Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Melanoma/Skin Cancer
The impact of incomplete clinical information and initial biopsy technique on the histopathological diagnosis of cutaneous melanoma
- First Published: 23 August 2021
Development of melanoma clinical quality indicators for the Australian melanoma clinical outcomes registry (MelCOR): A modified Delphi study
- First Published: 29 April 2022
RNA N6-methyladenosine connects YTHDF3 and LOXL3 to promote melanoma metastasis
- First Published: 12 December 2022
Commentary on: Pre-clinical platforms to study therapeutic efficacy of human γδ T cells
- First Published: 02 June 2022
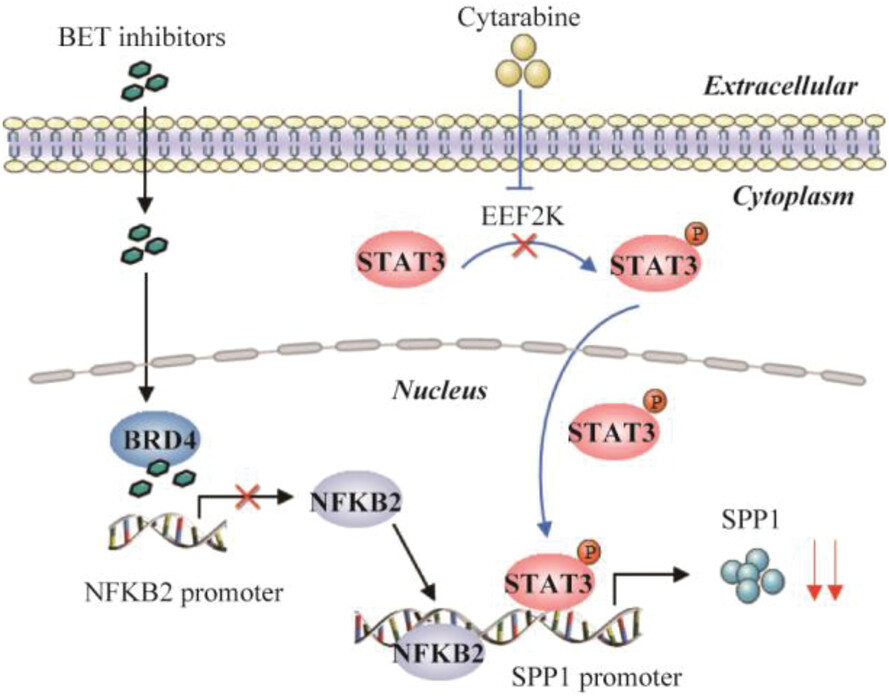
EEF2K silencing inhibits tumour progression through repressing SPP1 and synergises with BET inhibitors in melanoma
- First Published: 20 February 2022
Circulating cell-free messenger RNA enables non-invasive pan-tumour monitoring of melanoma therapy independent of the mutational genotype
- First Published: 01 November 2022
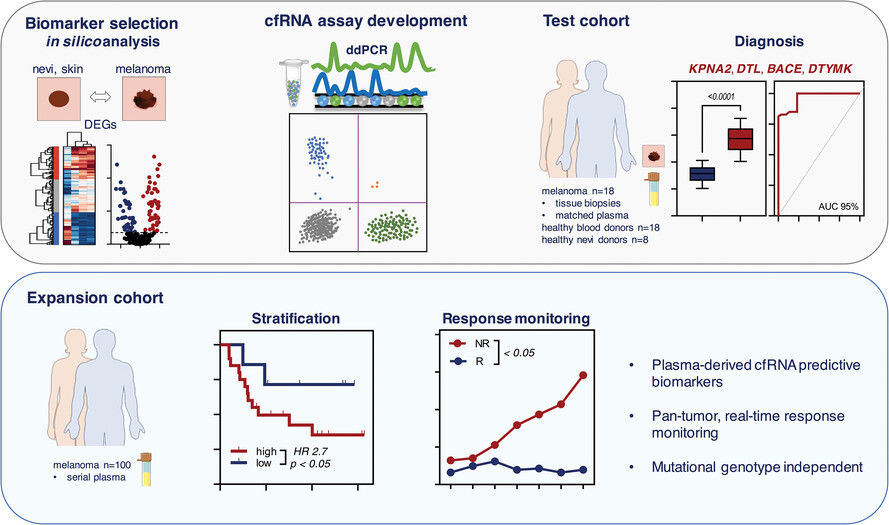
- Biomarker candidates were identified through unsupervised data mining of melanoma versus benign nevi or healthy skin transcriptomes.
- Droplet digital PCR (ddPCR) assays were developed for circulating cell-free RNA (cfRNA) quantification.
- KPNA2, DTL, BACE2 and DTYMK cfRNA demonstrated high diagnostic accuracy in melanoma.
- High baseline cfRNA levels were associated with significantly shorter progression-free survival.
- cfRNA copies significantly increased during therapy in non-responders regardless of therapy and mutational subtypes.
Interleukin-37 promotes DMBA/TPA skin cancer through SIGIRR-mediated inhibition of glycolysis in CD103+DC cells
- First Published: 05 March 2023
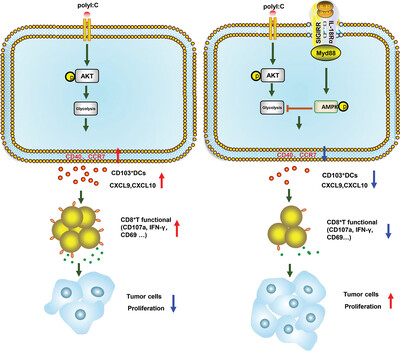
In the 7,12-dimethylbenzoanthracene/tetradecylphorbol-13-acetate two-stage skin cancer induction model, interleukin weakened the expression of CD40/CCR7 and the secretion of C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 9/CXCL10 in CD103+DCs through single immunoglobulin interleukin-1-related receptor-activated protein kinase-Akt signal axis, which leads to the suppression the function of CD8+T cells and accelerating the growth of tumor.
The diagnosis and initial management of melanoma in Australia: findings from the prospective, population-based QSkin study
- First Published: 11 April 2023
Circular RNAs: Biomarkers of cancer
- First Published: 21 September 2022
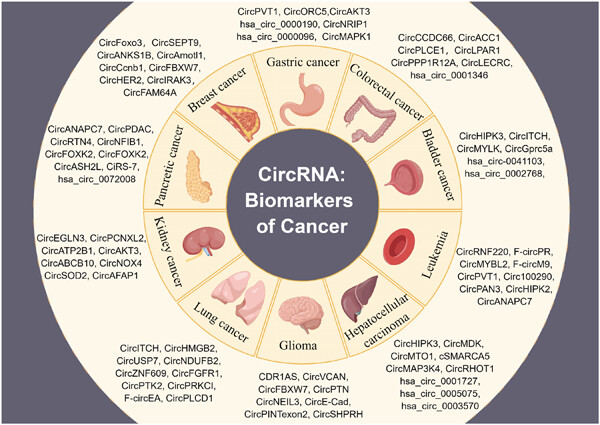
This study demonstrates that circular RNAs (circRNAs) have great potential as biomarkers for cancer diagnosis and prognosis, which is highlighted by their detectability in tissues and fluid biopsy samples. CircRNAs may act as biomarkers in cancers including glioma, bladder cancer, breast cancer, gastric cancer, hepatocellular carcinoma, colorectal cancer, lung cancer, kidney cancer, pancreatic cancer, and leukemia.
Ecological view of carcinogenesis: Niche-altering (NC3) mechanisms
- First Published: 21 February 2023
Pediatric Oncology
Spontaneous xenogeneic GvHD in Wilms' tumor Patient-Derived xenograft models and potential solutions
- First Published: 20 June 2022
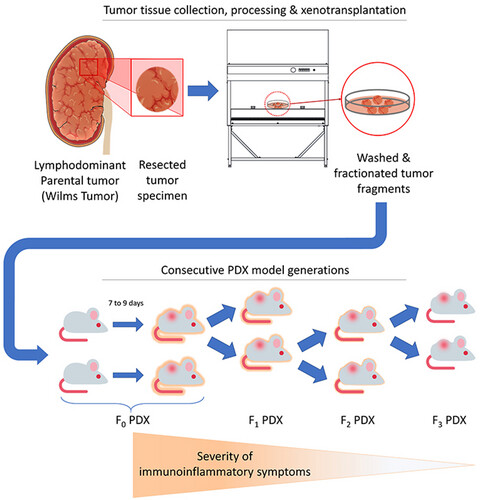
Three consecutive generations of NOG mice bearing Wilms tumor patient-derived xenografts from a single donor showed different degrees of immunoinflammatory symptoms. Histopathologic evaluations of the xenografts and parental tumor showed lymphoid infiltrates and human-originated CD3 and CD8 positive cells in the tissue blocks, while no lymphoproliferative disorder was evident (suggestive of a lymphodominant tumor graft). In the absence of microbial infection and lymphoproliferative disorder, the syndrome was suggestive of xenogeneic graft-versus-host disease.
Adverse late health outcomes among children treated with 3D radiotherapy techniques: Study design of the Dutch pediatric 3D-RT study
- First Published: 30 January 2023
Clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats screens in pediatric tumours: A review
- First Published: 10 December 2022
Functional genomic analysis of epithelioid sarcoma reveals distinct proximal and distal subtype biology
- First Published: 15 July 2022
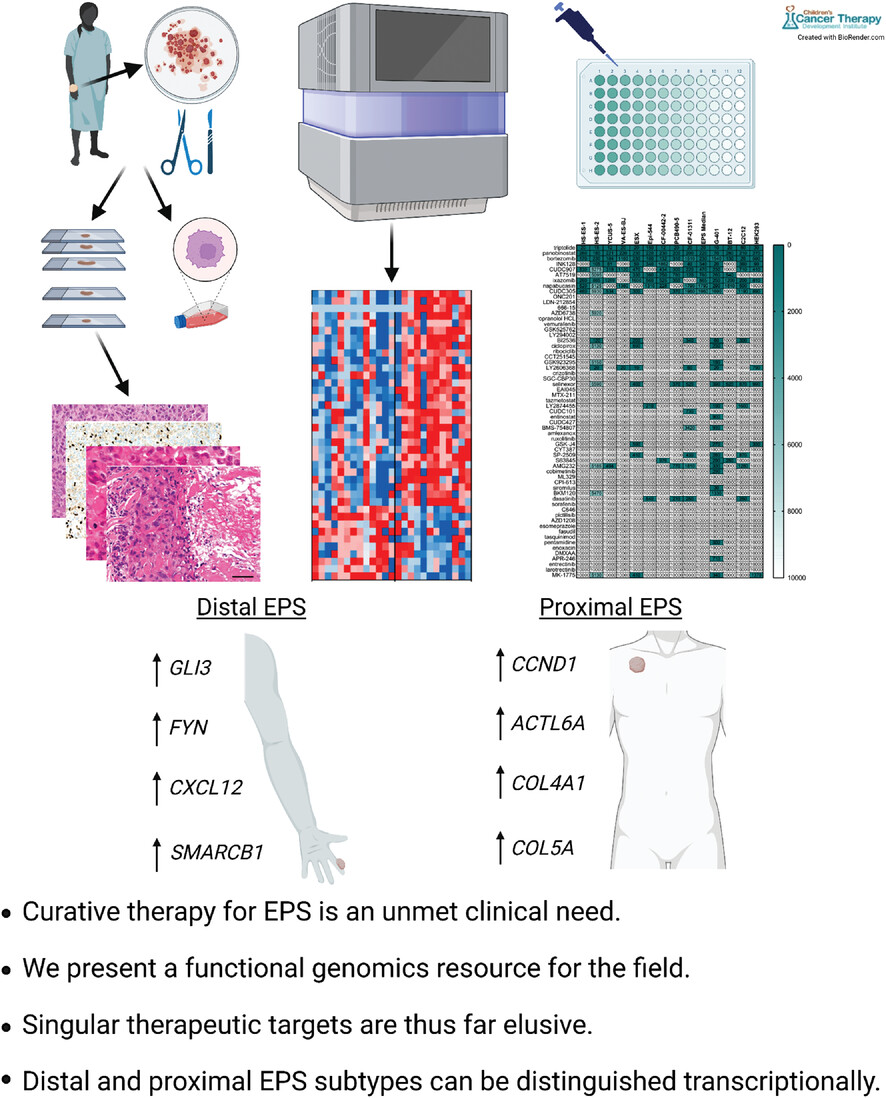
Metastatic Epithelioid Sarcoma has a largely unmet clinical need in pediatrics and young adults. To identify potential targets for inhibition we conducted next generation DNA exome and RNA deep sequencing and chemical screens in EPS patient samples and cell lines. We uncovered distinguishing features of the two subtypes of EPS, distal and proximal.
FABP4 deactivates NF-κB-IL1α pathway by ubiquitinating ATPB in tumor-associated macrophages and promotes neuroblastoma progression
- First Published: 01 May 2021
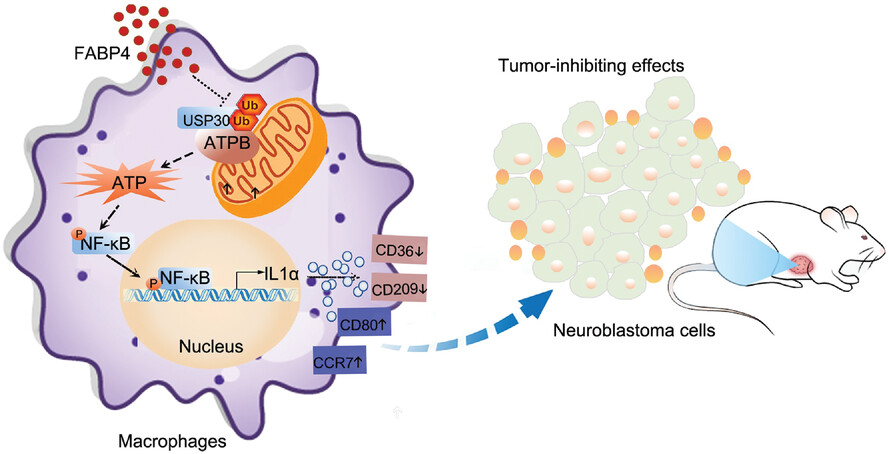
-
FABP4 in macrophages expression is correlated with advanced clinical stages and unfavorable histology of neuroblastoma.
-
FABP4 in macrophages increases migration, invasion, and tumor growth of neuroblastoma cells.
-
FABP4 in macrophages may promote proliferation and migration phenotypes in neuroblastoma cells through deactivating NF-κB-IL1α pathway by ubiquitinating ATPB.
Dosimetric evaluation of adult and paediatric brain tumours planned using mask-based cobalt-60 fractionated stereotactic radiotherapy compared to linear accelerator-based volumetric modulated arc therapy
- First Published: 01 October 2022
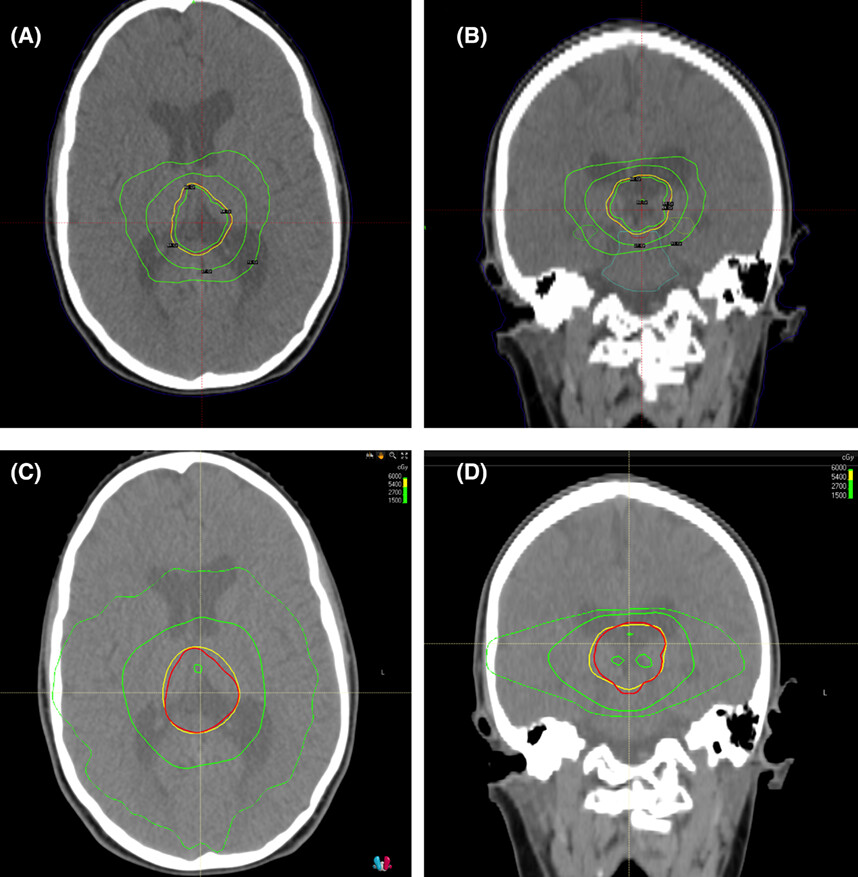
In this comparative dosimetry study, fractionated cobalt-60 radiosurgery plans (top panels) achieved equivalent target coverage but improved conformity and organ-at-risk sparing as compared to VMAT plans (bottom panels). Fractionated radiosurgery may be considered for future prospective study as a highly focused modality for photon radiation of intracranial tumours.
Radiation protection for comforters and carers in radiology and nuclear medicine
- First Published: 24 April 2023
Health-care workers' understanding of and barriers to palliative care services to Aboriginal children with cancer
- First Published: 30 April 2022
Social determinants of increased risk of cardiovascular disease in cancer survivors
- First Published: 14 January 2023
Promoting the application of pediatric radiomics via an integrated medical engineering approach
- First Published: 19 February 2023
Radiomics is widely used in adult tumors but has been rarely applied to the field of pediatrics. Promoting the application of radiomics in pediatric diseases, especially in the early diagnosis and stratified treatment of tumors, is of great value to the realization of the WHO 2030 “Global Initiative for Childhood Cancer.” This paper discusses the general characteristics of radiomics, the particularity of its application to pediatric diseases, and the current status and prospects of pediatric radiomics.