Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Reviews
Desktop NMR and Its Applications From Materials Science To Organic Chemistry
- First Published: 12 December 2017

NMR spectroscopy is known not only for its outstanding analytical power but also for the large size and costs of the instruments. In recent years, this family of instruments with bulky superconducting magnets has been complemented with compact tabletop and portable devices suitable for small-molecule analysis and nondestructive materials testing. The state-of-the-art of compact NMR instruments is reviewed and illustrated with selected examples.
Unraveling the Mechanism of Methane Activation on Zn-Modified Zeolites by Solid-State NMR
- First Published: 03 May 2021
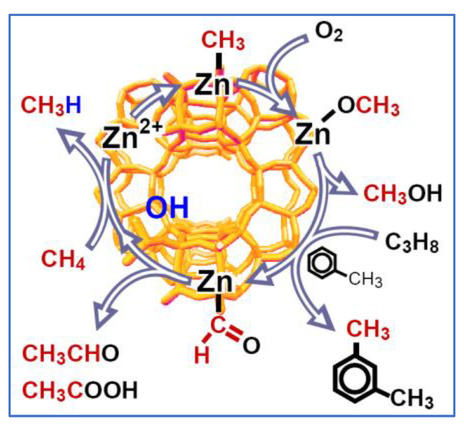
Solid-state NMR provides unique information on the peculiarities of methane activation on zeolite catalysts. This allowed to discover the possibilities of methane transformation to methanol and other oxygenates as well as to rationalize co-conversion of methane with higher alkanes under mild conditions on Zn-modified zeolites.
High-Throughput Metabolomics by 1D NMR
- First Published: 12 July 2018
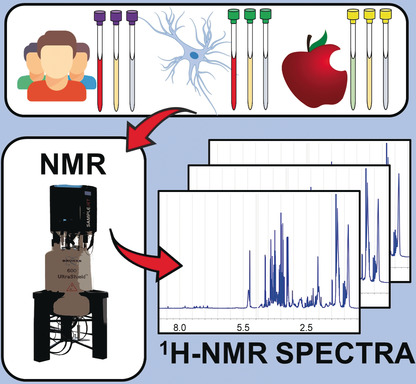
Metabolomics is the omic science that best represents the molecular phenotype. Among several applications it has the potential to be translated into the clinical practice. This Review presents the NMR-vision of metabolomics, highlighting the high degree of standardization needed along the entire workflow (pre-analytics, NMR spectra acquisition and processing, statistical analysis and data deposition) for reliable and reproducible results.
Design of Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Molecular Probes for Hyperpolarized Bioimaging
- First Published: 06 May 2020
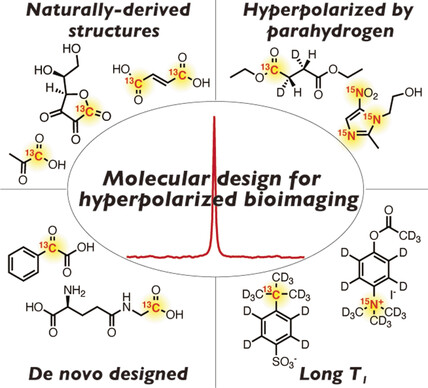
Nuclear hyperpolarization is a powerful method that can dramatically enhance the sensitivity of NMR spectroscopy. This technology has been applied to the biomedical molecular imaging of a range of small molecules with stable isotopes and has provided valuable metabolic and physiological information. This review focuses on strategies for the design of molecular probes for hyperpolarized bioimaging.
Enabling Clinical Technologies for Hyperpolarized 129Xenon Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Spectroscopy
- First Published: 20 May 2021
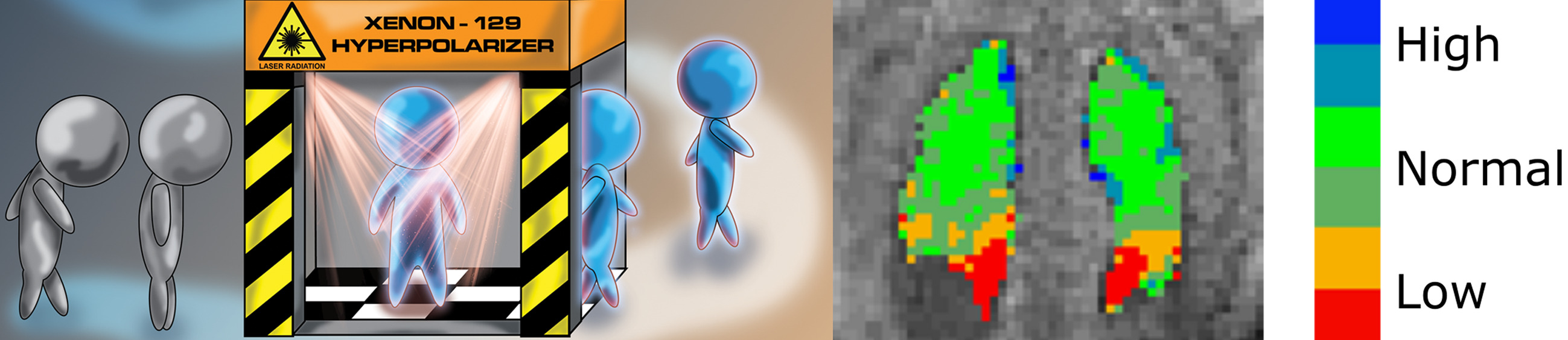

The use of hyperpolarized 129Xe has the potential to revolutionize clinical imaging, offering a non-ionizing contrast of organ function complementary to that of CT imaging and conventional MRI. In this Review, the physics of spin-exchange optical pumping (SEOP) is discussed, production modalities of hyperpolarized 129Xe are explained, and biomedical applications to lung imaging and beyond are described.
Original Research
PI by NMR: Probing CH–π Interactions in Protein–Ligand Complexes by NMR Spectroscopy
- First Published: 18 May 2020
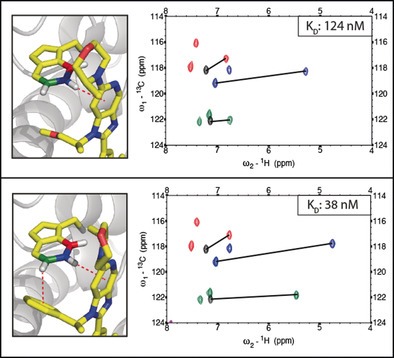
CH–π interactions are crucial determinants for the affinity of arguably every drug molecule. PI by NMR can differentiate the strength of protein–ligand CH–π interactions in solution. By combining selective amino-acid side-chain labeling with 1H-13C NMR, CH–π interactions can be identified based solely on 1H chemical shift values. This information serves as a proxy for the strength of each individual CH–π interaction.
SupraFit – An Open Source Qt Based Fitting Application to Determine Stability Constants from Titration Experiments
- First Published: 28 April 2022
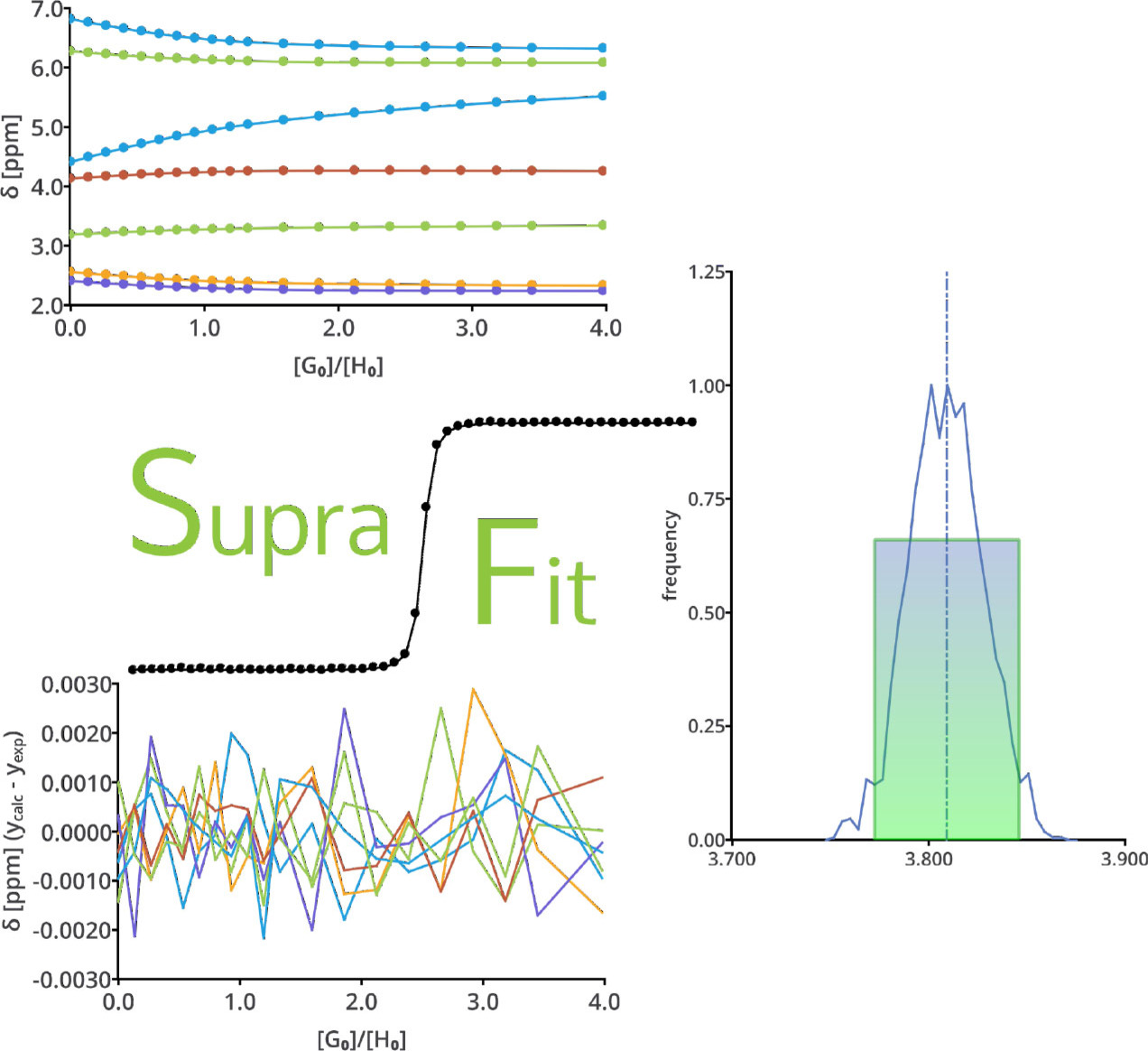
A graphical software package to analyse NMR titration and ITC experiments is presented. A brief introduction to the underlying mathematical and statistical aspects is given first. It is then followed by the demonstration of nonlinear fitting of models to example data and the application of statistical approaches like Monte Carlo simulation and F-test approaches to model functions, NMR titration data and results of ITC experiments.
DREAMTIME NMR Spectroscopy: Targeted Multi-Compound Selection with Improved Detection Limits
- First Published: 15 February 2022
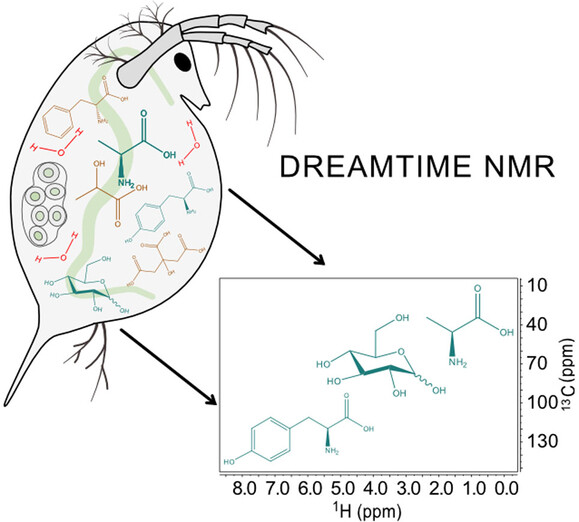
DREAMTIME NMR overcomes spectral overlap and increases sensitivity, opening a new world for targeted NMR detection. A user can define any unique suite of compounds and isolate them without complex sample preparation. DREAMTIME can be directly joined to any existing NMR experiment (1D, nD or MRI) and holds promise for all areas of science from chemical engineering, through environmental monitoring, to medical diagnosis.
Divide and Conquer: A Tailored Solid-state NMR Approach to Study Large Membrane Protein Complexes
- First Published: 17 June 2022
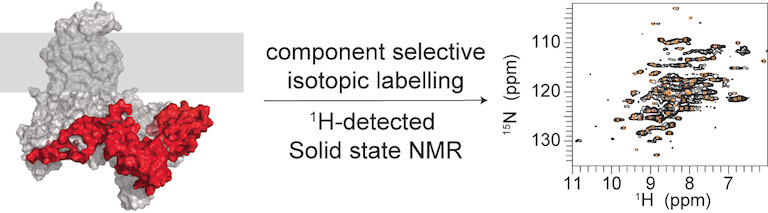
We describe a protein-selective labelling approach that allowed us to probe a single lipoprotein (BamC) in the pentameric BAM membrane protein complex by proton-detected solid-state NMR. Our results generate novel insights into the supramolecular structure of the BAM complex and provide evidence that the three BamC domains exhibit different dynamic properties within the 200 kDa complex embedded in lipid bilayers.
Extending NMR Tortuosity Measurements to Paramagnetic Catalyst Materials Through the Use of Low Field NMR
- First Published: 07 July 2022

Low field Pulsed Field Gradient (PFG) NMR is demonstrated as an effective tool for measuring the tortuosity of catalyst materials containing paramagnetic species, which are unmeasurable at high magnetic field strengths. The technique is applied to catalyst precursors with industrially relevant metal loadings (up to 20 wt.%) and allows a direct measurement of tortuosity
Insight into Carbocation-Induced Noncovalent Interactions in the Methanol-to-Olefins Reaction over ZSM-5 Zeolite by Solid-State NMR Spectroscopy
- First Published: 11 October 2021
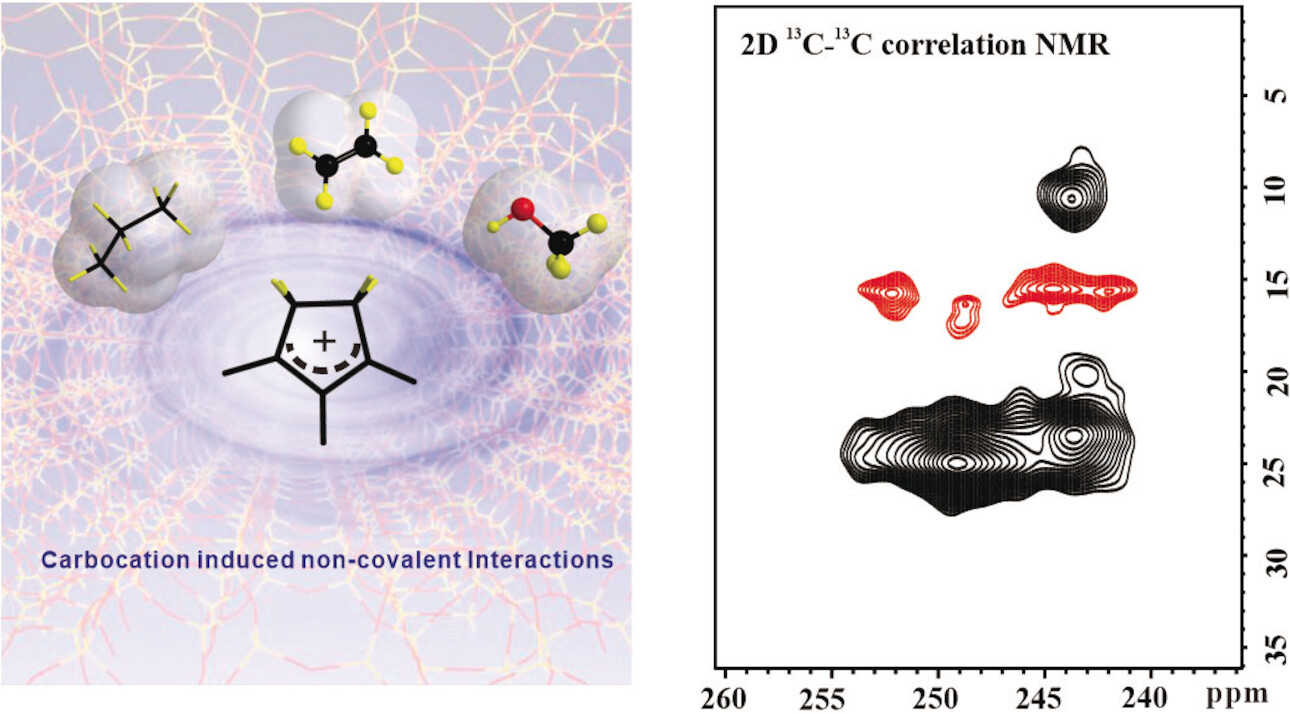
Multiple noncovalent interactions involving cyclopentenyl cations in the methanol-to-olefins (MTO) reaction over ZSM-5 zeolite were identified by using two-dimensional solid-state NMR spectroscopy. It was found that the hydrocarbon pool reaction is modulated by carbocation-induced noncovalent interactions.
NMR Spectroscopy of the Main Protease of SARS-CoV-2 and Fragment-Based Screening Identify Three Protein Hotspots and an Antiviral Fragment
- First Published: 27 September 2021
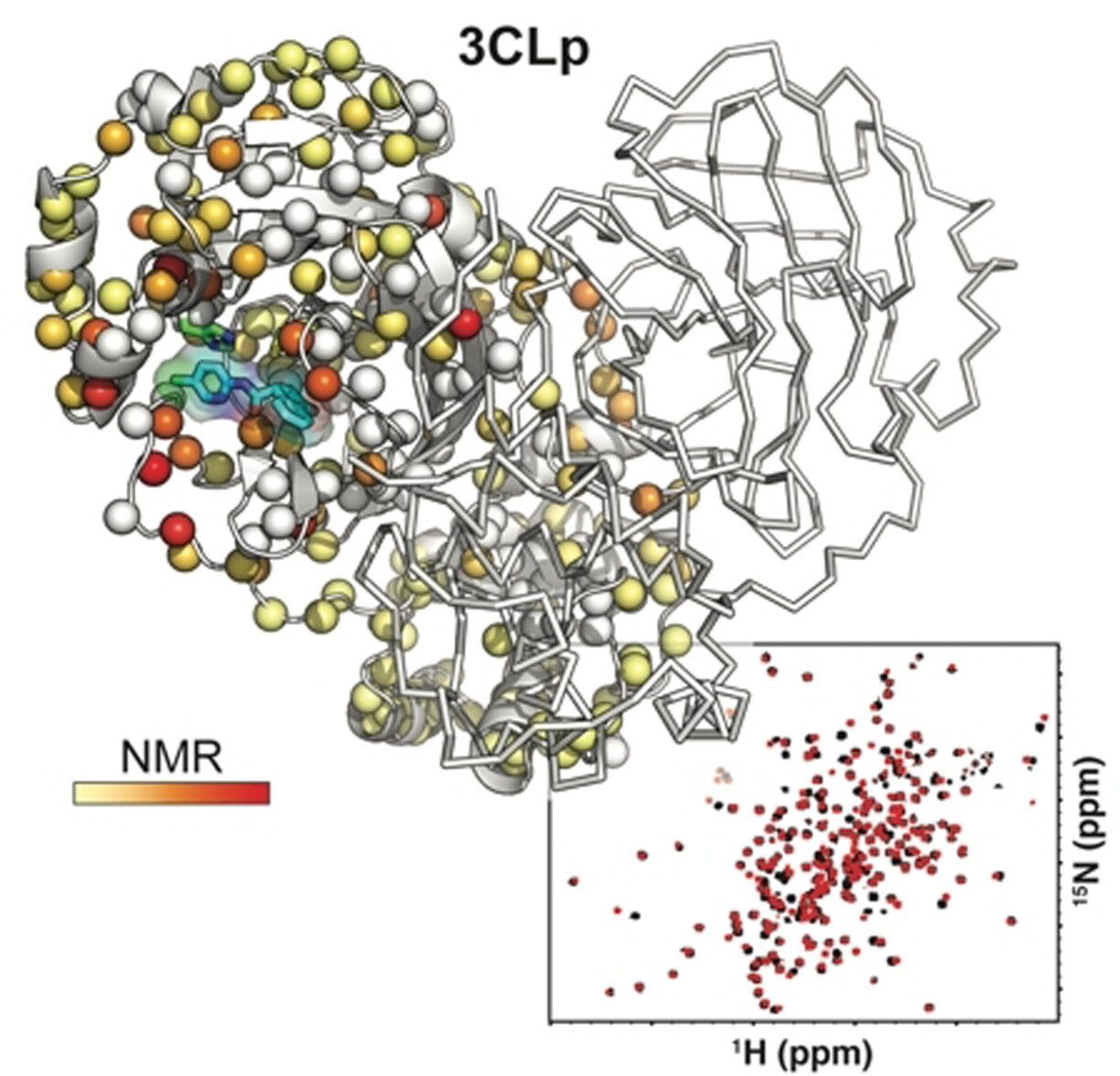
We report the liquid-sate NMR spectroscopy analysis of the dimeric SARS-CoV-2 main protease (3CLp), including its backbone assignments, to study its complex conformational regulation. Using fragment-based NMR screening, we highlighted three hotspots on the protein, two in the substrate binding pocket and one at the dimer interface, and we identified a non-covalent reversible inhibitor of 3CLp that has antiviral activity in infected cells.
Dimer Organization of Membrane-Associated NS5A of Hepatitis C Virus as Determined by Highly Sensitive 1H-Detected Solid-State NMR
- First Published: 18 November 2020

The membrane orientation of the hepatitis C virus NS5A protein was assessed by combining a cell-free protein synthesis approach with highly sensitive 1H-detected solid-state NMR. Insertion of lipids chelated with a paramagnetic Gd3+ ion allowed to orient the protein with respect to its membrane anchor using PRE. This information allowed to propose a model for the interaction of NS5A with a direct acting antiviral.
In-Cell NMR Spectroscopy of Functional Riboswitch Aptamers in Eukaryotic Cells
- First Published: 25 September 2020
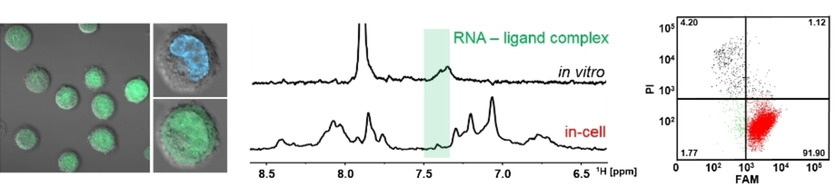
RNA aptamers find increasing application in synthetic biology as exogenous gene control elements, but high-resolution structural characterization in vivo is challenging. We report here the NMR-spectroscopic observation of ligand binding by the 2′-deoxyguanosine riboswitch aptamer in eukaryotic cells and show that the binding mode established by in vitro characterization of this aptamer is maintained in eukaryotic cellular environment.
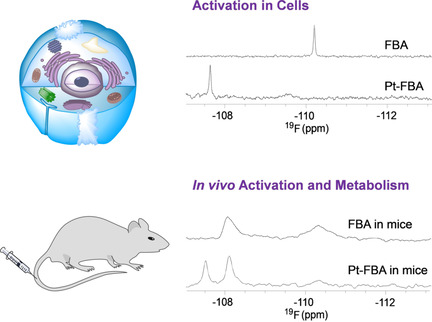
19F NMR Allows the Investigation of the Fate of Platinum(IV) Prodrugs in Physiological Conditions
- First Published: 20 November 2021
The Role of Rotational Motion in Diffusion NMR Experiments on Supramolecular Assemblies: Application to Sup35NM Fibrils
- First Published: 23 April 2021
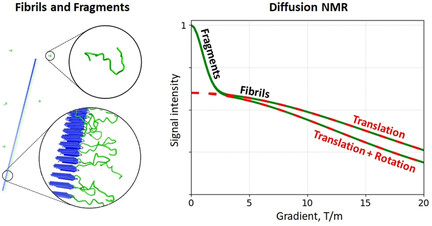
Diffusion of amyloid fibrils that contain disordered domains can be captured by pulsed-field-gradient NMR experiments. A new theory is presented that interprets the results of these measurements in terms of fibrils’ translational and rotational motion. Application to Sup35NM fibrils demonstrates the feasibility of diffusion-based sorting in complex amyloidogenic samples.
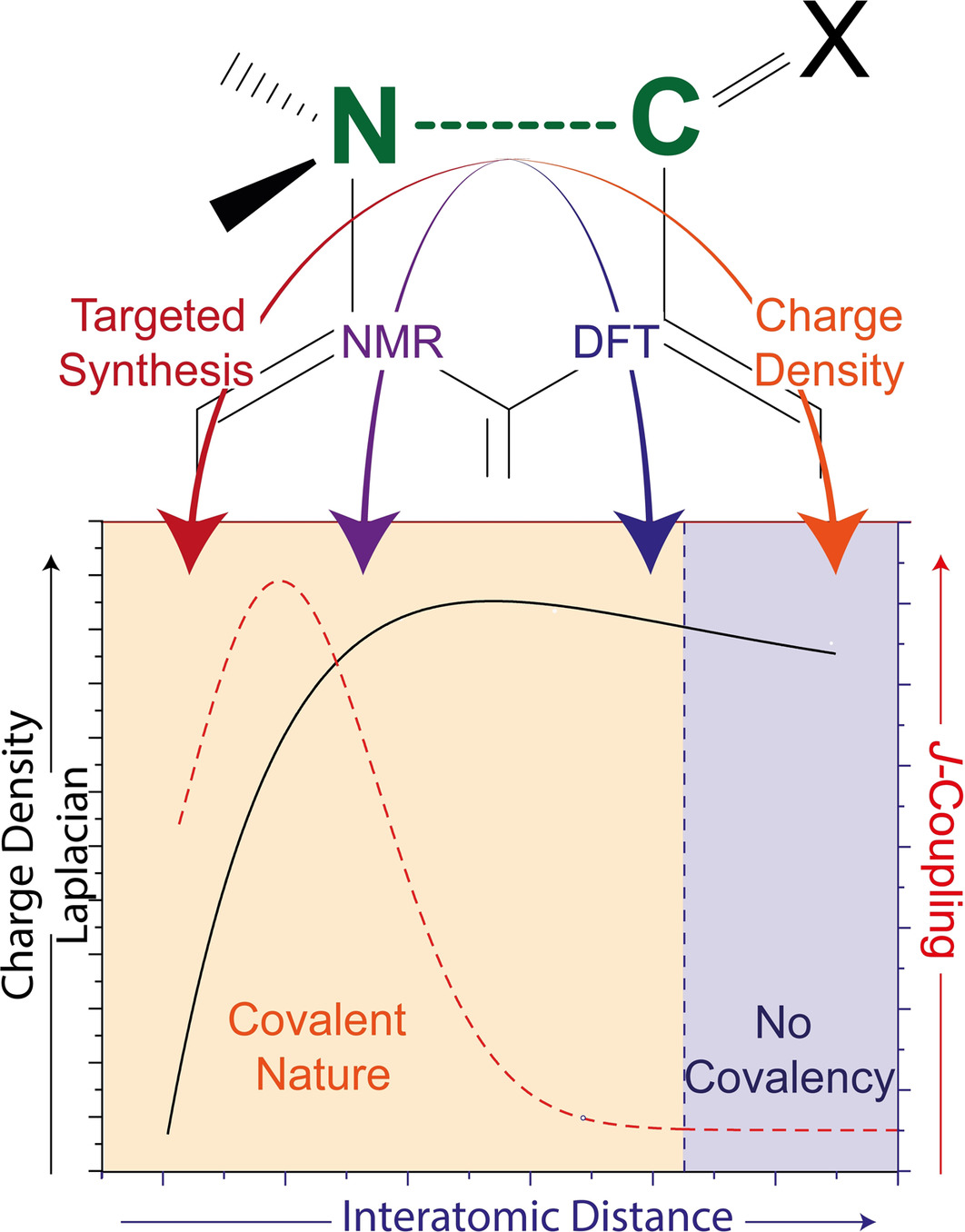
Mapping of N−C Bond Formation from a Series of Crystalline Peri-Substituted Naphthalenes by Charge Density and Solid-State NMR Methodologies
- First Published: 31 August 2021
Rapid Kinetic Screening via Transient Timesweep Experiments in Continuous Flow Reactors
- First Published: 15 December 2021
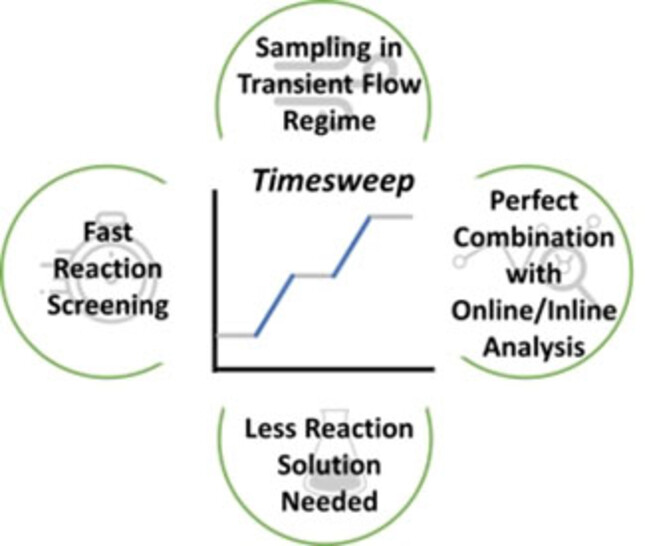
Transient timesweep experiments in continuous flow chemistry in conjunction with online monitoring allow for the recording of a wealth of kinetic data using minimal volumes of reactant at a minimum screening time required. The principle is introduced and discussed on the example of online benchtop NMR monitoring of a radical polymerization.
Experimentally Established Benchmark Calculations of 31P NMR Quantities
- First Published: 26 August 2020
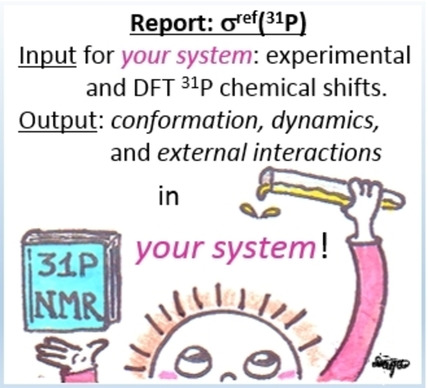
A 31Perfect model: Five small molecules in which 31P NMR chemical shift tensors are only weakly affected by intermolecular interactions have been investigated. They represent model systems suitable for determining the reference value of the absolute chemical shielding for any theoretical approximation of interest. This quantity allows to convert experimentally measured chemical shifts into theoretically calculated absolute chemical shieldings and vice versa.
Sensitive, Efficient and Portable Analysis of Molecular Exchange Processes by Hyperpolarized Ultrafast NMR
- First Published: 02 May 2022
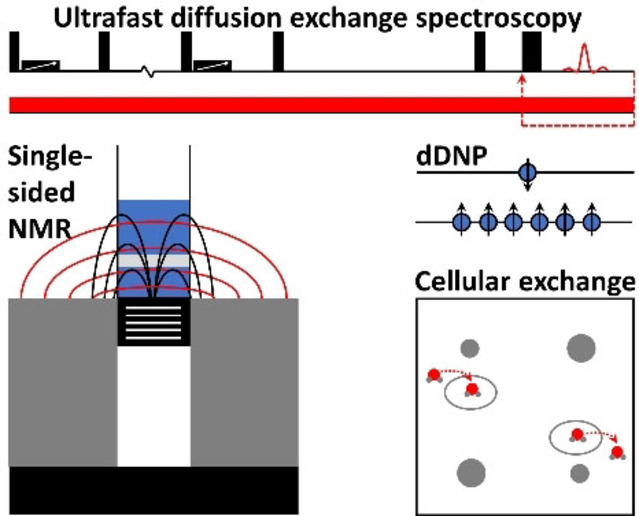
A hyperpolarized ultrafast diffusion exchange spectroscopy method is introduced, which allows highly sensitive and efficient quantification of molecular exchange rates by using low-cost, low-field, single-sided and portable NMR instruments. The method can be used to investigate exchange processes in many fields ranging from intra-extracellular exchange of metabolites to atmospheric surfactant solutions.




 methodologies not only allow for the comprehensive structural and compositional characterization of a sample, but also provide opportunities to study functional and even morphological aspects. To highlight the recent developments and applications in NMR methodologies, Angewandte Chemie along with our sister journal
methodologies not only allow for the comprehensive structural and compositional characterization of a sample, but also provide opportunities to study functional and even morphological aspects. To highlight the recent developments and applications in NMR methodologies, Angewandte Chemie along with our sister journal