Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
RESEARCH ARTICLE
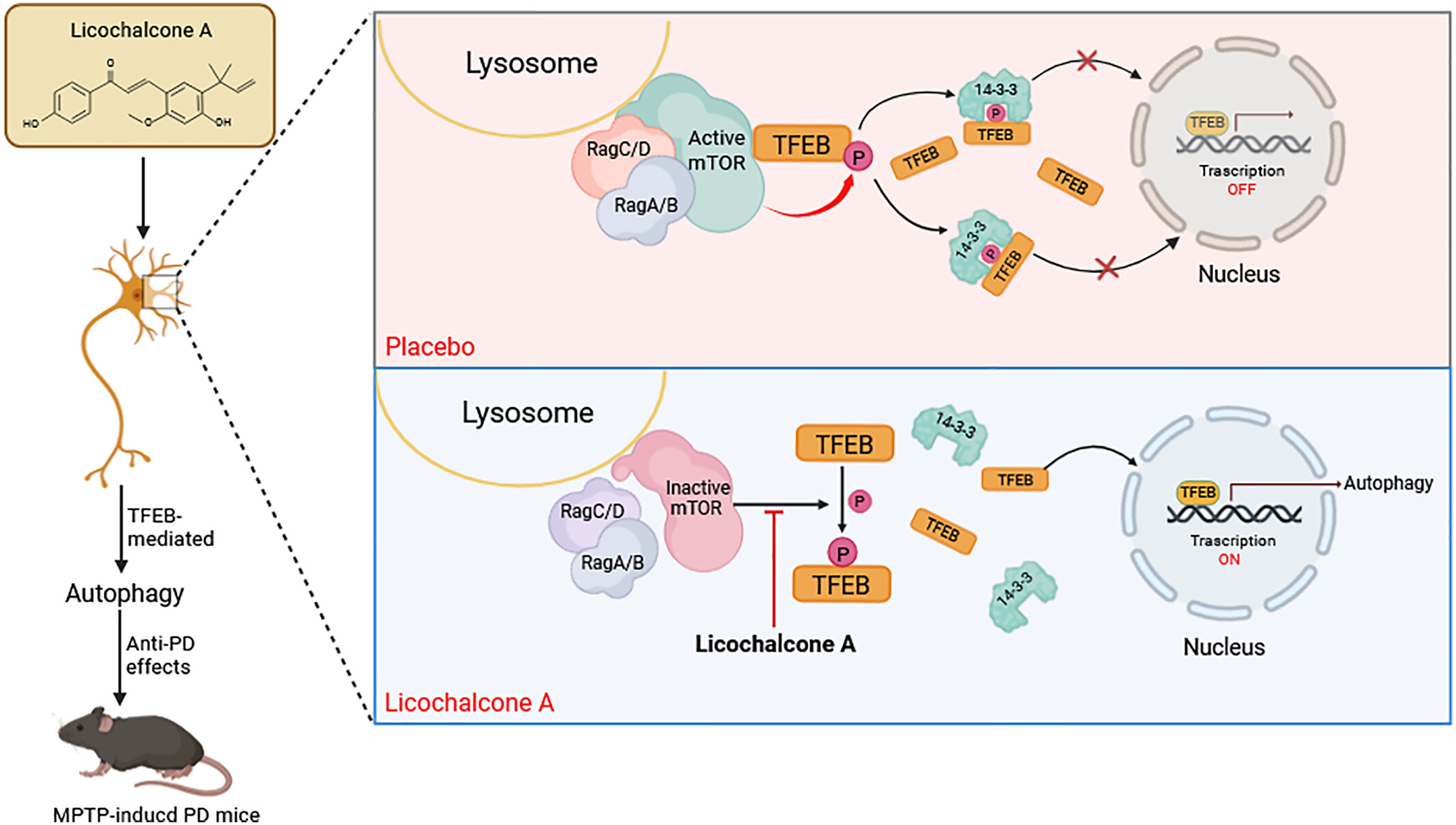
Licochalcone A selectively modulates mTORC1-TFEB to enhance autophagy and demonstrates neuroprotective effects in a mouse model of Parkinson's disease
- First Published: 27 June 2025
METHODS ARTICLE
From digitized whole-slide histology images to biomarker discovery: A protocol for handcrafted feature analysis in brain cancer pathology
- First Published: 28 May 2025
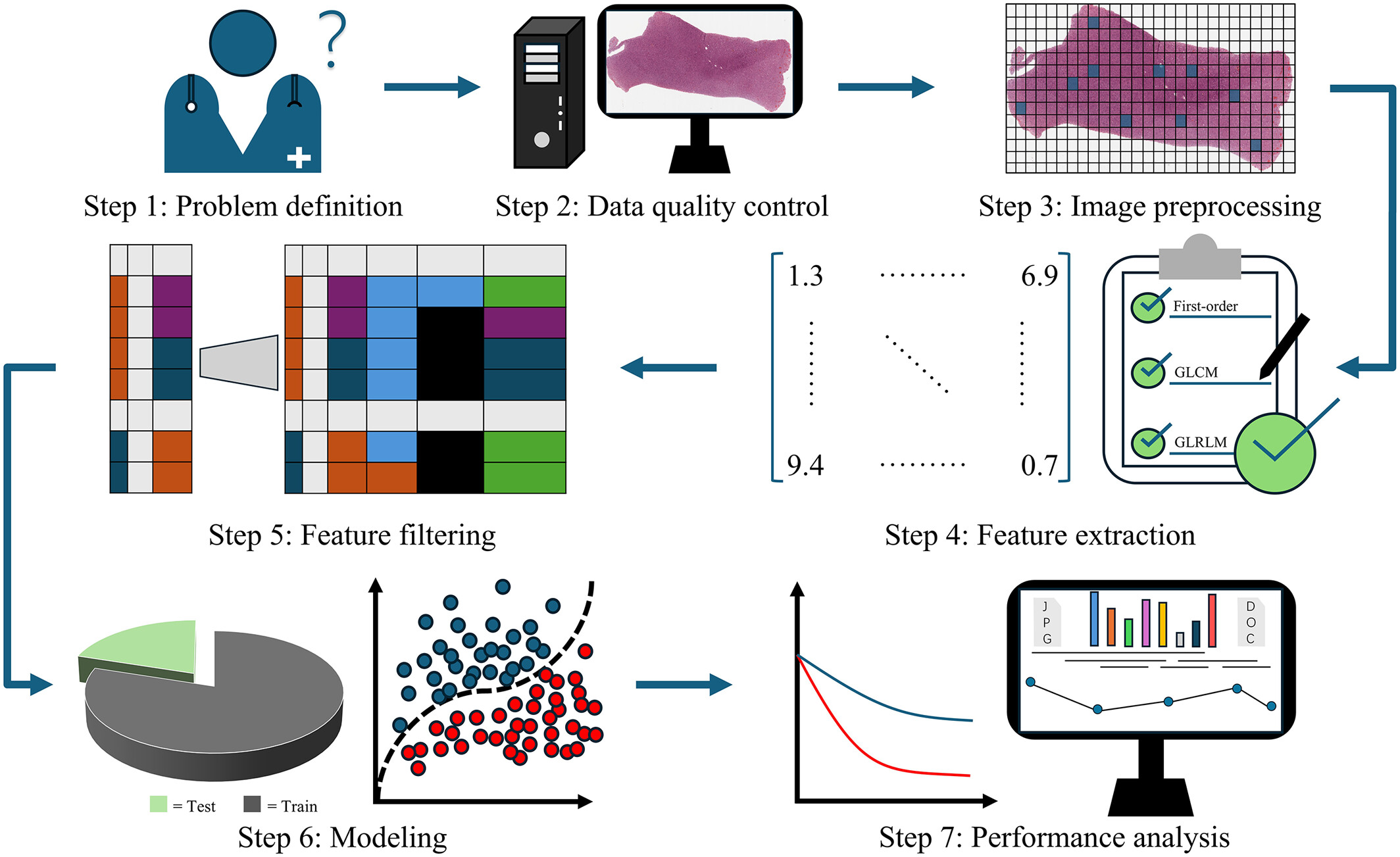
This protocol comprises seven steps: problem definition, data quality control, image preprocessing, feature extraction, feature filtering, modeling, and performance analysis. We present a standardized, handcrafted feature–based protocol for processing and analyzing whole-slide histology images, guiding readers through a detailed example of how to leverage digitized WSIs for biomarker discovery and validating the model's generalization performance in an external validation cohort.
PERSPECTIVE
Synergizing DeepSeek's artificial intelligence innovations with brain–computer interfaces
- First Published: 28 June 2025
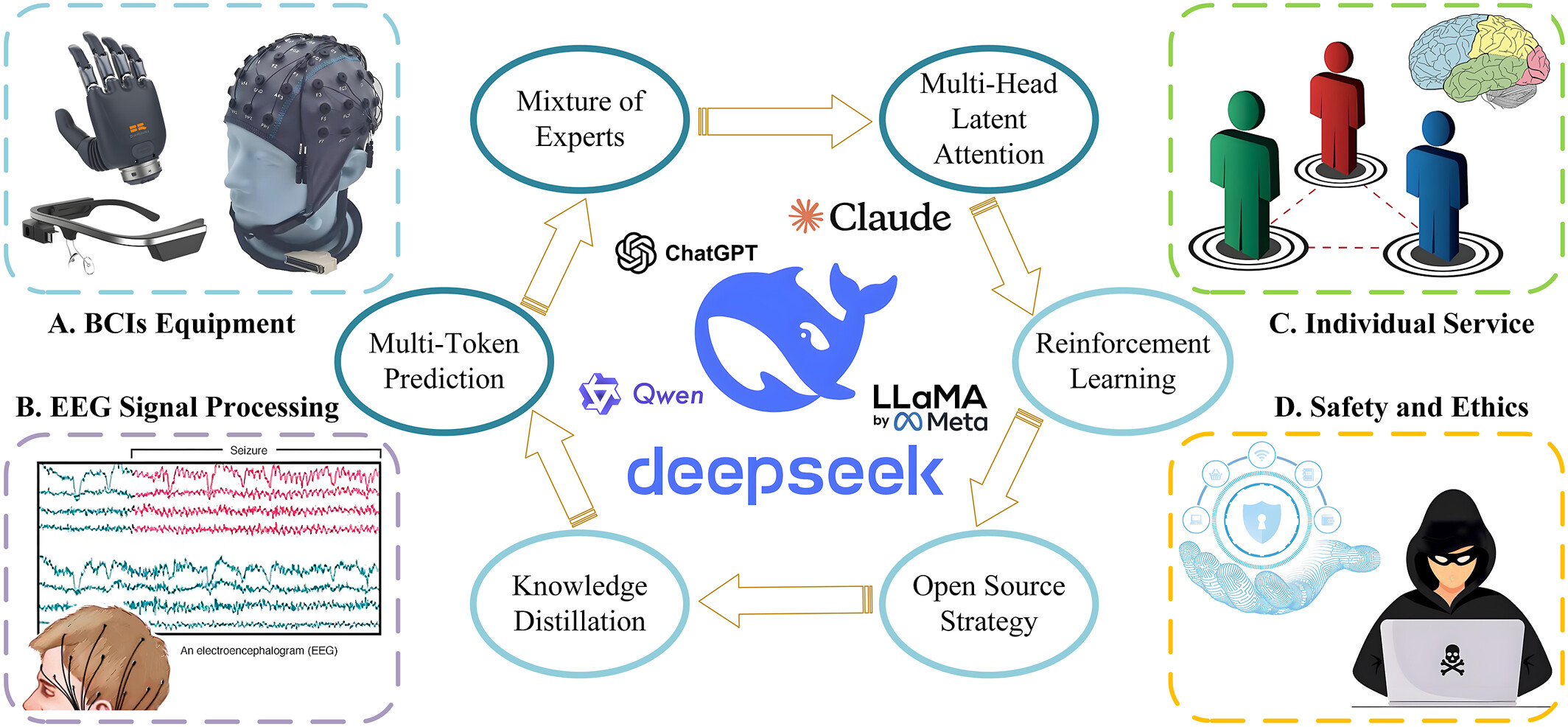
This perspective examines the synergy between DeepSeek, a leader in efficient, open-source artificial intelligence models, and next-generation brain–computer interface (BCI) technologies. Based on the advanced technology of DeepSeek, this study explores the fusion of large language models (LLMs) in the fields of BCI devices, electroencephalogram signal processing, and individual service, and deeply discusses the data safety and ethical issues that are inevitable with LLMs, providing unique insights into the path to democratizing neurotechnology.
REVIEW ARTICLE
Non-human primate models of Parkinson's disease: Decoding pathogenesis and advancing therapies
- First Published: 24 June 2025

Parkinson's disease ranks as the second most prevalent neurodegenerative disorder, and there is an urgent need for proper experimental models to enhance our understanding of this complex disease. Non-human primates exhibit various similarities to humans, particularly in terms of motor skills, cognitive functions, and the complexity of their neural architecture. Models of Parkinson's disease using non-human primates can help us to understand the pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease, advance current therapies, and develop new methods in neuroscience.
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Development of a plasma biomarker diagnostic model as a screening strategy for Alzheimer's disease in older inpatients
- First Published: 28 May 2025
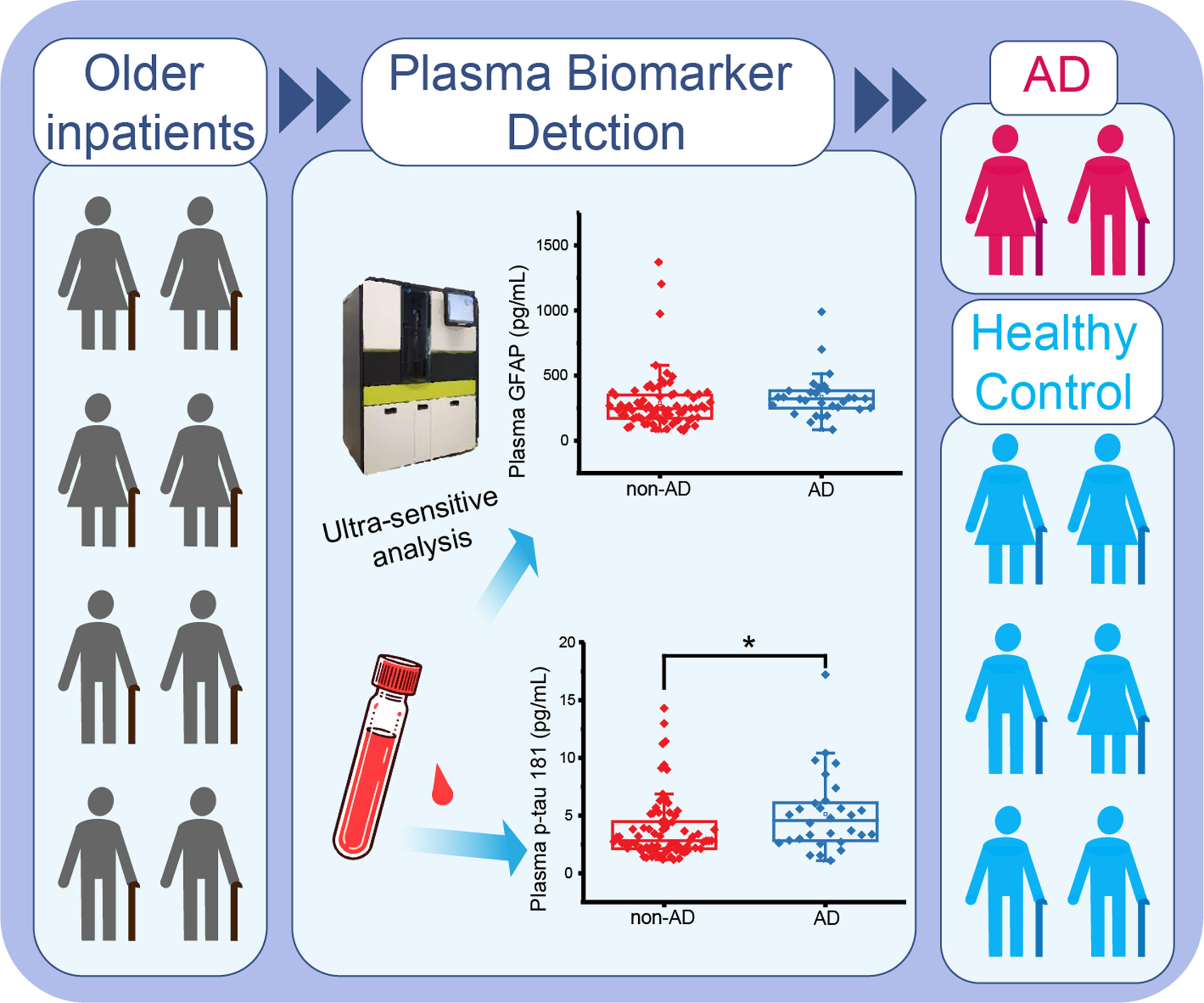
Early diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a challenge because of the invasive nature of the lumbar puncture for cerebrospinal fluid and the high cost of positron emission tomography imaging barriers for their common use as biomarkers. This study aimed to evaluate the diagnostic potential of blood-based neuro-markers in this advanced age group using an ultra-sensitive Single Molecule Array (SiMoA) platform. This simplified diagnostic model may offers a feasible approach for AD screening in both clinical and community-based settings.
Advancing brain tumor diagnosis: Deep siamese convolutional neural network as a superior model for MRI classification
- First Published: 25 April 2025
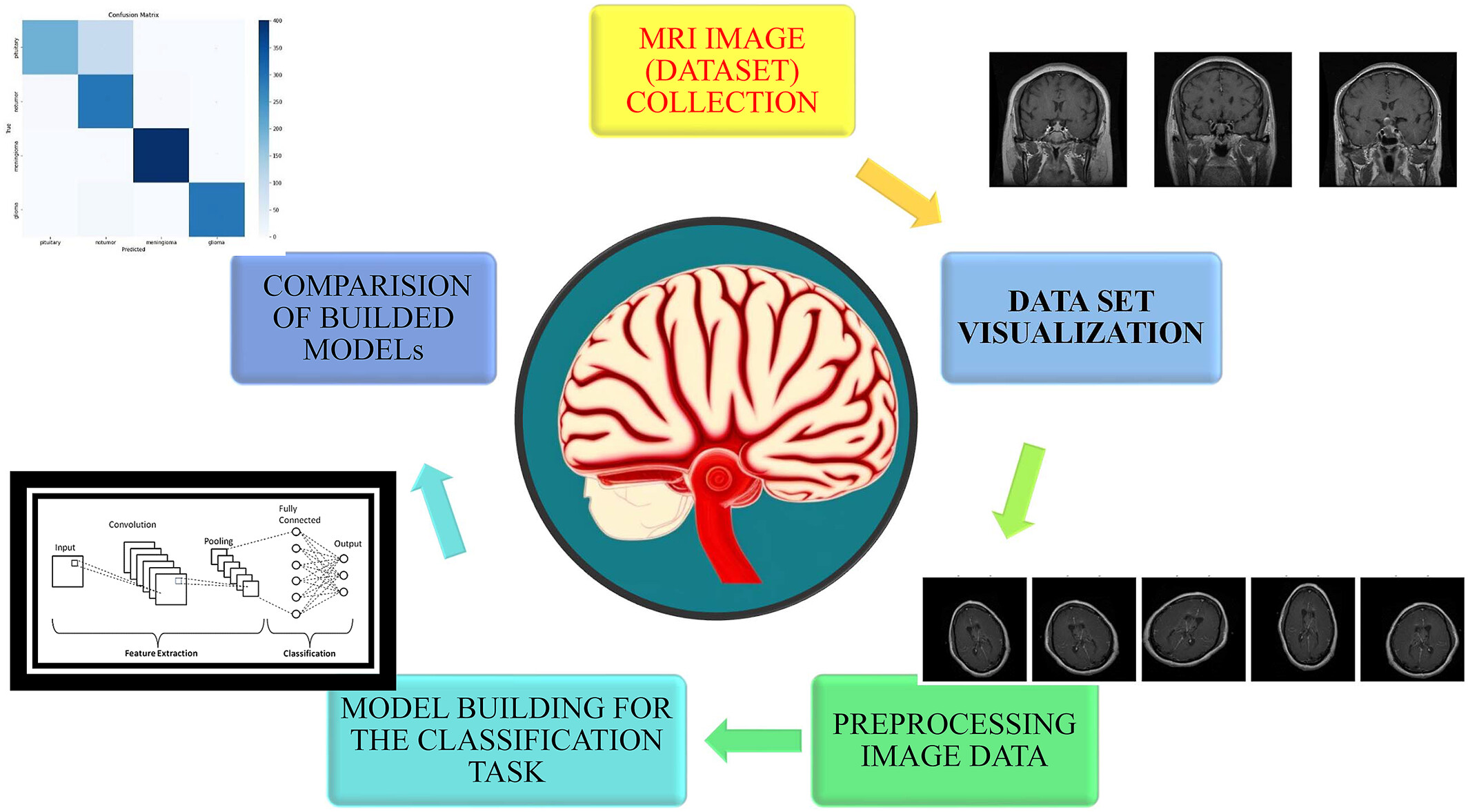
This study aims to address the challenges in brain tumor classification by leveraging magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to optimize diagnostic accuracy. Five classification models, namely machine learning, pre-trained deep learning, convolutional neural network (CNN), hyperparameter-tuned deep CNN, and deep siamese CNN (DeepSCNN), were evaluated. The high precision and robustness establish this model as a new benchmark in neuro-oncology diagnostics, facilitating more timely and accurate brain tumor identification for improved patient outcomes.






.png)