Brain‐X is an open access journal publishing cutting-edge discoveries and technologies to provide insight into the brain, neuroscience, and neurology. We're interested in interdisciplinary studies utilizing approaches from mathematics, physics, chemistry, engineering, materials, and information science to help understand the brain.
Journal Metrics
- 41%Acceptance rate
- 29 days Submission to first decision
Read more to learn about the journal.
Articles
The application and challenges of brain‐computer interfaces in the medical industry
- 1 July 2025
Graphical Abstract
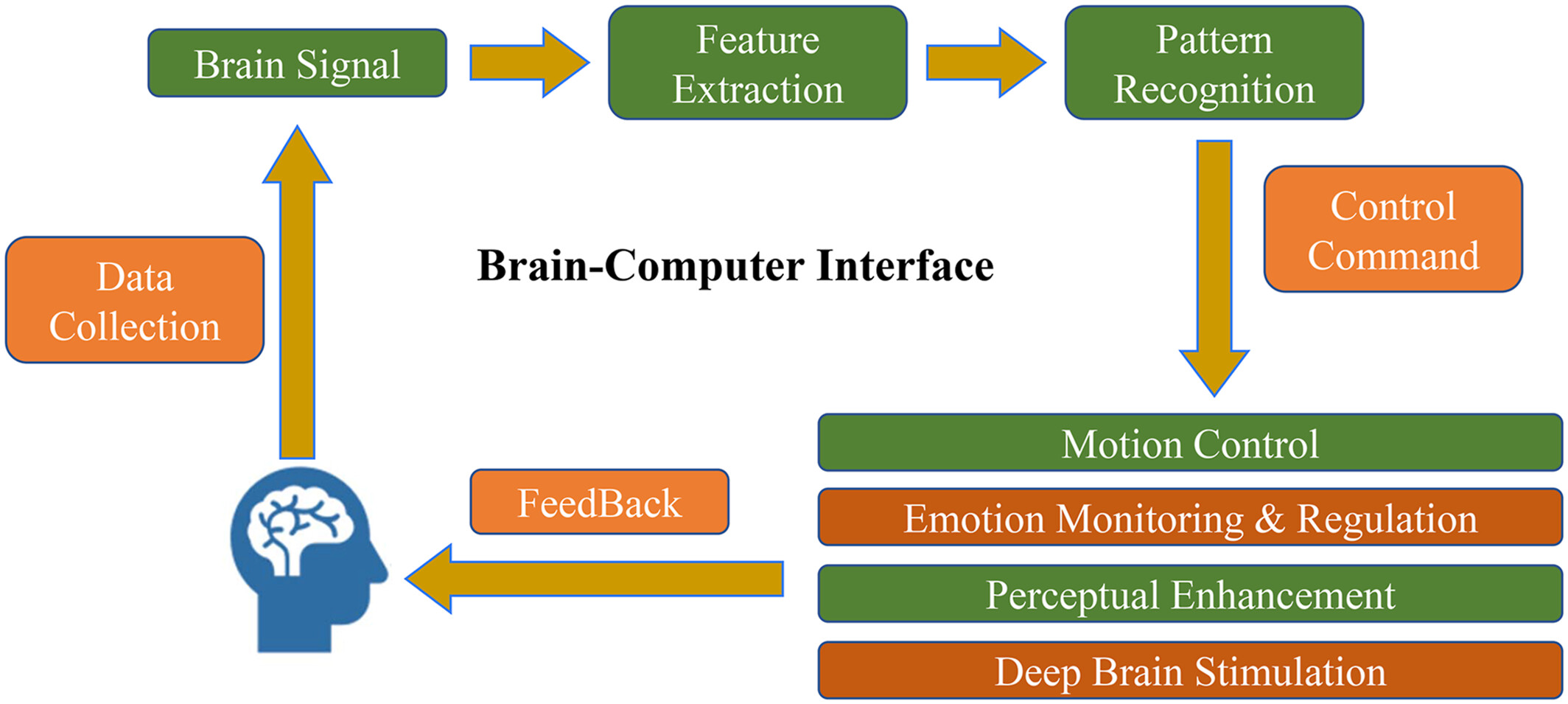
Brain-computer interfaces (BCIs) aim to create a connection pathway for information exchange between the brain and devices with computing capabilities. The complexities of non-invasive BCIs and the implantation risks associated with invasive BCIs have confined these technologies to laboratory settings. A lack of foundational technologies of non-invasive and invasive BCIs, the signal processing challenges associated with BCIs, the key components of BCIs, and the compatibility of BCI software and hardware are challenges that need to be solved for BCI commercialization.
Synergizing DeepSeek's artificial intelligence innovations with brain–computer interfaces
- 28 June 2025
Graphical Abstract
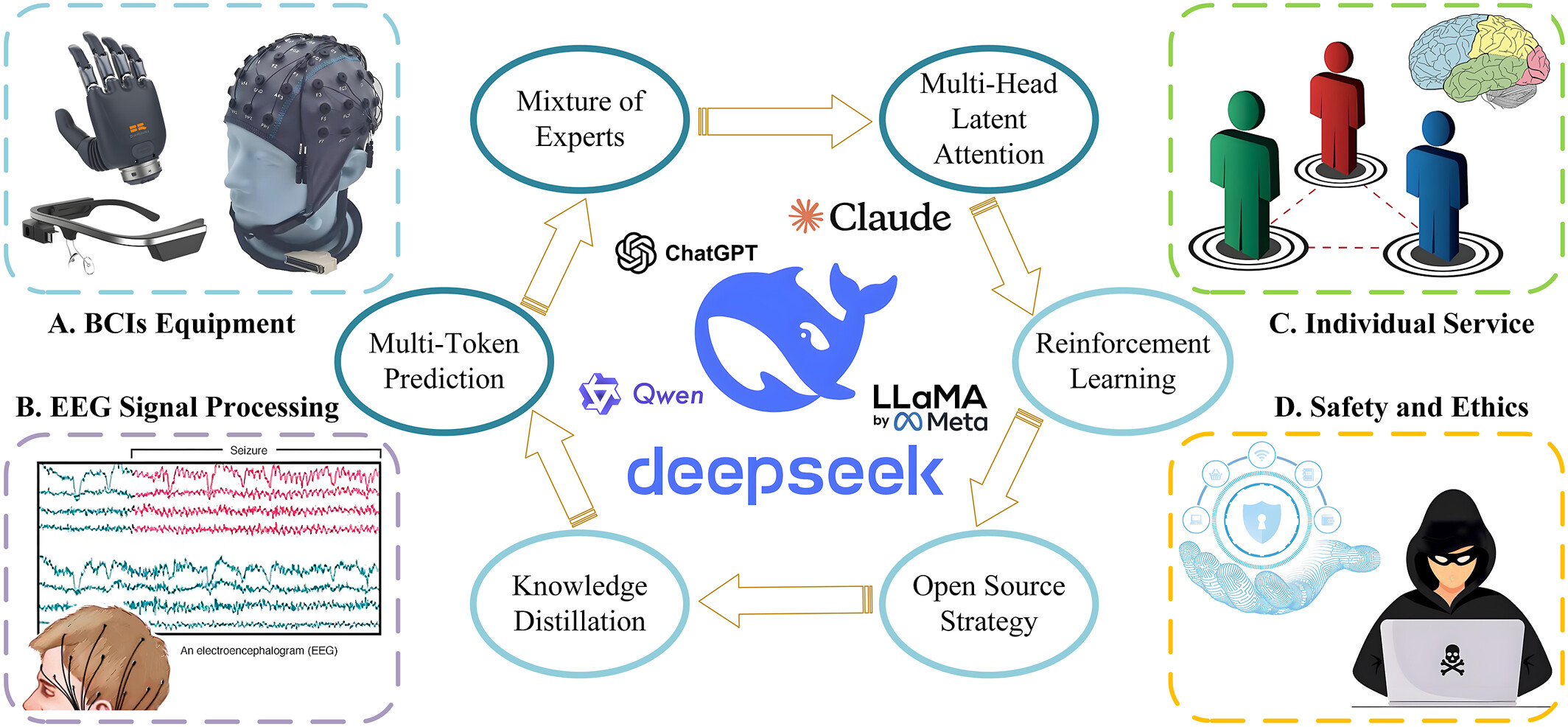
This perspective examines the synergy between DeepSeek, a leader in efficient, open-source artificial intelligence models, and next-generation brain–computer interface (BCI) technologies. Based on the advanced technology of DeepSeek, this study explores the fusion of large language models (LLMs) in the fields of BCI devices, electroencephalogram signal processing, and individual service, and deeply discusses the data safety and ethical issues that are inevitable with LLMs, providing unique insights into the path to democratizing neurotechnology.
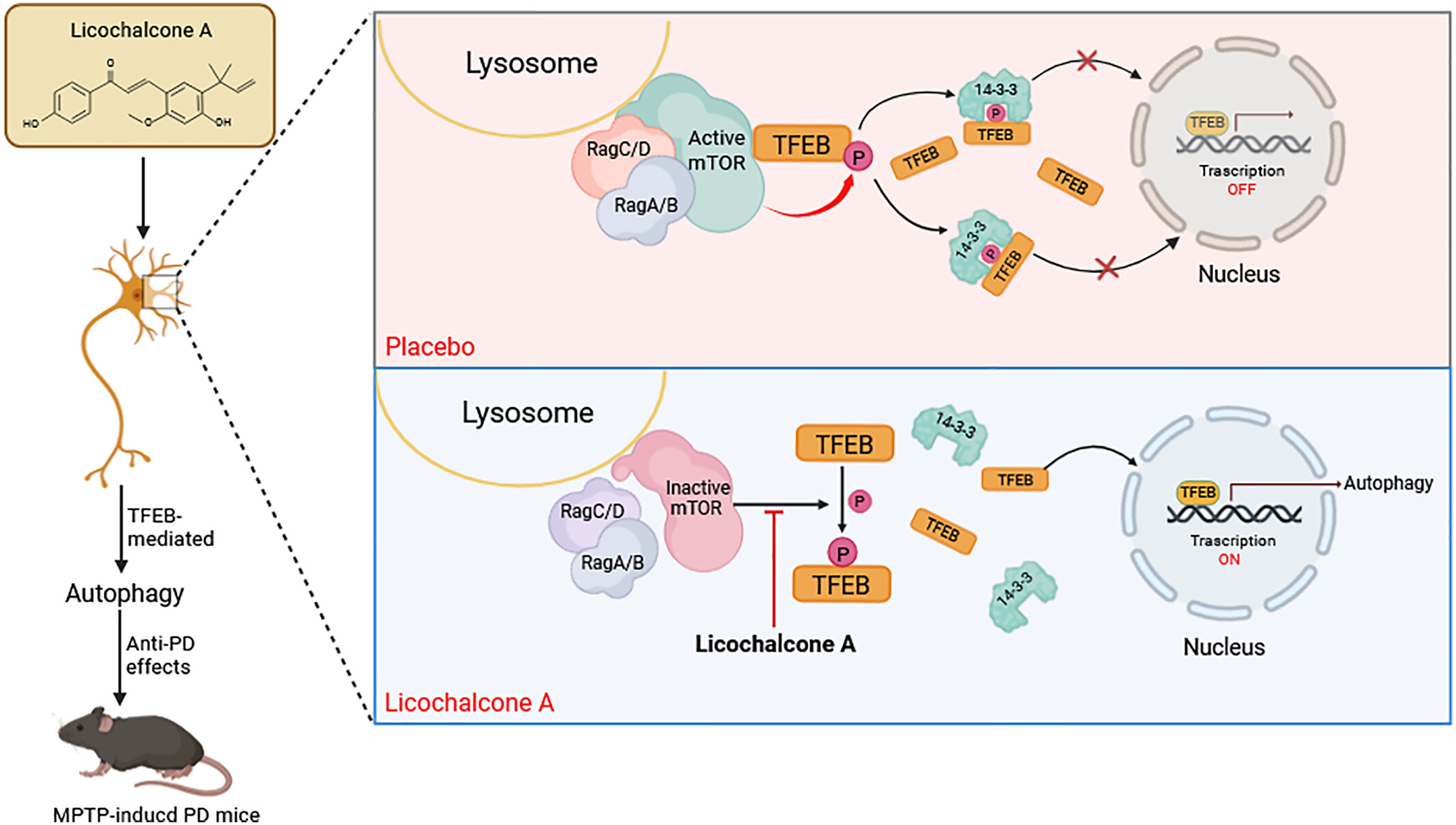
Licochalcone A selectively modulates mTORC1-TFEB to enhance autophagy and demonstrates neuroprotective effects in a mouse model of Parkinson's disease
- 27 June 2025
Non-human primate models of Parkinson's disease: Decoding pathogenesis and advancing therapies
- 24 June 2025
Graphical Abstract

Parkinson's disease ranks as the second most prevalent neurodegenerative disorder, and there is an urgent need for proper experimental models to enhance our understanding of this complex disease. Non-human primates exhibit various similarities to humans, particularly in terms of motor skills, cognitive functions, and the complexity of their neural architecture. Models of Parkinson's disease using non-human primates can help us to understand the pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease, advance current therapies, and develop new methods in neuroscience.
Development of a plasma biomarker diagnostic model as a screening strategy for Alzheimer's disease in older inpatients
- 28 May 2025
Graphical Abstract
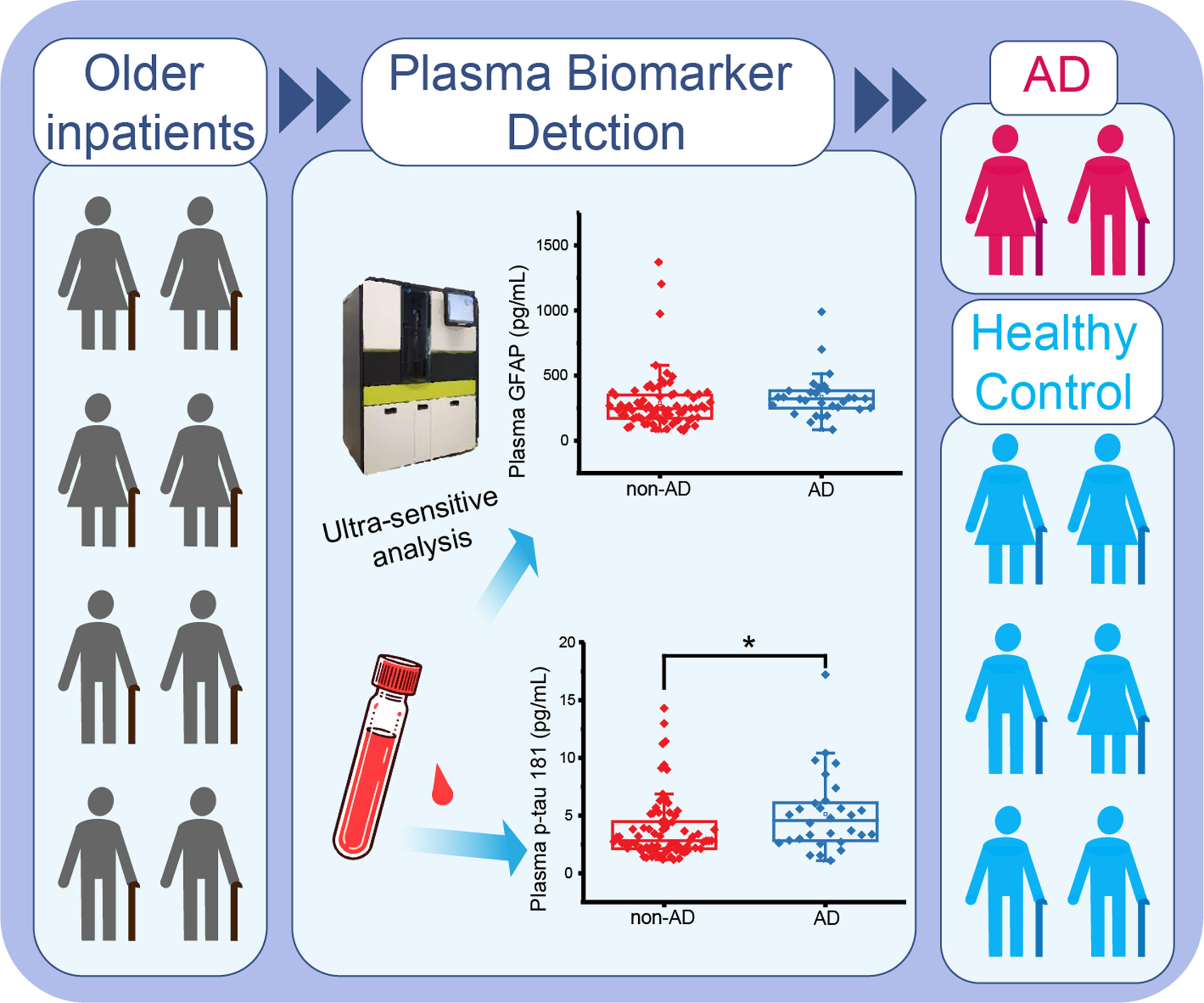
Early diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a challenge because of the invasive nature of the lumbar puncture for cerebrospinal fluid and the high cost of positron emission tomography imaging barriers for their common use as biomarkers. This study aimed to evaluate the diagnostic potential of blood-based neuro-markers in this advanced age group using an ultra-sensitive Single Molecule Array (SiMoA) platform. This simplified diagnostic model may offers a feasible approach for AD screening in both clinical and community-based settings.
Research progress and applications of optoelectronic synaptic devices based on 2D materials
- Brain‐X
- 20 October 2024
Graphical Abstract
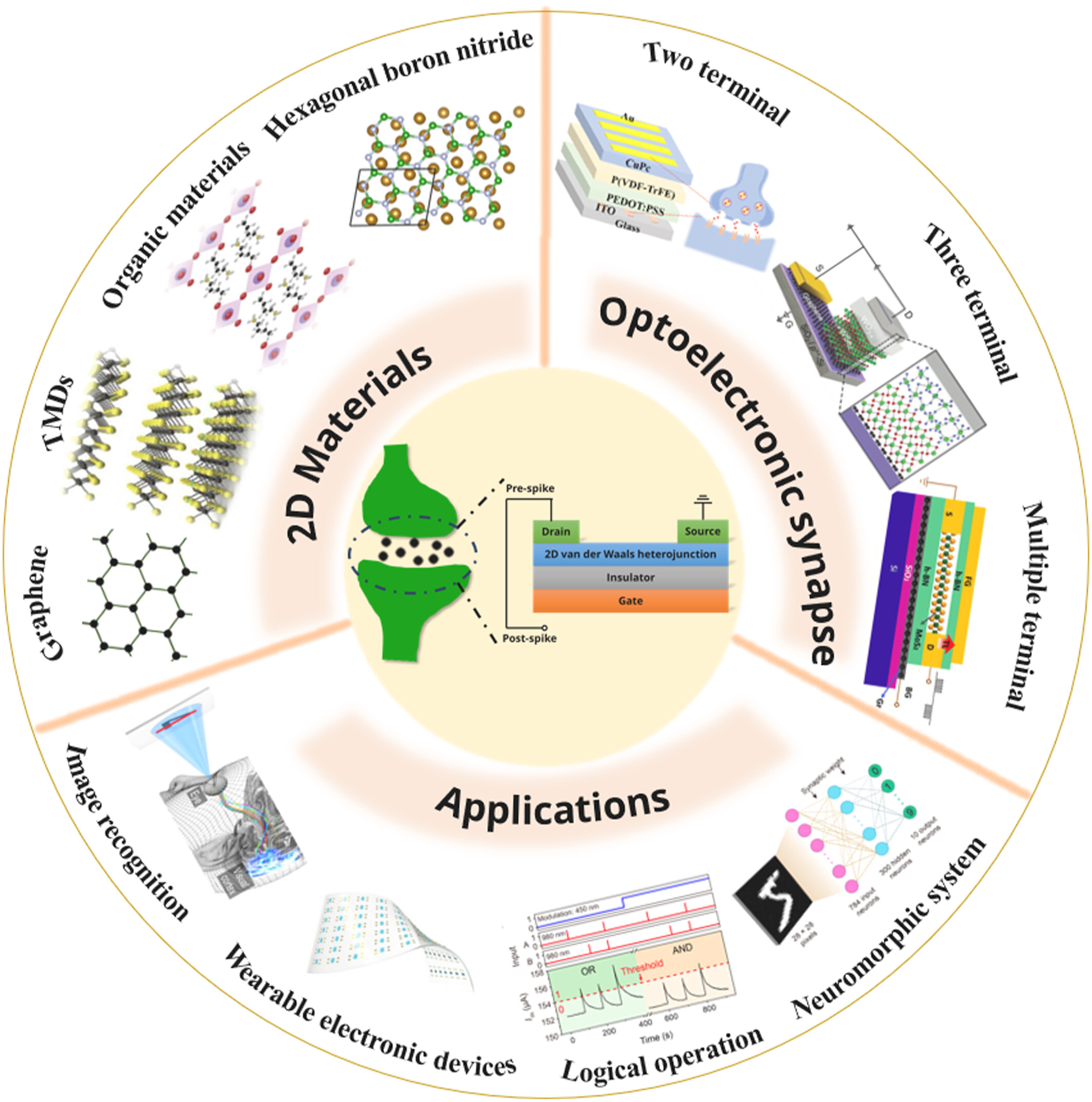
The inherent properties of two-dimensional (2D) materials make them ideal for use in artificial optoelectronic synaptic devices. This review explores synaptic devices based on 2D materials and examines their potential applications in image recognition, neuromorphic wearable electronic devices, logical operations and neuromorphic computing systems.
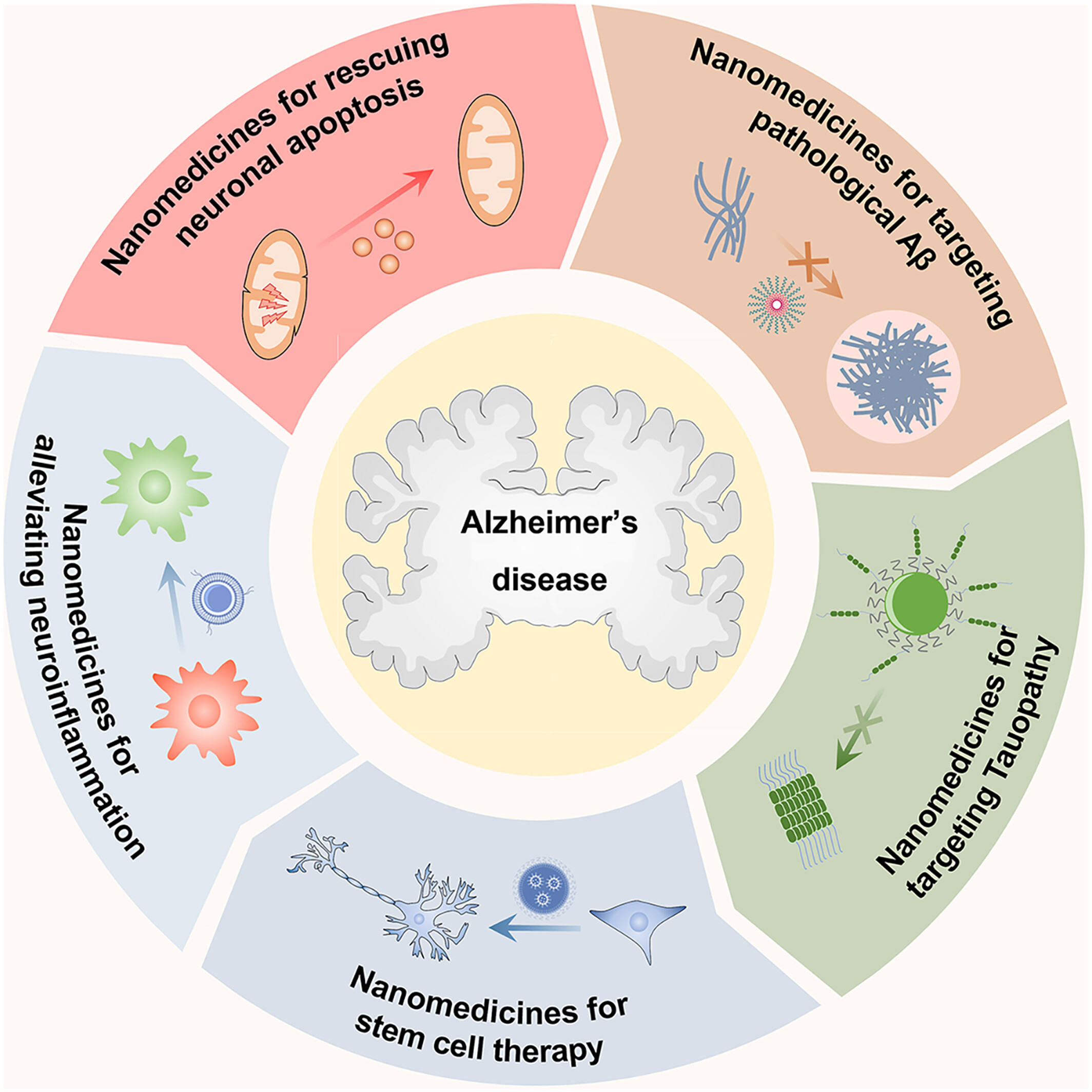
Nanomedicines for Alzheimer's disease: Therapies based on pathological mechanisms
- Brain‐X
- 28 July 2023
Advances of therapy for Alzheimer's disease: An updated review
- Brain‐X
- 15 July 2024
Graphical Abstract
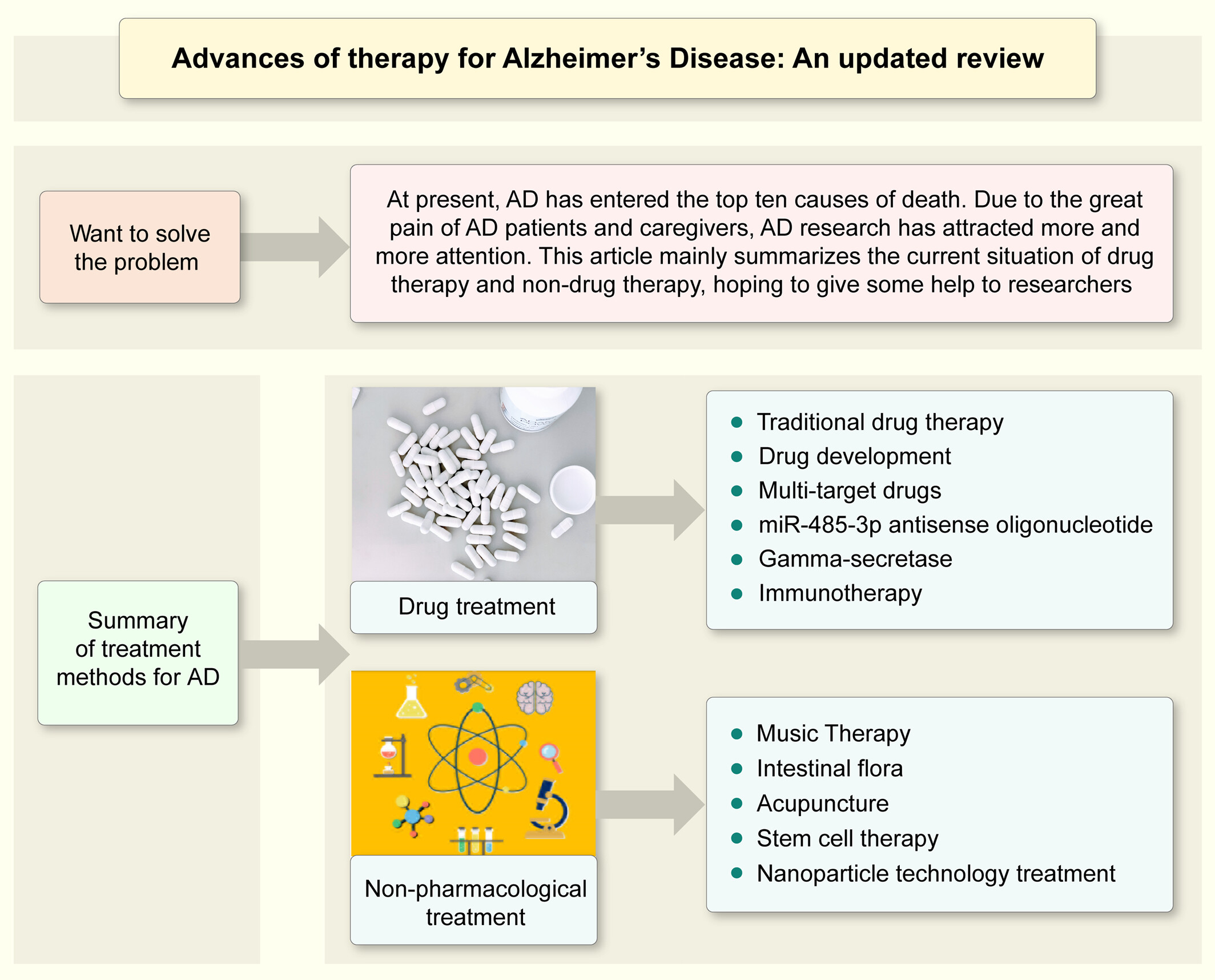
This article discusses the advancements in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease (AD) from both pharmacological and non-pharmacological perspectives. It elaborates on the advantages and disadvantages of each approach. In summary, the article documents five pharmaceutical treatment methods and five cutting-edge non-pharmacological treatment methods.
Advanced flexible brain‐computer interfaces and devices for the exploration of neural dynamics
- Brain‐X
- 12 December 2024
Graphical Abstract
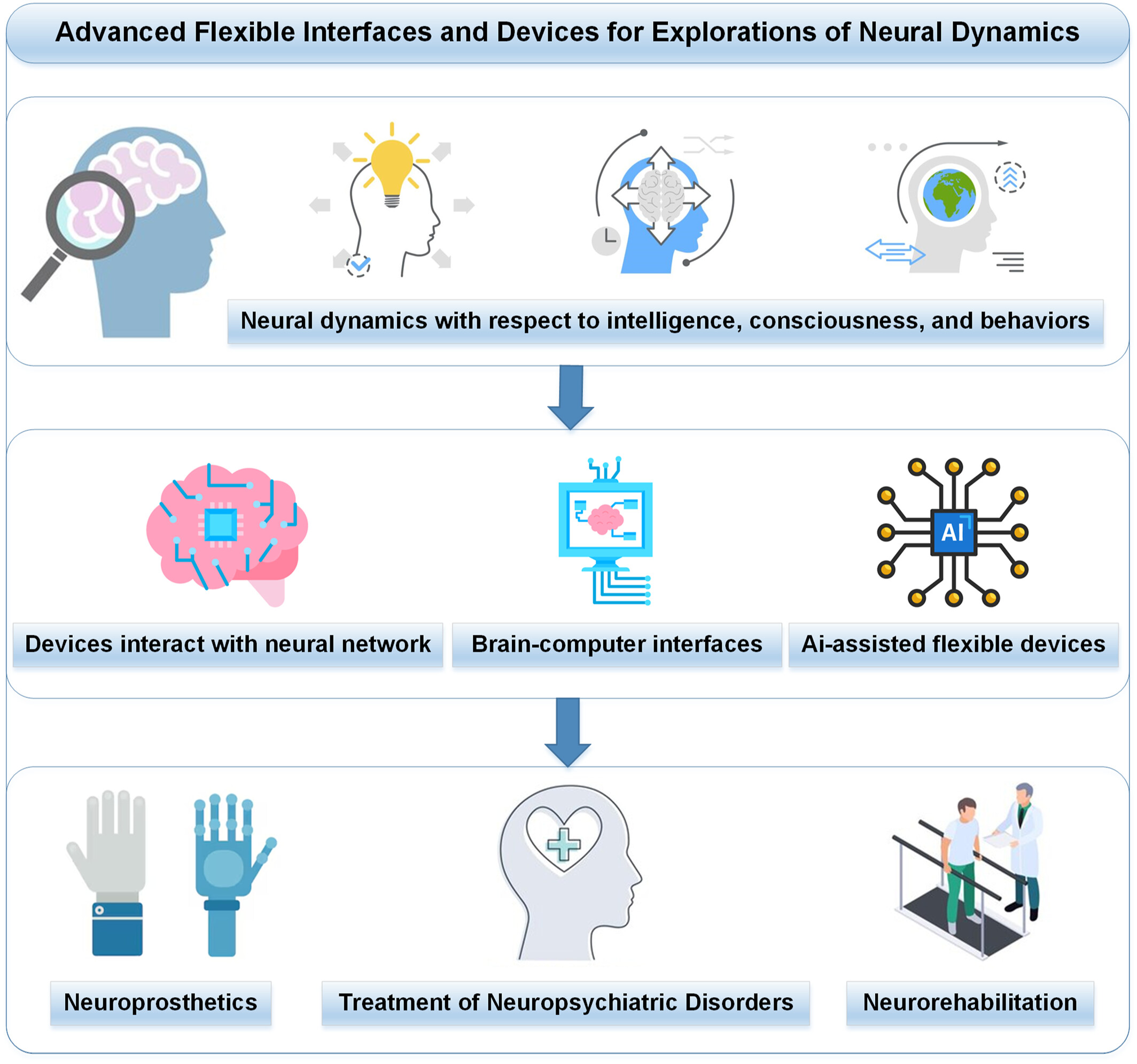
This perspective paper discusses how the development of flexible neural interfaces and devices can overcome the limitations of traditional neurotechnology and could revolutionize investigations into neural principles behind intelligence, consciousness, and behavior. Innovations in material science and device/system-level integrations further extend research capabilities to free-behaving animals, enabling profound insights into neurocognitive functions. Advances in artificial intelligence and brain organoids promise future decoding of complex neural signals. The development of transient materials and devices will provide the foundation for deploying next-generation neurotechnologies in clinics, aiming to treat complex neurogenic diseases and improve neurorehabilitation.
ChatGPT: The cognitive effects on learning and memory
- Brain‐X
- 20 September 2023
Graphical Abstract
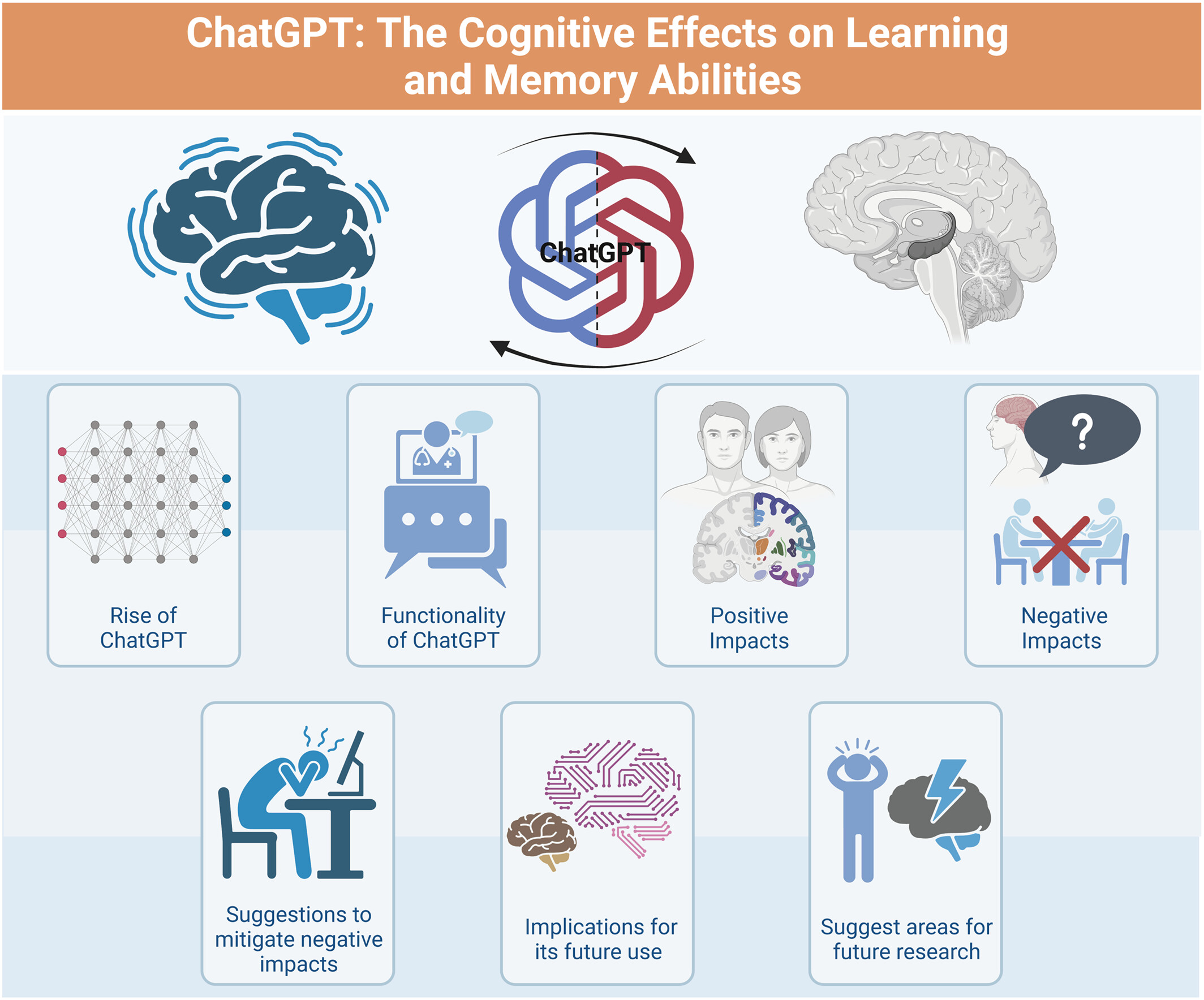
The integration of ChatGPT into the domains of learning and memory holds the potential to transform the entire field of education. This article explores the potential positive and negative effects of increased engagement with artificial intelligence, offering strategies for optimizing its benefits while mitigating its drawbacks, and highlights areas that can benefit from further research. In this way, it seeks to ensure that ChatGPT operates as an adjunctive educational tool that complements human cognitive processes without damaging them.
ChatGPT: The cognitive effects on learning and memory
- Brain‐X
- 20 Sep 2023
Graphical Abstract

The integration of ChatGPT into the domains of learning and memory holds the potential to transform the entire field of education. This article explores the potential positive and negative effects of increased engagement with artificial intelligence, offering strategies for optimizing its benefits while mitigating its drawbacks, and highlights areas that can benefit from further research. In this way, it seeks to ensure that ChatGPT operates as an adjunctive educational tool that complements human cognitive processes without damaging them.
Recent advances in the pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment of sepsis‐associated encephalopathy
- Brain‐X
- 30 Jun 2024
Graphical Abstract
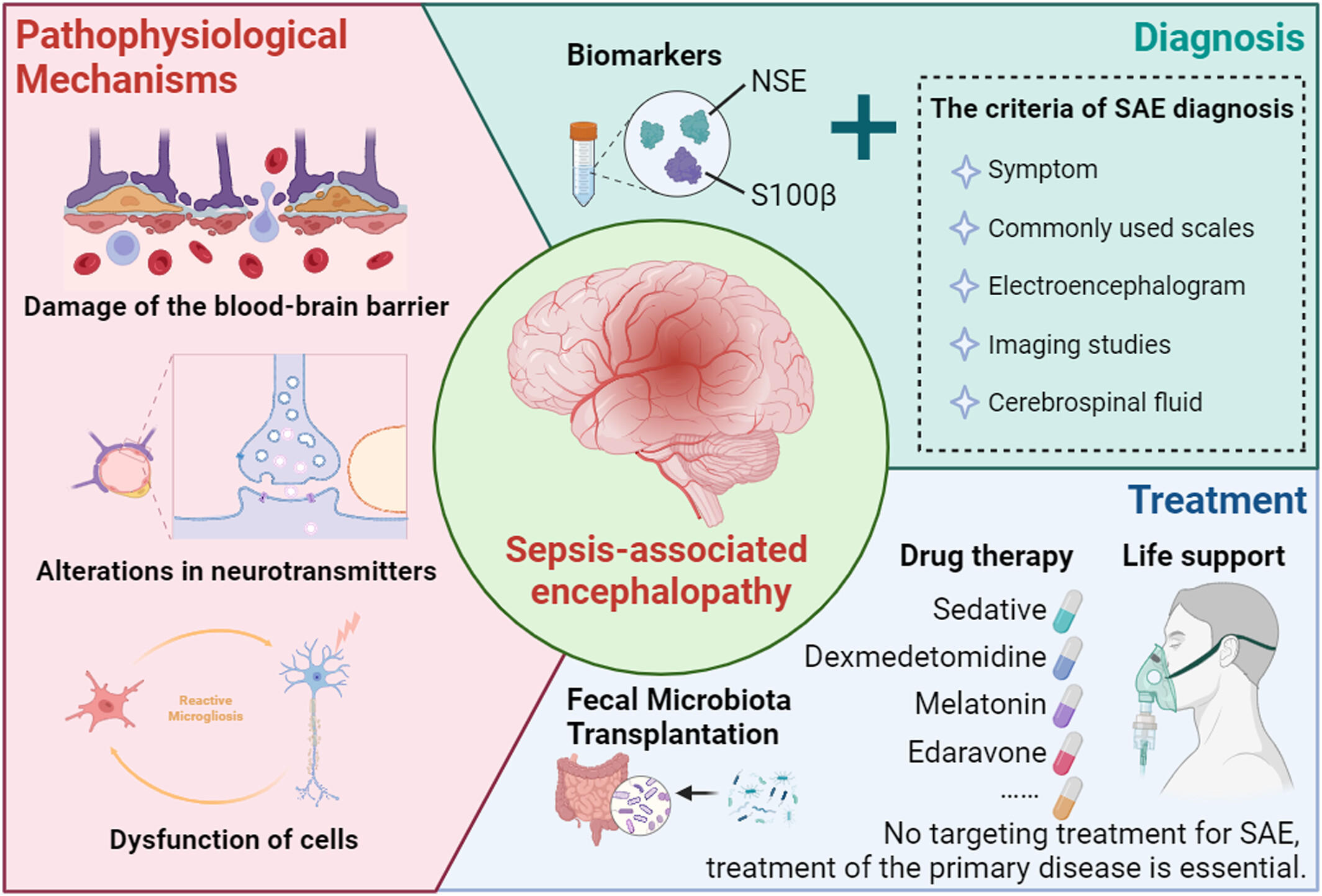
Sepsis-associated encephalopathy (SAE), one of the most severe complications of sepsis, presents with diverse clinical symptoms and involves complex pathophysiological mechanisms, making its early diagnosis and targeted treatment challenging. Its pathogenesis primarily arises from inflammation-induced disruption of the blood-brain barrier, aberrant activation and dysfunction of cells, and disturbances in neurotransmitter transmission. Leveraging these pathological insights, integrating biomarkers with existing diagnostic modalities, and targeting core mechanisms hold promise for achieving precise diagnosis and treatment of SAE.
An easy‐to‐follow handbook for electroencephalogram data analysis with Python
- Brain‐X
- 30 Jun 2024
Graphical Abstract
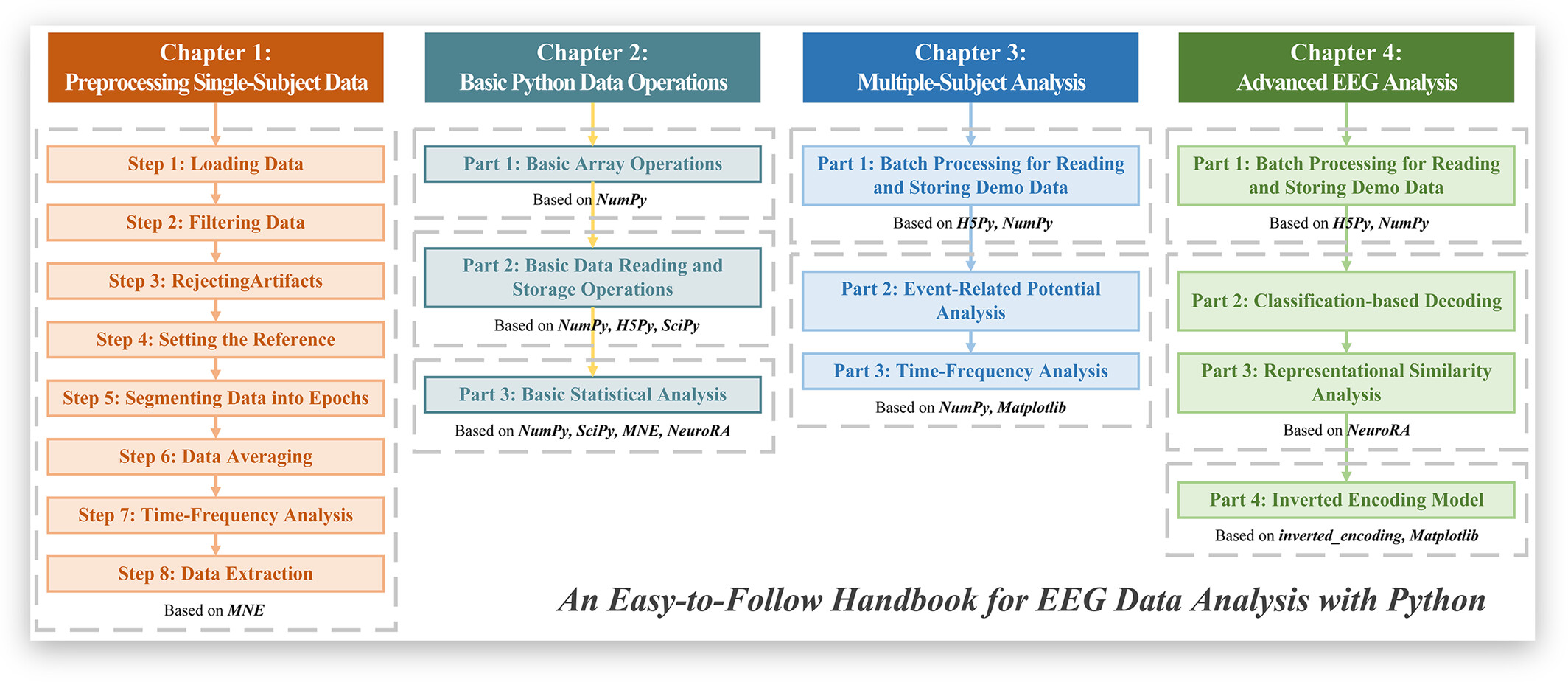
This handbook comprises four chapters: Preprocessing Single-Subject Data, Basic Python Data Operations, Multiple-Subject Analysis, and Advanced EEG Analysis. We provide a standardized procedure for preprocessing EEG data, guide readers through detailed examples on how to read data from multiple subjects, and delve into three popular analysis methodologies.
Music therapy for depression: A narrative review
- Brain‐X
- 17 Aug 2024
Graphical Abstract
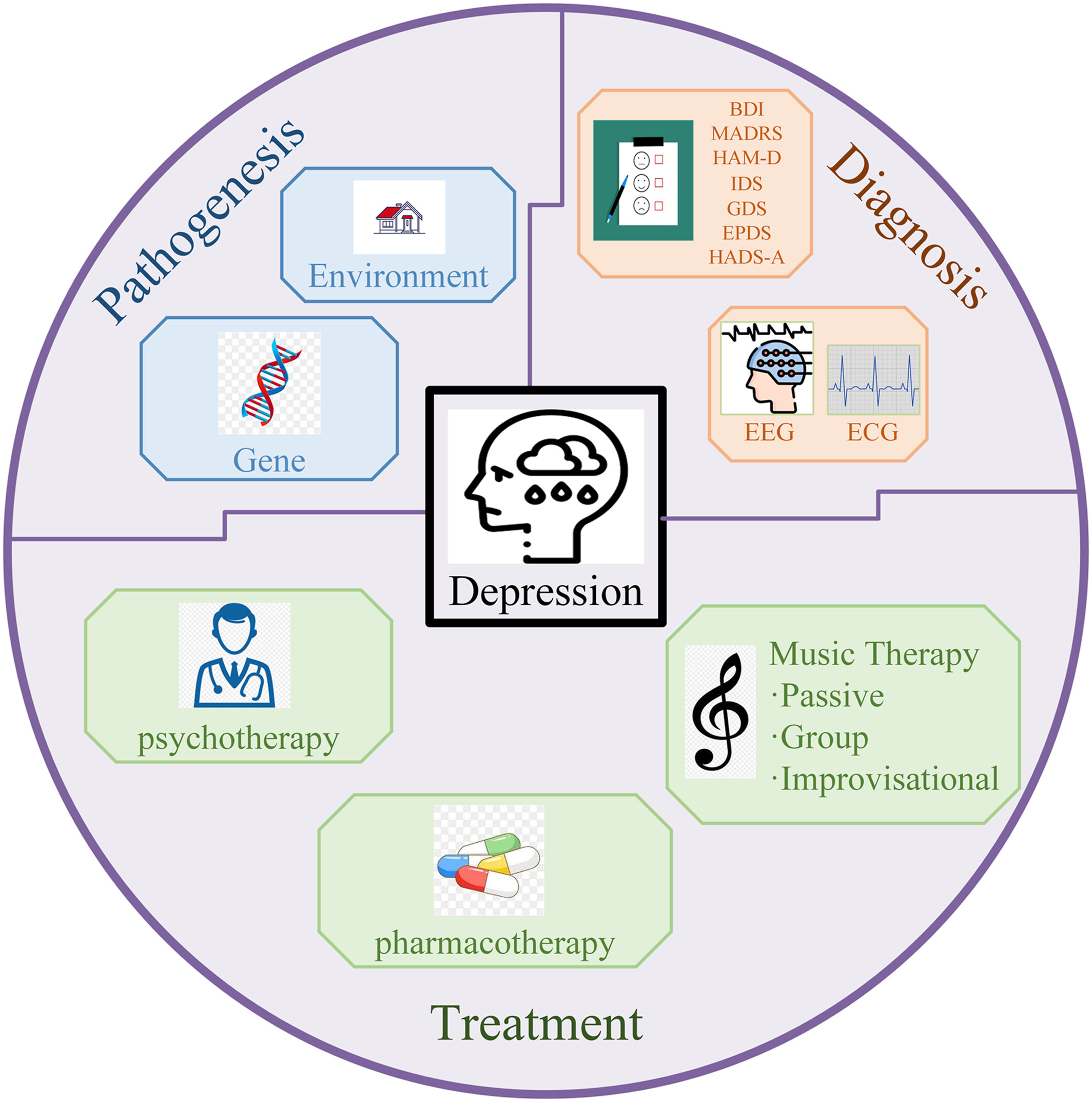
This review summarizes and classifies the research in recent years and introduces the pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment methods of depression. The study of the principles of musical interventions for depression and the practice of musical interventions for depression with various etiologies are highlighted. It is hoped to introduce the progress of depression research and the prospect of music therapy.
Comprehensive review of Transformer‐based models in neuroscience, neurology, and psychiatry
- Brain‐X
- 26 Apr 2024
Graphical Abstract
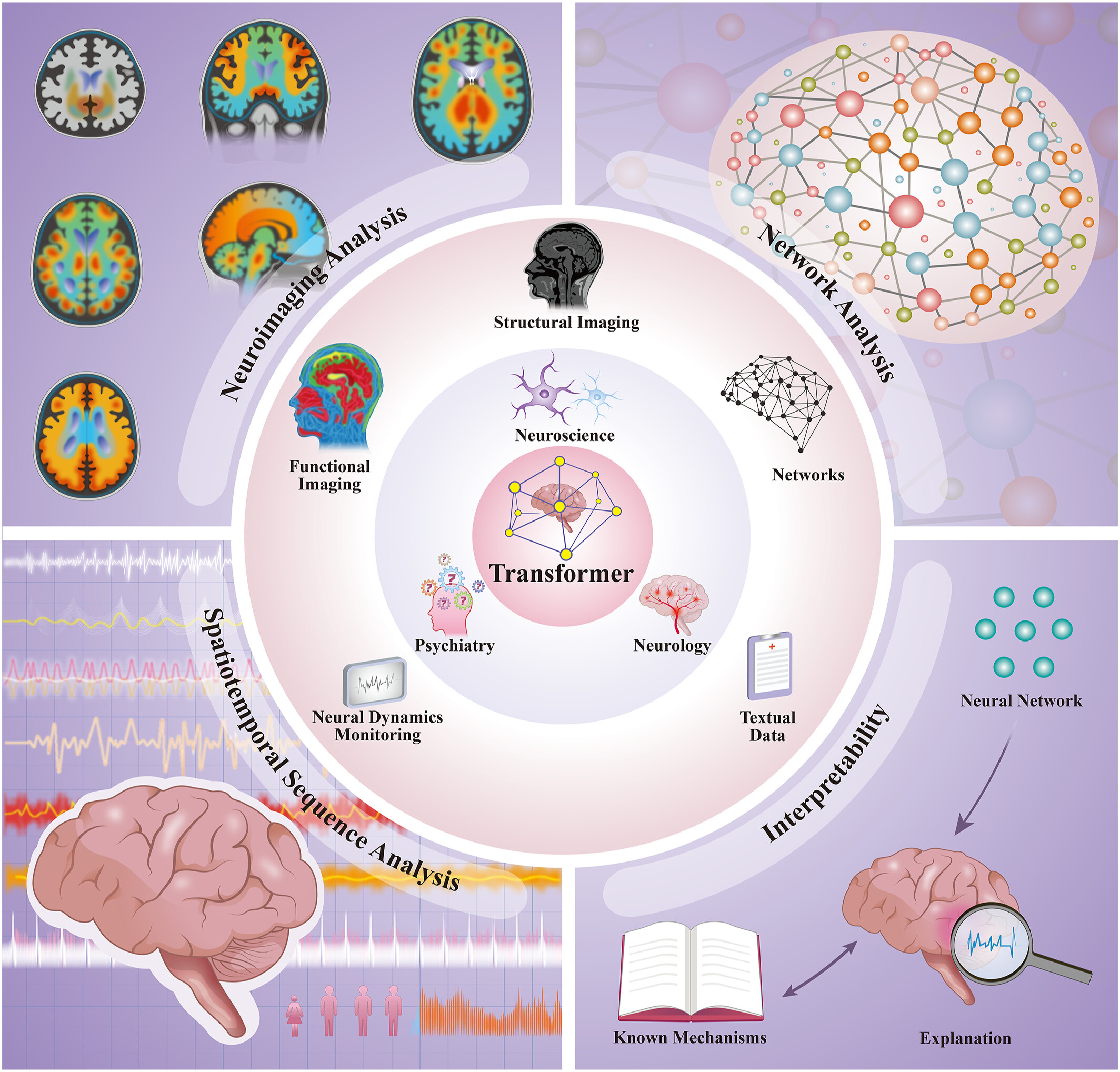
This comprehensive review introduces the transformative role of transformer-based models in neuroscience, neurology, and psychiatry. It discusses how these models, originally designed for sequential data analysis, have evolved to effectively analyze complex biomedical data, significantly enhancing our understanding of brain functions and dysfunctions.
Latest news
Recent issues
- Volume 3, Issue 3September 2025
- Volume 3, Issue 2June 2025
- Volume 3, Issue 1March 2025
- Volume 2, Issue 4December 2024










.png)