Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Oncogenic SLC2A11–MIF fusion protein interacts with polypyrimidine tract binding protein 1 to facilitate bladder cancer proliferation and metastasis by regulating mRNA stability
- First Published: 14 August 2024
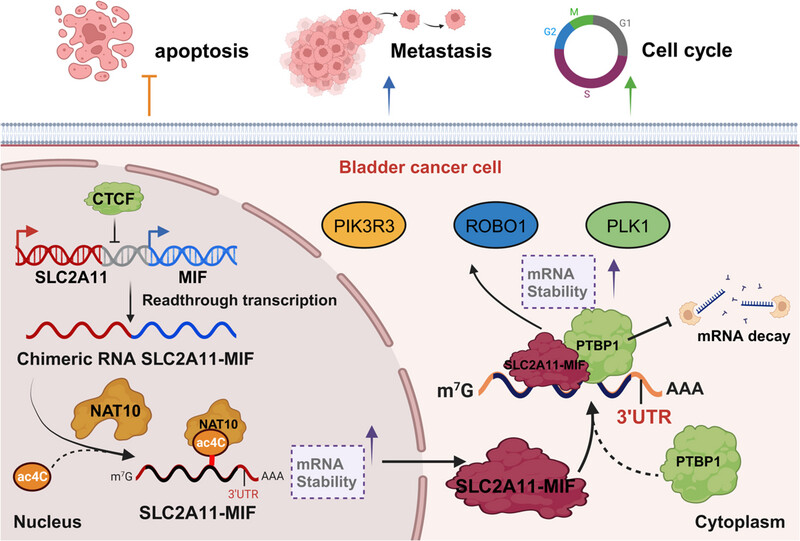
Chimeric RNA SLC2A11–MIF is upregulated and encodes a fusion protein in bladder cancer. The fusion protein SLC2A11–MIF localizes to the cytoplasm and interacts with PTBP1 to regulate the mRNA stability of PLK1, ROBO1, and PIK3R3. This ultimately leads to upregulation of these oncogenes, thereby controlling proliferation and metastasis. Additionally, SLC2A11–MIF mRNA is further regulated by CTCF and stabilized through ac4C modification facilitated by NAT10. Targeting SLC2A11–MIF represents a promising and versatile therapeutic strategy for patients with bladder cancer.
REVIEW
Current developments of gene therapy in human diseases
- First Published: 16 August 2024
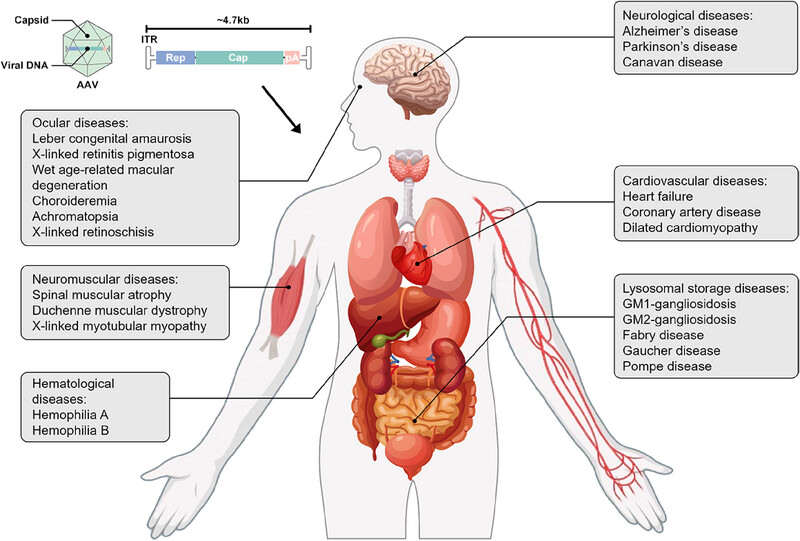
Gene therapy has seen remarkable advancements in recent decades, demonstrating its immense potential in treating a wide range of genetic and acquired diseases. Several AAV gene therapy products have been introduced to the market, addressing various conditions. This review explores the clinical applications of AAV in major human diseases, including ocular diseases, neuromuscular diseases, hematological diseases, neurological diseases, cardiovascular diseases, and lysosomal storage diseases.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
XBB.1.16-RBD-based trimeric protein vaccine can effectively inhibit XBB.1.16-included XBB subvariant infection
- First Published: 16 August 2024
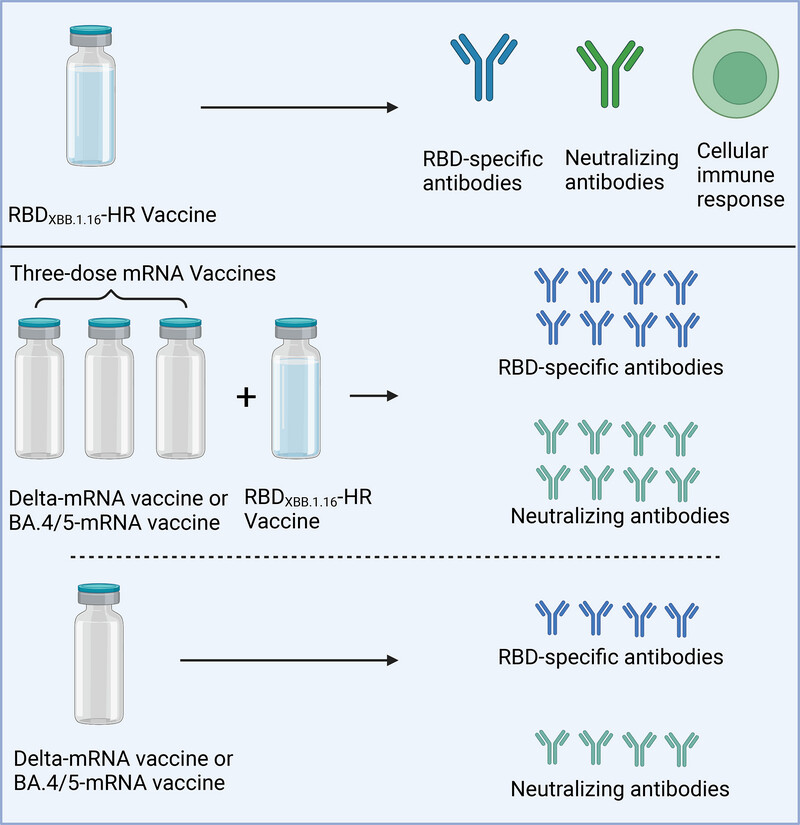
The RBDXBB.1.16-HR vaccine we formulated could elite high titers of receptor-binding domain (RBD)-specific binding antibodies, neutralizing antibodies against variants pseudovirus, and cellular immune responses. In addition, a heterologous RBDXBB.1.16-HR vaccine could improve both RBD-specific binding antibodies and neutralizing antibodies induced by Delta-mRNA vaccines and BA.4/5-mRNA vaccines. These data indicated that the recombinant RBDXBB.1.16-HR protein with a new T478R mutation could induce strong neutralizing antibodies to fight newly emerged XBB variants .
Recryopreservation impairs blastocyst implantation potential via activated endoplasmic reticulum stress pathway and induced apoptosis
- First Published: 16 August 2024

1. Recryo procedure in blastocysts results in impaired blastocyst developmental potential.
2. Recryo procedure impairs trophectoderm (TE) function of blastocysts.
3. Recryo procedure alters the transcriptome of human blastocysts.
4. Recryo procedure affects blastocyst adhesion, activates endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress pathway and induces apoptosis
Detection of Epstein‒Barr virus DNA methylation as tumor markers of nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients in saliva, oropharyngeal swab, oral swab, and mouthwash
- First Published: 19 August 2024
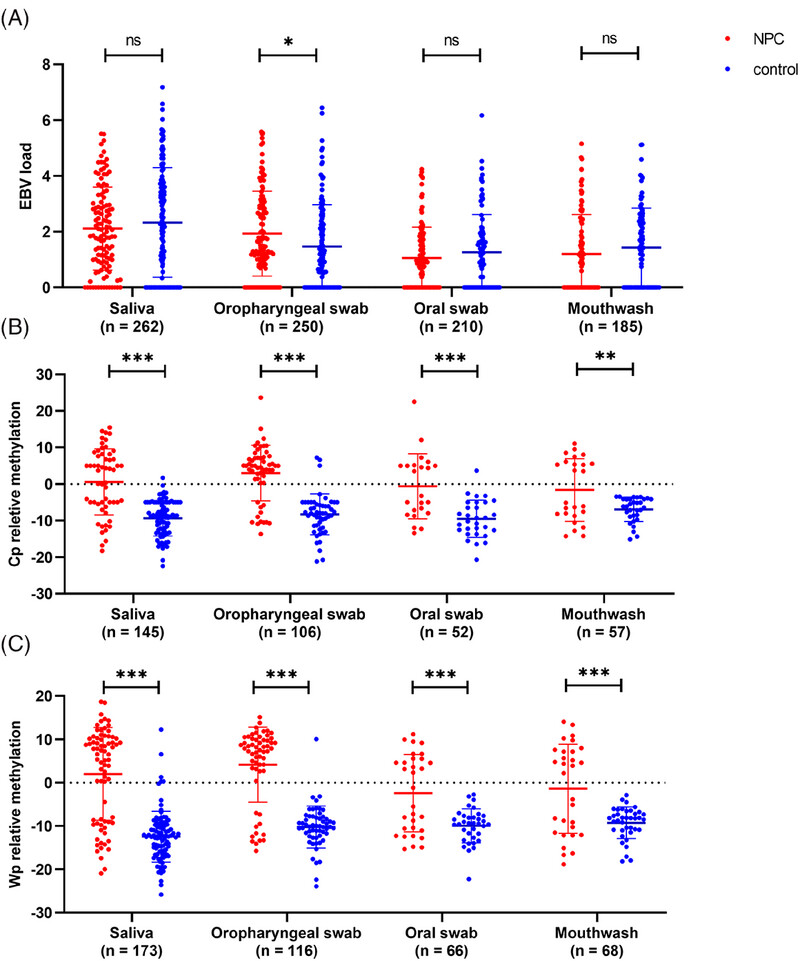
In oral cavity, self-sampling samples, including saliva, oropharyngeal swab, oral swab, and mouthwash, can all be done by donors themselves. In this study, EBV DNA methylation was detection and compared in these samples. Our study explored the optimal self-sampling types and detection targets for the detection of NPC and may facilitate the application of EBV DNA methylation detection in a home-based large-scale screening of NPC.
REVIEW
The dual role of cellular senescence in human tumor progression and therapy
- First Published: 19 August 2024
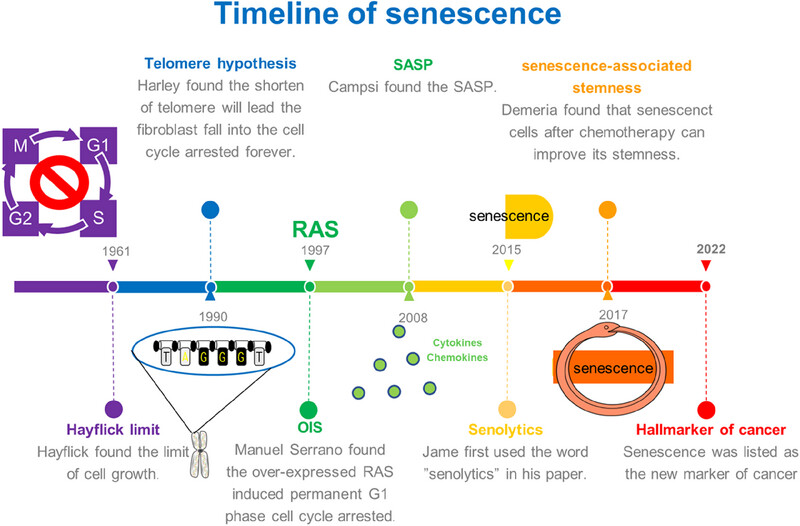
The study of cellular senescence is a long process, and people continue to explore new mechanisms to improve the role of cellular senescence in cancer, and now we can judge that cellular senescence plays different roles in a variety of cancers, and its duality in cancer requires the attention of doctors and researchers.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
miR-106b-5p protects against drug-induced liver injury by targeting vimentin to stimulate liver regeneration
- First Published: 21 August 2024
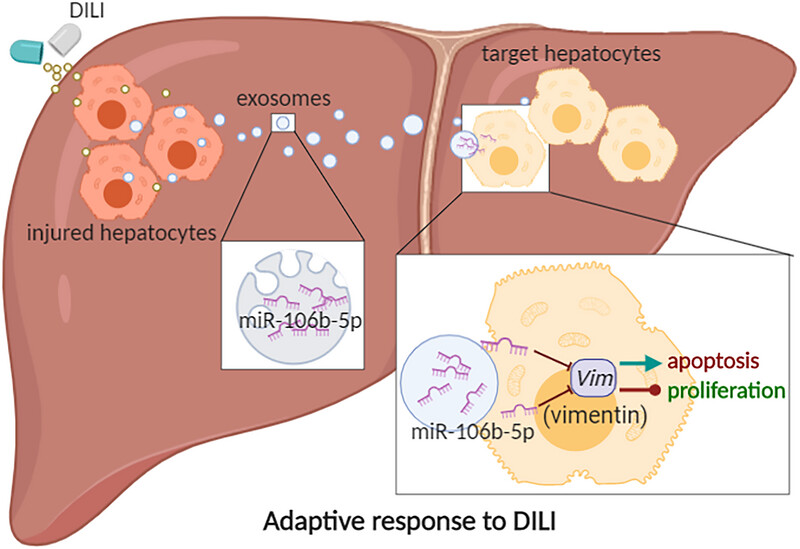
We showed that miR-106b-5p promotes robustly adaptive response to drug-induced liver injury in animal models of hepatotoxicity. Clinical validation confirms serum miR-106b-5p level and its target vimentin to be directly correlated with the severity of liver injury, therefore suggesting that miR-106b-5p may be a prognostic biomarker for resolution and has the potential to be exploited as a therapeutic agent.
REVIEW
Head and neck cancer: pathogenesis and targeted therapy
- First Published: 21 August 2024
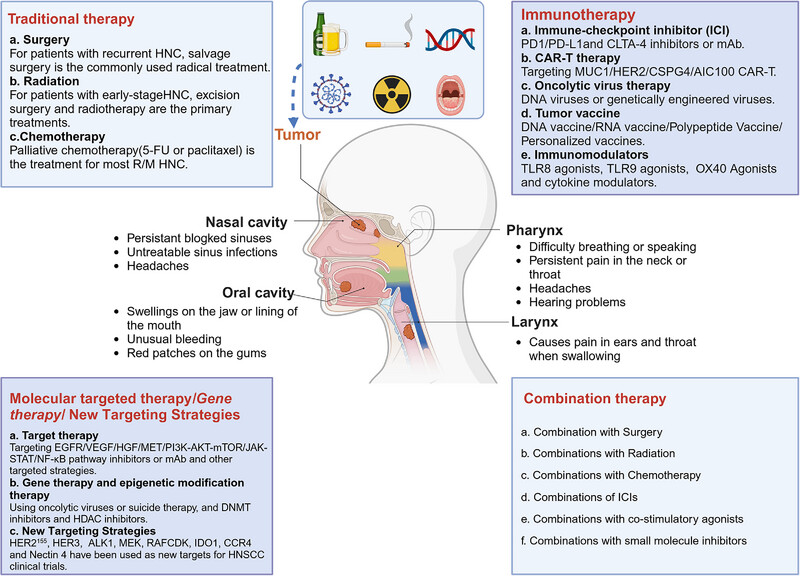
Current clinical treatment of HNC. Tobacco, alcohol, viral infection, genomic changes, head and neck X-ray exposure, and poor oral hygiene are the main causes of HNC. At present, the preferred treatment for most HNC patients is postoperative combined with chemotherapy or/and radiotherapy. Emerging therapeutic strategies mainly include immune checkpoint inhibitors, costimulatory agonists, antigen vaccines, OV therapy, CAR-T, multireceptor targeting MAb and small molecule inhibitors, gene therapy, natural medicine therapy, and combination therapy (created with BioRender.com).
HIGHLIGHT
Enhancing the effectiveness of anti-respiratory virus vaccines by bolstering mucosal immunity and cellular defenses
- First Published: 24 August 2024
REVIEW
Epigenetic reprogramming in gastrointestinal cancer: biology and translational perspectives
- First Published: 24 August 2024
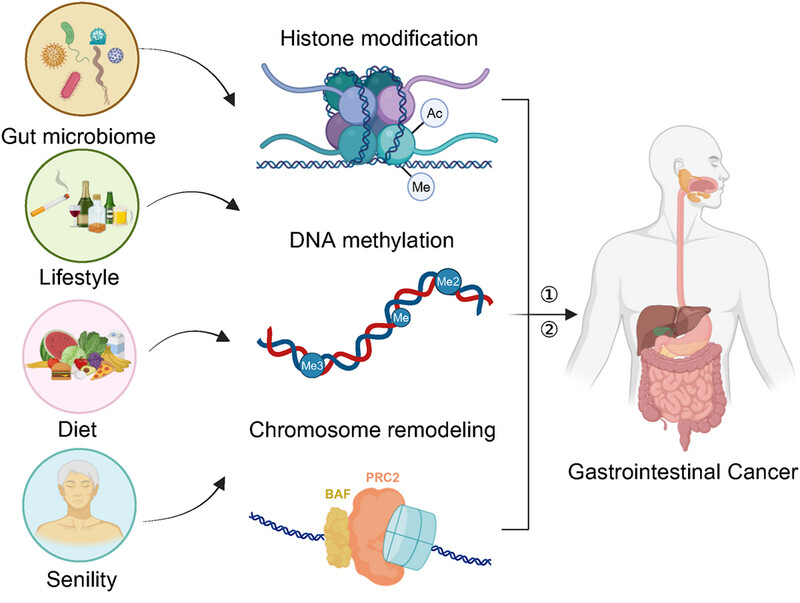
The overview of epigenomics in gastrointestinal cancer. Infection, smoking, alcohol, diet, senility, and other factors affect the reprogramming of the epigenetic genome and then promote the occurrence and development of gastrointestinal cancer. ① indicates “function despondently” and ② indicates “interaction.”
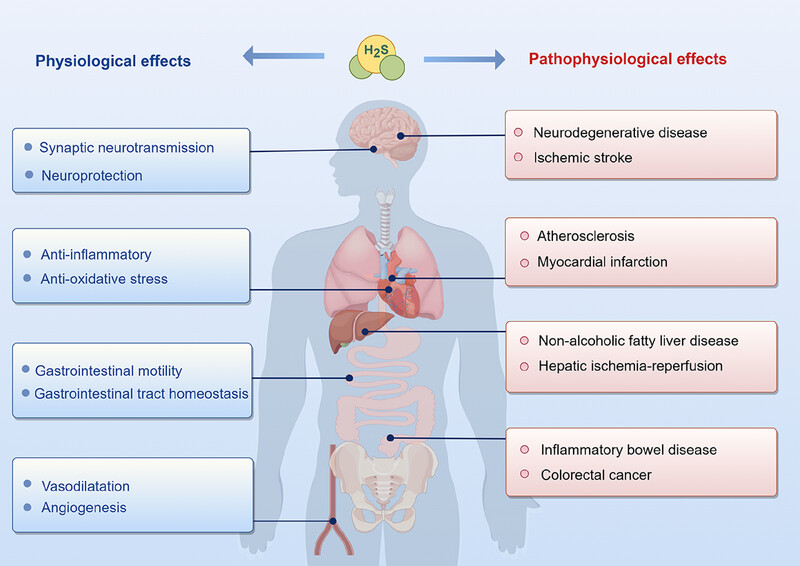
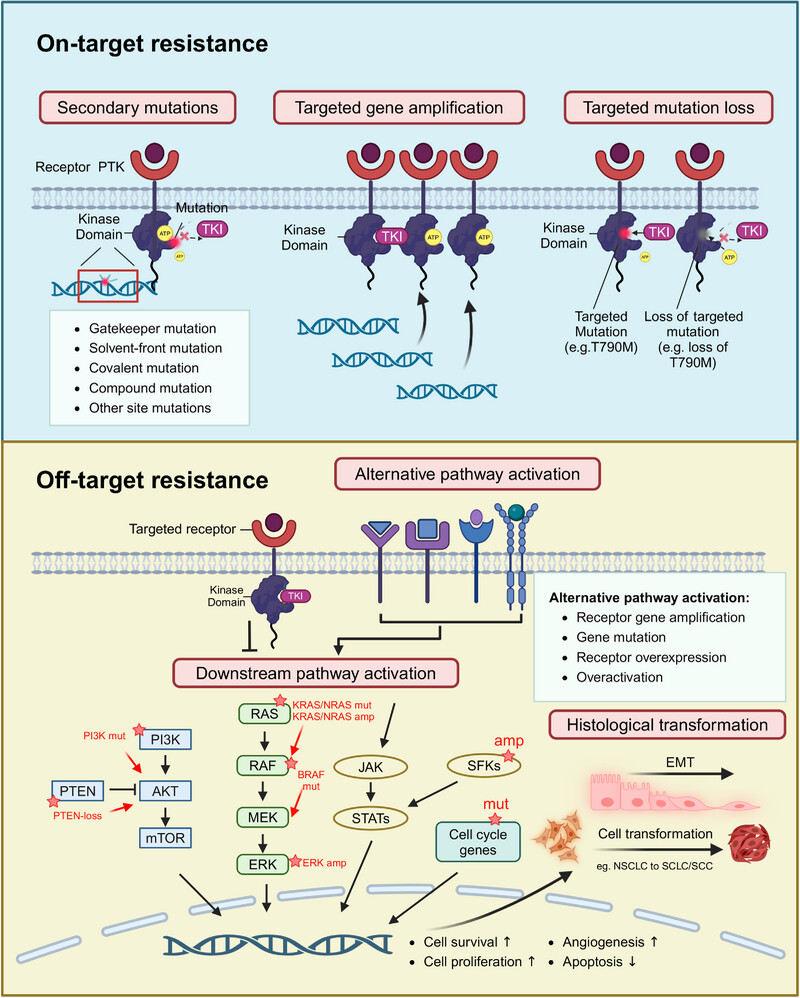
Mechanisms of resistance to tyrosine kinase inhibitor-targeted therapy and overcoming strategies
- First Published: 24 August 2024
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
An inflammatory liquid fingerprint predicting tumor recurrence after liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma
- First Published: 26 August 2024
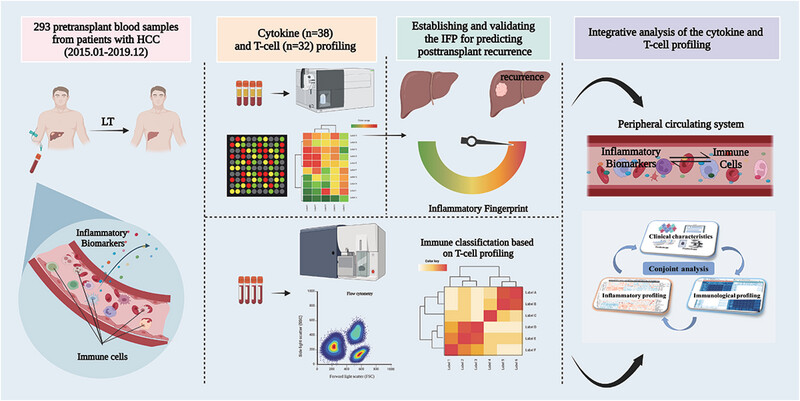
• Conjoint analysis of pretransplant peripheral inflammatory and T-cell profiling depicts recurrence-related immune status.
• The inflammatory fingerprint (IFP) incorporates interleukin 6, osteocalcin, systemic immune-inflammation index, and α-fetoprotein to predict recurrence after LT for HCC and significantly optimizes the current risk stratification system.
• Impaired T cell function could primly elucidate why the IFP can precisely predict tumor recurrence after LT for HCC.
REVIEW
Endoplasmic reticulum stress in diseases
- First Published: 26 August 2024
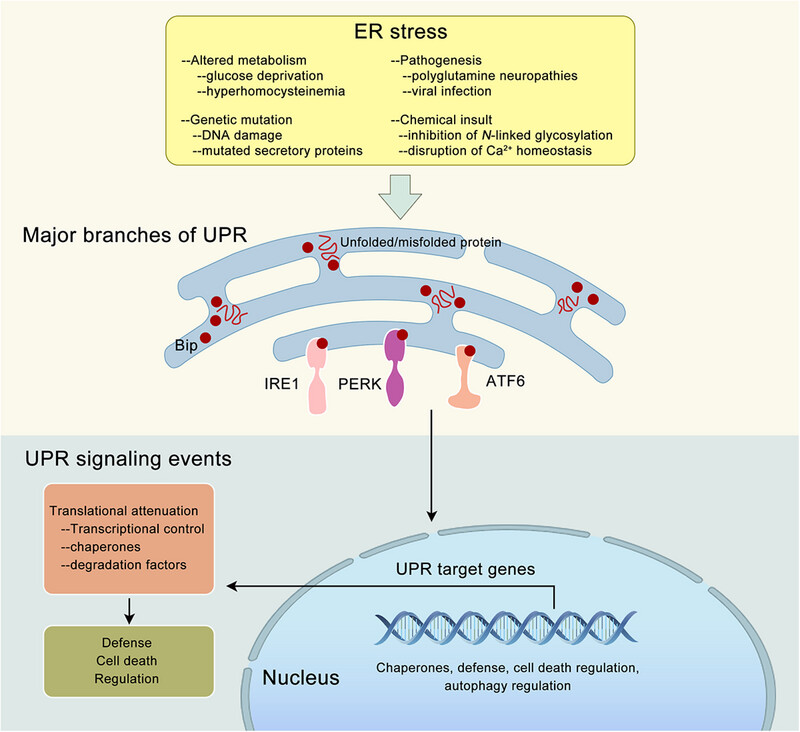
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) serves as a vital organelle in eukaryotic cells, performing essential roles such as protein folding, modification, and trafficking, lipid biosynthesis, and calcium regulation. Various conditions may disrupt ER function, potentially leading to the accumulation of unfolded and misfolded proteins, and triggering ER stress. This prompts the unfolded protein response (UPR), a conserved signaling cascade, to mitigate the stress by regulating gene expression and protein synthesis, aiming to restore ER equilibrium. However, prolonged or severe ER stress can lead to cell death. As our understanding of the molecular mechanisms linking ER stress to human diseases improves, ER stress and UPR activation are increasingly recognized as significant contributors to various diseases. The balancing of ER stress and the UPR is crucial for the pathogenesis of diseases, such as cardiovascular diseases, neurodegenerative diseases, metabolic diseases, autoimmune diseases, fibrotic diseases, viral infections, and cancer. It also considers how manipulation of this complex signaling pathway may provide a new target for drug discovery and innovative therapeutic strategies in human disease.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Manganese boosts natural killer cell function via cGAS–STING mediated UTX expression
- First Published: 28 August 2024
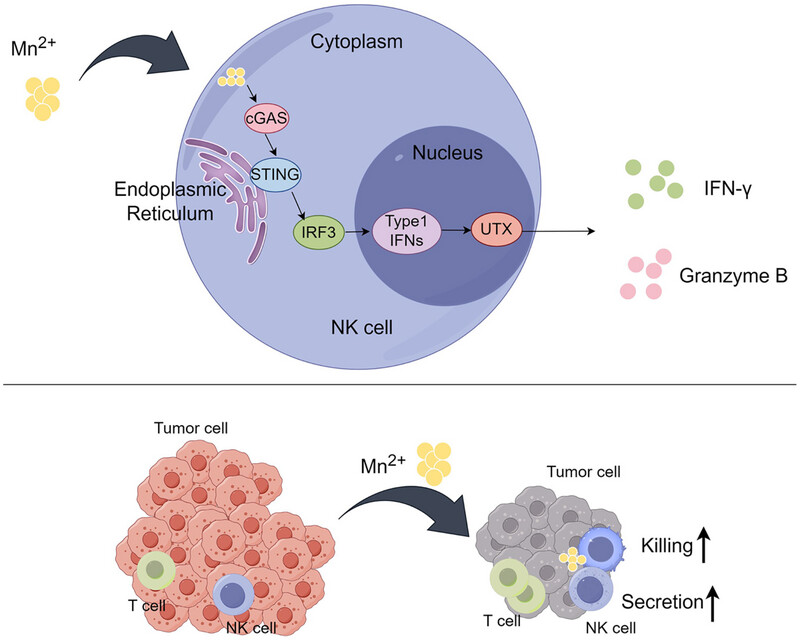
Schematic illustration of manganese promoting the activation and function of NK cells in tumor tissues. Manganese increased constitutive activation of cGAS and subsequently stimulated the STING/interferon regulatory factor 3 (IRF3)/Type-I interferon (IFN-I) pathway, promoting expression of UTX. Therefore, NK cells exhibited enhanced killing and secreting activity, and played a critical antitumor role in synergy with T cells.
Patient-derived ovarian cancer organoid carries immune microenvironment and blood vessel keeping high response to cisplatin
- First Published: 28 August 2024
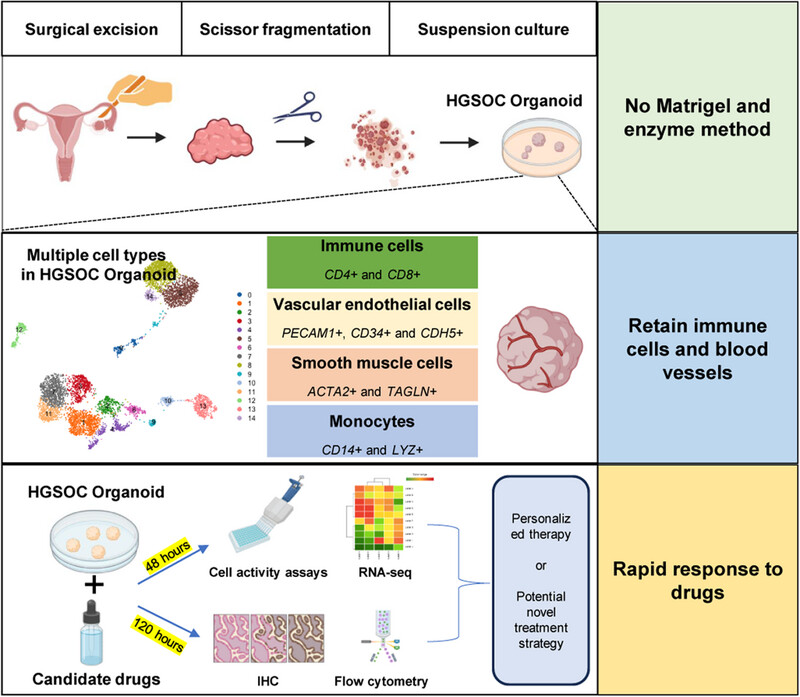
We have developed a matrigel and enzyme-free organoid culture method for High-Grade Serous Ovarian Cancer, enabling accurate representation of the tumor microenvironment and vascularization features. This approach facilitates a comprehensive understanding of the cellular composition and internal characteristics of ovarian cancer, while also demonstrating its potential in rapid drug screening and selection for clinical applications.
Statins, but not proprotein convertase subtilisin-kexin type 9 inhibitors, lower chemerin in hypercholesterolemia via low-density lipoprotein receptor upregulation
- First Published: 31 August 2024
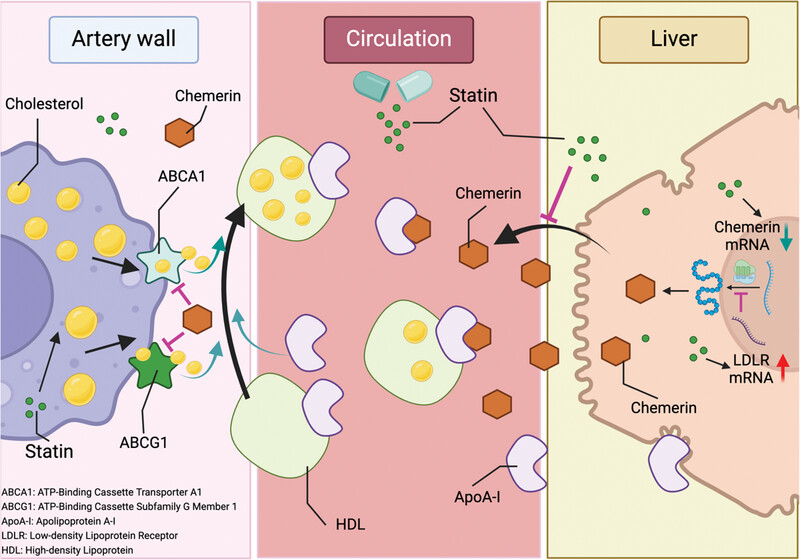
Chemerin, an adipokine and predictor of cardiovascular disease, is reduced by statins but not PCSK9 inhibitors in patients with hypercholesterolemia. This involves a direct effect of statins on chemerin release from hepatocytes, mediated via LDLR upregulation. Chemerin binds to ApoA-I in HDL and impairs HDL-mediated cholesterol efflux via ABCA1 and ABCG1. Chemerin-lowering by statins will prevent this.
HIGHLIGHT
Inhibitor of differentiation 3 confers the robust anti-tumor activity of Kupffer cells
- First Published: 31 August 2024
Tumor cells utilize acetate for tumor growth and immune evasion
- First Published: 31 August 2024
REVIEW
Posttransplant complications: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic interventions
- First Published: 02 September 2024
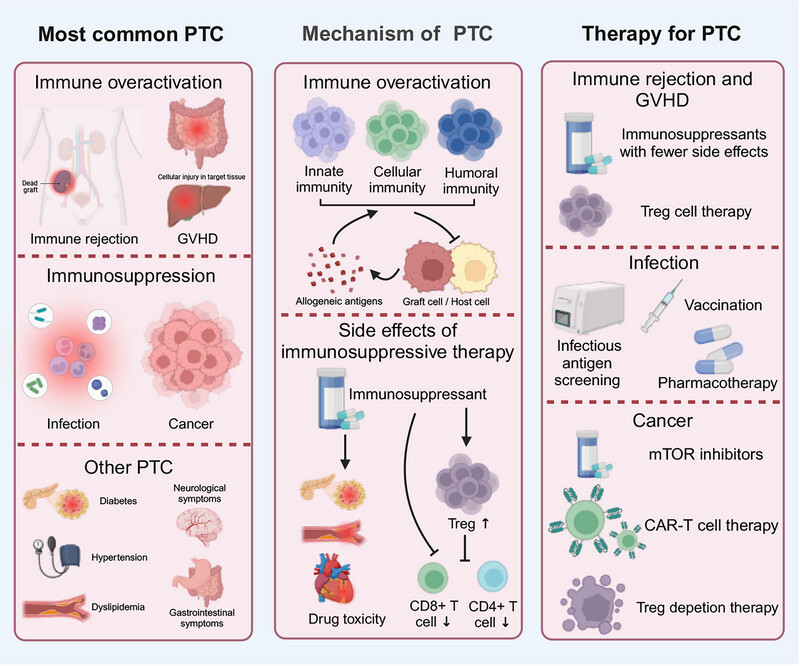
The most common posttransplant complications (PTC) include immune-mediated complications (rejection and graft-versus-host disease), infections, metabolic complications (diabetes, hypertension, and dyslipidemia), and malignancies.
The mechanisms underlying PTC mainly involve allogeneic antigen-activated innate immunity, cellular immunity, and humoral immunity responses, as well as the side effects and toxicity of immunosuppressants.
Treatment strategies for PTC include the use of immunosuppressants with fewer side effects, Treg cell therapy, infection screening and vaccination, mTOR inhibitors for cancer treatment, and CAR-T cell therapy and Treg depletion therapy.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Targeting chronic lymphocytic leukemia with B-cell activating factor receptor CAR T cells
- First Published: 02 September 2024
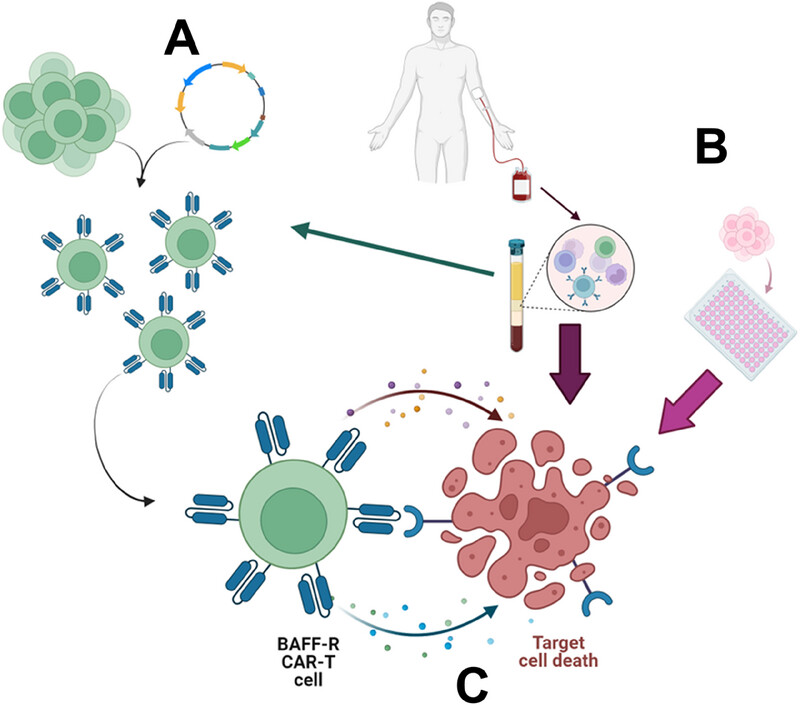
BAFF-R CAR T cells were created (A) using a lentiviral system and tested against various malignant B-cell lines, including CLL cells. CLL patient-derived BAFF-R CAR T cells were also generated to test their cytotoxicity on autologous primary malignant B cells (B). The cytotoxicity of CAR T cells was measured using degranulation, interferon-γ release, and green fluorescent protein-labeled killing assays (C).
Targeting RAC1 reactivates pyroptosis to reverse paclitaxel resistance in ovarian cancer by suppressing P21-activated kinase 4
- First Published: 02 September 2024
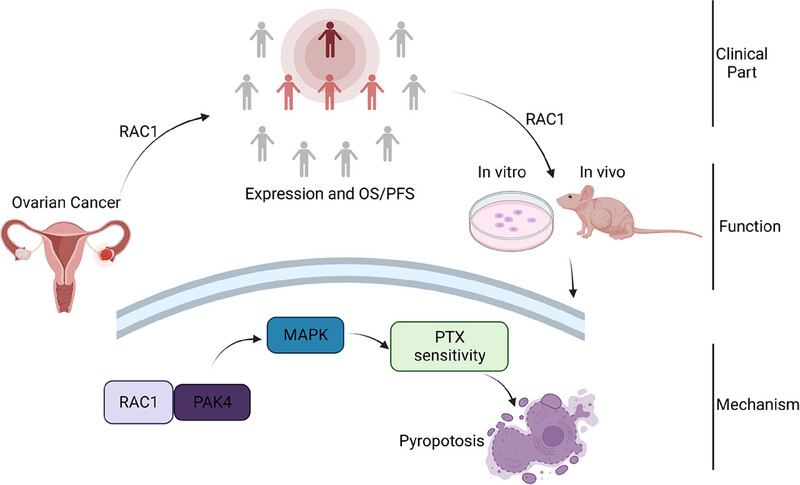
Pyroptosis may play an important role in chemotherapy resistance of ovarian cancer. RAS-associated C3 botulinum toxin substrate 1 (RAC1) is overexpressed in ovarian cancer patients and is negatively associated with patient outcomes. It can drive gasdermin D (GSDMD)-mediated pyroptosis reversal of paclitaxel resistance through the P21-activated kinase 4 (PAK4)/mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway. It was further demonstrated to reverse paclitaxel resistance via PAK4 in animal experiments and clinical samples.
REVIEW
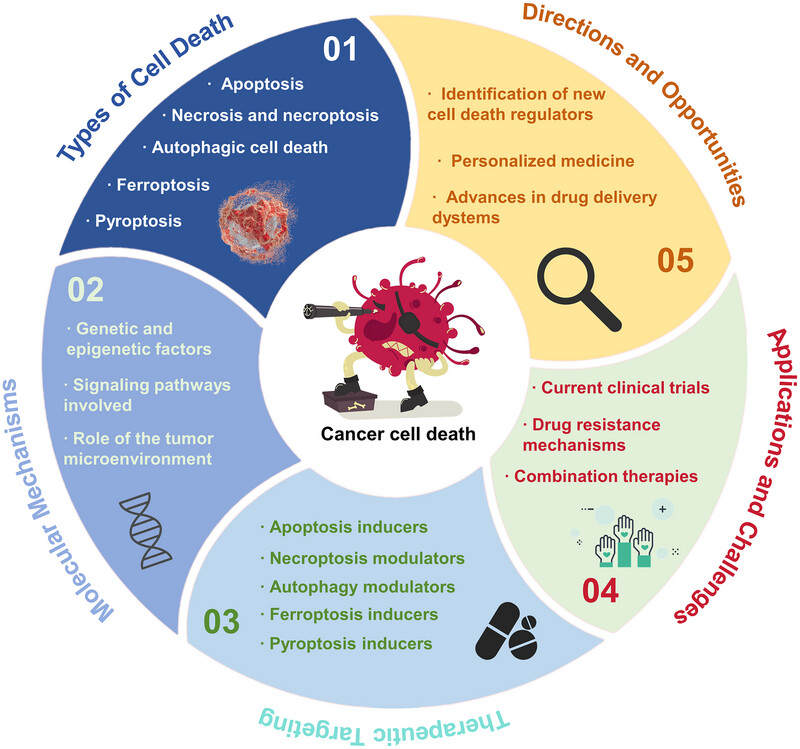
Cell death pathways: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic targets for cancer
- First Published: 04 September 2024
Circular RNAs in human diseases
- First Published: 04 September 2024
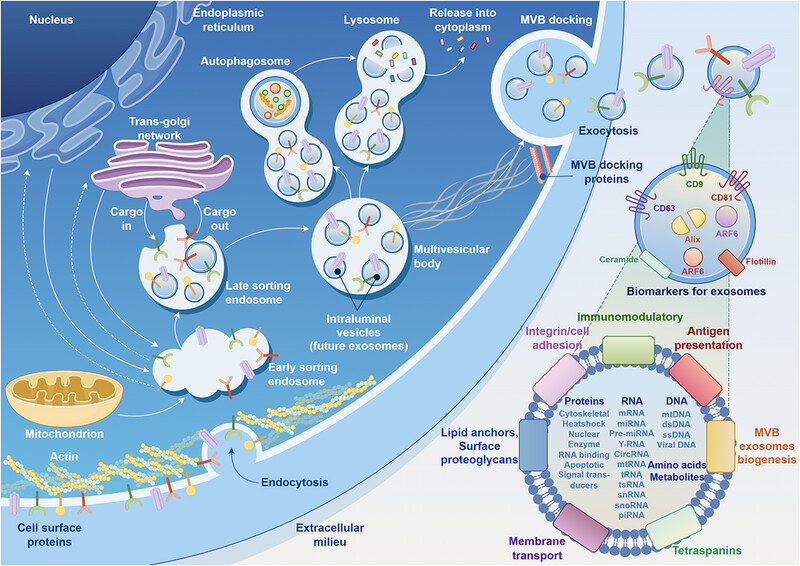
Circular RNAs (circRNAs) play significant roles in various human diseases, including respiratory, endocrine, metabolic, musculoskeletal, cardiovascular, renal diseases, and cancer. This review highlights their biogenesis, pathogenic potential, and potential applications as diagnostic biomarkers and therapeutic targets.
Aortic aneurysm: pathophysiology and therapeutic options
- First Published: 07 September 2024
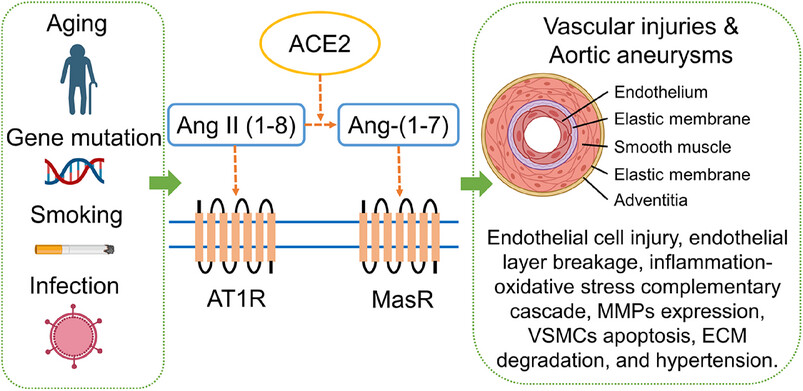
Activation of Ang-(1–7)/MasR axis protects vascular health and antagonizes the adverse effects of Ang II/ATIR activation on the development of vascular dysfunction, atherosclerosis, and aortic aneurysms (AAs). The discovery of the Ang-(1–7)/MasR pathway has provided an important therapeutic target for the prevention and treatment of AA. This review will outline the epidemiology of AA and current diagnostic and treatment strategies. Due to the highest incidence and most extensive research on abdominal AA, we will focus on AAA to explain the role of the RAS in its development, the protective function of Ang-(1–7)/MasR, and the mechanisms involved. We will also describe the roles of agonists and antagonists, suggest improvements in engineering and drug delivery, and provide evidence for Ang-(1–7)/MasR's clinical potential, discussing risks and solutions for clinical use.
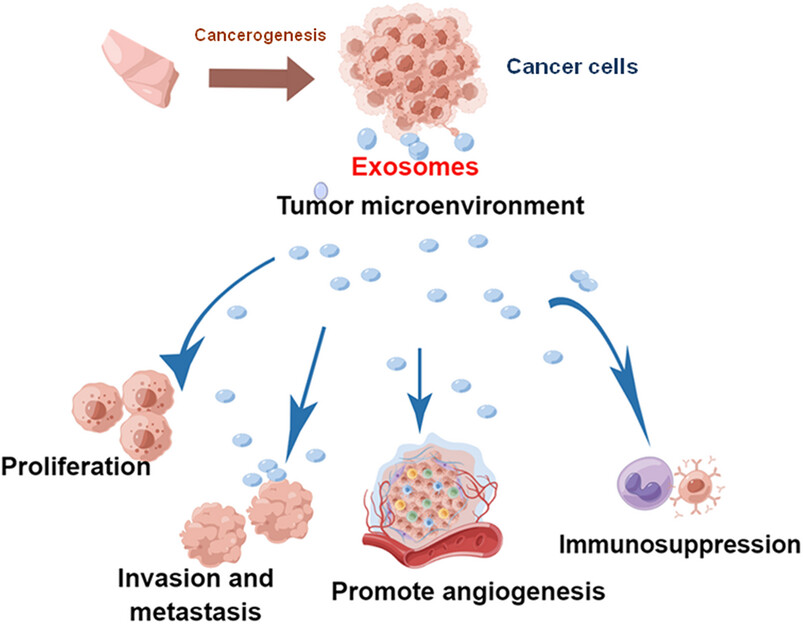
Tumor-associated exosomes in cancer progression and therapeutic targets
- First Published: 07 September 2024
HIGHLIGHT
The stiffness of the extracellular matrix is a key factor in tumor progression
- First Published: 07 September 2024
SMARCAL1: a new target for taming tumor immune evasion
- First Published: 07 September 2024
REVIEW
Radiogenomics: bridging the gap between imaging and genomics for precision oncology
- First Published: 09 September 2024
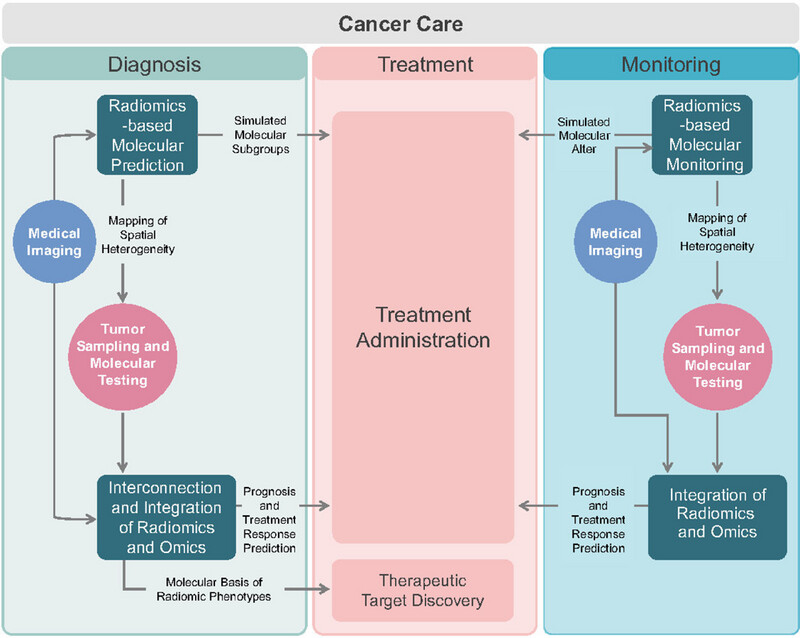
Radiogenomics is a new tool for precisive oncology by deeply integrating radiomics and genomics. This review deconstructs the current research status of radiogenomics through the multidimensional feature engineering of radiomics and the integration patterns of radiomics and genomics, and takes gliomas, lung cancers, breast cancers, and other common cancers as examples to show the advance of the application of radiogenomics in the diagnosis, treatment, and monitoring of tumors.
Role of N6-methyladenosine RNA modification in cancer
- First Published: 09 September 2024
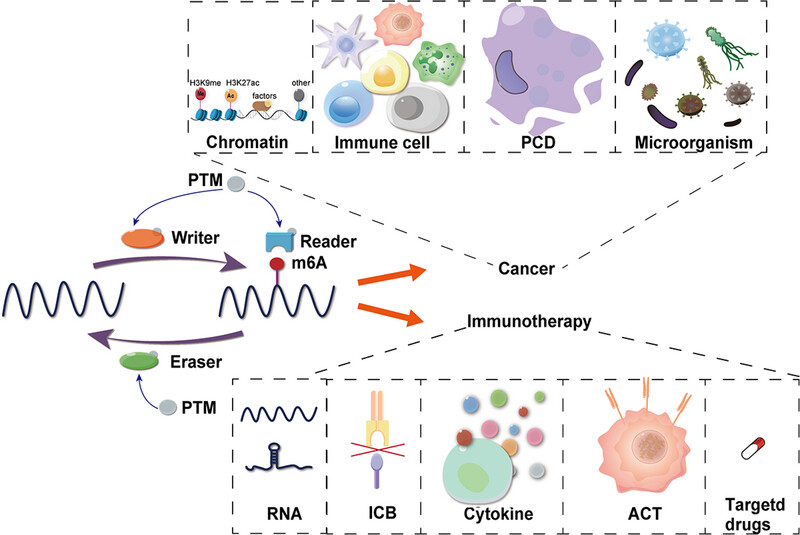
N6-methyladenosine (m6A) is the most abundant modification of RNA in eukaryotic cells. Previous studies have shown that m6A is pivotal in diverse diseases especially cancer. m6A corelates with the initiation, progression, resistance, invasion and metastasis of cancer. However, despite these insights, a comprehensive understanding of its specific roles and mechanisms within the complex landscape of cancer is still elusive. This review begins by outlining the key regulatory proteins of m6A modification and their posttranslational modifications, as well as the role in chromatin accessibility and transcriptional activity within cancer cells. Additionally, it highlights that m6A modifications impact cancer progression by modulating programmed cell death (PCD) mechanisms and affecting the tumor microenvironment through various cancer-associated immune cells. Furthermore, the review discusses how microorganisms can induce enduring epigenetic changes and oncogenic effect in microorganism-associated cancers by altering m6A modifications. Last, it delves into the role of m6A modification in cancer immunotherapy, encompassing RNA therapy, immune checkpoint blockade, cytokine therapy, adoptive cell transfer therapy, and direct targeting of m6A regulators. Overall, this review clarifies the multifaceted role of m6A modification in cancer and explores targeted therapies aimed at manipulating m6A modification, aiming to advance cancer research and improve patient outcomes .
LETTER
Structural insight into interleukin-4Rα and interleukin-5 inhibition by nanobodies from a bispecific antibody
- First Published: 09 September 2024
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Leveraging single-cell RNA-seq for uncovering naïve B cells associated with better prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma
- First Published: 09 September 2024
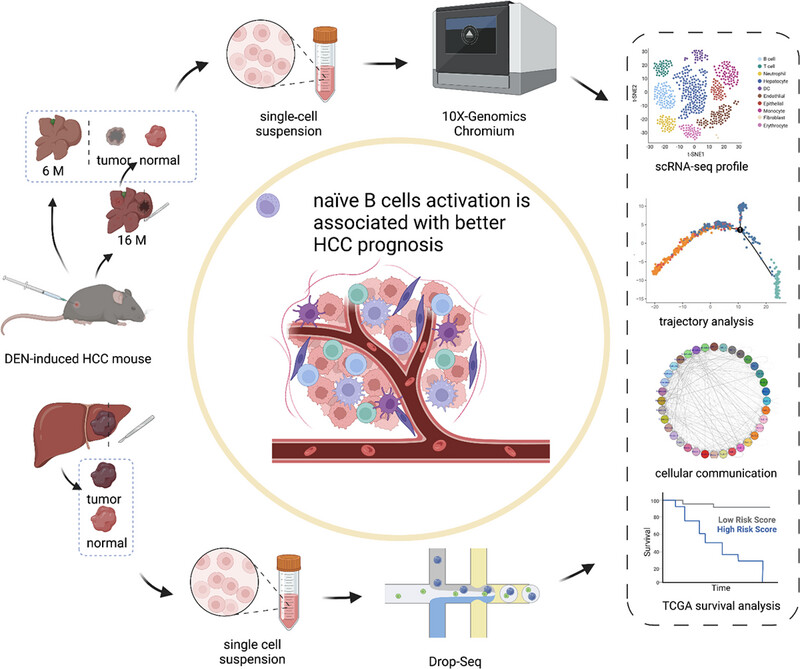
The workflow of the study. scRNA-seq was performed on diethylnitrosamine (DEN)-induced mouse HCC model to characterize the changes in immune cell composition, lineages, and functional activities in TME during tumorigenesis. Then, the signature genes were mapped for specific cell subpopulations (e.g., naïve B cells) to TCGA database for the HCC RNA-seq dataset. Finally cell interaction analysis was employed to reveal B cell activation in both mouse and human samples.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Loss-of-function variants in RNA binding motif protein X-linked induce neuronal defects contributing to amyotrophic lateral sclerosis pathogenesis
- First Published: 10 September 2024
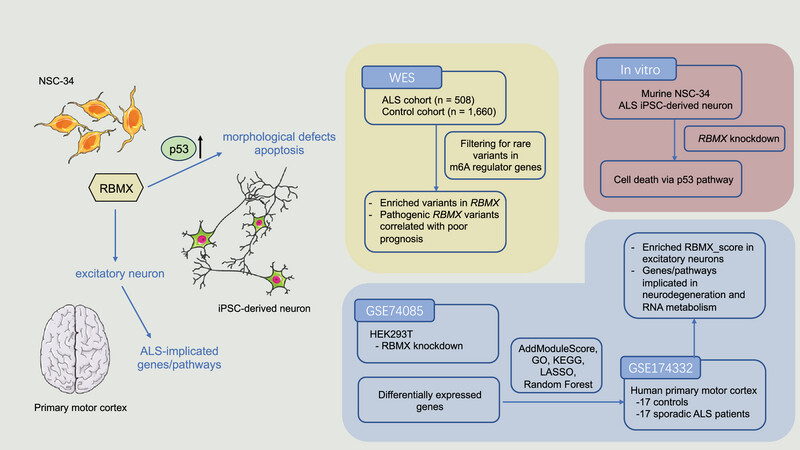
The dysregulation of m6A modification has gained recognition as a crucial factor in the development of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). Among the m6A reader proteins, RNA binding motif protein X-linked (RBMX) stands out with a notable enrichment of variants in ALS patients, and the presence of pathogenic RBMX variants is associated with a faster disease progression. In vitro experiments have provided evidence that reducing RBMX levels can result in neuronal defects. Additionally, bioinformatic analyses have supported these findings by revealing that RBMX-associated genes specifically impact excitatory neurons. Furthermore, these genes are involved in the regulation of pathways and genes associated with neurodegeneration and RNA metabolism, underscoring the relevance of RBMX in ALS pathogenesis.
LETTER
Antibacterial properties of natural cinnamon-alginate fibrous patches produced by modified nozzle-pressurized spinning
- First Published: 10 September 2024
REVIEW
Adenoid cystic carcinoma: insights from molecular characterization and therapeutic advances
- First Published: 11 September 2024
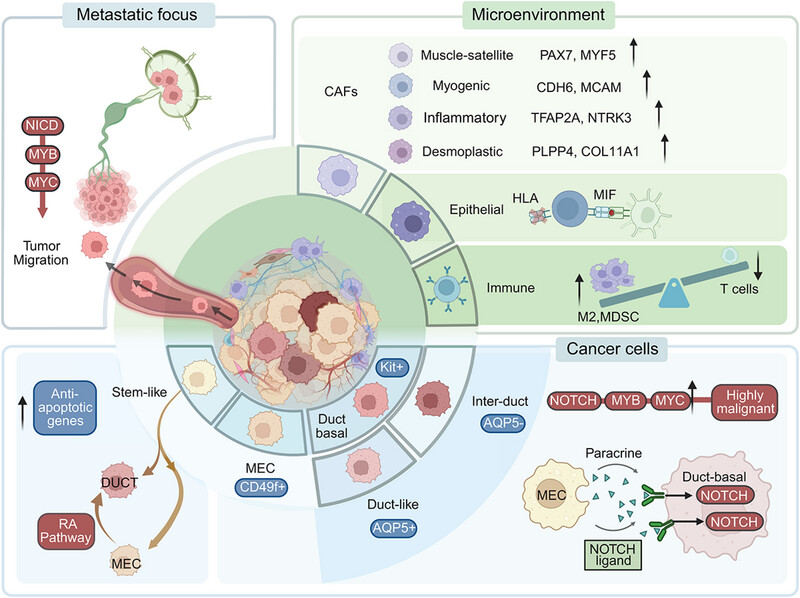
Adenoid cystic carcinoma exhibits significant cellular heterogeneity, with tumor cells primarily composed of myoepithelial cells and ductal-like cells. The tumor microenvironment is immunosuppressive, characterized by cancer-associated fibroblasts, low HLA expression in epithelial cells, and elevated M2 macrophages and myeloid-derived suppressor cells. Metastatic lesions show increased NOTCH and MYB expression, promoting tumor migration.
Krüppel-like factors family in health and disease
- First Published: 10 September 2024
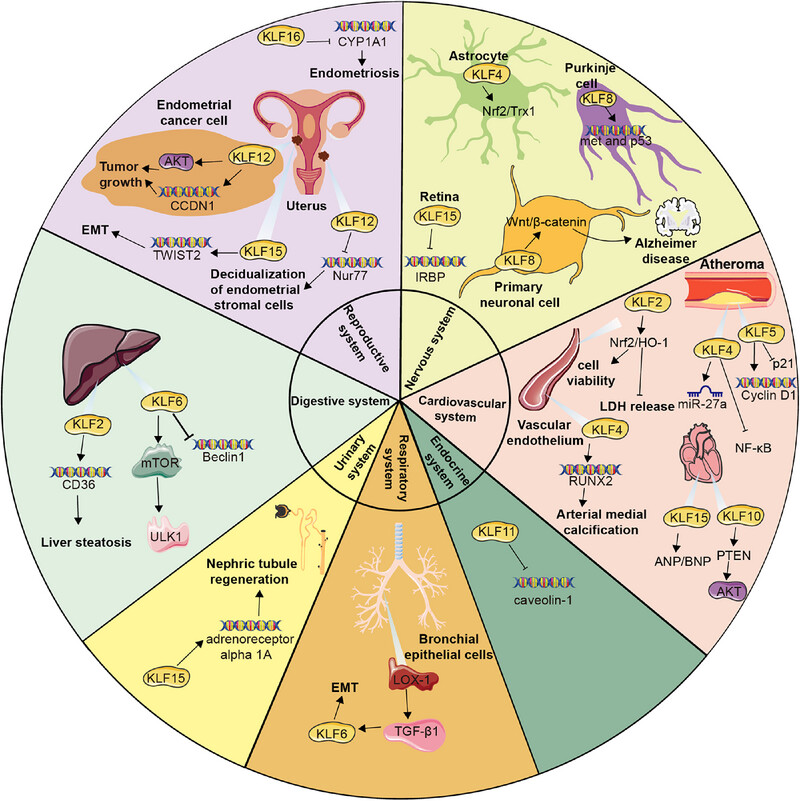
KLFs are pivotal factors in regulating essential processes across eight major systems: nervous, cardiovascular, respiratory, digestive, endocrine, urinary, reproductive, and musculoskeletal systems. This graphic illustrated how KLFs influenced cellular functions and disease mechanisms within each system, highlighting their diverse roles in maintaining health and their involvement in various pathologies.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
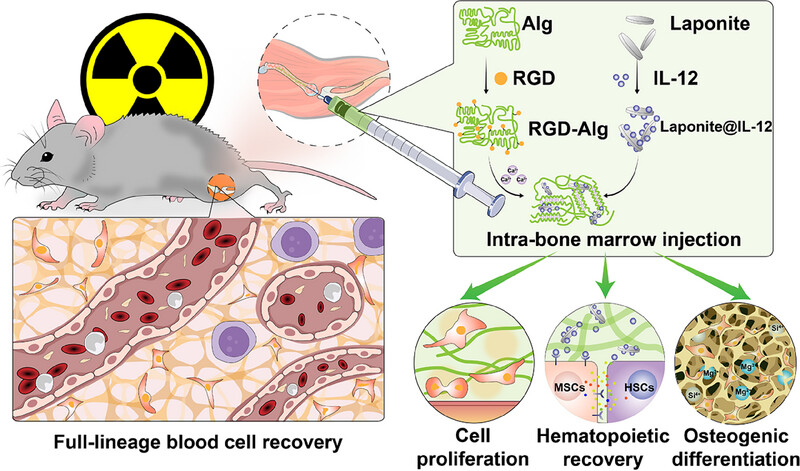
Interleukin-12 sustained release system promotes hematopoietic recovery after radiation injury
- First Published: 12 September 2024
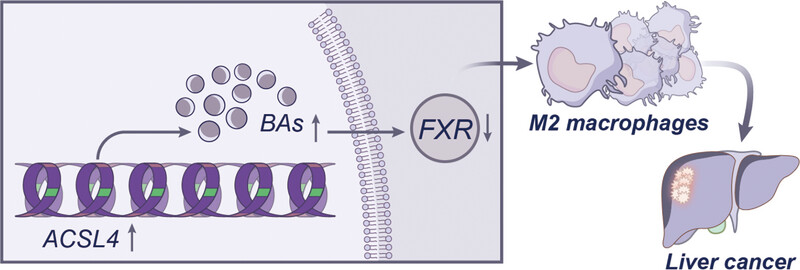
Role of ACSL4 in modulating farnesoid X receptor expression and M2 macrophage polarization in HBV-induced hepatocellular carcinoma
- First Published: 12 September 2024