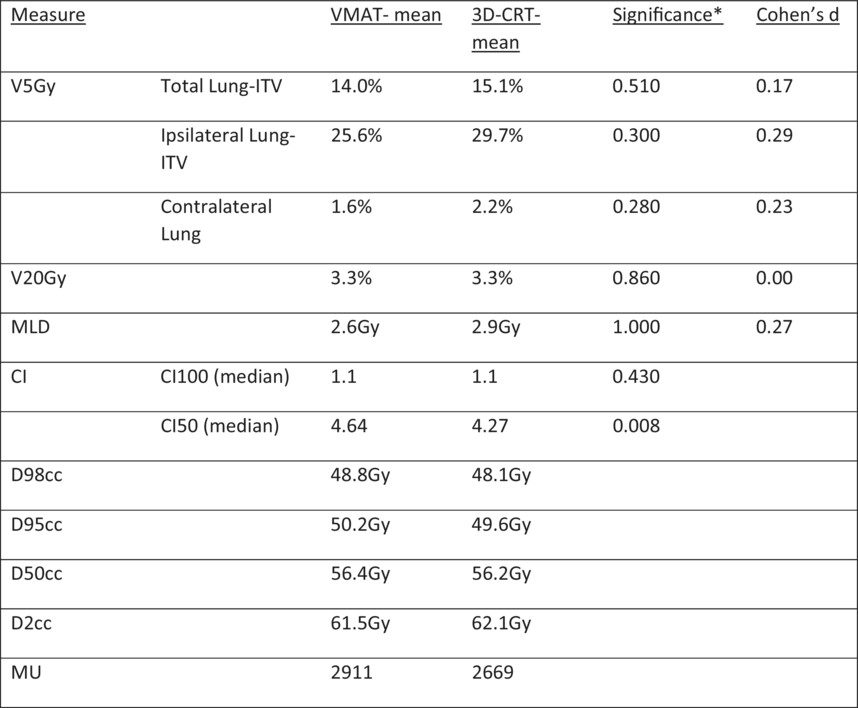
This paper evaluates the dosimetry of volumetric arc therapy in comparison to 3D-Conformal technique in delivery of lung stereotactic ablative radiotherapy. No significant dosimetric differences were found between the two techniqiues that could potentially lead to an increased risk of radiation pneumonitis.