Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Care Delivery and Regulatory Policy
A study in patient satisfaction regarding telemedicine consultations in radiation oncology
- First Published: 16 March 2022
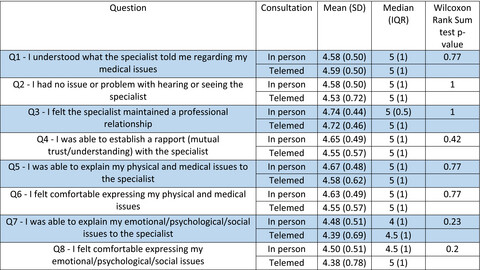
Telemedicine consultations can be a cost effective and convenient method of communication particularly with patients living in remote areas. Given the dearth of patient reported satisfaction data with this form of consultation in Radiation Oncology, we surveyed patients to assess this in our department.
Telemedicine platforms must be leveraged to strengthen rural health systems
- First Published: 03 August 2022
Geographic variation in out-of-pocket costs for radiation oncology services
- First Published: 22 March 2023
A narrative medicine-based training program increases the humanistic care quality of new nurses in cancer hospital
- First Published: 01 January 2023
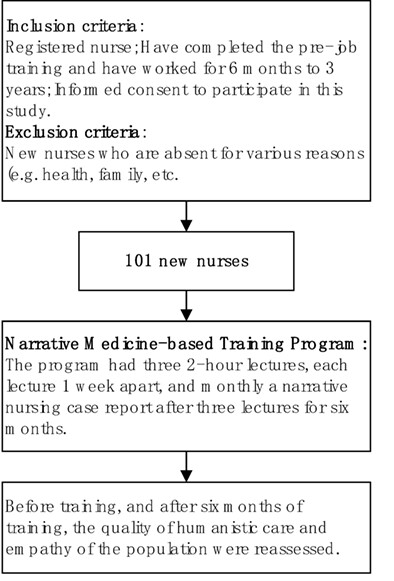
First, we recruit 101 new nurses (Inclusion criteria: registered nurse; have completed the prejob training and have worked for 6 months to 3 years; informed consent to participate in this study). Exclusion criteria: new nurses who are absent for various reasons (e.g., health, family, etc.). A narrative medicine-based training program is implemented for these new nurses. The program had three 2-h lectures, each lecture 1 week apart, and monthly a narrative nursing case report after three lectures for 6 months. Before training, the humanistic care quality and empathy ability of these nurses were assessed. After 6 months of training, the quality of humanistic care and empathy of the population were reassessed.
Pathway to excellence in cancer care: learning from Qatar's experience
- First Published: 18 November 2020
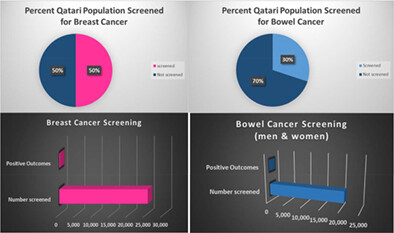
Qatar provides a model that illustrates how the principles of good cancer control are internationally applicable but need to be locally owned and adapted to the country and be culturally specific. Critical to the success were robust governance structures, informed and committed leadership, comprehensive involvement of all sectors including public and private providers, charities, private sector employers, academic partners and the judicious use of expert groups and subject matter experts. Population based screening programs were established to enable eligible individuals with services via walk-in, self-referral or a physician's referral. Primary healthcare is presently delivering three cancer screening programs (breast, bowel & cervical) to improve cancer burden. We propose a policy framework and make further recommendations to solidify current gains and enhance services, outcomes, and experiences for cancer patients and their families.
Chinese expert consensus on the diagnosis and treatment of HER2-altered non–small cell lung cancer
- First Published: 28 November 2022
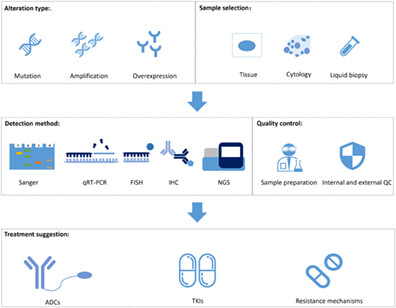
To improve the diagnosis and treatment of HER2-altered non-small cell lung cancer in China, we reached consensus on detection strategy based on alteration type, sample selection, detection method, quality control, and treatment suggestion. Moreover, we systematically reviewed the clinical efficacy, resistance mechanisms, and development status of HER2- targeting drugs.
Expert consensus on the diagnosis and treatment of NTRK gene fusion solid tumors in China
- First Published: 20 September 2022
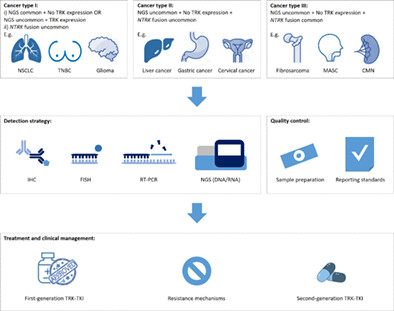
To improve the diagnosis and treatment of NTRK gene fusion solid tumors in China, we reached consensus on detection strategy based on cancer type classification, quality control requirements, treatment and clinical management. Moreover, we systematically reviewed the clinical efficacy, resistance mechanisms and development status of TRK inhibitors.
Clustering of prostate cancer healthcare pathways in the French National Healthcare database
- First Published: 17 January 2023
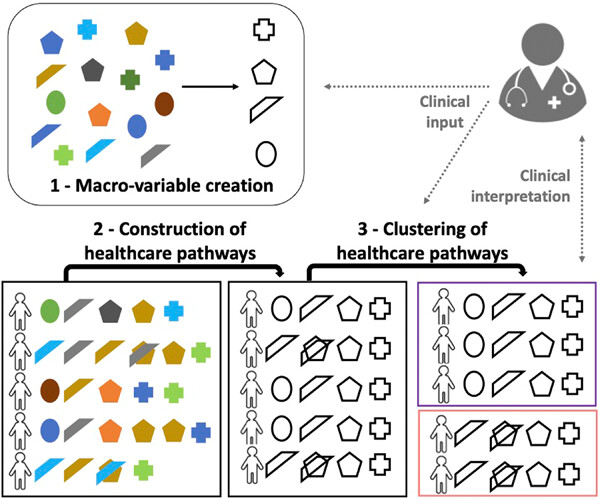
Patients with prostate cancer go through multiple heterogeneous healthcare encounters. Clustering methods were used to summarize correlated encounters in macro-variables and reconstitute patient healthcare pathways. In the second stage, clinically relevant patterns of prostate cancer management (e.g., watchful waiting and active surveillance) were revealed by applying clustering methods to these healthcare pathways according to the patient cancer stage, highlighting the interest of this approach in real-world research.
Advances and prospects of drug clinical research in colorectal cancer in 2022
- First Published: 05 March 2023
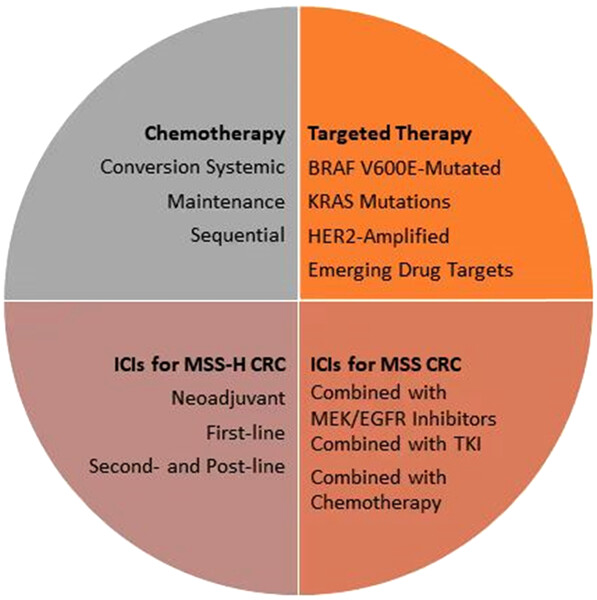
Colorectal cancer (CRC) represents the leading cause of cancer-related death worldwide. The advent of fluorouracil in 1962 ushered in a new era of anticolorectal cancer drugs in the treatment of CRC; the rapid advancement of molecularly targeted therapy and immunotherapy has also offered a new therapeutic paradigm for patients. This article reviews the most recent studies in the field of CRC in 2022, which will be presented in terms of three aspects: chemotherapy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy.
Central Nervous System Tumors
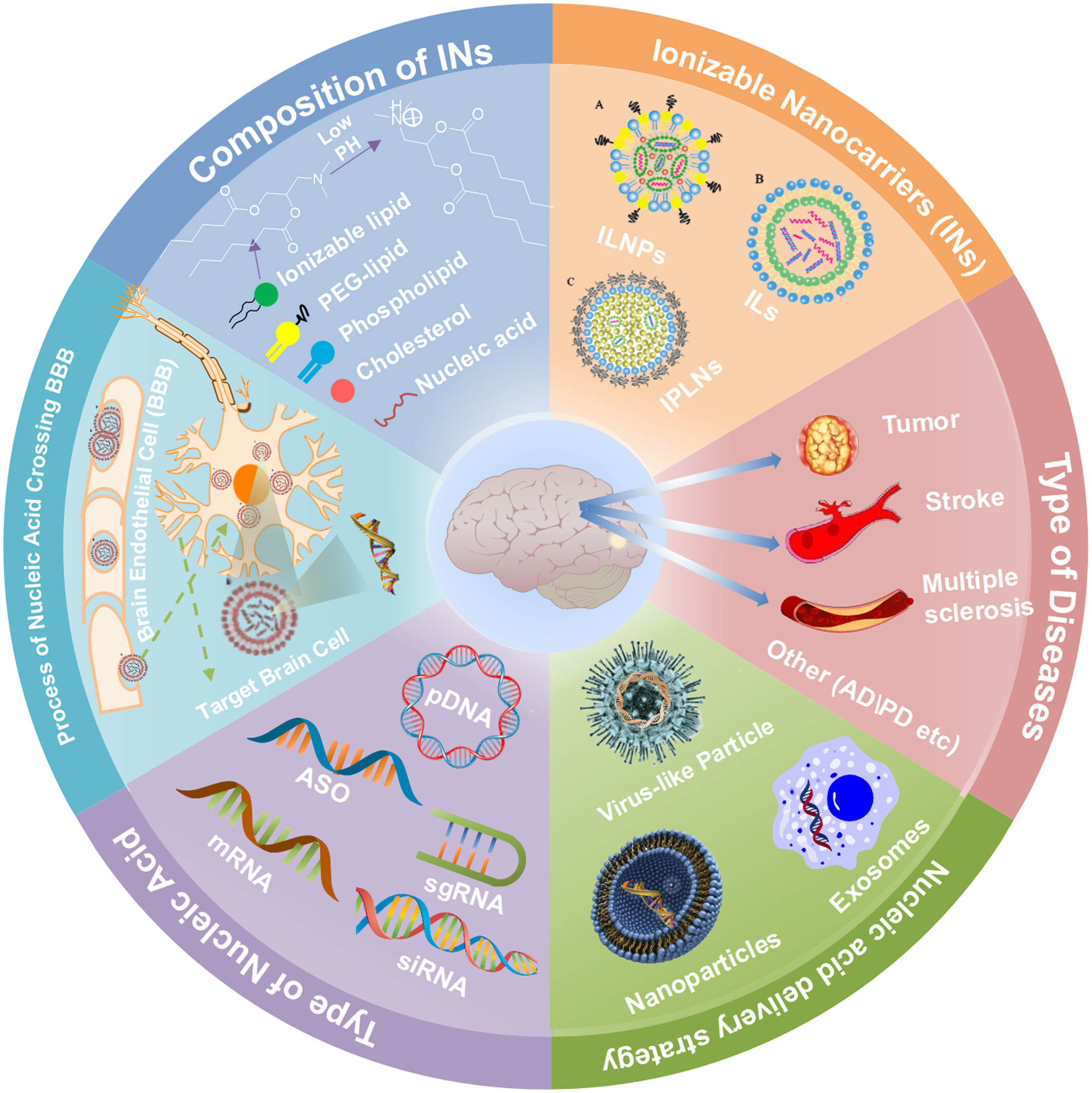
Nucleic acid delivery by ionizable nanocarriers for brain disease treatment
- First Published: 26 March 2023
Rhythmic calcium ion activity related to glioma growth reveals the mechanism of ion transmission
- First Published: 21 March 2023
Pre-transplantation cytoreduction does not benefit advanced myelodysplastic syndrome patients after myeloablative transplantation with grafts from family donors
- First Published: 10 February 2021
An update on the molecular biology of glioblastoma, with clinical implications and progress in its treatment
- First Published: 21 September 2022
Gut microbiome and neurosurgery: Implications for treatment
- First Published: 10 October 2022
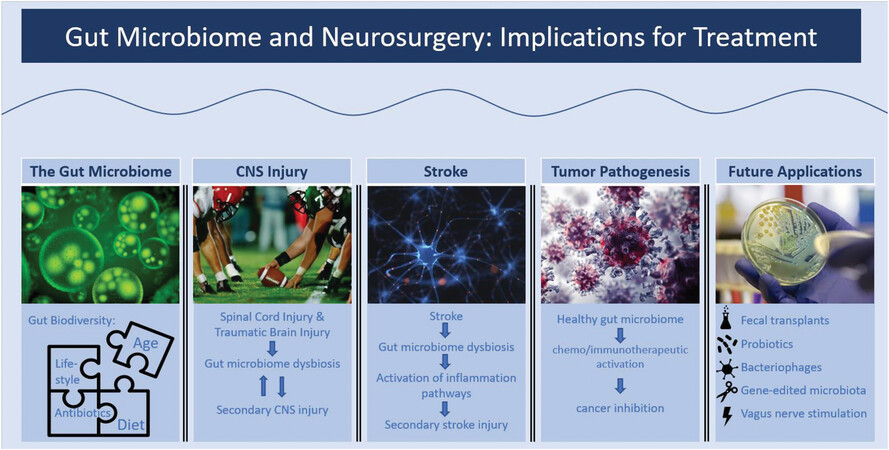
There is a strong bidirectional link between gut microbiome dysbiosis and worsening secondary injury post-stroke, SCI, and TBI.These deficits may be rescued by timely rejuvenation of the gut microbiome. The maintenance of a healthy microbiome plays a protective role in the setting of tumor chemotherapy and immunotherapy. The future of gut microbiome modulation for neurosurgical therapeutic goals appears increasingly promising.
Association of circulating tumor DNA from the cerebrospinal fluid with high-risk CNS involvement in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
- First Published: 15 January 2021
Single-cell RNA sequencing reveals cellular and molecular reprograming landscape of gliomas and lung cancer brain metastases
- First Published: 06 November 2022
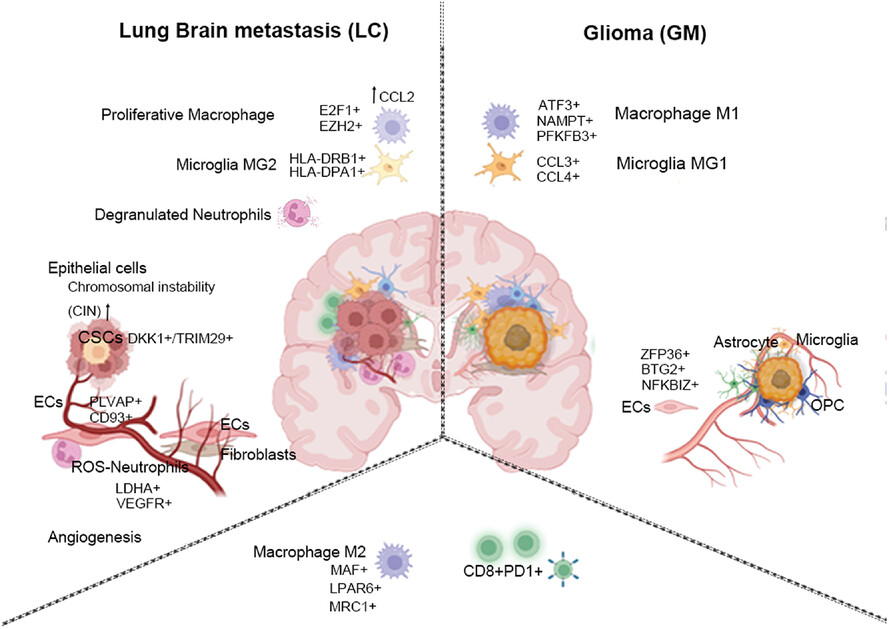
- Single-cell transcriptional profiles in gliomas and lung-to-brain metastases.
- TAMs (macrophage and microglia) exhibited phenotypic and functional diversity.
- Endothelial cells communicated with neutrophils or fibroblasts to support angiogenesis.
- Metastatic epithelial cells exhibited higher chromosomal instability and enriched a subpopulation with stem cell-like phenotype.
Protein phosphorylation: A potential target in glioma development
- First Published: 08 May 2022

Glioma is a common primary brain tumor, and its mortality rate is extremely high. Protein phosphorylation regulates a number of cellular functions like cell growth, differentiation, apoptosis, and cell signaling, so it can also be used as a target to regulate the development of glioma. This review is a discussion on the growth, migration and invasion, resistance, and death of glioma in phosphorylation and the possibility of treating glioma by phosphorylation.
Interaction among long non-coding RNA, micro-RNA and mRNA in glioma
- First Published: June 2021
Association of antidepressant drug use with outcome of patients with glioblastoma
- First Published: 08 November 2022
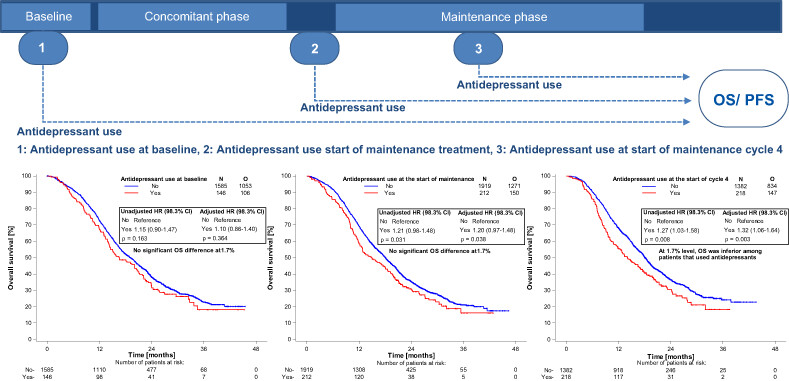
What's new?
Depressive symptoms are common yet often undertreated in patients with glioblastoma, in part due to limited evidence on the association of antidepressant drug use with survival. Among 1,700 patients with glioblastoma derived from clinical trials, the authors found no significant association between progression-free or overall survival and the use of antidepressant drugs at baseline or at the start of maintenance therapy. While overall survival was worse at the start of maintenance cycle 4 in patients using antidepressant drugs, progression-free survival was not significantly changed. The findings suggest that antidepressants should not be withheld from patients with glioblastoma.
Modified volumetric modulated arc therapy technique with reduced planning and treatment time for craniospinal irradiation utilising two isocentres
- First Published: 22 April 2022
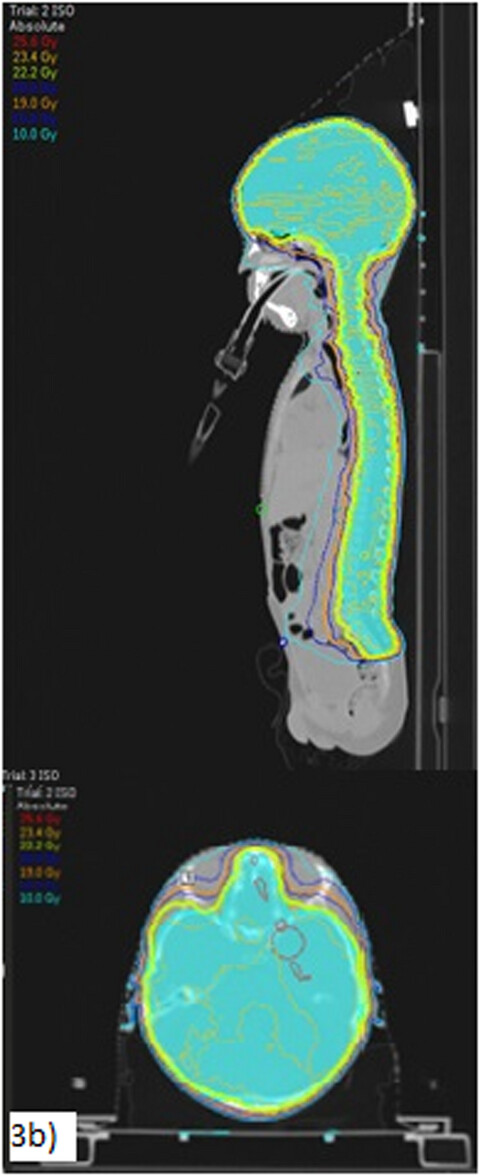
A modified two isocentre (2-ISO) volumetric modulated arc therapy (VMAT) technique was investigated to determine whether it was dosimetrically equivalent to a 3-ISO VMAT technique and whether it can provide for an improved workflow process for planning and treatment of CSI patients. The new 2-ISO VMAT technique provided comparable dose distribution and patient-specific QA results to the 3-ISO technique. Its reduced planning and treatment times allows patients to commence treatment earlier, reduces sedation time during treatment if it is required and assists with limiting intra-fraction motion while potentially increasing treatment accuracy.